
SQL (Structured Query Language) is a standard as a standard language for accessing [relational databases]. Many database products such as Oracle, DB2, SQL Server, PostgreSQL, MySQL support it. Over the past few years, NoSQL initially claimed that it did not require SQL, but eventually had to be revised to "Not Only SQL" in order to be compatible with SQL technology.
The current typical version is the SQL 92 standard. Other databases, including MySql, have also extended some of their own SQL statements based on the standards of SQL 92 or SQL 99, such as the limit keyword in MySQL.
DDL
Data definition language, used to define database objects, databases, tables, columns, etc. Such as create, alter, drop, etc.
DML
Data manipulation language is used to update records in tables in the database. Such as insert, update, delete, etc.
DCL
Data control language is used to define database access permissions, security levels, etc. Such as grant, etc.
DQL:
Data query language, used for query. Such as select, from, where, etc.
# 语法顺序 SELECT DISTINCT <select_list> FROM <left_table> <join_type> JOIN <right_table> ON <join_condition> WHERE <where_condition> GROUP BY <group_by_list> HAVING <having_condition> ORDER BY <order_by_condition> LIMIT <limit_number> # 解析顺序 FROM <left_table> ON <join_condition> <join_type> JOIN <right_table> -- 这一步和上一步,会循环执行 WHERE <where_condition> -- 这一步会循环执行,多个条件从左往右 GROUP BY <group_by_list> HAVING <having_condition> SELECT -- 分组之后才执行SELECT DISTINCT <select_list> ORDER BY <order_by_condition> LIMIT <limit_number> -- 这一步是MySQL独有的语法,前面都是SQL92标准
Calculate the left table and right table of FROMCartesian product, generate virtual table VT1
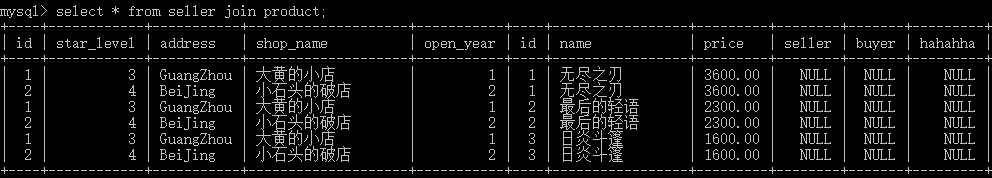
select * from seller join product;
select * from seller s join product p on s.id = p.id;
 ##OUTER JOIN
##OUTER JOIN
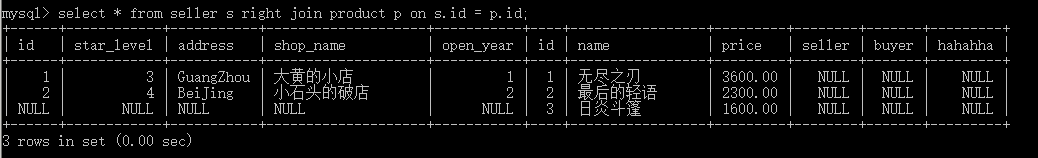
select * from seller s right join product p on s.id = p.id;
 If the FROM clause contains more than 2 tables, the above steps will be repeated for the result VT3 generated by the previous join connection and the next table
If the FROM clause contains more than 2 tables, the above steps will be repeated for the result VT3 generated by the previous join connection and the next table
WHERE
GROUP BY
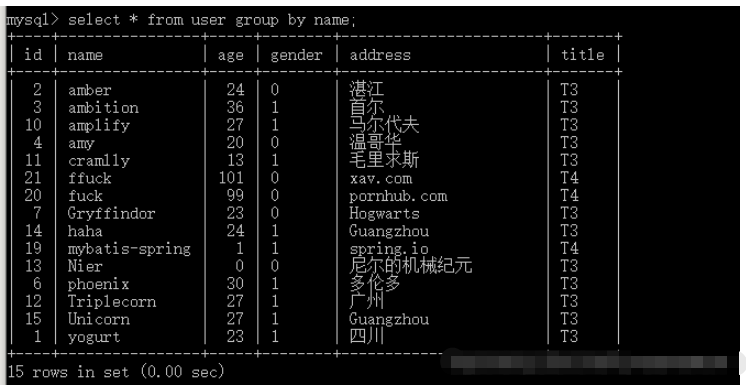
-- mysql 8 默认开启了 only_full_group_by select version(),@@sql_mode; -- 需要把这个选项关掉, set global sql_mode='STRICT_TRANS_TABLES,NO_ZERO_IN_DATE,NO_ZERO_DATE,ERROR_FOR_DIVISION_BY_ZERO,NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION'; set session sql_mode='STRICT_TRANS_TABLES,NO_ZERO_IN_DATE,NO_ZERO_DATE,ERROR_FOR_DIVISION_BY_ZERO,NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION'; -- 后执行group by 正常 select * from user group by name;
 HAVING
HAVING
SELECT
DISTINCT
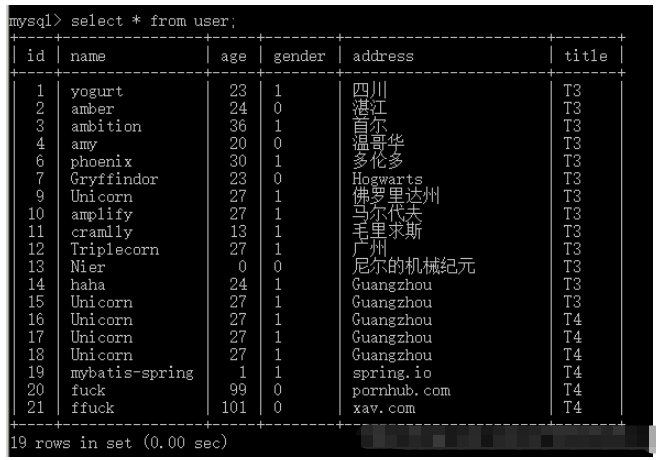
-- 下面无效 select id, distinct name from user; -- 下面有效 select distinct name from user;
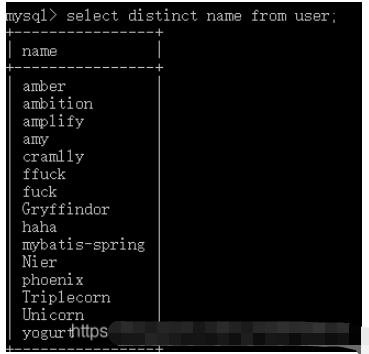 If you add multiple columns after distinct, then Splicing multiple columns together to remove duplication
If you add multiple columns after distinct, then Splicing multiple columns together to remove duplication
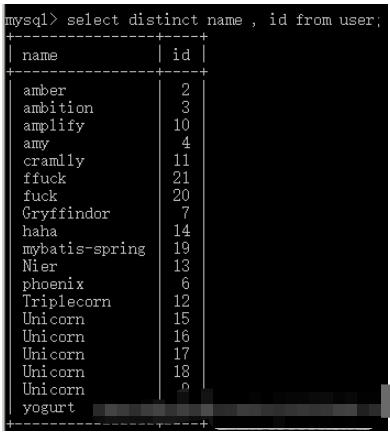 If you want to remove duplication based on a certain column and display the entire row of data, you can use GROUP BY
If you want to remove duplication based on a certain column and display the entire row of data, you can use GROUP BY
ORDER BY
LIMIT
Note: The aliases of columns in select can only be used in order by, as shown above The SQL parsing sequence can be known
The above is the detailed content of MySQL SQL syntax and SQL parsing sequence source code analysis. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




