How SpringBoot integrates Redis cache implementation
Cache components supported by SpringBoot
In SpringBoot, the cache management and storage of data relies on the cache-related org.springframework.cache.Cache and org.springframework.cache.CacheManager cache manager interfaces in the Spring framework. .
If there is no Bean component of type CacheManager or a CacheResolver cache resolver named cacheResolver defined in the program, SpringBoot will try to enable the following cache components (in the specified order):
( 1) Generic
(2) JCache (JSR-107) (EhCache 3, Hazelcast, Infinispan, etc.)
(3) EhCache 2.x
(4) Hazelcast
(5)Infinispan
(6)Couchbase
(7)Redis
(8)Caffeine
(9)Simple
The above lists 9 cache components supported by SpringBoot according to the loading order of SpringBoot cache components. After adding a cache management component (such as Redis) to the project, the SpringBoot project will select and enable the corresponding cache manager. . If multiple cache components are added to the project at the same time, and no cache manager or cache resolver (CacheManager or cacheResolver) is specified, SpringBoot will preferentially enable the first one among the multiple cache components added in the above order. The cache component performs cache management (for example, if the two cache components Couchbase and Redis are added at the same time, then the Couchbase component is enabled first).
In the default cache management introduced in the previous article SpringBoot Cache Management (1) Default Cache Management, the project we built did not add any cache management components, but cache management was still implemented. This is because after cache management is enabled, SpringBoot will search for valid cache components for cache management in the order of the above cache components. If there is no cache component, the last Simple cache component will be used by default for management . The Simple cache component is SpringBoot's default cache management component. It uses ConcurrentMap in memory for cache storage by default, so without adding any third-party cache components, in-memory cache management can still be achieved, but it is not recommended. This cache management method.
Annotation-based Redis cache implementation
Introduce the Redis cache component based on the project built by SpringBoot Cache Management (1) Default Cache Management, and use annotation-based methods to explain the specific details of SpringBoot's integration of Redis cache accomplish.
(1) Add Spring Data Redis dependency starter
Add Spring Data Redis dependency starter in the pom.xml file:
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId> </dependency>
When we add Redis-related dependencies After the launcher, SpringBoot will use RedisCacheConfigratioin as the automatic configuration class to carry out cache-related automatic assembly classes (previously the default SimpleCacheConfiguration), the cache manager used in the container becomes RedisCacheManager (previously the default cacheManager), this cache manager creates The Cache is RedisCache, which controls Redis to cache data.
(2) Redis server connection configuration
Add the connection configuration of the Redis database in the global configuration file application.properties of the project. The sample code is as follows:
# Redis服务器地址 spring.redis.host=127.0.0.1 # Redis服务器连接端口 spring.redis.port=6379 # Redis服务器连接密码(默认为空) spring.redis.password=
(3) Modify the methods in the CommentService class
Use the three annotations @Cacheable, @CachePut, and @CacheEvict for cache management, and perform operations such as cache storage, cache update, and cache deletion respectively:
package com.hardy.springbootdatacache.service;
import com.hardy.springbootdatacache.entity.Comment;
import com.hardy.springbootdatacache.repository.CommentRepository;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CacheEvict;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CachePut;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.Optional;
/**
* @Author: HardyYao
* @Date: 2021/6/19
*/
@Service
public class CommentService {
@Autowired
private CommentRepository commentRepository;
/**
* 根据评论id查询评论
* @Cacheable:将该方法的查询结果comment存放在SpringBoot默认缓存中
* cacheNames:起一个缓存命名空间,对应缓存唯一标识
* @param id
* @return
*/
@Cacheable(cacheNames = "comment", unless = "#result==null")
public Comment findCommentById(Integer id){
Optional<Comment> comment = commentRepository.findById(id);
if(comment.isPresent()){
Comment comment1 = comment.get();
return comment1;
}
return null;
}
/**
* 更新评论
* @param comment
* @return
*/
@CachePut(cacheNames = "comment",key = "#result.id")
public Comment updateComment(Comment comment) {
commentRepository.updateComment(comment.getAuthor(), comment.getaId());
return comment;
}
/**
* 删除评论
* @param comment_id
*/
@CacheEvict(cacheNames = "comment")
public void deleteComment(int comment_id) {
commentRepository.deleteById(comment_id);
}
}In the above code, the @Cacheable, @CachePut, and @CacheEvict annotations are used to perform cache management on data query, data update, and data deletion methods.
Among them, there is no mark key value in the query cache @Cacheable annotation, and the default parameter value comment_id will be used as the key to save the data. The same key must be used when updating the cache; similarly, when using the query cache In the @Cacheable annotation, unless= "#result==null" is defined to indicate that the query result will not be cached if it is empty.
(4) Add two new interfaces to the CommentController class
Add new update and delete interfaces:
package com.hardy.springbootdatacache.controller;
import com.hardy.springbootdatacache.entity.Comment;
import com.hardy.springbootdatacache.service.CommentService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* @Author: HardyYao
* @Date: 2021/6/19
*/
@RestController
public class CommentController {
@Autowired
private CommentService commentService;
@RequestMapping(value = "/findCommentById")
public Comment findCommentById(Integer id){
Comment comment = commentService.findCommentById(id);
return comment;
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/updateComment")
public Comment updateComment(Comment comment){
Comment oldComment = commentService.findCommentById(comment.getId());
oldComment.setAuthor(comment.getAuthor());
Comment comment1 = commentService.updateComment(oldComment);
return comment1;
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/deleteComment")
public void deleteComment(Integer id){
commentService.deleteComment(id);
}
}(5) Annotation-based Redis query cache test
Enter in the browser: http://localhost:8080/findCommentById?id=1 to access:
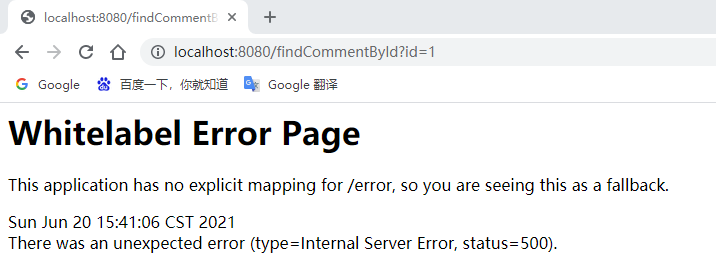
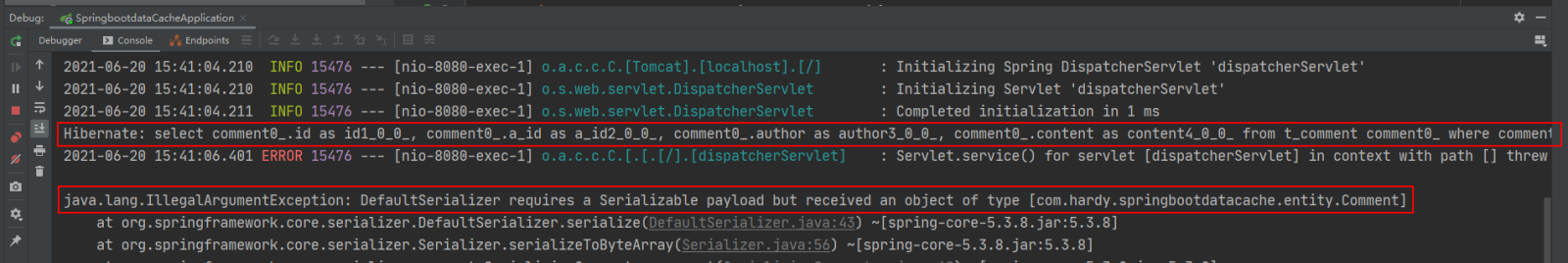
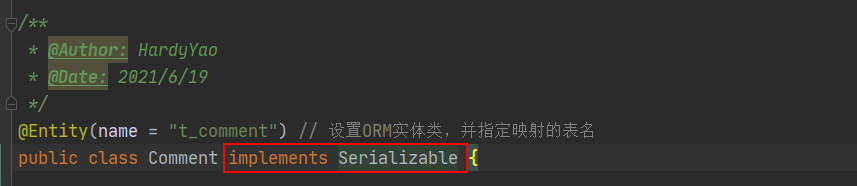
在浏览器中输入:http://localhost:8080/findCommentById?id=1 进行访问(连续访问三次):
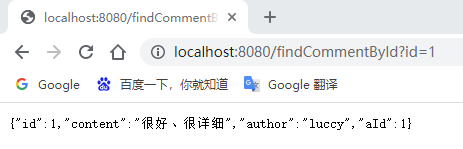
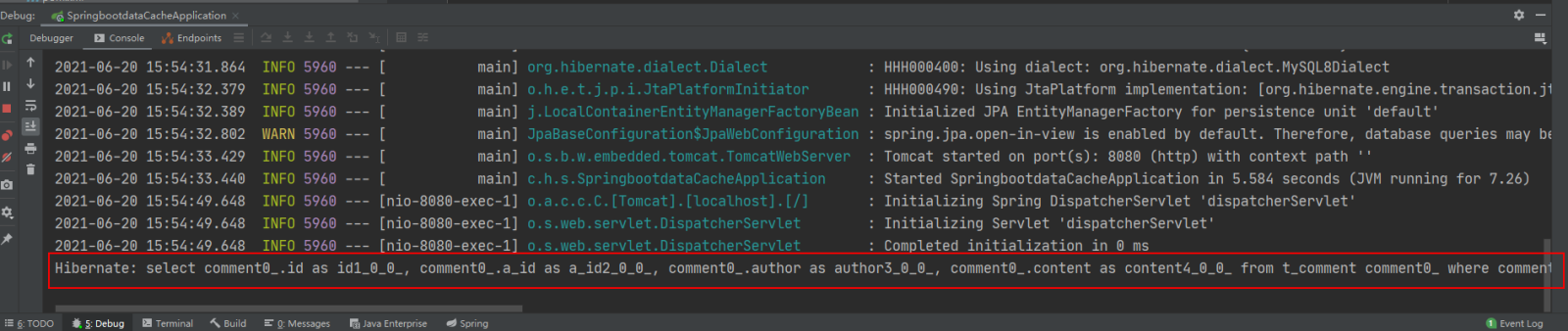
打开Redis客户端可视化工具Redis Desktop Manager,连接本地启用的Redis服务,查看具体的数据缓存效果:
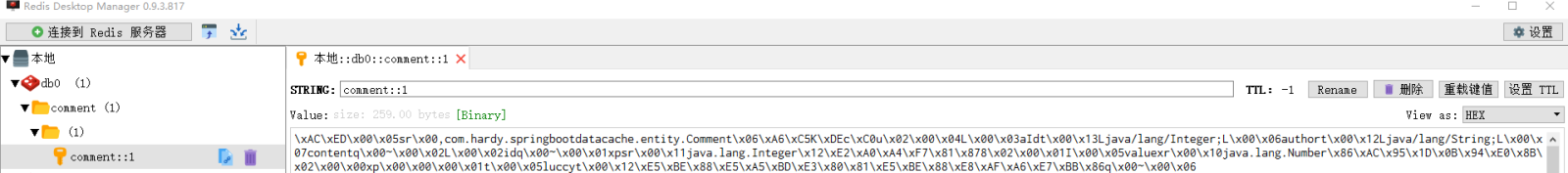
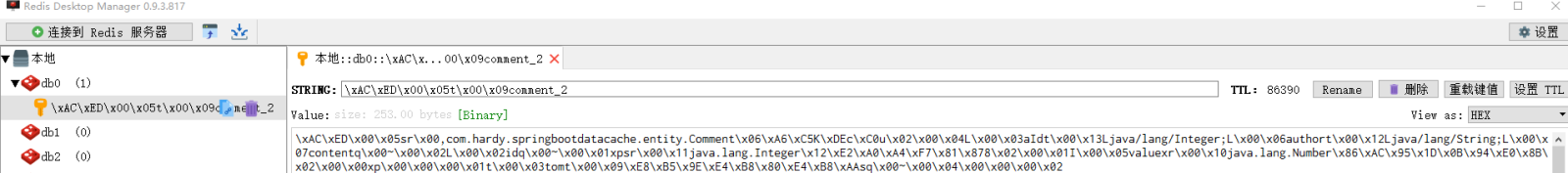
执行findById()方法查询出的用户评论信息Comment正确存储到了Redis缓存库中名为comment的名称空间下。
其中缓存数据的唯一标识key值是以“名称空间comment::+参数值(comment::1)”的字符串形式体现的,而value值则是经过JDK默认序列格式化后的HEX格式存储。这种JDK默认序列格式化后的数据显然不方便缓存数据的可视化查看和管理,所以在实际开发中,通常会自定义数据的序列化格式,这方面的内容在后面会介绍。
(8)基于注解的Redis缓存更新测试
先通过浏览器访问:http://localhost:8080/updateComment?id=1&author=hardy;
接着在访问:http://localhost:8080/findCommentById?id=1,查看浏览器返回信息及控制台打印信息:
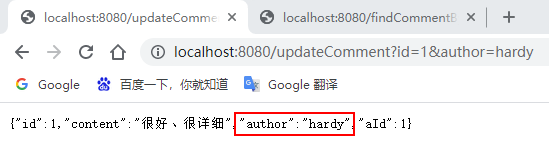

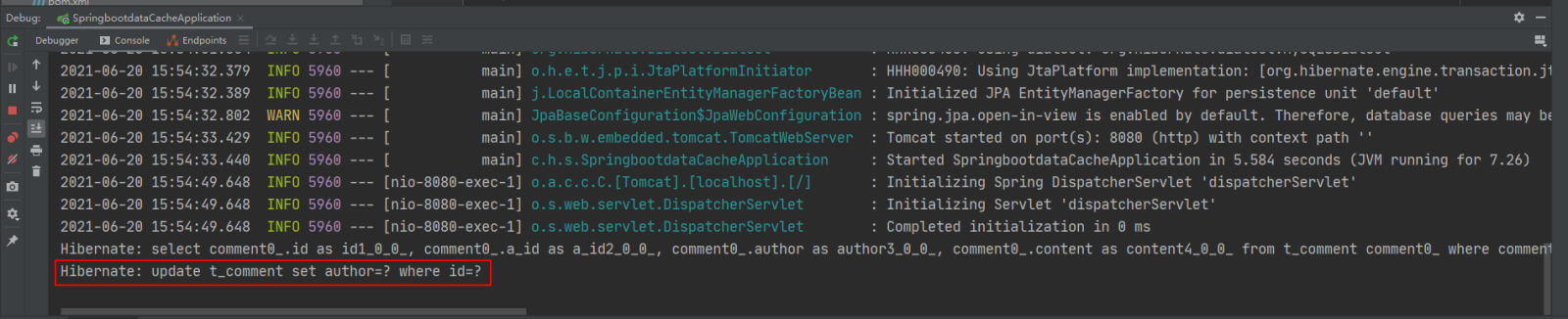
可以看到,执行updateComment()更新id为1的数据时执行了一条更新的SQL语句,后续调用findById()方法查询id为1的用户评论信息时没有再次执行查询的SQL语句,且浏览器返回了更新后的正确结果,这说明@CachePut缓存更新配置成功。
(9)基于注解的Redis缓存删除测试
通过浏览器访问:http://localhost:8080/deleteComment?id=1 和 http://localhost:8080/findCommentById?id=1
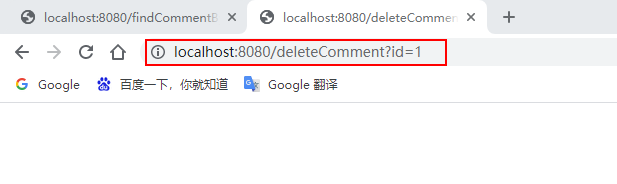
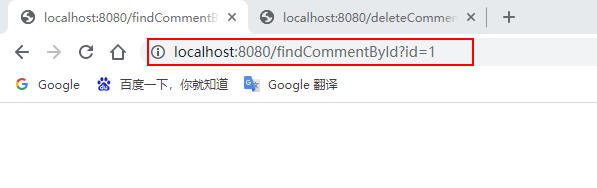
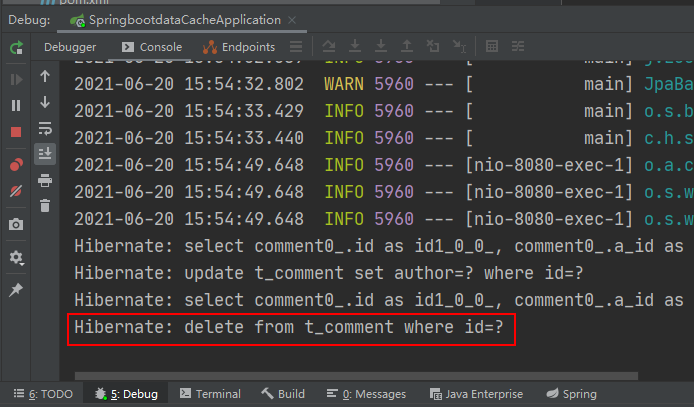
执行deleteComment()方法删除id为1的数据后查询结果为空,查看Redis缓存数据库:
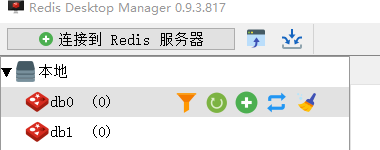
可以看到之前存储的comment相关数据被删除掉了,这表明@CacheEvict注解缓存删除成功实现。
通过上面的案例可以看出:使用基于注解的Redis缓存实现只需要添加Redis依赖、并使用几个注解在对应的方法上,就可以实现对数据的缓存管理。
另外,还可以在SpringBoot全局配置文件中配置Redis有效期,示例代码如下:
# 对基于注解的Redis缓存数据统一设置有效期为1分钟,单位毫秒 spring.cache.redis.time-to-live=60000
上述代码中,在SpringBoot全局配置文件中添加了“spring.cache.redis.time-to-live”属性统一设置Redis数据的有效期(单位为毫秒),但这种方式不够灵活,因此一般不用。
基于API的Redis缓存实现
在SpringBoot整合Redis缓存实现中,除了基于注解形式的Redis缓存形式外,还有一种开发中更常用的方式——基于API的Redis缓存实现。这种基于API的Redis缓存实现,需要在某种业务需求下通过Redis提供的API调用相关方法实现数据缓存管理。同时,这种方法还可以手动管理缓存的有效期。
下面,通过Redis API的方式讲解SpringBoot整合Redis缓存的具体实现。
(1)使用Redis API进行业务数据缓存管理
在 com.hardy.springbootdatacache.service 包下新建一个 ApiCommentService:
package com.hardy.springbootdatacache.service;
import com.hardy.springbootdatacache.entity.Comment;
import com.hardy.springbootdatacache.repository.CommentRepository;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CacheEvict;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CachePut;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.Optional;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* @Author: HardyYao
* @Date: 2021/6/19
*/
@Service
public class ApiCommentService {
@Autowired
private CommentRepository commentRepository;
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
/**
* 根据评论id查询评论
* @param id
* @return
*/
public Comment findCommentById(Integer id){
// 先查Redis缓存
Object o = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("comment_" + id);
if (o != null) {
return (Comment) o;
} else {
// 如果缓存中没有,则从数据库查询
Optional<Comment> dbComment = commentRepository.findById(id);
if (dbComment.isPresent()) {
Comment redisComment = dbComment.get();
// 将查询结果存储到缓存中,并设置有效期为1天
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("comment_"+id, redisComment,1, TimeUnit.DAYS);
return redisComment;
} else {
return null;
}
}
}
/**
* 更新评论
* @param comment
* @return
*/
public Comment updateComment(Comment comment) {
commentRepository.updateComment(comment.getAuthor(), comment.getId());
// 更新数据库数据后进行缓存更新
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("comment_" + comment.getId(), comment);
return comment;
}
/**
* 删除评论
* @param comment_id
*/
public void deleteComment(int comment_id) {
commentRepository.deleteById(comment_id);
// 删除数据库数据后进行缓存删除
redisTemplate.delete("comment_" + comment_id);
}
}(2)编写Web访问层ApiCommentController
package com.hardy.springbootdatacache.controller;
import com.hardy.springbootdatacache.entity.Comment;
import com.hardy.springbootdatacache.service.ApiCommentService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* @Author: HardyYao
* @Date: 2021/6/19
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("api") // 改变请求路径
public class ApiCommentController {
@Autowired
private ApiCommentService apiCommentService;
@RequestMapping(value = "/findCommentById")
public Comment findCommentById(Integer id){
Comment comment = apiCommentService.findCommentById(id);
return comment;
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/updateComment")
public Comment updateComment(Comment comment){
Comment oldComment = apiCommentService.findCommentById(comment.getId());
oldComment.setAuthor(comment.getAuthor());
Comment comment1 = apiCommentService.updateComment(oldComment);
return comment1;
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/deleteComment")
public void deleteComment(Integer id){
apiCommentService.deleteComment(id);
}
}(3)测试基于API的Redis缓存实现
输入:http://localhost:8080/api/findCommentById?id=2(连续输入三次)、http://localhost:8080/api/updateComment?id=2&author=hardy、http://localhost:8080/deleteComment?id=2进行访问:
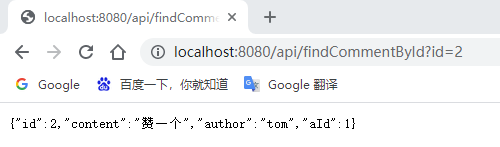
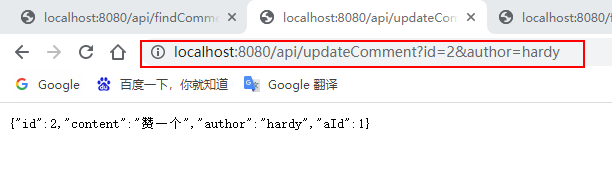
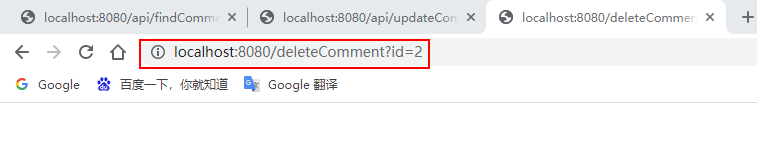
View console messages and Redis database:
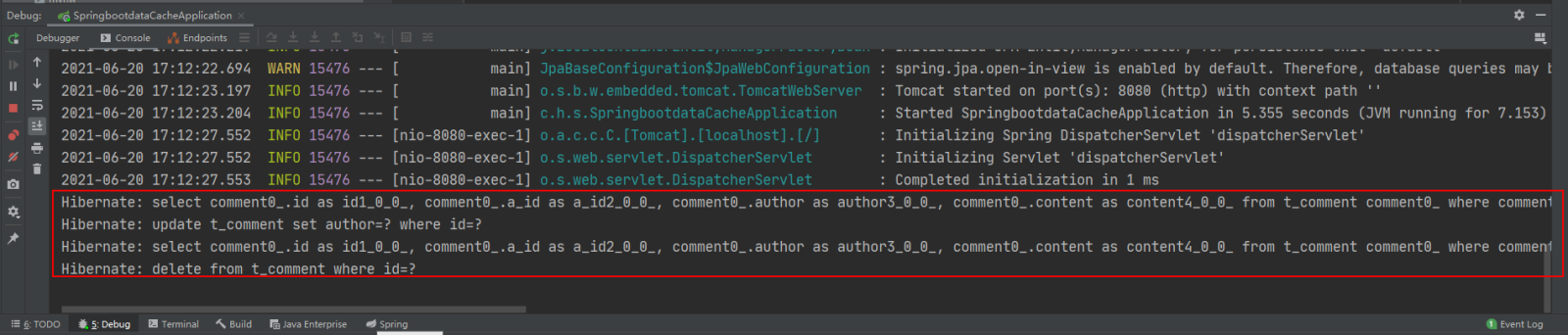
API-based Relevant configuration of Redis cache implementation: The API-based Redis cache implementation does not require the @EnableCaching annotation to enable annotation-based caching support, so here you can choose to delete or annotate the @EnableCaching annotation added to the project startup class. No Influence the functional implementation of the project.
The above is the detailed content of How SpringBoot integrates Redis cache implementation. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
Redis cluster mode deploys Redis instances to multiple servers through sharding, improving scalability and availability. The construction steps are as follows: Create odd Redis instances with different ports; Create 3 sentinel instances, monitor Redis instances and failover; configure sentinel configuration files, add monitoring Redis instance information and failover settings; configure Redis instance configuration files, enable cluster mode and specify the cluster information file path; create nodes.conf file, containing information of each Redis instance; start the cluster, execute the create command to create a cluster and specify the number of replicas; log in to the cluster to execute the CLUSTER INFO command to verify the cluster status; make
 How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear Redis data: Use the FLUSHALL command to clear all key values. Use the FLUSHDB command to clear the key value of the currently selected database. Use SELECT to switch databases, and then use FLUSHDB to clear multiple databases. Use the DEL command to delete a specific key. Use the redis-cli tool to clear the data.
 How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
To read a queue from Redis, you need to get the queue name, read the elements using the LPOP command, and process the empty queue. The specific steps are as follows: Get the queue name: name it with the prefix of "queue:" such as "queue:my-queue". Use the LPOP command: Eject the element from the head of the queue and return its value, such as LPOP queue:my-queue. Processing empty queues: If the queue is empty, LPOP returns nil, and you can check whether the queue exists before reading the element.
 How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
Using the Redis directive requires the following steps: Open the Redis client. Enter the command (verb key value). Provides the required parameters (varies from instruction to instruction). Press Enter to execute the command. Redis returns a response indicating the result of the operation (usually OK or -ERR).
 How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
Using Redis to lock operations requires obtaining the lock through the SETNX command, and then using the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time. The specific steps are: (1) Use the SETNX command to try to set a key-value pair; (2) Use the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time for the lock; (3) Use the DEL command to delete the lock when the lock is no longer needed.
 How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
The best way to understand Redis source code is to go step by step: get familiar with the basics of Redis. Select a specific module or function as the starting point. Start with the entry point of the module or function and view the code line by line. View the code through the function call chain. Be familiar with the underlying data structures used by Redis. Identify the algorithm used by Redis.
 How to solve data loss with redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:24 PM
How to solve data loss with redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:24 PM
Redis data loss causes include memory failures, power outages, human errors, and hardware failures. The solutions are: 1. Store data to disk with RDB or AOF persistence; 2. Copy to multiple servers for high availability; 3. HA with Redis Sentinel or Redis Cluster; 4. Create snapshots to back up data; 5. Implement best practices such as persistence, replication, snapshots, monitoring, and security measures.
 How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
Use the Redis command line tool (redis-cli) to manage and operate Redis through the following steps: Connect to the server, specify the address and port. Send commands to the server using the command name and parameters. Use the HELP command to view help information for a specific command. Use the QUIT command to exit the command line tool.




