How Springboot reads custom pro files and injects static variables
Springboot reads the pro file and injects static variables
mailConfig.properties
#服务器 mail.host=smtp.qq.com #端口号 mail.port=587 #邮箱账号 mail.userName=hzy_daybreak_lc@foxmail.com #邮箱授权码 mail.passWord=vxbkycyjkceocbdc #时间延迟 mail.timeout=25000 #发送人 mail.emailForm=hzy_daybreak_lc@foxmail.com #发件人 mail.personal=华夏衣裳 #主题 mail.subject=同袍用户激活 #内容模板 mail.html=您的邮箱验证码为:
MailConfig.java
/*
* @(#)MailConfig.java Created on 2019年9月11日
* Copyright (c) 2019 ZDSoft Networks, Inc. All rights reserved.
* $Id$
*/
package com.hxyc.config.properties;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @author huangzy
* @version $Revision: 1.0 $, $Date: 2019年9月11日 上午10:29:35 $
*/
@Configuration
@PropertySource(value = "classpath:config/mailConfig.properties", encoding = "UTF-8")
@Component
public class MailConfig {
public static String host;
public static Integer port;
public static String userName;
public static String passWord;
public static String emailForm;
public static String timeout;
public static String personal;
public static String html;
public static String subject;
/**
* @return Returns the host.
*/
public static String getHost() {
return host;
}
/**
* @param host
* The host to set.
*/
@Value("${mail.host}")
public void setHost(String host) {
MailConfig.host = host;
}
/**
* @return Returns the port.
*/
public static Integer getPort() {
return port;
}
/**
* @param port
* The port to set.
*/
@Value("${mail.port}")
public void setPort(Integer port) {
MailConfig.port = port;
}
/**
* @return Returns the userName.
*/
public static String getUserName() {
return userName;
}
/**
* @param userName
* The userName to set.
*/
@Value("${mail.userName}")
public void setUserName(String userName) {
MailConfig.userName = userName;
}
/**
* @return Returns the passWord.
*/
public static String getPassWord() {
return passWord;
}
/**
* @param passWord
* The passWord to set.
*/
@Value("${mail.passWord}")
public void setPassWord(String passWord) {
MailConfig.passWord = passWord;
}
/**
* @return Returns the emailForm.
*/
public static String getEmailForm() {
return emailForm;
}
/**
* @param emailForm
* The emailForm to set.
*/
@Value("${mail.emailForm}")
public void setEmailForm(String emailForm) {
MailConfig.emailForm = emailForm;
}
/**
* @return Returns the timeout.
*/
public static String getTimeout() {
return timeout;
}
/**
* @param timeout
* The timeout to set.
*/
@Value("${mail.timeout}")
public void setTimeout(String timeout) {
MailConfig.timeout = timeout;
}
/**
* @return Returns the personal.
*/
public static String getPersonal() {
return personal;
}
/**
* @param personal
* The personal to set.
*/
@Value("${mail.personal}")
public void setPersonal(String personal) {
MailConfig.personal = personal;
}
/**
* @return Returns the html.
*/
public static String getHtml() {
return html;
}
/**
* @param html
* The html to set.
*/
@Value("${mail.html}")
public void setHtml(String html) {
MailConfig.html = html;
}
/**
* @return Returns the subject.
*/
public static String getSubject() {
return subject;
}
/**
* @param subject
* The subject to set.
*/
@Value("${mail.subject}")
public void setSubject(String subject) {
MailConfig.subject = subject;
}
}springboot static property injection solution
The first way
Assign attributes (objects) through the springboot component initialization life cycle
@Component
public class DSHWechatApiUtil extends DSHBaseController {
@Autowired
private IThirdPartyAuthDao thirdPartyAuthDao;
private static IThirdPartyAuthDao staticThirdPartyAuthDao;
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
staticThirdPartyAuthDao = thirdPartyAuthDao;
}
public static JSONObject getAuthorizerToken(String componentAccessToken, String authorizerAppid, String authorizerRefreshToken) {
JSONObject returnObject = new JSONObject();
try {
if (DSHUtils.isEmpty(componentAccessToken)) {
componentAccessToken = staticThirdPartyAuthDao.selectWechatValue(DSHConstants.WECHAT_PARAMS.COMPONENT_ACCESS_TOKEN);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return returnObject;
}
}You can see that when the DSHWechatApiUtil tool class component is initialized, the method marked with the @PostConstruct annotation is called. Static variables are assigned values.
The second way
Through @Value() annotation
@Value() annotation will not inject attributes into static variables. By thinking in the first way, Then we must find a way to assign values when this component is initialized.
The first method is certainly possible. First write a property, then assign the value to the property through the @Value() annotation, and finally assign the value to the static property through the @PostConstruct annotation.
Here we have to use another method. The method here is to assign values through the set method. The attribute is statically modified, and the get method is also statically modified, but the set method cannot be statically modified. Use the @Value() annotation to modify the set method.
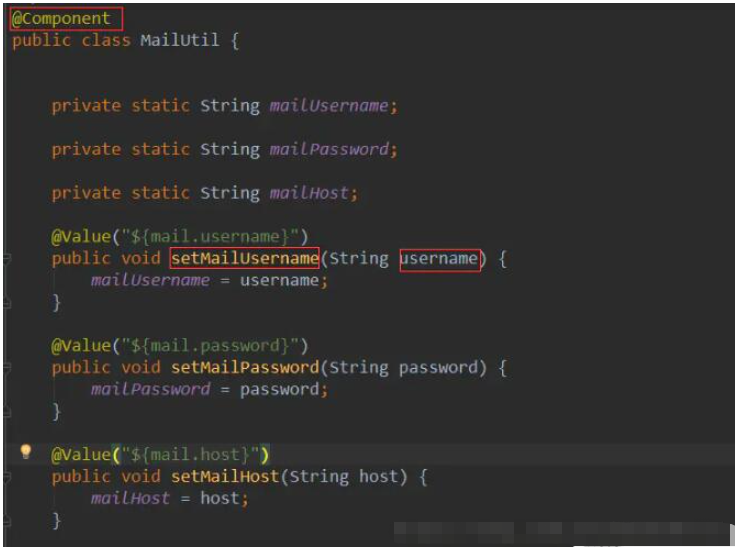
This will allow successful injection.
The third way
The third way is similar to the second way.
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = ProjectConfig.PROJECT_PREFIX)
public class ProjectConfig {
public static final String PROJECT_PREFIX = "project";
/**
* 系统版本号
*/
private String version;
/**
* 项目名称
*/
private String name;
/**
* 版权年份
*/
private String copyrightYear;
/**
* 实例演示开关
*/
private static boolean demoEnabled;
/**
* 获取地址ip开关
*/
private static boolean addressEnabled;
public String getVersion() {
return version;
}
public void setVersion(String version) {
this.version = version;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getCopyrightYear() {
return copyrightYear;
}
public void setCopyrightYear(String copyrightYear) {
this.copyrightYear = copyrightYear;
}
public boolean isDemoEnabled() {
return demoEnabled;
}
public void setDemoEnabled(boolean demoEnabled) {
ProjectConfig.demoEnabled = demoEnabled;
}
public static boolean isAddressEnabled() {
return addressEnabled;
}
public void setAddressEnabled(boolean addressEnabled) {
ProjectConfig.addressEnabled = addressEnabled;
}
}As shown in the above code, as long as the set method is set to non-static, then this configuration class The static properties can be injected successfully.
The above is the detailed content of How Springboot reads custom pro files and injects static variables. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 Which one is worth buying, Xiaomi Mi Pad 6 or Pro?
Feb 07, 2024 pm 08:36 PM
Which one is worth buying, Xiaomi Mi Pad 6 or Pro?
Feb 07, 2024 pm 08:36 PM
Many users are not sure which one is worth buying, Xiaomi Mi Pad 6 or Mi Pad 6. From the configuration point of view, the higher configuration of Pro is definitely recommended, but it also depends on the price and their own budget, and the different product positioning groups are also different. Which one is worth buying, Xiaomi Mi Pad 6 or Pro? Answer: Xiaomi Mi Pad 6 Pro will be better, both in terms of performance and camera battery life. 1. Processor Xiaomi Pad 6: Snapdragon 870 Xiaomi Mi Pad 6 Pro: more powerful first-generation Snapdragon 8+ processor 2. Battery size Xiaomi Mi Pad 6: 8840mAh, 67W second charge Xiaomi Mi Pad 6 Pro: 8600mAh, 33W The fast-charging Xiaomi Mi Pad 6 will have better battery life, but charging will be slower. 3. Take photos with Xiaomi Mi Pad 6
 iPhone 15 Pro Max vs iPhone 14 Pro Max: What are the comparisons and differences between them?
Sep 19, 2023 pm 08:29 PM
iPhone 15 Pro Max vs iPhone 14 Pro Max: What are the comparisons and differences between them?
Sep 19, 2023 pm 08:29 PM
iPhone 15 Pro vs. iPhone 14 Pro: Specs Comparison Here is a spec comparison between iPhone 15 Pro Max and iPhone 14 Pro Max: iPhone 15 Pro Max iPhone 14 Pro Max Display size 6.7 inches 6.7 inches Display technology Super Retina 2,000 nits Dimensions 6.29x3.02x0.32 inches 6.33x3.06x0.31 inches Weight 221 grams 240 grams
 How to start Xiaomi Mi Band 8pro
Jan 14, 2024 am 08:51 AM
How to start Xiaomi Mi Band 8pro
Jan 14, 2024 am 08:51 AM
Many users don’t know how to turn on the Xiaomi Mi Band 8 when they first come into contact with it. In fact, the method is very simple. We only need to find the USB data cable and connect the watch to the power supply, and then charge it for a while. You can press the button to turn on. How to turn on Xiaomi Mi Band 8pro 1. First install the watch, that is, connect the theme and the strap on both sides. 2. Then when we turn on the watch for the first time, we need to connect the charging cable. The connection method is at the bottom of the watch. 3. Wait for the watch to vibrate to power on, and then connect to your phone. >>>
 Comparison and difference analysis between SpringBoot and SpringMVC
Dec 29, 2023 am 11:02 AM
Comparison and difference analysis between SpringBoot and SpringMVC
Dec 29, 2023 am 11:02 AM
SpringBoot and SpringMVC are both commonly used frameworks in Java development, but there are some obvious differences between them. This article will explore the features and uses of these two frameworks and compare their differences. First, let's learn about SpringBoot. SpringBoot was developed by the Pivotal team to simplify the creation and deployment of applications based on the Spring framework. It provides a fast, lightweight way to build stand-alone, executable
 The difference between macbook air and pro
Feb 08, 2024 am 09:57 AM
The difference between macbook air and pro
Feb 08, 2024 am 09:57 AM
MacBook Air is an Apple laptop. Many users are curious about the differences between MacBook Air and Pro. These two notebooks have some differences in processor core, main frequency and graphics card type. The differences between MacBook Air and Pro: 1. Different processor cores and threads: MacBook Air's processor has dual cores and four threads. The Pro is more powerful than the MacBook Air, with four cores and eight threads. 2. The main frequency of the processor is different: the processor of MacBook Air has a main frequency of 1.6GHz. The main frequency of the pro's processor is 1.4GHz, which is slightly lower than that of the macbook air. 3. Different graphics cards: macbookair adopts
 Xiaomi Pro14 release date
Jan 05, 2024 pm 02:50 PM
Xiaomi Pro14 release date
Jan 05, 2024 pm 02:50 PM
Xiaomi pro14 is already on the market, and its configuration is very good for a business office notebook. There are three processor configurations to choose from, and the price is not particularly high. Many friends don’t know the specific launch time of Xiaomi Pro14. Xiaomi Pro14 launch time A: Xiaomi Pro14 Ryzen Edition will be available for pre-order on November 10, 2021, with an initial price starting from 5,299 yuan. Xiaomi Notebook Pro 14 will be released on July 4, 2022, and will officially go on sale at midnight on July 8. Xiaomi pro14 introduction 1. The screen is equipped with a 14-inch 2.5K Super Retina screen with a resolution of 2560x1600, a screen-to-body ratio of up to 88%, a 100% sRGB color gamut, and a refresh rate of 120Hz. 2. Appearance adopts 6 series
 How to get the value in application.yml in springboot
Jun 03, 2023 pm 06:43 PM
How to get the value in application.yml in springboot
Jun 03, 2023 pm 06:43 PM
In projects, some configuration information is often needed. This information may have different configurations in the test environment and the production environment, and may need to be modified later based on actual business conditions. We cannot hard-code these configurations in the code. It is best to write them in the configuration file. For example, you can write this information in the application.yml file. So, how to get or use this address in the code? There are 2 methods. Method 1: We can get the value corresponding to the key in the configuration file (application.yml) through the ${key} annotated with @Value. This method is suitable for situations where there are relatively few microservices. Method 2: In actual projects, When business is complicated, logic
 SpringBoot+Dubbo+Nacos development practical tutorial
Aug 15, 2023 pm 04:49 PM
SpringBoot+Dubbo+Nacos development practical tutorial
Aug 15, 2023 pm 04:49 PM
This article will write a detailed example to talk about the actual development of dubbo+nacos+Spring Boot. This article will not cover too much theoretical knowledge, but will write the simplest example to illustrate how dubbo can be integrated with nacos to quickly build a development environment.




