How to use SpringBoot+RabbitMQ to achieve reliable message transmission
Environment configuration
SpringBoot Integration RabbitMQ realizes the sending of messages.
1. Add maven dependencies
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId>
</dependency>2. Add application.yml configuration file
spring:
rabbitmq:
host: 192.168.3.19
port: 5672
username: admin
password: xxxx3. Configure switches, queues and bindings
@Bean
public DirectExchange myExchange() {
DirectExchange directExchange = new DirectExchange("myExchange");
return directExchange;
}
@Bean
public Queue myQueue() {
Queue queue = new Queue("myQueue");
return queue;
}
@Bean
public Binding binding() {
return BindingBuilder.bind(myQueue()).to(myExchange()).with("myRoutingKey");
}4. Production sends messages
@Autowired
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
@GetMapping("/send")
public String send(String message) {
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("myExchange","myRoutingKey",message);
System.out.println("【发送消息】" + message)
return "【send message】" + message;
}5. Consumers receive messages
@RabbitListener(queuesToDeclare = @Queue("myQueue"))
public void process(String msg, Channel channel, Message message) {
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
Date date = new Date();
String time = sdf.format(date);
System.out.println("【接收信息】" + msg + " 当前时间" + time);6. Call the production end to send messages hello, console output:
[Send message] hello
[Receive message] hello Current time 2022-05-12 10:21:14
Indicates that the message has been successfully received.
Message loss analysis
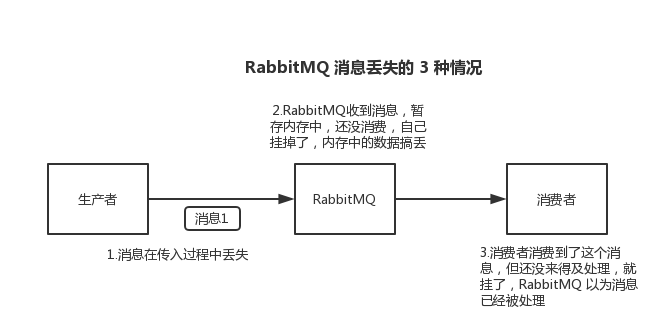
From production to consumption of a message, message loss may occur in the following stages:
Lost on the production side: The producer cannot transmit to
RabbitMQLost on the storage side:
RabbitMQThe storage itself is downLost at the consumer end: The storage cannot be sent to the consumer end due to network problems, or consumption hangs and normal consumption cannot be sent
RabbitMQ Provides good support for reliable transmission from the production side, storage side, and consumer side.
Production phase
The production phase uses the request confirmation mechanism to ensure reliable transmission of messages. After sending a message to the RabbitMQ server, RabbitMQ receives the message and returns a request confirmation to the sender, indicating that the RabbitMQ server has successfully received the message.
Configuration application.yml
spring:
rabbitmq:
# 消息确认机制 生产者 -> 交换机
publisher-confirms: true
# 消息返回机制 交换机 -> 队列
publisher-returns: trueConfiguration
@Configuration
@Slf4j
public class RabbitConfig {
@Autowired
private ConnectionFactory connectionFactory;
@Bean
public RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate() {
RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate = new RabbitTemplate(connectionFactory);
rabbitTemplate.setConfirmCallback(new RabbitTemplate.ConfirmCallback() {
@Override
public void confirm(CorrelationData correlationData, boolean ack, String cause) {
log.info("【correlationData】:" + correlationData);
log.info("【ack】" + ack);
log.info("【cause】" + cause);
if (ack) {
log.info("【发送成功】");
} else {
log.info("【发送失败】correlationData:" + correlationData + " cause:" + cause);
}
}
});
rabbitTemplate.setMandatory(true);
rabbitTemplate.setReturnCallback(new RabbitTemplate.ReturnCallback() {
@Override
public void returnedMessage(Message message, int replyCode, String replyText, String exchange, String routingKey) {
log.warn("【消息发送失败】");
log.info("【message】" + message);
log.info("【replyCode】" + replyCode);
}
});
return rabbitTemplate;
}
}Messages from producer to switch, there is confirmCallback Confirm mode. After the message is successfully sent, the message will call the method confirm(CorrelationData correlationData, boolean ack, String cause), and determine whether the message is successfully sent based on ack.
Messages from switch to queue have returnCallback return mode.
Send message product message The console output is as follows:
[Send message]product message
[Receive message]product message Current time 2022-05 -12 11:27:56
[correlationData]:null
[ack]true
[cause]null
[Send successfully]
The production end simulation message is lost
There are two solutions here:
Close the broker immediately after sending the message. The latter shuts down the network, but after the broker is closed, the console will always report an error and send the message. Also reported a 500 error.
Send non-existent switch:
// myExchange 修改成 myExchangexxxxx
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("myExchangexxxxx","myRoutingKey",message);Result:
[correlationData]:null
【ack】false
【cause】channel error; protocol method: #method(reply-code=404, reply-text=NOT_FOUND - no exchange 'myExchangexxxxx' in vhost '/', class-id =60, method-id=40)
[Failed to send]
When sending fails, you can retry the message
The switch is correct and the queue that does not exist is sent:
The switch receives the message and returns a success notification. The console output:
[correlationData]:CorrelationData [id=7d468b47-b422-4523-b2a2-06b14aef073c]
[ack ]true
[cause]null
[Send successfully]
The switch did not find the queue and returned failure information:
[Message sending failed]
[message]product message
[replyCode]312
RabbitMQ
Enable queue persistence, create queues and switchesThe default configuration is persistence of. First, set the queue and switch correctly, and modify the queue for consumption monitoring so that messages are stored in the queue.
Modify the persistence of the queue to non-persistence:
@Bean
public Queue myQueue() {
Queue queue = new Queue("myQueue",false);
return queue;
}After sending the message, the message is stored in the queue, and then restarts RabbitMQ, the message no longer exists.
Set queue persistence:
@Bean
public Queue myQueue() {
Queue queue = new Queue("myQueue",true);
return queue;
}After restarting, the messages in the queue still exist.
Consumer end
The consumer end starts by default ack Automatic confirmation mode. When the queue message is received by the consumer, it will be automatically deleted from the queue regardless of whether there is a message from the consumer end. news. Therefore, in order to ensure that the consumer can successfully consume the message, change the automatic mode to manual confirmation mode:
Modify the application.yml file
spring:
rabbitmq:
# 手动消息确认
listener:
simple:
acknowledge-mode: manualAfter consuming and receiving the message, manual confirmation is required:
channel.basicAck(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(),false);
@RabbitListener(queuesToDeclare = @Queue("myQueue"))
public void process(String msg, Channel channel, Message message) {
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
Date date = new Date();
String time = sdf.format(date);
System.out.println("【接收信息】" + msg + " 当前时间" + time);
System.out.println(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag());
try {
channel.basicAck(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(),false);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}If not added:
channel.basicAck(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(),false);
Send two messages
After the message is received, there is no confirmation and it is put back into the queue:
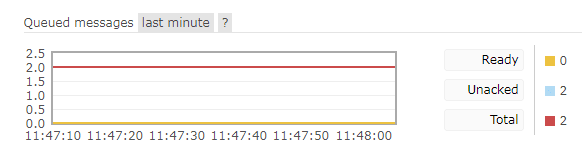
Restart the project. After that, the messages in the queue will be sent to the consumer, but without ack confirmation, they will continue to be put back into the queue.
After adding channel.basicAck, restart the project
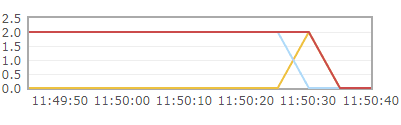
The queue message will be deleted
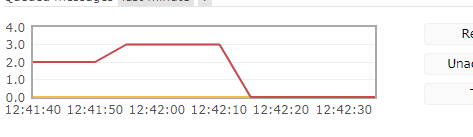
basicAck The last parameter of the method multiple means deleting the previous queue.
multiple is set to true, and all subsequent queues are cleared
The above is the detailed content of How to use SpringBoot+RabbitMQ to achieve reliable message transmission. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1385
1385
 52
52
 How to build a reliable messaging app with React and RabbitMQ
Sep 28, 2023 pm 08:24 PM
How to build a reliable messaging app with React and RabbitMQ
Sep 28, 2023 pm 08:24 PM
How to build a reliable messaging application with React and RabbitMQ Introduction: Modern applications need to support reliable messaging to achieve features such as real-time updates and data synchronization. React is a popular JavaScript library for building user interfaces, while RabbitMQ is a reliable messaging middleware. This article will introduce how to combine React and RabbitMQ to build a reliable messaging application, and provide specific code examples. RabbitMQ overview:
 How to use RabbitMQ to implement distributed message processing in PHP
Jul 18, 2023 am 11:00 AM
How to use RabbitMQ to implement distributed message processing in PHP
Jul 18, 2023 am 11:00 AM
How to use RabbitMQ to implement distributed message processing in PHP Introduction: In large-scale application development, distributed systems have become a common requirement. Distributed message processing is a pattern that improves the efficiency and reliability of the system by distributing tasks to multiple processing nodes. RabbitMQ is an open source, reliable message queuing system that uses the AMQP protocol to implement message delivery and processing. In this article we will cover how to use RabbitMQ in PHP for distribution
 Comparison and difference analysis between SpringBoot and SpringMVC
Dec 29, 2023 am 11:02 AM
Comparison and difference analysis between SpringBoot and SpringMVC
Dec 29, 2023 am 11:02 AM
SpringBoot and SpringMVC are both commonly used frameworks in Java development, but there are some obvious differences between them. This article will explore the features and uses of these two frameworks and compare their differences. First, let's learn about SpringBoot. SpringBoot was developed by the Pivotal team to simplify the creation and deployment of applications based on the Spring framework. It provides a fast, lightweight way to build stand-alone, executable
 Using RabbitMQ in Go: A Complete Guide
Jun 19, 2023 am 08:10 AM
Using RabbitMQ in Go: A Complete Guide
Jun 19, 2023 am 08:10 AM
As modern applications increase in complexity, messaging has become a powerful tool. In this area, RabbitMQ has become a very popular message broker that can be used to deliver messages between different applications. In this article, we will explore how to use RabbitMQ in Go language. This guide will cover the following: Introduction to RabbitMQ RabbitMQ Installation RabbitMQ Basic Concepts Getting Started with RabbitMQ in Go RabbitMQ and Go
 SpringBoot+Dubbo+Nacos development practical tutorial
Aug 15, 2023 pm 04:49 PM
SpringBoot+Dubbo+Nacos development practical tutorial
Aug 15, 2023 pm 04:49 PM
This article will write a detailed example to talk about the actual development of dubbo+nacos+Spring Boot. This article will not cover too much theoretical knowledge, but will write the simplest example to illustrate how dubbo can be integrated with nacos to quickly build a development environment.
 Solution for real-time data synchronization between Golang and RabbitMQ
Sep 27, 2023 pm 10:41 PM
Solution for real-time data synchronization between Golang and RabbitMQ
Sep 27, 2023 pm 10:41 PM
Introduction to the solution for real-time data synchronization between Golang and RabbitMQ: In today's era, with the popularity of the Internet and the explosive growth of data volume, real-time data synchronization has become more and more important. In order to solve the problems of asynchronous data transmission and data synchronization, many companies have begun to use message queues to achieve real-time synchronization of data. This article will introduce a real-time data synchronization solution based on Golang and RabbitMQ, and provide specific code examples. 1. What is RabbitMQ? Rabbi
 Application practice of go-zero and RabbitMQ
Jun 23, 2023 pm 12:54 PM
Application practice of go-zero and RabbitMQ
Jun 23, 2023 pm 12:54 PM
Now more and more companies are beginning to adopt the microservice architecture model, and in this architecture, message queues have become an important communication method, among which RabbitMQ is widely used. In the Go language, go-zero is a framework that has emerged in recent years. It provides many practical tools and methods to allow developers to use message queues more easily. Below we will introduce go-zero based on practical applications. And the usage and application practice of RabbitMQ. 1.RabbitMQ OverviewRabbit
 Golang RabbitMQ: Architectural design and implementation of a highly available message queue system
Sep 28, 2023 am 08:18 AM
Golang RabbitMQ: Architectural design and implementation of a highly available message queue system
Sep 28, 2023 am 08:18 AM
GolangRabbitMQ: The architectural design and implementation of a highly available message queue system requires specific code examples. Introduction: With the continuous development of Internet technology and its wide application, message queues have become an indispensable part of modern software systems. As a tool to implement decoupling, asynchronous communication, fault-tolerant processing and other functions, message queue provides high availability and scalability support for distributed systems. As an efficient and concise programming language, Golang is widely used to build high-concurrency and high-performance systems.




