How SpringBoot integrates Redis to achieve high concurrent data caching
What is cache
Cache is a memory for high-speed data exchange, which can be used to quickly access and operate data.
Give a simple example.
Xiao Ming runs a restaurant. When it first opened, due to lack of reputation and few customers, the business was not very busy. He usually stayed idle when there was nothing to do, and went into the kitchen to arrange cooking when guests came. With the increasing development of hotels, the hotels at this time are different from the past. They have a large number of stable customers, and they are even full during certain holidays. According to the previous practice, it will definitely not work. During the peak dining period, customers have to wait for a long time due to slow meal preparation, which has caused repeated complaints to the hotel.
In order to solve this problem, Xiao Ming thought of a way. When he is free, he can cook popular dishes in advance and put them in the warming cabinet. He can then take them out to heat them during the peak dining period and serve them directly. This avoids the problem of slow meal preparation caused by a large number of customers in a short period of time. Through this method, it can be well handled even during peak periods.
The core of caching is to pre-store frequently accessed resources (high-frequency reading, low-frequency writing) in a location closest to the user and with faster access speed to improve access speed.
Why use cache
After using cache, the efficiency will be greatly improved, unnecessary resource consumption will be reduced, and the user experience will be improved.
Features of redis:
redis supports data persistence. It can save the data in the memory to the disk and add it again when restarting. for use.
redis not only supports simple key-value type data, but also provides storage of list, set, zset, hash and other data structures
redis supports data backup, that is, data backup in master-slave mode
Advantages of redis:
Extremely high performance—&mdash ;Redis can read at a speed of 110,000 times/s and write at a speed of 81,000 times/s.
Rich data types - redis supports Strings, Lists, Hashes, Sets and Ordered Sets data type operations for binary cases.
Atomic - All operations of redis are atomic, which means that they are either executed successfully or not executed at all. Individual operations are atomic. Multiple operations also support transactions, that is, atomicity, wrapped by the multi and exec instructions.
Rich features redis also supports publish/subscribe, notification, key expiration and other features
Why is Redis so fast
(1) Completely based on memory, the data is stored in the memory, and most requests are pure memory operations, which are very fast. Compared with traditional disk file data storage, it avoids the overhead of reading the memory through disk IO.
(2) The data structure is simple and the data operations are also simple. Each data structure is supported by one or more data structures specially designed in Redis. Redis utilizes these flexible data structures to enhance its read and write performance.
(3) Using a single thread saves a lot of context switching time and CPU consumption. There is no competition condition, and there is no need to consider various lock issues. There is no lock-release lock operation, and no Performance consumption caused by deadlock.
(4) Using the thread model based on the IO multiplexing mechanism can handle concurrent links.
Implementing a cache of user information
Database table structure:
CREATE TABLE `blade_user` ( `id` bigint(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '主键', `tenant_id` varchar(12) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_general_ci DEFAULT '000000' COMMENT '租户ID', `code` varchar(12) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_general_ci DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '用户编号', `user_type` int(11) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '用户平台', `account` varchar(45) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_general_ci DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '账号', `password` varchar(100) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_general_ci DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '密码', `name` varchar(20) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_general_ci DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '昵称', `real_name` varchar(10) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_general_ci DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '真名', `avatar` varchar(500) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_general_ci DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '头像', `email` varchar(45) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_general_ci DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '邮箱', `phone` varchar(45) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_general_ci DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '手机', `birthday` datetime DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '生日', `sex` int(11) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '性别', `role_id` varchar(1000) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_general_ci DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '角色id', `dept_id` varchar(1000) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_general_ci DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '部门id', `post_id` varchar(1000) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_general_ci DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '岗位id', `create_user` bigint(20) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '创建人', `create_dept` bigint(20) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '创建部门', `create_time` datetime DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '创建时间', `update_user` bigint(20) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '修改人', `update_time` datetime DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '修改时间', `status` int(11) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '状态', `is_deleted` int(11) DEFAULT '0' COMMENT '是否已删除', PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_general_ci ROW_FORMAT=DYNAMIC COMMENT='用户表';
Method 1: Use RedisTemplate to implement import dependencies
Complete pom.xml file:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.7.8</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.redis.demo</groupId>
<artifactId>springboot-redis</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>springboot-redis</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!--mybatis-plus的springboot支持-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.4.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--mysql驱动-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.15</version>
</dependency>
<!-- hutool 工具包,各种封装功能 一应俱全-->
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.hutool</groupId>
<artifactId>hutool-all</artifactId>
<version>5.8.5</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>1.2.41</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<excludes>
<exclude>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</exclude>
</excludes>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>Add configuration
application.yml file:
server:
port: 8081
spring:
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://3.129.36.183:3306/test?serverTimezone=GMT%2B8&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8
username: root
password: root
#redis
redis:
host: 3.129.36.183
#Redis服务器连接端口
port: 6379
#Redis服务器连接密码
password: 123456
mybatis-plus:
configuration:
log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl #开启sql日志
# 将带有下划线的表字段映射为驼峰格式的实体类属性
map-underscore-to-camel-case: true
#配置类型别名所对应的包
type-aliases-package: com.redis.demo.entity
#配置SQL输出语句com.winsun.dataclean.mapper
mapper-locations: com/redis/demo/dao/*.xmlAdd redis tool class and configuration class
RedisUtils:
package com.redis.demo.utils;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.util.CollectionUtils;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* Redis工具类
*
* @author
*/
@Component
public class RedisUtils {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
// =============================common============================
/**
* 指定缓存失效时间
*
* @param key 键
* @param time 时间(秒)
* @return
*/
public boolean expire(String key, long time) {
try {
if (time > 0) {
redisTemplate.expire(key, time, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
return true;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
}
/**
* 根据key 获取过期时间
*
* @param key 键 不能为null
* @return 时间(秒) 返回0代表为永久有效
*/
public long getExpire(String key) {
return redisTemplate.getExpire(key, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
/**
* 判断key是否存在
*
* @param key 键
* @return true 存在 false不存在
*/
public boolean hasKey(String key) {
try {
return redisTemplate.hasKey(key);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
}
/**
* 删除缓存
*
* @param key 可以传一个值 或多个
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public void del(String... key) {
if (key != null && key.length > 0) {
if (key.length == 1) {
redisTemplate.delete(key[0]);
} else {
redisTemplate.delete(CollectionUtils.arrayToList(key));
}
}
}
// ============================String=============================
/**
* 普通缓存获取
*
* @param key 键
* @return 值
*/
public Object get(String key) {
return key == null ? null : redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
}
/**
* 普通缓存放入
*
* @param key 键
* @param value 值
* @return true成功 false失败
*/
public boolean set(String key, Object value) {
try {
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, value);
return true;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
}
/**
* 普通缓存放入并设置时间
*
* @param key 键
* @param value 值
* @param time 时间(秒) time要大于0 如果time小于等于0 将设置无限期
* @return true成功 false 失败
*/
public boolean set(String key, Object value, long time) {
try {
if (time > 0) {
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, value, time, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
} else {
set(key, value);
}
return true;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
}
/**
* 递增
*
* @param key 键
* @param delta 要增加几(大于0)
* @return
*/
public long incr(String key, long delta) {
if (delta < 0) {
throw new RuntimeException("递增因子必须大于0");
}
return redisTemplate.opsForValue().increment(key, delta);
}
/**
* 递减
*
* @param key 键
* @param delta 要减少几(小于0)
* @return
*/
public long decr(String key, long delta) {
if (delta < 0) {
throw new RuntimeException("递减因子必须大于0");
}
return redisTemplate.opsForValue().increment(key, -delta);
}
// ================================Map=================================
/**
* HashGet
*
* @param key 键 不能为null
* @param item 项 不能为null
* @return 值
*/
public Object hget(String key, String item) {
return redisTemplate.opsForHash().get(key, item);
}
/**
* 获取hashKey对应的所有键值
*
* @param key 键
* @return 对应的多个键值
*/
public Map<Object, Object> hmget(String key) {
return redisTemplate.opsForHash().entries(key);
}
/**
* HashSet
*
* @param key 键
* @param map 对应多个键值
* @return true 成功 false 失败
*/
public boolean hmset(String key, Map<String, Object> map) {
try {
redisTemplate.opsForHash().putAll(key, map);
return true;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
}
/**
* HashSet 并设置时间
*
* @param key 键
* @param map 对应多个键值
* @param time 时间(秒)
* @return true成功 false失败
*/
public boolean hmset(String key, Map<String, Object> map, long time) {
try {
redisTemplate.opsForHash().putAll(key, map);
if (time > 0) {
expire(key, time);
}
return true;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
}
/**
* 向一张hash表中放入数据,如果不存在将创建
*
* @param key 键
* @param item 项
* @param value 值
* @return true 成功 false失败
*/
public boolean hset(String key, String item, Object value) {
try {
redisTemplate.opsForHash().put(key, item, value);
return true;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
}
/**
* 向一张hash表中放入数据,如果不存在将创建
*
* @param key 键
* @param item 项
* @param value 值
* @param time 时间(秒) 注意:如果已存在的hash表有时间,这里将会替换原有的时间
* @return true 成功 false失败
*/
public boolean hset(String key, String item, Object value, long time) {
try {
redisTemplate.opsForHash().put(key, item, value);
if (time > 0) {
expire(key, time);
}
return true;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
}
/**
* 删除hash表中的值
*
* @param key 键 不能为null
* @param item 项 可以使多个 不能为null
*/
public void hdel(String key, Object... item) {
redisTemplate.opsForHash().delete(key, item);
}
/**
* 判断hash表中是否有该项的值
*
* @param key 键 不能为null
* @param item 项 不能为null
* @return true 存在 false不存在
*/
public boolean hHasKey(String key, String item) {
return redisTemplate.opsForHash().hasKey(key, item);
}
/**
* hash递增 如果不存在,就会创建一个 并把新增后的值返回
*
* @param key 键
* @param item 项
* @param by 要增加几(大于0)
* @return
*/
public double hincr(String key, String item, double by) {
return redisTemplate.opsForHash().increment(key, item, by);
}
/**
* hash递减
*
* @param key 键
* @param item 项
* @param by 要减少记(小于0)
* @return
*/
public double hdecr(String key, String item, double by) {
return redisTemplate.opsForHash().increment(key, item, -by);
}
// ============================set=============================
/**
* 根据key获取Set中的所有值
*
* @param key 键
* @return
*/
public Set<Object> sGet(String key) {
try {
return redisTemplate.opsForSet().members(key);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
/**
* 根据value从一个set中查询,是否存在
*
* @param key 键
* @param value 值
* @return true 存在 false不存在
*/
public boolean sHasKey(String key, Object value) {
try {
return redisTemplate.opsForSet().isMember(key, value);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
}
/**
* 将数据放入set缓存
*
* @param key 键
* @param values 值 可以是多个
* @return 成功个数
*/
public long sSet(String key, Object... values) {
try {
return redisTemplate.opsForSet().add(key, values);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return 0;
}
}
/**
* 将set数据放入缓存
*
* @param key 键
* @param time 时间(秒)
* @param values 值 可以是多个
* @return 成功个数
*/
public long sSetAndTime(String key, long time, Object... values) {
try {
Long count = redisTemplate.opsForSet().add(key, values);
if (time > 0)
expire(key, time);
return count;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return 0;
}
}
/**
* 获取set缓存的长度
*
* @param key 键
* @return
*/
public long sGetSetSize(String key) {
try {
return redisTemplate.opsForSet().size(key);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return 0;
}
}
/**
* 移除值为value的
*
* @param key 键
* @param values 值 可以是多个
* @return 移除的个数
*/
public long setRemove(String key, Object... values) {
try {
Long count = redisTemplate.opsForSet().remove(key, values);
return count;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return 0;
}
}
// ===============================list=================================
/**
* 获取list缓存的内容
*
* @param key 键
* @param start 开始
* @param end 结束 0 到 -1代表所有值
* @return
*/
public List<Object> lGet(String key, long start, long end) {
try {
return redisTemplate.opsForList().range(key, start, end);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
/**
* 获取list缓存的长度
*
* @param key 键
* @return
*/
public long lGetListSize(String key) {
try {
return redisTemplate.opsForList().size(key);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return 0;
}
}
/**
* 通过索引 获取list中的值
*
* @param key 键
* @param index 索引 index>=0时, 0 表头,1 第二个元素,依次类推;index<0时,-1,表尾,-2倒数第二个元素,依次类推
* @return
*/
public Object lGetIndex(String key, long index) {
try {
return redisTemplate.opsForList().index(key, index);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
/**
* 将list放入缓存
*
* @param key 键
* @param value 值
* @return
*/
public boolean lSet(String key, Object value) {
try {
redisTemplate.opsForList().rightPush(key, value);
return true;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
}
/**
* 将list放入缓存
*
* @param key 键
* @param value 值
* @param time 时间(秒)
* @return
*/
public boolean lSet(String key, Object value, long time) {
try {
redisTemplate.opsForList().rightPush(key, value);
if (time > 0)
expire(key, time);
return true;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
}
/**
* 将list放入缓存
*
* @param key 键
* @param value 值
* @return
*/
public boolean lSet(String key, List<Object> value) {
try {
redisTemplate.opsForList().rightPushAll(key, value);
return true;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
}
/**
* 将list放入缓存
*
* @param key 键
* @param value 值
* @param time 时间(秒)
* @return
*/
public boolean lSet(String key, List<Object> value, long time) {
try {
redisTemplate.opsForList().rightPushAll(key, value);
if (time > 0)
expire(key, time);
return true;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
}
/**
* 根据索引修改list中的某条数据
*
* @param key 键
* @param index 索引
* @param value 值
* @return
*/
public boolean lUpdateIndex(String key, long index, Object value) {
try {
redisTemplate.opsForList().set(key, index, value);
return true;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
}
/**
* 移除N个值为value
*
* @param key 键
* @param count 移除多少个
* @param value 值
* @return 移除的个数
*/
public long lRemove(String key, long count, Object value) {
try {
Long remove = redisTemplate.opsForList().remove(key, count, value);
return remove;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return 0;
}
}
}RedisConfig:
package com.redis.demo.config;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonAutoDetect;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.PropertyAccessor;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import com.redis.demo.utils.MapUtil;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.cache.interceptor.KeyGenerator;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.RedisSerializer;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* @Author: laz
* @CreateTime: 2023-02-20 11:55
* @Version: 1.0
*
* 序列化
*/
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
initRedisTemplate();
}
private void initRedisTemplate() {
RedisSerializer stringSerializer = redisTemplate.getStringSerializer();
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(stringSerializer);
redisTemplate.setHashKeySerializer(stringSerializer);
redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(stringSerializer);
redisTemplate.setHashValueSerializer(stringSerializer);
}
}Develop mapper interface
package com.redis.demo.dao;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.mapper.BaseMapper;
import com.redis.demo.entity.BladeUser;
/**
* <p>
* 用户表 Mapper 接口
* </p>
*
* @author laz
* @since 2023-03-09
*/
public interface BladeUserMapper extends BaseMapper<BladeUser> {
}service layer
IBladeUserService:
package com.redis.demo.service;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.service.IService;
import com.redis.demo.entity.BladeUser;
import com.redis.demo.result.DealResult;
/**
* <p>
* 用户表 服务类
* </p>
*
* @author laz
* @since 2023-03-09
*/
public interface IBladeUserService extends IService<BladeUser> {
DealResult getById(Long id);
}BladeUserServiceImpl:
package com.redis.demo.service.impl;
import cn.hutool.core.bean.BeanUtil;
import cn.hutool.json.JSONUtil;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.service.impl.ServiceImpl;
import com.redis.demo.constant.RedisConstants;
import com.redis.demo.dao.BladeUserMapper;
import com.redis.demo.entity.BladeUser;
import com.redis.demo.result.DealResult;
import com.redis.demo.service.IBladeUserService;
import com.redis.demo.status.CacheNameStatus;
import com.redis.demo.utils.RedisUtils;
import org.springframework.beans.BeanUtils;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.util.ObjectUtils;
/**
* <p>
* 用户表 服务实现类
* </p>
*
* @author laz
* @since 2023-03-09
*/
@Service
public class BladeUserServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<BladeUserMapper, BladeUser> implements IBladeUserService {
@Autowired
private RedisUtils redisUtils;
@Override
public DealResult getById(Long id) {
String userKey = RedisConstants.CACHE_USER_KEY+id;
Object user = redisUtils.get(userKey);
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(user)){
return DealResult.data(JSONUtil.toBean(JSONUtil.toJsonStr(user),BladeUser.class));
}
BladeUser bladeUser = baseMapper.selectById(id);
redisUtils.set(userKey, JSON.toJSONString(bladeUser));
return DealResult.data(bladeUser);
}
}controller layer
package com.redis.demo.controller;
import com.redis.demo.result.DealResult;
import com.redis.demo.service.IBladeUserService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* <p>
* 用户表 前端控制器
* </p>
*
* @author laz
* @since 2023-03-09
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/bladeUser")
public class BladeUserController {
@Autowired
private IBladeUserService bladeUserService;
@RequestMapping("getById/{id}")
public DealResult getById(@PathVariable("id")Long id){
return bladeUserService.getById(id);
}
}Test
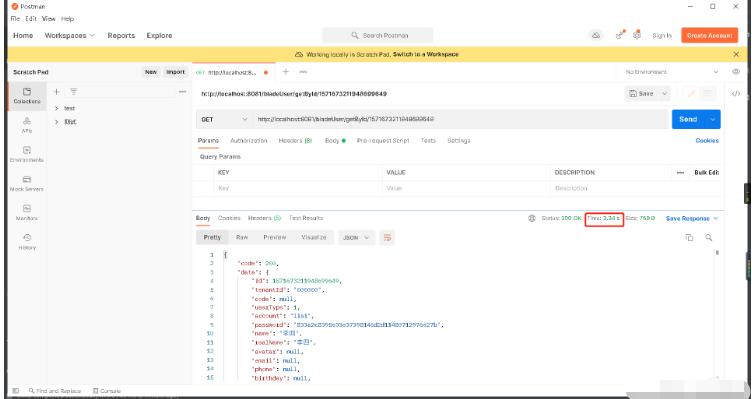
Start the project, use postman to access the interface, make two consecutive requests, and observe the response time:
First time:
Second time:
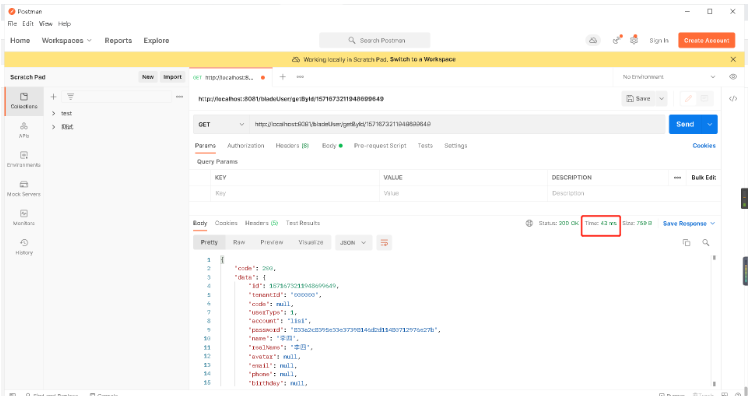
You can see that the first time is 3.34s and the second time is 43ms, the efficiency is significantly improved!
Method 2: Use SpringBoot annotation enables caching
Subject to method 1
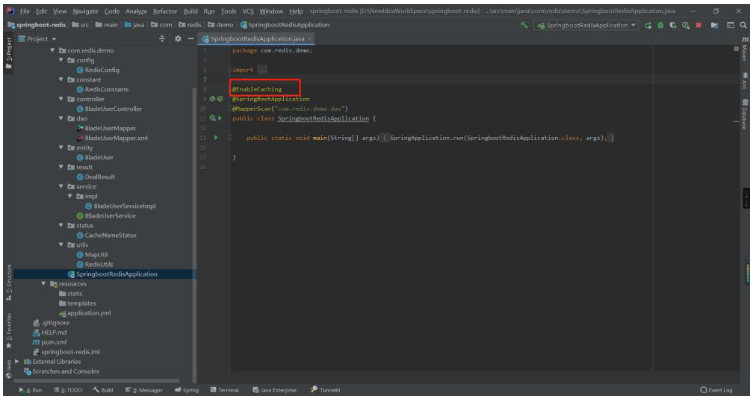
Add @EnableCachingannotation to the startup class
Modify Service layer implementation class code
package com.redis.demo.service.impl;
import cn.hutool.core.bean.BeanUtil;
import cn.hutool.json.JSONUtil;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.service.impl.ServiceImpl;
import com.redis.demo.constant.RedisConstants;
import com.redis.demo.dao.BladeUserMapper;
import com.redis.demo.entity.BladeUser;
import com.redis.demo.result.DealResult;
import com.redis.demo.service.IBladeUserService;
import com.redis.demo.status.CacheNameStatus;
import com.redis.demo.utils.RedisUtils;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.beans.BeanUtils;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.util.ObjectUtils;
/**
* <p>
* 用户表 服务实现类
* </p>
*
* @author laz
* @since 2023-03-09
*/
@Service
public class BladeUserServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<BladeUserMapper, BladeUser> implements IBladeUserService {
@Autowired
private RedisUtils redisUtils;
// @Override
// public DealResult getById(Long id) {
//
// String userKey = RedisConstants.CACHE_USER_KEY+id;
// Object user = redisUtils.get(userKey);
// if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(user)){
//
// return DealResult.data(JSONUtil.toBean(JSONUtil.toJsonStr(user),BladeUser.class));
// }
//
// BladeUser bladeUser = baseMapper.selectById(id);
// redisUtils.set(userKey, JSON.toJSONString(bladeUser));
// return DealResult.data(bladeUser);
// }
@Cacheable(cacheNames = CacheNameStatus.BLADE_USER,keyGenerator = CacheNameStatus.KEY_GENERATOR)
@Override
public DealResult getById(Long id) {
BladeUser bladeUser = baseMapper.selectById(id);
return DealResult.data(bladeUser);
}
}Modify the RedisConfig configuration class
Add a custom KeyGenerator in the configuration class
/**
* 自定义KeyGenerator
* @return
*/
@Bean
public KeyGenerator simpleKeyGenerator() {
return (o, method, objects) -> {
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
stringBuilder.append(o.getClass().getSimpleName());
stringBuilder.append(".");
stringBuilder.append(method.getName());
stringBuilder.append("[");
for (Object obj : objects) {
if(obj.toString().indexOf("Vo@")!= -1)
{
Map<String, Object> map = MapUtil.getAttrFromModel(obj);
stringBuilder.append("[");
for(String item:map.keySet())
{
stringBuilder.append(",");
stringBuilder.append(map.get(item));
}
stringBuilder.append(",");
stringBuilder.deleteCharAt(stringBuilder.length() - 1);
stringBuilder.append("]");
}
else {
stringBuilder.append(obj);
stringBuilder.append(",");
}
}
stringBuilder.append("]");
return stringBuilder.toString();
};
}Note : Regarding the parameters of the @Cacheable annotation, if you don’t understand, you can click to view it.
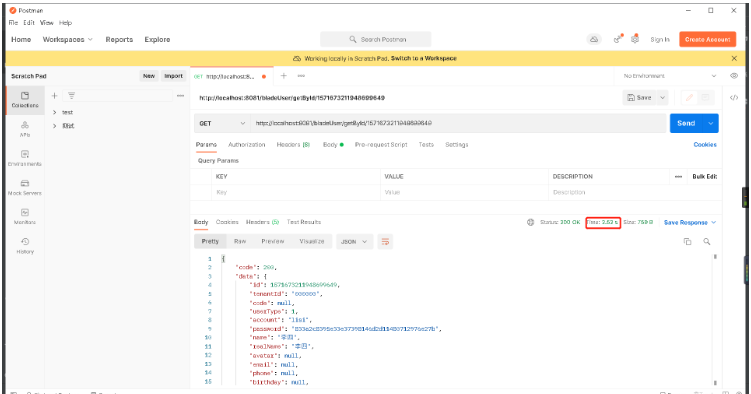
Restart the project, access the above interface again, and observe the response time:
First time:
Second time:
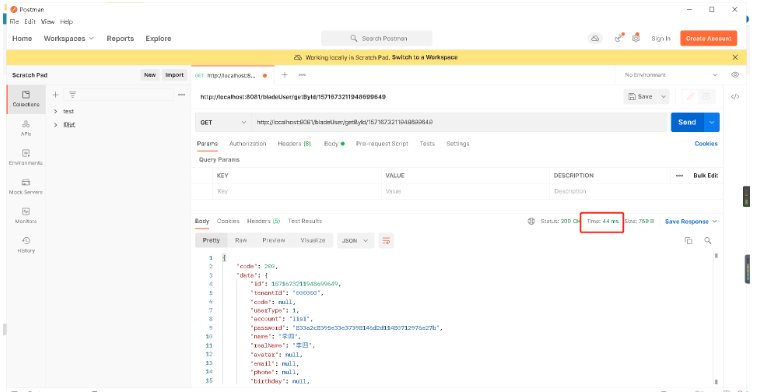
You can see that the first time is 2.52s and the second time is 44ms, the efficiency is significantly improved!
Observe the cache data through the Redis visualization tool:
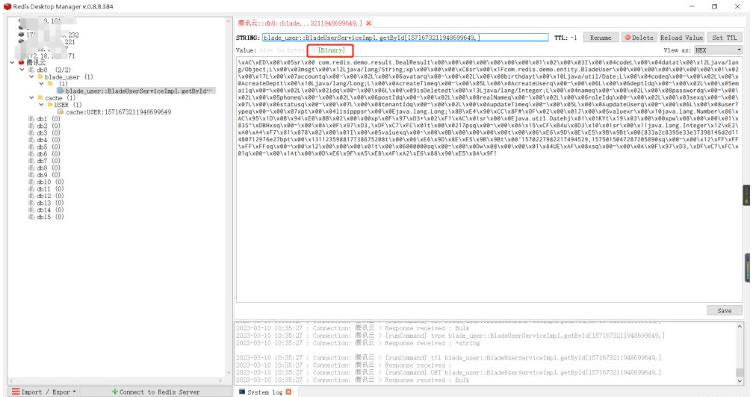
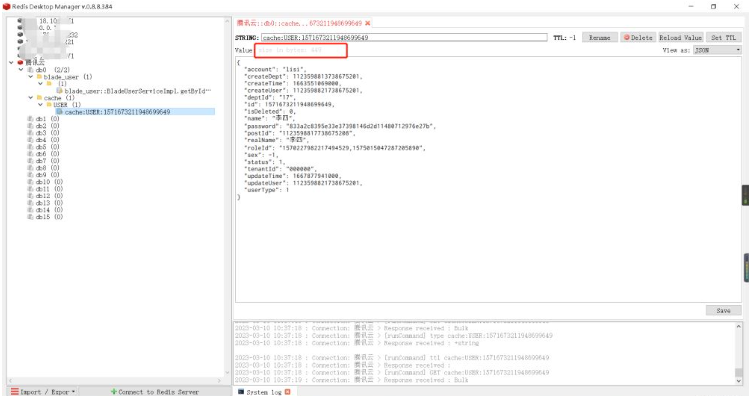
RedisTemplate method for caching, because this method occupies relatively less memory.
The above is the detailed content of How SpringBoot integrates Redis to achieve high concurrent data caching. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
Redis cluster mode deploys Redis instances to multiple servers through sharding, improving scalability and availability. The construction steps are as follows: Create odd Redis instances with different ports; Create 3 sentinel instances, monitor Redis instances and failover; configure sentinel configuration files, add monitoring Redis instance information and failover settings; configure Redis instance configuration files, enable cluster mode and specify the cluster information file path; create nodes.conf file, containing information of each Redis instance; start the cluster, execute the create command to create a cluster and specify the number of replicas; log in to the cluster to execute the CLUSTER INFO command to verify the cluster status; make
 How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear Redis data: Use the FLUSHALL command to clear all key values. Use the FLUSHDB command to clear the key value of the currently selected database. Use SELECT to switch databases, and then use FLUSHDB to clear multiple databases. Use the DEL command to delete a specific key. Use the redis-cli tool to clear the data.
 How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
Using the Redis directive requires the following steps: Open the Redis client. Enter the command (verb key value). Provides the required parameters (varies from instruction to instruction). Press Enter to execute the command. Redis returns a response indicating the result of the operation (usually OK or -ERR).
 How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
To read a queue from Redis, you need to get the queue name, read the elements using the LPOP command, and process the empty queue. The specific steps are as follows: Get the queue name: name it with the prefix of "queue:" such as "queue:my-queue". Use the LPOP command: Eject the element from the head of the queue and return its value, such as LPOP queue:my-queue. Processing empty queues: If the queue is empty, LPOP returns nil, and you can check whether the queue exists before reading the element.
 How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
Using Redis to lock operations requires obtaining the lock through the SETNX command, and then using the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time. The specific steps are: (1) Use the SETNX command to try to set a key-value pair; (2) Use the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time for the lock; (3) Use the DEL command to delete the lock when the lock is no longer needed.
 How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
The best way to understand Redis source code is to go step by step: get familiar with the basics of Redis. Select a specific module or function as the starting point. Start with the entry point of the module or function and view the code line by line. View the code through the function call chain. Be familiar with the underlying data structures used by Redis. Identify the algorithm used by Redis.
 How to solve data loss with redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:24 PM
How to solve data loss with redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:24 PM
Redis data loss causes include memory failures, power outages, human errors, and hardware failures. The solutions are: 1. Store data to disk with RDB or AOF persistence; 2. Copy to multiple servers for high availability; 3. HA with Redis Sentinel or Redis Cluster; 4. Create snapshots to back up data; 5. Implement best practices such as persistence, replication, snapshots, monitoring, and security measures.
 How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
Use the Redis command line tool (redis-cli) to manage and operate Redis through the following steps: Connect to the server, specify the address and port. Send commands to the server using the command name and parameters. Use the HELP command to view help information for a specific command. Use the QUIT command to exit the command line tool.




