What are the basic knowledge points of Redis?
1. What is Redis
Let’s first take a look at the introduction given by the Redis official website:
Redis is an open source (BSD licensed), in-memory data structure store, used as a database, cache and message broker. It supports data structures such as strings, hashes, lists, sets, sorted sets with range queries, bitmaps, hyperloglogs, geospatial indexes with radius queries and streams. Redis has built-in replication, Lua scripting, LRU eviction, transactions and different levels of on-disk persistence, and provides high availability via Redis Sentinel and automatic partitioning with Redis Cluster.
In short, Redis is an open source using ANSI It is written in C language, complies with the BSD protocol, supports the network, can be based on memory and can be persisted, and is a log-type Key-Value database. It also provides a variety of data types and is very powerful.
2. The Father of Redis
The father of Redis is Salvatore Sanfilippo, a programmer from Sicily, Italy. Everyone is more accustomed to calling him Antirez. If you are interested in him, you can visit his blog or follow his GitHub.
3. What are the advantages of Redis
Fast speed: Redis uses memory to store data sets and supports Pipelining commands, which can send multiple data sets at once. command.
Persistence: The data in the memory can be saved on the disk and can be reloaded during restart.
Atomicity: All operations are atomic and transactions are supported.
Rich data structures: supports strings, lists, hashes, sets and ordered sets to meet most usage needs.
Supports multiple languages: Redis supports many languages, such as C, C, C#, Go, Java, JavaScript, PHP, etc.
Various features: Redis also supports publish/subscribe, notifications, key expiration and other features.
4. What can Redis do
Because Redis exchanges data quickly, it is often used in servers to store data that needs to be adjusted frequently. Compared with directly reading the disk to obtain the data, using Redis can save a lot of time and improve efficiency. For example:
There are 1 million people visiting the recommended video column on the homepage of a video website every day. If they are all read from the database, there will be at least 1 million more database query requests every day. If Redis is used, frequently retrieved data is stored in memory, saving 0.1 seconds each time, which is 100,000 seconds for 1 million times, which greatly improves the speed and cost.
In short, Redis has a wide range of application scenarios and is extremely valuable. Let’s start learning the basics now.
5. Install Redis
If you want to do a good job, you must first prepare the tools; if you want to learn Redis, then of course the first step is to install Redis. I only show installing Redis under Windows system because I am using Windows operating system. When you want to try Redis but don't want to install it, you can use the official online test website, which also has a simple introduction and tutorials.
Installing Redis under Windows Here we download the Redis-x64-3.2.100.zip compressed package file (if there is a newer version, you can download the recently updated stable version).
download
After downloading, extract it to your own folder. For example, I unzipped it to D:\redis.
unzip
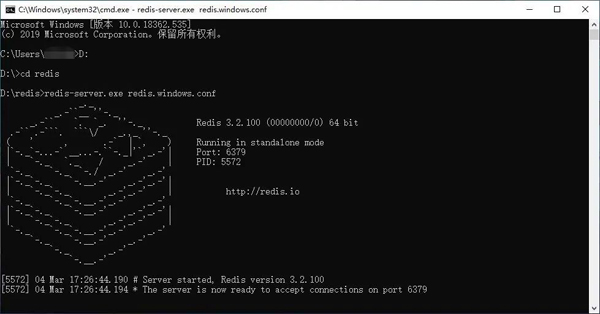
Open a cmd window and use the cd command to switch the directory to the decompressed folder path (for example, I switch the directory to D:\redis) , and then run the command:
redis-server.exe redis.windows.conf。
After input, the following interface will be displayed:
redis-server
We successfully started the Redis server , as shown in the figure, you can see the port number is 6379 and other related information. When using the redis server, we need to open a new cmd window and keep the original window open, otherwise we will not be able to access the server. Also switch the path to the redis directory, and then run:
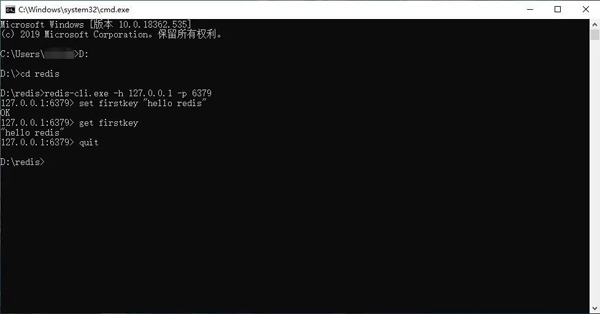
redis-cli.exe -h 127.0.0.1 -p 6379
Save a key-value pair:
set firstkey "hello redis"
Remove the key-value pair:
get firstkey
Close the connection:
quit
first_use
We successfully installed Redis under the Windows operating system and experienced the key-value pair storage mode of Redis for the first time.
6. Redis data structure
Redis supports five data structures: String (string), Hash (hash), List (list), Set (set) ) and SortedSet (ordered set). Below we briefly introduce each data structure and their basic commands.
Hongmeng Official Strategic Cooperation and Co-construction——HarmonyOS Technology Community
StringString是Redis最基本的数据结构,也是任何存储系统都必备的数据类型。String类型是二进制安全的,简单来说,基本上你什么都能用字符串存储,你可以把图片文件的内容或者序列化的对象作为字符串来存储。String类型的值最大可以存512MB,确实基本什么都够存了。
> set mykey "hello world" OK
> gey mykey "hello world"
> getrange mykey 6 10 "world" > getrange mykey 0 20 "hello world" > getrange mykey 0 -1 "hello world"
Tips:从上面几个实例,我们不难看出字符串起始从0开始;若end大于字符串长度时返回完整字符串;而当end为-1时,end为字符串最后一个字符。
> getset database "mysql" (nil) > get database "mysql" > getset database "redis" "mysql" > get database "redis"
Tips: 当键未设置时,会返回(nil)。
> strlen mykey (integer) 11
> append mykey ", hello redis" 24 >get mykey "hello world, hello redis"
> set incr_num 10 OK >get incr_num "10" >incr incr_num (integer) 11
> incrby incr_num 4 (intrger) 15
> incrbyfloat incr_num 0.5 15.5
Tips:整数值会显示为integer,当变为浮点型后并不会提示为float
> set decr_num 10 OK > get decr_num "10" > decr decr_num (integer) 9
> decrby decr_num 4 (integer) 5
Tips:redis并没有数字值减少给定浮点值的命令,如果我们想要decr_num减少2.5,可以用incrbyfloat命令执行incrbyfloat decr_num -2.5。
> incrbyfloat decr_num -2.5 2.5
decrby key decrement:整数值减少给定整数值(decrement)
decr key:整数值-1
incrbyfloat key increment:数字值增加给定浮点值(increment)
incrby key increment:整数值增加给定整数值(increment)
ncr key:整数值+1
append key value:如果可以已存在且是一个字符串,则将指定value添加到原值末尾,会返回操作后字符串长度
strlen key:返回键所存储的字符串值的长度
getset key value:设置指定键的新值,并返回旧值
getrange key start end:返回key中字符串的子串
get key:获取指定键的值
set key value:设置指定键的值
2. HashHash存储的是field和value的映射关系,适合用户存储对象。比如要存储一个用户的姓名、年龄、地址等,就可以使用Hash。每个Hash可以存储232>-1个field-value对(4294967295,40多亿)。
> hset myhash name "test" (integer) 1 > hget myhash name "NPC" > hset myhash name "NPC" (integer) 0
Tips:使用hset命令,新建字段并设置值成功后返回1,如果修改已有字段的值则返回0。
> hmset myhash age "20" country "China" OK
> hexists myhash name (integer) 1 > hexists myhash phone (integer) 0
Tips:哈希表key中含有字段field返回1,不含有或对应key不存在返回0。
> hmget myhash name age phone 1) "NPC" 2) "20" 3) (nil)
> hgetall myhash 1) "name" 2) "NPC" 3) "age" 4) "20" 5) "country" 6) "China"
> hkeys myhash 1) "name" 2) "age" 3) "country"
> hvals myhash 1) "NPC" 2) "20" 3) "China"
> hlen myhash 3
> hdel myhash age (integer) 1
hdel key field1:删除哈希表key中一个field
hlen key:获取哈希表key中字段的数量
hvals key:获取哈希表key中所有value
hkeys key:获取哈希表key中所有field
hgetall key:获取哈希表key中所有field-value对
hmget key field1 [field2]:获取哈希表key中所有给定field的value
hexists key field:查看field是否存在于哈希表key中
hmset key field1 value1 [field2 value2]:同时设置哈希表key中的多个field-value对。
hset key field value:设置哈希表中key中field的值为value
hget key field:获取哈希表key中field对应的value
3. ListRedis的List类型是简单的字符串列表,在底层实现上相当于一个链表,我们可以在列表的头部(左边)或尾部(右边)添加值。列表最多可以存储232>-1个元素(4294967295,40多亿)。
> lpush mylist "a" "b" (integer) 2 > rpush mylist "c" "d" (integer) 4
Tips:执行lpush和rpush命令后返回列表的长度。
> llen mylist (integer) 4
> lrange mylist 0 -1 1) "b" 2) "a" 3) "c" 4) "d" > lrange mylist 1 -2 1) "a" 2) "c"
Tips:由上述例子我们不难看出lrange命令中的start和end参数都是索引值,其中0代表第一个元素,-1表示最后一个元素。
> lindex mylist 0 "b"
> lpop mylist "b" > rpop mylist "d"
> rpush rem "hello" "hello" "redis" "hello" (integer) 4 > lrange rem 0 -1 1) "hello" 2) "hello" 3) "redis" 4) "hello" > lrem rem -2 "hello" (integer) 2 >lrange rem 0 -1 1) "hello" 2) "redis"
在列表中从左到右搜索,移除数量为count且与value相等的元素。count
lrem key count value:根据count的值,移除列表中与参数value相等的元素
lpop key:移除并获取列表头部的值
rpop key:移除并获取列表尾部的值
lindex key index:通过索引获取列表中元素
lrange key start end:获取列表指定范围内的值
llen key:获取列表长度
lpush key value1 [value2]:将一个或多个值插入到列表头部(左边)
rpush key value1 [value2]:将一个或多个值插入到列表尾部(右边)
4. SetSet(集合)存储string类型的值,集合不允许重复元素,但集合里面的元素没有先后顺序。集合中最大的成员数为232>-1(4294967295,40多亿)。
> sadd myset1 "hello" "redis" (integer) 2 > sadd myset1 "hello" (integer) 0
Tips:当向集合添加重复成员时,返回0
> scard myset1 2
> smembers myset1 1) "hello" 2) "redis"
> sadd myset2 "hello" "world" (integer) 2 > sdiff myset1 myset2 1) "redis" > sdiff myset2 myset1 1) "world"
> sinter myset1 myset2 1) "hello"
> sunion myset1 myset2 1) "hello" 2) "redis" 3) "world"
> sadd myset1 "NPC" (integer) 1 >spop myset1 "redis" >smembers myset1 1) "NPC" 2) "hello"
spop key:移除并返回集合中的一个随机元素
sunion key1 [key2]:返回所有给定集合的并集
sinter key1 [key2]:返回所有给定集合的交集
sdiff key1 [key2]:返回所有给定集合的差集
smembers key:返回集合中的所有成员
scard key:获取集合成员数量
sadd key member1 [member2]:向集合添加一个或多个成员
5. SortedSet除了无序集合(Set),Redis还提供了有序集合(SortedSet),有序集合不允许重复的成员,且每个不同的成员都关联一个double类型的分数,redis通过这些分数对成员进行从小到大排序。有序集合有时也被称为ZSet,因为其命令都是以字母Z开头的。
> zadd myzset 10 "one" 20 "two" 30 "three" (integer) 3
> zcard myzset 3
> zscore myzset "one" 10.0
> zrange myzset 0 -1 1) "one" 2) "two" 3) "three" > zrange myzset 0 -1 withscores 1) "one" 2) 10.0 3) "two" 4) 20.0 5) "three" 6) 30.0 > zrevrange myzset 0 -1 withscores 1) "three" 2) 30.0 3) "two" 4) 20.0 5) "one" 6) 10.0
> zrank myzset "one" 0 >zrank myzset "three" 2 > zrevrank myzset "one" 2 > zrevrank myzset "three" 0
> zcount myzset 15 40 2
> zrange myzset 0 -1 withscores 1) "one" 2) 10.0 3) "two" 4) 20.0 5) "three" 6) 30.0 > zincrby myzset 40 "one" 50.0 > zrange myzset 0 -1 withscores 1) "two" 2) 20.0 3) "three" 4) 30.0 5) "one" 6) 50.0
zincrby key increment member:将指定成员的分数增加increment
zcount key min max:返回分数在min和max之间的成员数量
zrank key member:返回指定成员的排名,从小到大排序
zrevrank key member:返回指定成员的排名,从大到小排序
zrange key start end [withscores]:通过索引start和end从小到大返回成员
zrevrange key start end [withscores]:通过索引start和end从大到小返回成员
zscore key member:返回指定成员的分数
zcard key:获取有序集合的成员数量
zadd key score1 member1 [score2 member2]:向有序集合中添加一个或多个成员,或者更新已有成员分数
The above is the detailed content of What are the basic knowledge points of Redis?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1376
1376
 52
52
 How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
Redis cluster mode deploys Redis instances to multiple servers through sharding, improving scalability and availability. The construction steps are as follows: Create odd Redis instances with different ports; Create 3 sentinel instances, monitor Redis instances and failover; configure sentinel configuration files, add monitoring Redis instance information and failover settings; configure Redis instance configuration files, enable cluster mode and specify the cluster information file path; create nodes.conf file, containing information of each Redis instance; start the cluster, execute the create command to create a cluster and specify the number of replicas; log in to the cluster to execute the CLUSTER INFO command to verify the cluster status; make
 How to implement the underlying redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:21 PM
How to implement the underlying redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:21 PM
Redis uses hash tables to store data and supports data structures such as strings, lists, hash tables, collections and ordered collections. Redis persists data through snapshots (RDB) and append write-only (AOF) mechanisms. Redis uses master-slave replication to improve data availability. Redis uses a single-threaded event loop to handle connections and commands to ensure data atomicity and consistency. Redis sets the expiration time for the key and uses the lazy delete mechanism to delete the expiration key.
 How to view all keys in redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:15 PM
How to view all keys in redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:15 PM
To view all keys in Redis, there are three ways: use the KEYS command to return all keys that match the specified pattern; use the SCAN command to iterate over the keys and return a set of keys; use the INFO command to get the total number of keys.
 How to view the version number of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 05:57 PM
How to view the version number of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 05:57 PM
To view the Redis version number, you can use the following three methods: (1) enter the INFO command, (2) start the server with the --version option, and (3) view the configuration file.
 What to do if redis-server can't be found
Apr 10, 2025 pm 06:54 PM
What to do if redis-server can't be found
Apr 10, 2025 pm 06:54 PM
Steps to solve the problem that redis-server cannot find: Check the installation to make sure Redis is installed correctly; set the environment variables REDIS_HOST and REDIS_PORT; start the Redis server redis-server; check whether the server is running redis-cli ping.
 How to use redis zset
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:27 PM
How to use redis zset
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:27 PM
Redis Ordered Sets (ZSets) are used to store ordered elements and sort by associated scores. The steps to use ZSet include: 1. Create a ZSet; 2. Add a member; 3. Get a member score; 4. Get a ranking; 5. Get a member in the ranking range; 6. Delete a member; 7. Get the number of elements; 8. Get the number of members in the score range.
 How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
Using the Redis directive requires the following steps: Open the Redis client. Enter the command (verb key value). Provides the required parameters (varies from instruction to instruction). Press Enter to execute the command. Redis returns a response indicating the result of the operation (usually OK or -ERR).
 How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
The best way to understand Redis source code is to go step by step: get familiar with the basics of Redis. Select a specific module or function as the starting point. Start with the entry point of the module or function and view the code line by line. View the code through the function call chain. Be familiar with the underlying data structures used by Redis. Identify the algorithm used by Redis.




