How to use the SDS data structure of Redis
序言
Redis的几种基本数据结构有字符串(String)、哈希(Hash)、列表(List)、集合(Set)、有序集合(Sorted Set),这些是最常见的,也能在官网上查看到。
字符串
前面也提到过字符串是设计了简单动态字符串SDS(Simple Dynamic String)结构来表示字符串。这种数据结构可以提升字符串的操作效率,并可以保存二进制数据。
先思考一个问题:
Redis是用C语言实现的,那么为什么没有复用C语言的字符串实现方法,而选用了SDS呢?
char*字符串数组
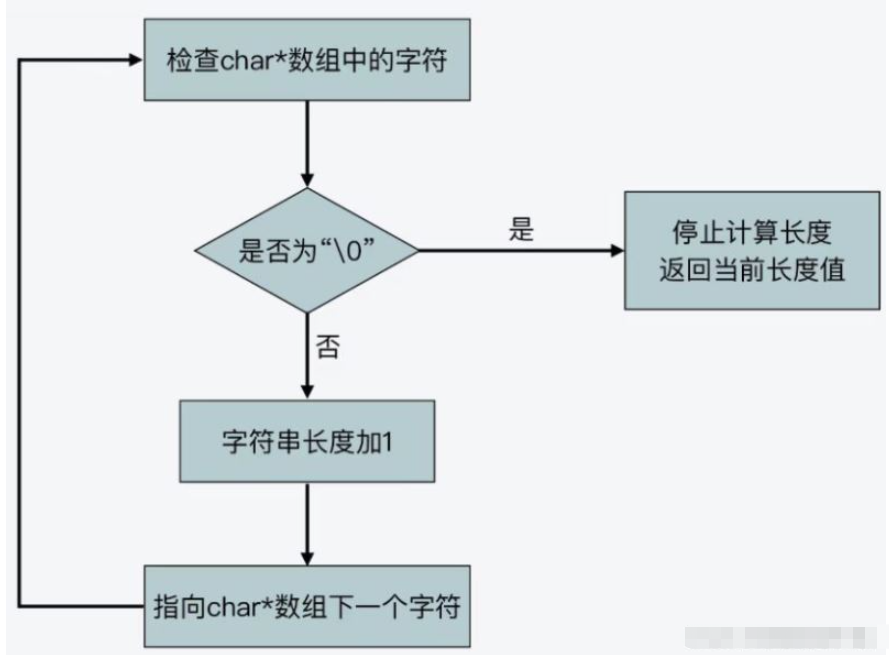
C语言实现字符串使用的是char*字符串数组,它是一块连续的内存空间,一次存放了字符串的每一个字符,并且最后一个字符是“\0”,用来标识字符串的结尾位置,如下图,

如果没有分隔符将连续的内存空间中的字符串区分开来,计算机将无法识别它们之间的位置。C语言标准库中,字符串操作函数根据在字符串数组中是否存在“\0”来判断字符串是否结束。例如字符串操作函数strlen函数,它就是在遍历字符串数组中的每一个字符,并进行计数,直到检查到“\0”,它的时间复杂度是O(n)。流程如下,
简单动态字符串SDS
SDS的数据结构里包含:字符串实际长度,字符串分配空间长度,SDS类型,字符数组,其中字符数组buf[]用来保存实际数据,如下图

再来看看类似的字符操作函数sdslen函数的源码(在sds.h文件中),直接根据SDS类型返回对应的字符串现有长度,避免了对字符串的遍历,时间复杂度变成了O(1),当然也会付出一点代价增加了空间复杂度。这都是设计人员让数据操作更加高效。源码如下,
static inline size_t sdslen(const sds s) {
unsigned char flags = s[-1];
switch(flags&SDS_TYPE_MASK) {
case SDS_TYPE_5:
return SDS_TYPE_5_LEN(flags);
case SDS_TYPE_8:
return SDS_HDR(8,s)->len;
case SDS_TYPE_16:
return SDS_HDR(16,s)->len;
case SDS_TYPE_32:
return SDS_HDR(32,s)->len;
case SDS_TYPE_64:
return SDS_HDR(64,s)->len;
}
return 0;
}再来看一下字符串的拷贝源码,操作都使用了字符串的现有长度,拷贝后进行更新。
sds sdscpylen(sds s, const char *t, size_t len) {
// 判断字符串数组分配的空间长度是不是小于字符串数组当前长度
if (sdsalloc(s) < len) {
// 根据要追加的长度len-sdslen(s)和现有长度,判断是否增加新的空间
s = sdsMakeRoomFor(s,len-sdslen(s));
if (s == NULL) return NULL;
}
// 将源字符串t中len长度的数据拷贝到目标字符串结尾
memcpy(s, t, len);
// 拷贝完后,在目标字符串结尾加上\0
s[len] = '\0';
// 设置字符串数组最新当前长度
sdssetlen(s, len);
return s;
}SDS把目标字符串的空间检查和扩容封装在了sdsMakeRoomFor函数中,追加、打印、复制等操作都会调用该函数。可以看到该函数根据sds的信息进行动态扩容,源码如下,
sds sdsMakeRoomFor(sds s, size_t addlen) {
void *sh, *newsh;
// 获取sds可用空间
size_t avail = sdsavail(s);
size_t len, newlen;
char type, oldtype = s[-1] & SDS_TYPE_MASK;
int hdrlen;
// 如果可用空间大于等于要增加的空间,则直接返回
if (avail >= addlen) return s;
// sds长度
len = sdslen(s);
// sds指针
sh = (char*)s-sdsHdrSize(oldtype);
// 新字符串长度
newlen = (len+addlen);
// 如果新长度小于最大预分配长度,则进行两倍扩容
if (newlen < SDS_MAX_PREALLOC)
newlen *= 2;
else
newlen += SDS_MAX_PREALLOC;
type = sdsReqType(newlen);
// SDS类型5转换为类型8
if (type == SDS_TYPE_5) type = SDS_TYPE_8;
hdrlen = sdsHdrSize(type);
if (oldtype==type) {
newsh = s_realloc(sh, hdrlen+newlen+1);
if (newsh == NULL) return NULL;
s = (char*)newsh+hdrlen;
} else {
/* Since the header size changes, need to move the string forward,
* and can't use realloc */
newsh = s_malloc(hdrlen+newlen+1);
if (newsh == NULL) return NULL;
memcpy((char*)newsh+hdrlen, s, len+1);
s_free(sh);
s = (char*)newsh+hdrlen;
s[-1] = type;
sdssetlen(s, len);
}
sdssetalloc(s, newlen);
return s;
}可以看到sdsMakeRoomFor函数中sdshdr5类型不再使用直接转换成了sdshdr8类型,它们是SDS设计的5种类型,分别表示sdshdr5、sdshdr8、sdshdr16、sdshdr32和sdshdr64,下面就看一下这几种类型的结构源码,如下图,
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr5 {
unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, and 5 msb of string length */
char buf[];
};
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr8 {
uint8_t len; /* used */
uint8_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */
unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */
char buf[];
};
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr16 {
uint16_t len; /* used */
uint16_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */
unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */
char buf[];
};
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr32 {
uint32_t len; /* used */
uint32_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */
unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */
char buf[];
};
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr64 {
uint64_t len; /* used */
uint64_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */
unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */
char buf[];
};sdshdr5已不再使用,所以在函数中做了处理,把sdshdr5类型转换为sdshdr8类型。前面也提到过SDS是紧凑型字符串数据结构,以sdshdr8为例,它是用的是uint8_t即8位无符号整型,会占用1字节的内存空间。SDS之所以设计不同的结构是为了能灵活保存不同大小的字符串,从而有效节省内存空间。
另外,__attribute__ ((__packed__))标志可以告诉编译器在编译以上数据结构时,不实用字节对齐的方式(不满8字节的整数倍,则会自动补齐),而是采用紧凑的方式分配内存。
The above is the detailed content of How to use the SDS data structure of Redis. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1387
1387
 52
52
 How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
Redis cluster mode deploys Redis instances to multiple servers through sharding, improving scalability and availability. The construction steps are as follows: Create odd Redis instances with different ports; Create 3 sentinel instances, monitor Redis instances and failover; configure sentinel configuration files, add monitoring Redis instance information and failover settings; configure Redis instance configuration files, enable cluster mode and specify the cluster information file path; create nodes.conf file, containing information of each Redis instance; start the cluster, execute the create command to create a cluster and specify the number of replicas; log in to the cluster to execute the CLUSTER INFO command to verify the cluster status; make
 How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear Redis data: Use the FLUSHALL command to clear all key values. Use the FLUSHDB command to clear the key value of the currently selected database. Use SELECT to switch databases, and then use FLUSHDB to clear multiple databases. Use the DEL command to delete a specific key. Use the redis-cli tool to clear the data.
 How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
To read a queue from Redis, you need to get the queue name, read the elements using the LPOP command, and process the empty queue. The specific steps are as follows: Get the queue name: name it with the prefix of "queue:" such as "queue:my-queue". Use the LPOP command: Eject the element from the head of the queue and return its value, such as LPOP queue:my-queue. Processing empty queues: If the queue is empty, LPOP returns nil, and you can check whether the queue exists before reading the element.
 How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
Using the Redis directive requires the following steps: Open the Redis client. Enter the command (verb key value). Provides the required parameters (varies from instruction to instruction). Press Enter to execute the command. Redis returns a response indicating the result of the operation (usually OK or -ERR).
 How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
Using Redis to lock operations requires obtaining the lock through the SETNX command, and then using the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time. The specific steps are: (1) Use the SETNX command to try to set a key-value pair; (2) Use the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time for the lock; (3) Use the DEL command to delete the lock when the lock is no longer needed.
 How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
The best way to understand Redis source code is to go step by step: get familiar with the basics of Redis. Select a specific module or function as the starting point. Start with the entry point of the module or function and view the code line by line. View the code through the function call chain. Be familiar with the underlying data structures used by Redis. Identify the algorithm used by Redis.
 How to solve data loss with redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:24 PM
How to solve data loss with redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:24 PM
Redis data loss causes include memory failures, power outages, human errors, and hardware failures. The solutions are: 1. Store data to disk with RDB or AOF persistence; 2. Copy to multiple servers for high availability; 3. HA with Redis Sentinel or Redis Cluster; 4. Create snapshots to back up data; 5. Implement best practices such as persistence, replication, snapshots, monitoring, and security measures.
 How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
Use the Redis command line tool (redis-cli) to manage and operate Redis through the following steps: Connect to the server, specify the address and port. Send commands to the server using the command name and parameters. Use the HELP command to view help information for a specific command. Use the QUIT command to exit the command line tool.




