
When reading network resources, the mutual conversion between strings and input streams is often used. I found some methods and recorded them.
Convert the string into an input stream, the code is as follows:
public static InputStream getStringStream(String sInputString){
if (sInputString != null && !sInputString.trim().equals("")){
try{
ByteArrayInputStream tInputStringStream = new ByteArrayInputStream(sInputString.getBytes());
return tInputStringStream;
}catch (Exception ex){
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
return null;
}Convert the input stream into a string, the code is as follows:
public static String getStreamString(InputStream tInputStream){
if (tInputStream != null){
try{
BufferedReader tBufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(tInputStream));
StringBuffer tStringBuffer = new StringBuffer();
String sTempOneLine = new String("");
while ((sTempOneLine = tBufferedReader.readLine()) != null){
tStringBuffer.append(sTempOneLine);
}
return tStringBuffer.toString();
}catch (Exception ex){
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
return null;
}Or the following method, the code is as follows :
public class StreamTool {
/**
* 把输入流的内容转化成字符串
* @param is
* @return
*/
public static String readInputStream(InputStream is){
try {
ByteArrayOutputStream baos=new ByteArrayOutputStream();
int length=0;
byte[] buffer=new byte[1024];
while((length=is.read(buffer))!=-1){
baos.write(buffer, 0, length);
}
is.close();
baos.close();
//或者用这种方法
//byte[] result=baos.toByteArray();
//return new String(result);
return baos.toString();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return "获取失败";
}
}
}java.io.Reader abstraction is the parent class of all character input streams, used to read file content
Character input stream structure:
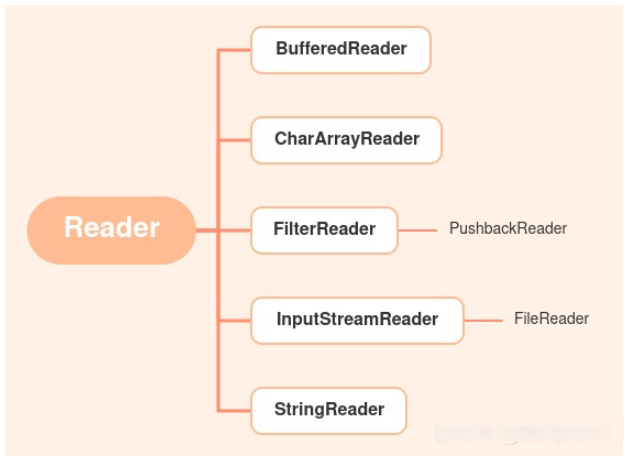
For the convenience of reading, Java provides a convenient class for reading character files.
FileReader class
Construction method:
FileReader(File file); Create a new FileReader given a File to read data from.
FileReader(String fileName); Creates a new FileReader given the name of a file to read data from.
Commonly used reading methods:
| Description | |
|---|---|
| Read one character, and return -1 if all characters are reached to the end | |
| Read the read cbuf.length characters into the char array | |
| Read offset off to len characters from this character input stream into the char array | |
| Reset the stream | |
| Judge whether the stream is ready to be read | |
| Close the character input stream and release all system resources | |
| Skip reading n characters and return The number of skipped characters | |
| Mark this input stream. When the reset method is used, it returns to this position and starts reading from this position. Enter characters |
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
public class dome2{
public static void main(String[] args){
File file=new File("D:/../...txt"); //创建file对象
FileReader fr=null;
try {
fr=new FileReader(file);
int c;
while((c=fr.read())!=-1) {
System.out.print((char)c); //强制转换成字符
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(fr!=null) {
try {
fr.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
public class dome2{
public static void main(String[] args){
File file=new File("D:/../...txt");
FileReader fr=null;
try {
fr=new FileReader(file);
char[] c=new char[100];
int length;
while((length=fr.read(c))!=-1) {
System.out.println(new String(c,0,length));
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(fr!=null) {
try {
fr.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}Character output stream structure:
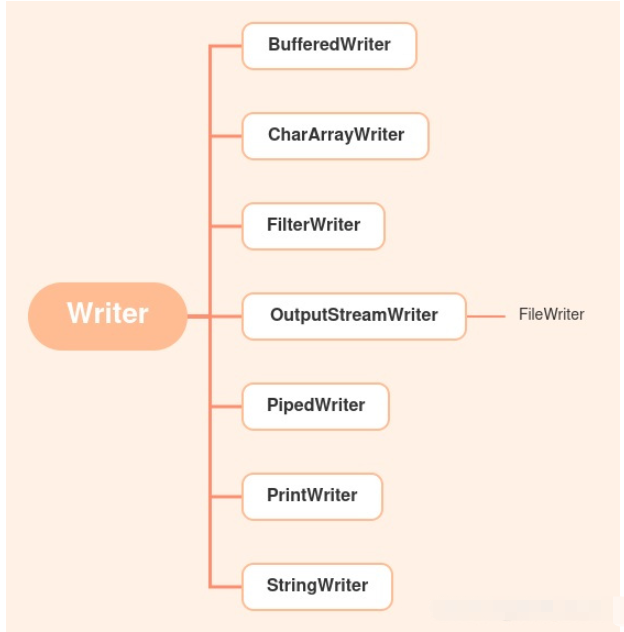
FileWriter class
Construction method:
FileWriter(File file) and FileWriter(String fileName); Construct a FileWriter object using the given file object or the given file path name.
FileWriter(File file, boolean append) and FileWriter(String fileName, boolean append); Through the given file object or file The pathname constructs the FileWriter object and whether it is appended or overwritten.
Common reading methods
| Description | |
|---|---|
| Write all character arrays specified by cbuf to the character output stream | |
| Write a character to the character output stream | |
| Write the characters in the cbuf array from offset off to length len characters into this output stream. | |
| Write a string to the character input stream | |
| Write str string from offset off, length len string to this output stream. | |
| Refresh the current output stream and force writing of all character data | |
| Close this output stream |
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
public class dome2{
public static void main(String[] args){
File file=new File("D:/../...txt"); //创建file对象
FileWriter fw=null;
try {
fw=new FileWriter(file);
char c='你';
fw.write((int)c);
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(fw!=null) {
try {
fw.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
public class dome2{
public static void main(String[] args){
File file=new File("D:/../...txt"); //创建file对象
FileWriter fw=null;
try {
fw=new FileWriter(file);
String str="你好,java";
fw.write(str); //写入一个字符串,等价于write(str,0,str.length);
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(fw!=null) {
try {
fw.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}The above is the detailed content of How to convert strings and input streams in Java. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




