How to use Java+mysql to implement student status management system
1. myswql database table
The project uses the mysql database and has 2 tables. A user table is used for login verification, and a student table is used for addition, deletion, modification and query.
creat table t_user( id int primary key auto_increment, login_name varchar(255), login_pwd varchar(255), real_name varchar(255), ); insert into t_user(id,login_name,login_pwd,real_name) values('akm',"123",'萝卜蹲'); CREATE TABLE t_user( id char(12) PRIMARY KEY, name char(6), pwd varchar(255), );
2. Function implementation
1. Actual demonstration
1.1 Login interface
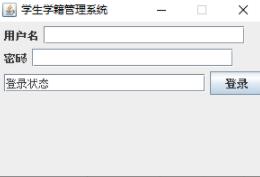
Input in the user's password field: akm
Input in the password field: 123
Click the login button to enter the system directly.
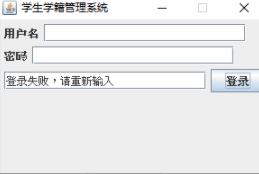
#If you enter incorrectly, the status bar will show login failure and the login account and password will be cleared.
1.2 System main interface
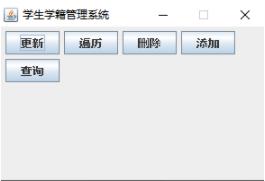
The system main interface consists of 5 buttons
To add student information, please select the add button on the main interface and click to enter the adding interface as shown above. Add corresponding student information, ID, name, age, student status, etc. to the interface.
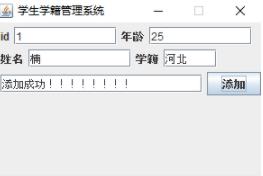
1.3 Query information
Query student information by id.
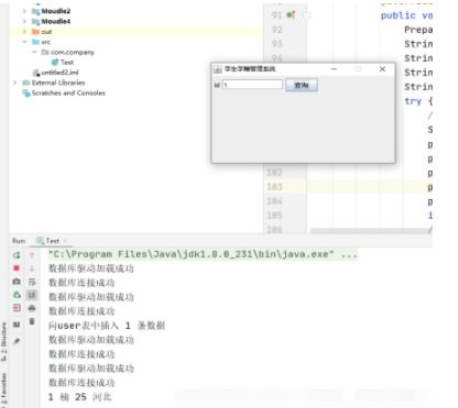
1.4 Traverse information

1.5 Delete information
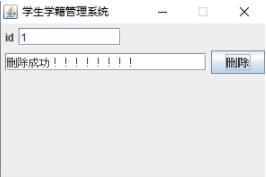
Enter the id to delete directly.
1.6 Update information
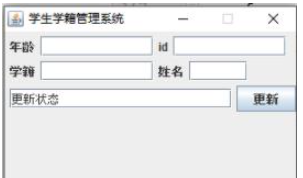
2.test.java file source code
The project has only one test file, no Encapsulation, friends who need it can encapsulate it themselves.
The code is as follows:
package com.company;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import java.sql.*;
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test {
static Connection conn ;
static Statement statement;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
login();
}
public static void control() {
JFrame jf = new JFrame("学生学籍管理系统");
jf.setLayout(new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.LEFT));
jf.setBounds(400, 300, 300, 200);
JButton button = new JButton("更新");
JButton button1=new JButton("遍历");
JButton button2=new JButton("删除");
JButton button3=new JButton("添加");
JButton button4=new JButton("查询");
jf.add(button);
jf.add(button1);
jf.add(button2);
jf.add(button3);
jf.add(button4);
button.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
update();
}
});
button1.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
query();
}
});
button2.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
delete();
}
});
button3.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
insert();
}
});
button4.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {onequery();}
});
jf.setVisible(true);
jf.setResizable(false);
button.setSize(40, 20);
jf.setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
public static void update() {
conn = getConnection();
JFrame jf = new JFrame("学生学籍管理系统");
jf.setLayout(new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.LEFT));
jf.setBounds(400, 300, 300, 200);
JLabel label1 = new JLabel("年龄");
JTextField agetext = new JTextField("", 10);
JLabel label2 = new JLabel("id");
JTextField idtext = new JTextField("", 10);
JLabel label3 = new JLabel("学籍");
JTextField addresstext = new JTextField("", 10);
JLabel label4 = new JLabel("姓名");
JTextField nametext = new JTextField("", 5);
JTextField out = new JTextField("更新状态", 20);
JButton button = new JButton("更新");
jf.add(label1);
jf.add(agetext);
jf.add(label2);
jf.add(idtext);
jf.add(label3);
jf.add(addresstext);
jf.add(label4);
jf.add(nametext);
jf.add(out);
jf.add(button);
button.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
PreparedStatement ps=null;
String age = agetext.getText();
String id = idtext.getText();
String address= addresstext.getText();
String name=nametext.getText();
try {
// 更新数据的sql语句
String sql = "update student set age =? , address =?, name=? where id = ?";
ps=conn.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setString(1,agetext.getText());
ps.setString(2,addresstext.getText());
ps.setString(3,nametext.getText());
ps.setString(4,idtext.getText());
int count = ps.executeUpdate();//记录操作次数
// 输出插入操作的处理结果
System.out.println("user表中更新 " + count + " 条数据");
ps.close();
//关闭数据库连接
conn.close();
out.setText("更新成功!!!!!!!!");
// 创建用于执行静态sql语句的Statement对象,st属局部变量
} catch (SQLException a) {
System.out.println("更新数据失败");
}
}
});
jf.setVisible(true);
jf.setResizable(false);
button.setSize(40, 20);
jf.setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
public static void query() {
PreparedStatement ps=null;
conn = getConnection();
JFrame jf = new JFrame("学生学籍管理系统");
jf.setLayout(null);
jf.setBounds(400, 300, 350, 200);
JButton button = new JButton("查询");
JTextArea jm=new JTextArea("ID\t姓名\t年龄\t学籍");//显示界面
jm.setBounds(10,50,350,100);//定义显示界面位置
jf.add(button);
jf.add(jm);
button.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
PreparedStatement ps=null;
try {
String sql = "select * from Student";
//创建用于执行静态sql语句的Statement对象,statement属局部变量
statement = conn.createStatement();//获取操作对象
ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql);// executeQuery执行单个SQL语句,返回单个ResultSet对象是
while (resultSet.next())//循环没有数据的时候返回flase退出循环
{
Integer Id = resultSet.getInt("id");//resultSet.next()是一个光标
String name = resultSet.getString("name");//getString返回的值一定是string
Integer age = resultSet.getInt("age");
String address=resultSet.getString("address");
//String adress = resultSet.getString("adress");
//输出查到的记录的各个字段的值
jm.append("\n"+Id + "\t" + name + "\t" + age+ "\t" + address );
}
statement.close();
conn.close();
}catch (SQLException b){
System.out.println("查询失败!!!!!!!!");
}
}
});
jf.setVisible(true);
jf.setResizable(false);
button.setSize(40, 20);
jf.setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
public static void delete() {
conn = getConnection();
JFrame jf = new JFrame("学生学籍管理系统");
jf.setLayout(new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.LEFT));
jf.setBounds(400, 300, 300, 200);
JLabel label2 = new JLabel("id");
JTextField idtext = new JTextField("", 10);
JTextField out = new JTextField("删除状态", 20);
JButton button = new JButton("删除");
jf.add(label2);
jf.add(idtext);
jf.add(out);
jf.add(button);
button.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
String id = idtext.getText();
PreparedStatement ps=null;
try {
// 删除数据的sql语句
String sql = "delete from Student where id = ?";
ps=conn.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setString(1,idtext.getText());
int count = ps.executeUpdate();//记录操作次数
// 输出插入操作的处理结果
System.out.println("student表中删除 " + count + " 条数据");
ps.close();
out.setText("删除成功!!!!!!!!");
// 关闭数据库连接
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException c) {
System.out.println("删除数据失败");
}
}
});
jf.setVisible(true);
jf.setResizable(false);
button.setSize(40, 20);
jf.setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
public static void insert() {
// 首先要获取连接,即连接到数据库
conn = getConnection();
JFrame jf = new JFrame("学生学籍管理系统");
jf.setLayout(new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.LEFT));
jf.setBounds(400, 300, 300, 200);
JLabel label3 = new JLabel("id");
JTextField idtext = new JTextField("", 10);
JLabel label1 = new JLabel("年龄");
JTextField agetext = new JTextField("", 10);
JLabel label2 = new JLabel("姓名");
JTextField nametext = new JTextField("", 10);
JLabel label4 = new JLabel("学籍");
JTextField addresstext = new JTextField("", 5);
JTextField out = new JTextField("添加状态", 20);
JButton button = new JButton("添加");
jf.add(label3);
jf.add(idtext);
jf.add(label1);
jf.add(agetext);
jf.add(label2);
jf.add(nametext);
jf.add(label4);
jf.add(addresstext);
jf.add(out);
jf.add(button);
button.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
String age = agetext.getText();
String name = nametext.getText();
String id=idtext.getText();
String address=addresstext.getText();
try {
PreparedStatement ps=null;
// 插入数据的sql语句
String sql = "INSERT INTO Student( id,age,name,address) VALUES ( ?,?,?,?)";
ps=conn.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setString(1,idtext.getText());
ps.setString(2,agetext.getText());
ps.setString(3,nametext.getText());
ps.setString(4,addresstext.getText());
int count = ps.executeUpdate();//记录操作次数
// 输出插入操作的处理结果
System.out.println("向user表中插入 " + count + " 条数据");
ps.close();
out.setText("添加成功!!!!!!!!");
// 关闭数据库连接
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException d) {
System.out.println("插入数据失败" + d.getMessage());
}
}
});
jf.setVisible(true);
jf.setResizable(false);
button.setSize(40, 20);
jf.setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
public static boolean login(){
conn = getConnection();
JFrame jf = new JFrame("学生学籍管理系统");
jf.setLayout(new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.LEFT));
jf.setBounds(400, 300, 300, 200);
JLabel label1 = new JLabel("用户名");
JTextField usernametext = new JTextField("", 20);
JLabel label2 = new JLabel("密码");
JPasswordField pwdtext = new JPasswordField("", 20);
JTextField out = new JTextField("登录状态", 20);
JButton button = new JButton("登录");
jf.add(label1);
jf.add(usernametext);
jf.add(label2);
jf.add(pwdtext);
jf.add(out);
jf.add(button);
button.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
// 插入数据的sql语句
PreparedStatement ps=null;
try {
statement = conn.createStatement();//获取操作对象
String x = usernametext.getText();
String y = pwdtext.getText();
String sql ="select * from user";
ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql);
while(resultSet.next()){
String a=resultSet.getString("login_name");
String b=resultSet.getString("login_pwd");
if(a.equals(x)&&b.equals(y))
{
control();
out.setText("!!!!!登录成功!!!!!");
}
else if(x!=a&&y!=b){
out.setText("登录失败,请重新输入");
}
}
usernametext.setText("");
pwdtext.setText("");
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
jf.setVisible(true);
jf.setResizable(false);
button.setSize(40, 20);
jf.setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
boolean ok = true;
return ok;
}
public static void onequery() {
PreparedStatement ps=null;
conn = getConnection();
JFrame jf = new JFrame("学生学籍管理系统");
jf.setLayout(new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.LEFT));
jf.setBounds(400, 300, 350, 200);
JLabel label3 = new JLabel("id");
JTextField idtext = new JTextField("", 10);
JLabel label1 = new JLabel("条件");
JTextField atext = new JTextField("", 10);
JButton button = new JButton("查询");
//JTextArea jm=new JTextArea("ID\t姓名\t年龄\t学籍");//显示界面
//jm.setBounds(10,50,350,100);//定义显示界面位置
jf.add(label3);
jf.add(idtext);
jf.add(button);
//jf.add(jm);
button.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
PreparedStatement ps=null;
String id=idtext.getText();
conn = getConnection();
try {
String sql = "select * from student where id = ?";
//创建用于执行静态sql语句的Statement对象,statement属局部变量
ps=conn.prepareStatement(sql);//获取操作对象
ps.setString(1,idtext.getText().toString());
ResultSet resultSet = ps.executeQuery();// executeQuery执行单个SQL语句,返回单个ResultSet对象是
while (resultSet.next())//循环没有数据的时候返回flase退出循环
{
Integer Id = resultSet.getInt("id");//resultSet.next()是一个光标
String name = resultSet.getString("name");//getString返回的值一定是string
Integer age = resultSet.getInt("age");
String address=resultSet.getString("address");
System.out.println(Id + " " + name + " " + age + " "+ address + " " );
//输出查到的记录的各个字段的值
//jm.append("\n"+Id + "\t" + name + "\t" + age+ "\t" + address );
}
statement.close();
conn.close();
}catch (SQLException m){
System.out.println(m.getMessage());
System.out.println("查询失败!!!!!!!!");
}
}
});
jf.setVisible(true);
jf.setResizable(false);
button.setSize(40, 20);
jf.setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
public static Connection getConnection(){
//创建用于连接数据库的Connection对象
Connection connection = null;
try {
// 加载Mysql数据驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
System.out.println("数据库驱动加载成功");
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai";
// 创建数据连接
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, "root", "root");
System.out.println("数据库连接成功");
}catch (ClassNotFoundException | SQLException e){
System.out.println("数据库连接失败" + e.getMessage());//处理查询结果
}
return connection;
}
}The above is the detailed content of How to use Java+mysql to implement student status management system. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 PHP vs. Python: Understanding the Differences
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP vs. Python: Understanding the Differences
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP and Python each have their own advantages, and the choice should be based on project requirements. 1.PHP is suitable for web development, with simple syntax and high execution efficiency. 2. Python is suitable for data science and machine learning, with concise syntax and rich libraries.
 How to open phpmyadmin
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
How to open phpmyadmin
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
You can open phpMyAdmin through the following steps: 1. Log in to the website control panel; 2. Find and click the phpMyAdmin icon; 3. Enter MySQL credentials; 4. Click "Login".
 MySQL: Simple Concepts for Easy Learning
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:29 AM
MySQL: Simple Concepts for Easy Learning
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:29 AM
MySQL is an open source relational database management system. 1) Create database and tables: Use the CREATEDATABASE and CREATETABLE commands. 2) Basic operations: INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE and SELECT. 3) Advanced operations: JOIN, subquery and transaction processing. 4) Debugging skills: Check syntax, data type and permissions. 5) Optimization suggestions: Use indexes, avoid SELECT* and use transactions.
 How to create navicat premium
Apr 09, 2025 am 07:09 AM
How to create navicat premium
Apr 09, 2025 am 07:09 AM
Create a database using Navicat Premium: Connect to the database server and enter the connection parameters. Right-click on the server and select Create Database. Enter the name of the new database and the specified character set and collation. Connect to the new database and create the table in the Object Browser. Right-click on the table and select Insert Data to insert the data.
 MySQL and SQL: Essential Skills for Developers
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:30 AM
MySQL and SQL: Essential Skills for Developers
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:30 AM
MySQL and SQL are essential skills for developers. 1.MySQL is an open source relational database management system, and SQL is the standard language used to manage and operate databases. 2.MySQL supports multiple storage engines through efficient data storage and retrieval functions, and SQL completes complex data operations through simple statements. 3. Examples of usage include basic queries and advanced queries, such as filtering and sorting by condition. 4. Common errors include syntax errors and performance issues, which can be optimized by checking SQL statements and using EXPLAIN commands. 5. Performance optimization techniques include using indexes, avoiding full table scanning, optimizing JOIN operations and improving code readability.
 How to create a new connection to mysql in navicat
Apr 09, 2025 am 07:21 AM
How to create a new connection to mysql in navicat
Apr 09, 2025 am 07:21 AM
You can create a new MySQL connection in Navicat by following the steps: Open the application and select New Connection (Ctrl N). Select "MySQL" as the connection type. Enter the hostname/IP address, port, username, and password. (Optional) Configure advanced options. Save the connection and enter the connection name.
 How to recover data after SQL deletes rows
Apr 09, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
How to recover data after SQL deletes rows
Apr 09, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
Recovering deleted rows directly from the database is usually impossible unless there is a backup or transaction rollback mechanism. Key point: Transaction rollback: Execute ROLLBACK before the transaction is committed to recover data. Backup: Regular backup of the database can be used to quickly restore data. Database snapshot: You can create a read-only copy of the database and restore the data after the data is deleted accidentally. Use DELETE statement with caution: Check the conditions carefully to avoid accidentally deleting data. Use the WHERE clause: explicitly specify the data to be deleted. Use the test environment: Test before performing a DELETE operation.
 How to use single threaded redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:12 PM
How to use single threaded redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:12 PM
Redis uses a single threaded architecture to provide high performance, simplicity, and consistency. It utilizes I/O multiplexing, event loops, non-blocking I/O, and shared memory to improve concurrency, but with limitations of concurrency limitations, single point of failure, and unsuitable for write-intensive workloads.




