 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals
 AI
AI
 Within 24 hours and $200 to copy the RLHF process, Stanford open sourced the 'Alpaca Farm'
Within 24 hours and $200 to copy the RLHF process, Stanford open sourced the 'Alpaca Farm'
Within 24 hours and $200 to copy the RLHF process, Stanford open sourced the 'Alpaca Farm'
At the end of February, Meta open sourced a large model series, LLaMA (literally translated as alpaca), with parameters ranging from 7 billion to 65 billion, which is called the prototype of the Meta version of ChatGPT. Afterwards, institutions such as Stanford University and the University of California, Berkeley, carried out "secondary innovations" based on LLaMA, and successively launched multiple open source large models such as Alpaca and Vicuna. For a time, "Alpaca" became the top model in the AI circle. These ChatGPT-like models built by the open source community iterate very quickly and are highly customizable. They are called the open source replacement of ChatGPT.
However, the reason why ChatGPT can show powerful capabilities in text understanding, generation, reasoning, etc. is because OpenAI uses a new training paradigm-RLHF for large models such as ChatGPT. (Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback), which uses reinforcement learning to optimize the language model based on human feedback. Using RLHF methods, large language models can be aligned with human preferences, follow human intent, and minimize unhelpful, distorted, or biased output. However, the RLHF method relies on extensive manual annotation and evaluation, which often requires weeks and thousands of dollars to collect human feedback, which is costly.
Now, Stanford University, which launched the open source model Alpaca, has proposed another simulator - AlpacaFarm (literally translated as alpaca farm). AlpacaFarm can replicate the RLHF process in 24 hours for only about $200, allowing open source models to quickly improve human assessment results, which can be called the equivalent of RLHF.

AlpacaFarm attempts to quickly and cheaply develop ways to learn from human feedback. To do this, the Stanford research team first identified three main difficulties in studying RLHF methods: the high cost of human preference data, the lack of trustworthy evaluations, and the lack of reference implementations.
To solve these three problems, AlpacaFarm built concrete implementations of simulation annotators, automatic evaluation, and SOTA methods. Currently, the AlpacaFarm project code is open source.
- GitHub address: https://github.com/tatsu-lab/alpaca_farm
- Paper address: https://tatsu-lab.github.io/alpaca_farm_paper.pdf
As shown in the figure below, researchers can use the AlpacaFarm simulator to quickly develop new methods of learning from human feedback data, and can also migrate existing SOTA methods to actual on human preference data.
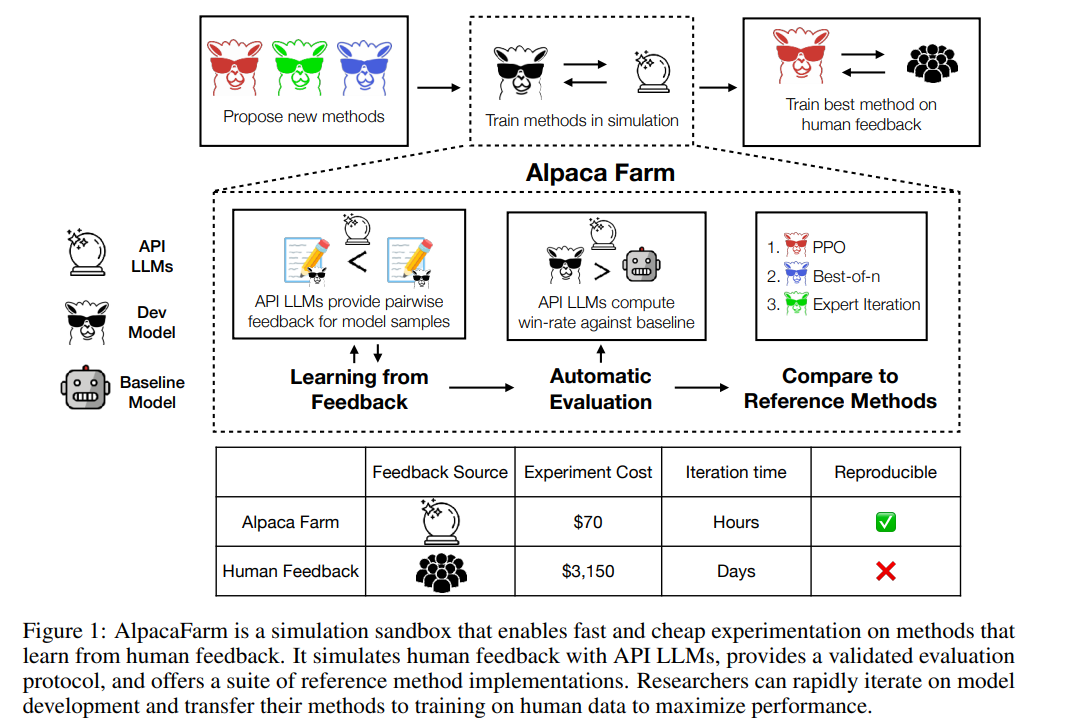
Simulation annotator
AlpacaFarm 52k instructions based on Alpaca dataset Build, of which 10k instructions are used to fine-tune the basic instruction following model, the remaining 42k instructions are used to learn human preferences and evaluation, and most of them are used to learn from simulated annotators. This study addresses the three major challenges of annotation cost, evaluation and verification implementation of the RLHF method, and proposes solutions one by one.
First, in order to reduce annotation costs, this study created prompts for API-accessible LLMs (such as GPT-4, ChatGPT), allowing AlpacaFarm to simulate human feedback at a cost of only RLHF Method 1/45 of the data collected. This study designed a random, noisy annotation scheme using 13 different prompts to extract different human preferences from multiple LLMs. This annotation scheme aims to capture different aspects of human feedback, such as quality judgments, variability between annotators, and style preferences.
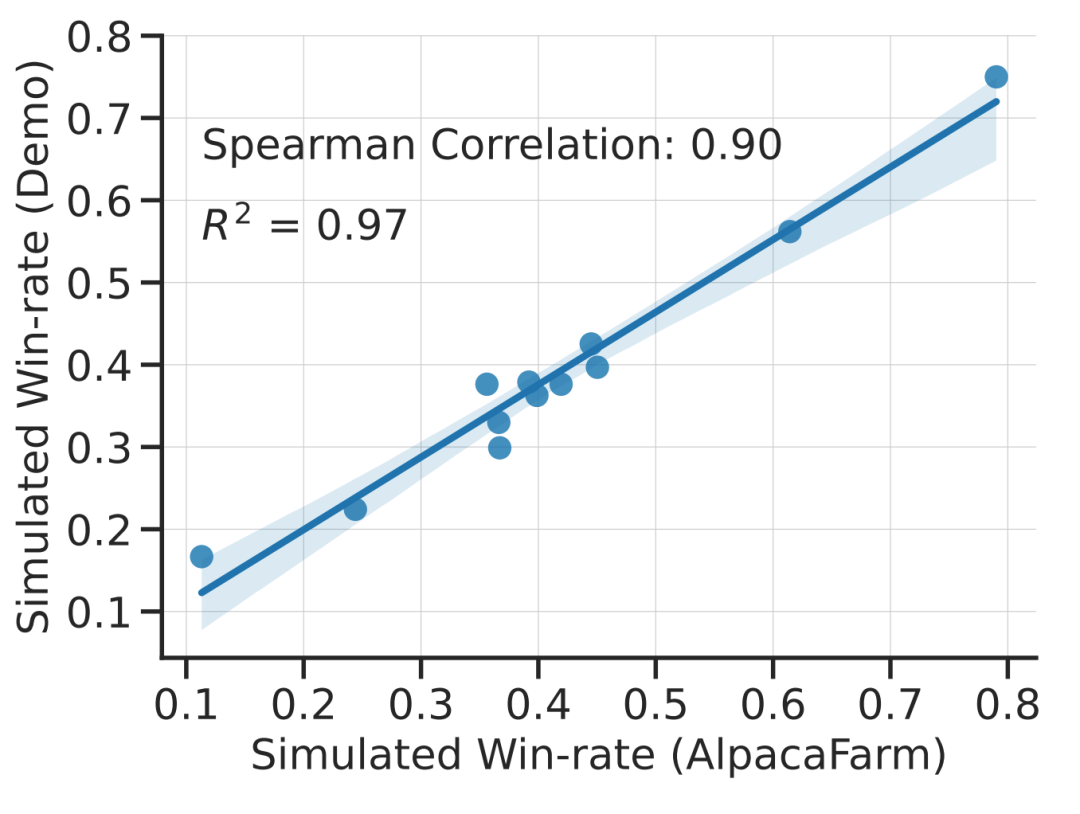
The study experimentally demonstrates that AlpacaFarm’s simulations are accurate. When the research team used AlpacaFarm to train and develop methods, the methods ranked very consistently with the same methods trained and developed using actual human feedback. The figure below shows the high correlation in rankings between methods resulting from the AlpacaFarm simulation workflow and the human feedback workflow. This property is crucial because it shows that experimental conclusions drawn from simulations are likely to hold true in real situations.
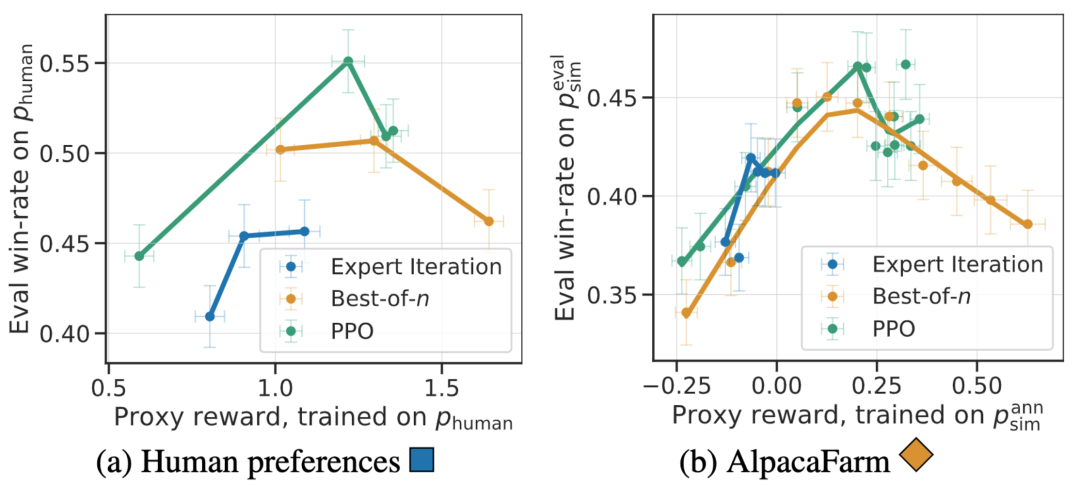
In addition to method-level correlation, the AlpacaFarm simulator can also replicate qualitative phenomena such as reward model over-optimization, but continuous RLHF training for surrogate rewards may damage Model performance. The following figure shows this phenomenon in the two cases of human feedback (left) and AlpacaFarm (right). We can see that AlpacaFarm initially captures the correct deterministic behavior of model performance improvement, and then as RLHF training continues, model performance decreases.
For evaluation, the research team used Alpaca 7B real-time user interaction as a guide, and simulates instruction distribution by combining several existing public datasets, including the self-instruct dataset, the anthropopic helpfulness dataset, and the evaluation sets of Open Assistant, Koala, and Vicuna. Using these evaluation instructions, the study compared the response of the RLHF model to the Davinci003 model and used a score to measure the number of times the RLHF model responded better, calling this score the win-rate. As shown in the figure below, a quantitative evaluation of system rankings on the study's evaluation data shows that system rankings and real-time user commands are highly correlated. This result shows that aggregating existing public data can achieve performance similar to simple real instructions.
For the third challenge——Lack of reference Implementation,The research team implemented and tested several popular,learning algorithms (such as PPO, expert iteration, best-of-n,sampling). The research team found that simpler methods that worked in other domains were no better than the study's original SFT model, suggesting that it is important to test these algorithms in a real instruction-following environment.
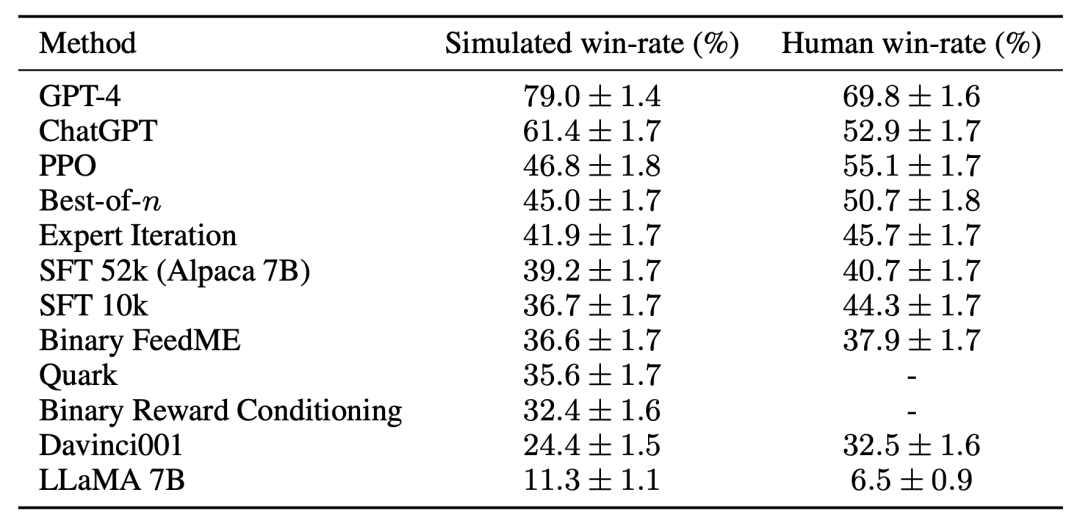
Based on manual evaluation, the PPO algorithm proved to be the most effective, combining the model with The winning rate compared to Davinci003 increased from 44% to 55%, even surpassing ChatGPT.
These results show that the PPO algorithm is very effective in optimizing the winning rate for the model. It is important to note that these results are specific to the evaluation data and annotators of this study. While the study's evaluation instructions represent real-time user instructions, they may not cover more challenging problems, and it is not certain how much improvements in win rate come from exploiting style preferences rather than factuality or correctness. For example, the study found that the PPO model produced much longer output and often provided more detailed explanations for the answers, as shown below:


Overall, using AlpacaFarm to train the model on simulated preferences can significantly improve the human evaluation results of the model without having to subject the model to Retraining on human preferences. Although this transfer process is fragile and still slightly less effective than retraining the model on human preference data. However, it can copy the RLHF pipeline within 24 hours with only $200, allowing the model to quickly improve human evaluation performance. The simulator AlpacaFarm is still too good. It is made by the open source community to replicate the powerful functions of models such as ChatGPT. Another effort.
The above is the detailed content of Within 24 hours and $200 to copy the RLHF process, Stanford open sourced the 'Alpaca Farm'. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 What are the types of return values of c language function? Summary of types of return values of c language function?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 11:18 PM
What are the types of return values of c language function? Summary of types of return values of c language function?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 11:18 PM
The return value types of C language function include int, float, double, char, void and pointer types. int is used to return integers, float and double are used to return floats, and char returns characters. void means that the function does not return any value. The pointer type returns the memory address, be careful to avoid memory leakage.结构体或联合体可返回多个相关数据。
 CS-Week 3
Apr 04, 2025 am 06:06 AM
CS-Week 3
Apr 04, 2025 am 06:06 AM
Algorithms are the set of instructions to solve problems, and their execution speed and memory usage vary. In programming, many algorithms are based on data search and sorting. This article will introduce several data retrieval and sorting algorithms. Linear search assumes that there is an array [20,500,10,5,100,1,50] and needs to find the number 50. The linear search algorithm checks each element in the array one by one until the target value is found or the complete array is traversed. The algorithm flowchart is as follows: The pseudo-code for linear search is as follows: Check each element: If the target value is found: Return true Return false C language implementation: #include#includeintmain(void){i
 How to use C language function pointer to find the maximum value of a one-dimensional array
Apr 03, 2025 pm 11:45 PM
How to use C language function pointer to find the maximum value of a one-dimensional array
Apr 03, 2025 pm 11:45 PM
Flexible application of function pointers: use comparison functions to find the maximum value of an array. First, define the comparison function type CompareFunc, and then write the comparison function compareMax(a, b). The findMax function accepts array, array size, and comparison function parameters, and uses the comparison function to loop to compare array elements to find the maximum value. This method has strong code reusability, reflects the idea of higher-order programming, and is conducive to solving more complex problems.
 What are c language function pointers and pointer functions? What's the difference?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 11:54 PM
What are c language function pointers and pointer functions? What's the difference?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 11:54 PM
A function pointer is a pointer to a function, and a pointer function is a function that returns a pointer. Function pointers point to functions, used to select and execute different functions; pointer functions return pointers to variables, arrays or other functions; when using function pointers, pay attention to parameter matching and checking pointer null values; when using pointer functions, pay attention to memory management and free dynamically allocated memory; understand the differences and characteristics of the two to avoid confusion and errors.
 What are the formats of function definition in C language?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 11:51 PM
What are the formats of function definition in C language?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 11:51 PM
The key elements of C function definition include: return type (defining the value returned by the function), function name (following the naming specification and determining the scope), parameter list (defining the parameter type, quantity and order accepted by the function) and function body (implementing the logic of the function). It is crucial to clarify the meaning and subtle relationship of these elements, and can help developers avoid "pits" and write more efficient and elegant code.
 What are the pointer parameters in the parentheses of the C language function?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 11:48 PM
What are the pointer parameters in the parentheses of the C language function?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 11:48 PM
The pointer parameters of C language function directly operate the memory area passed by the caller, including pointers to integers, strings, or structures. When using pointer parameters, you need to be careful to modify the memory pointed to by the pointer to avoid errors or memory problems. For double pointers to strings, modifying the pointer itself will lead to pointing to new strings, and memory management needs to be paid attention to. When handling pointer parameters to structures or arrays, you need to carefully check the pointer type and boundaries to avoid out-of-bounds access.
 What do nested calls and recursive calls of c language functions mean respectively?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 11:09 PM
What do nested calls and recursive calls of c language functions mean respectively?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 11:09 PM
C language function calls can be divided into nested calls and recursive calls. Nested calls refer to calling other functions within a function, nesting them layer by layer. Recursive calls refer to the function itself calling itself, which can be used to deal with self-similar structure problems. The key difference is that the functions in nested calls are called in sequence, with independent interaction scopes, while the functions in recursive calls are constantly called, so you need to pay attention to the recursive basis and stack overflow issues. Which calling method to choose depends on the specific requirements and performance requirements of the problem.
 What does the c language function return pointer output?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
What does the c language function return pointer output?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
The C language function returns a pointer to output a memory address. The pointing content depends on the operation inside the function, which may point to local variables (be careful, memory has been released after the function ends), dynamically allocated memory (must be allocated with malloc and free), or global variables.





