What are the common ways to use Redis?
1. Common usage methods
Several common usage methods of Redis include:
1.Redis single copy;
2.Redis multiple copies (master-slave) ;
3.Redis Sentinel;
4.Redis Cluster;
5.Redis self-developed.
2. Advantages and disadvantages of various usage methods
1. Redis single copy
Redis single copy adopts a single Redis node deployment architecture, and there is no backup node to synchronize data in real time. It does not provide data persistence and backup strategies, and is suitable for pure caching business scenarios with low data reliability requirements.
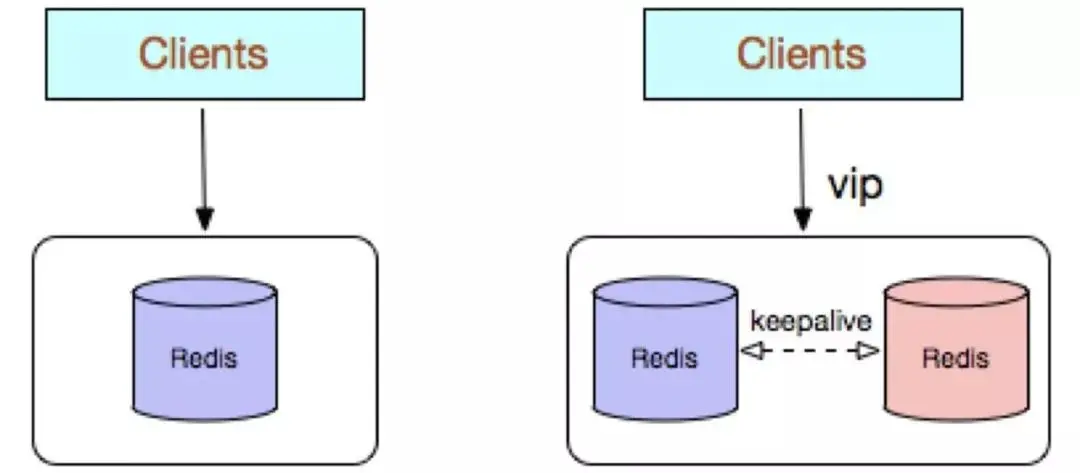
Advantages:
Simple architecture and easy deployment;
High cost performance: no backup node is required when using the cache (single instance Availability can be guaranteed with supervisor or crontab). Of course, in order to meet the high availability of the business, a backup node can also be sacrificed, but only one instance can provide external services at the same time;
High performance.
Disadvantages:
Does not guarantee data reliability;
When cache is used, data is lost after the process is restarted. Even if there are backup nodes to solve high availability, it still cannot Solve the problem of cache preheating, so it is not suitable for businesses with high data reliability requirements;
High performance is limited by the processing power of a single-core CPU (Redis is a single-thread mechanism), and the CPU is the main bottleneck, so it is suitable Scenarios with simple operation commands and less sorting and calculation. You can also consider using Memcached instead.
2. Redis multi-copy (master-slave)
Redis multi-copy adopts master-slave (replication) deployment structure. Compared with single copy, the biggest feature is the data between master and slave instances. Real-time synchronization and data persistence and backup strategies are provided. The company's basic environment configuration allows master-slave instances to be deployed on different physical servers, thereby achieving simultaneous provision of external services and a read-write separation strategy.
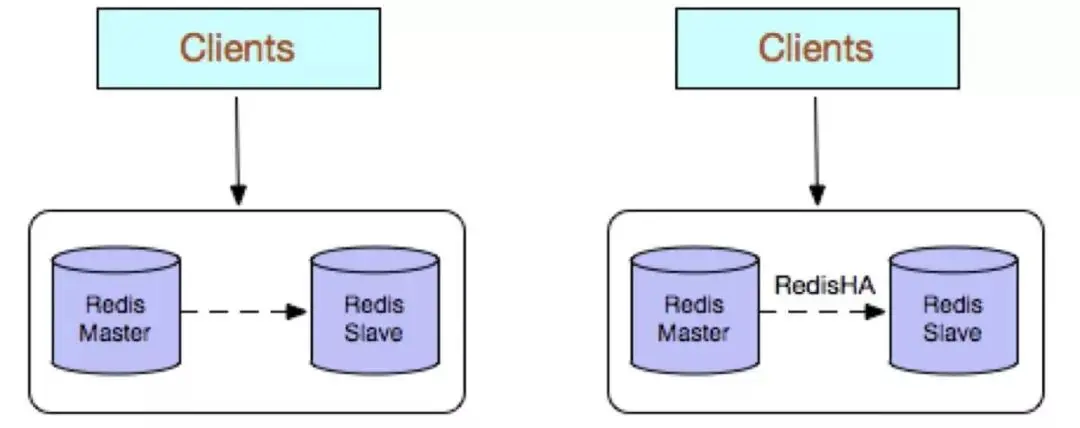
Advantages:
High reliability: On the one hand, it adopts a dual-machine active and standby architecture, which can automatically perform the active operation when the main database fails. Standby switching, the slave database is promoted to provide services to the main database to ensure smooth operation of the service; on the other hand, turning on the data persistence function and configuring a reasonable backup strategy can effectively solve the problems of data misoperation and abnormal data loss;
Read and write separation strategy: The slave node can expand the reading capability of the main database node and effectively cope with large concurrent read operations.
Disadvantages:
Failure recovery is complex. If there is no RedisHA system (requires development), when the main database node fails, a slave node needs to be manually promoted to the master node, and the business party needs to be notified. Change the configuration and need to let other slave database nodes copy the new master database node. The whole process requires human intervention and is relatively cumbersome;
The writing ability of the master database is limited by a single machine, so sharding can be considered;
The storage capacity of the main library is limited by a single machine, you can consider Pika;
The disadvantages of native replication will also be more prominent in early versions, such as: after Redis replication is interrupted, Slave will initiate pync. This If the synchronization is unsuccessful, full synchronization will be performed. When the main library performs full backup, it may cause millisecond or second-level lag; and due to the COW mechanism, the main library memory overflows in extreme cases, and the program exits abnormally or crashes. machine; the main library node generates backup files, which causes server disk IO and CPU (compression) resource consumption; sending backup files of several GB causes the server export bandwidth to increase dramatically and blocks requests. It is recommended to upgrade to the latest version.
3. Redis Sentinel (Sentinel)
Redis Sentinel is a native high-availability solution launched in the community version. Its deployment architecture mainly includes two parts: Redis Sentinel cluster and Redis data cluster.
The Redis Sentinel cluster is a distributed cluster composed of several Sentinel nodes, which can realize fault discovery, automatic failover, configuration center and client notification. The number of nodes to satisfy Redis Sentinel must be an odd number, and the number is 2n 1 (n≥1).
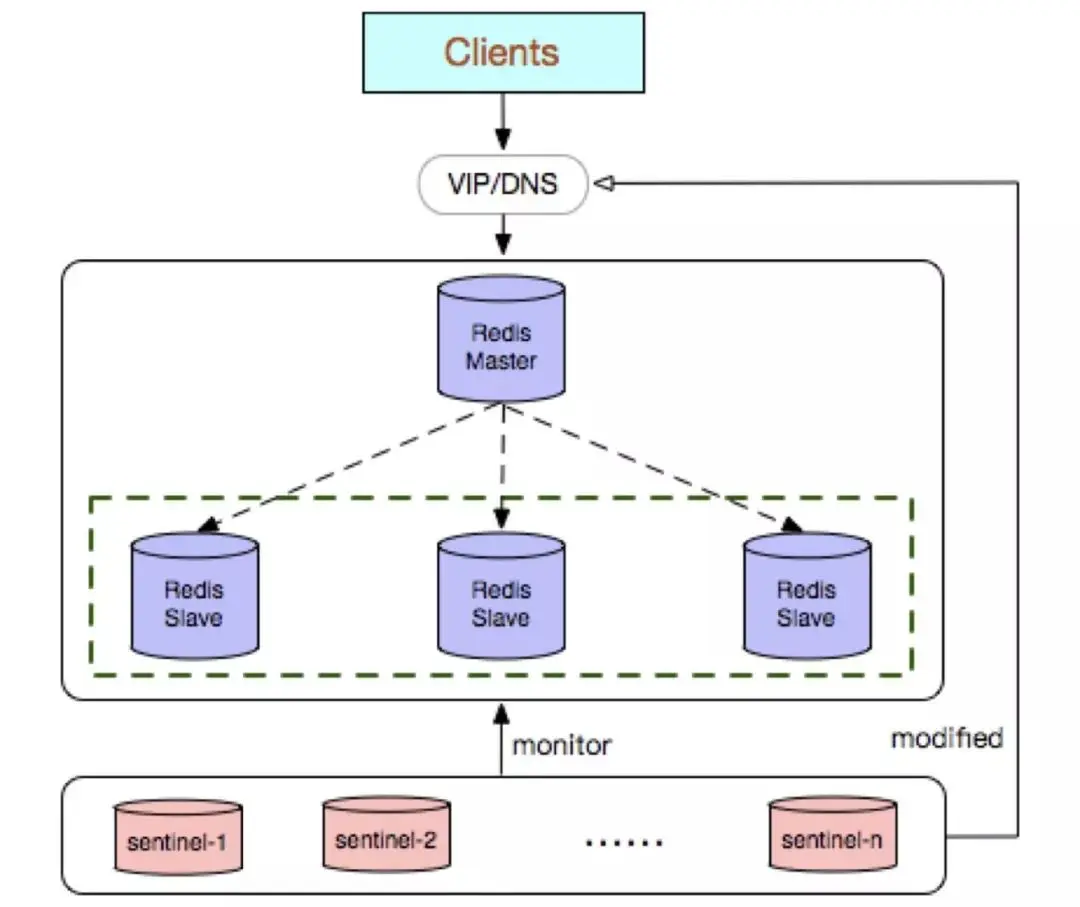
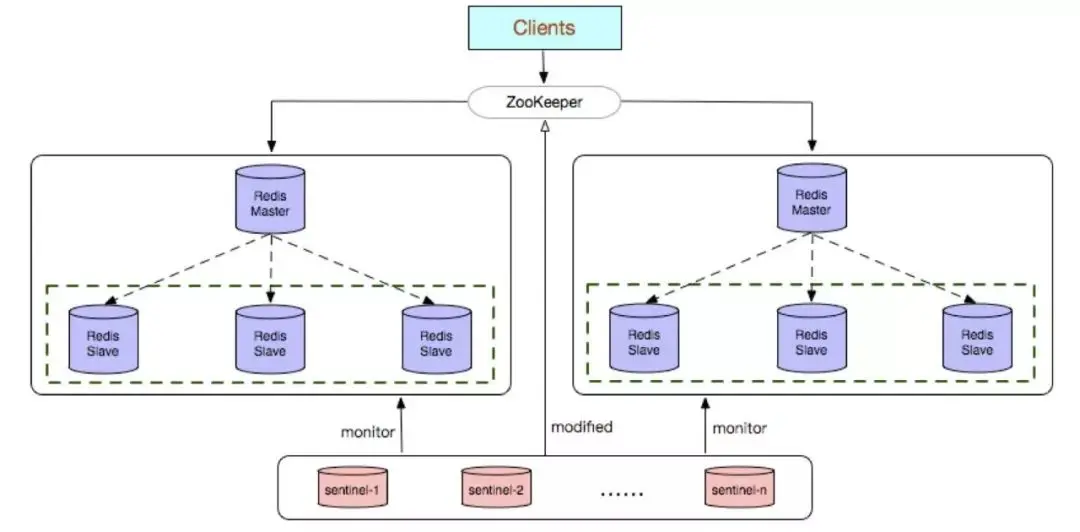
Advantages:
Redis Sentinel cluster deployment is simple;
It can solve the high-availability switching problem in Redis master-slave mode;
It is very convenient to realize the linear expansion of Redis data nodes, easily break through the single-thread bottleneck of Redis itself, and can greatly meet the large-capacity or high-performance business needs of Redis. ;
A set of Sentinel can be implemented to monitor a group of Redis data nodes or multiple groups of data nodes.
Disadvantages:
The deployment is more complicated than the Redis master-slave mode, and the principle understanding is more cumbersome;
Waste of resources, the slave node in the Redis data node serves as a backup node and does not provide services ;
Redis Sentinel is mainly aimed at high-availability switching of the master node in the Redis data node. The failure determination of the Redis data node is divided into two types: subjective offline and objective offline. For the Redis slave node: The node is taken offline subjectively and no failover is performed.
cannot solve the problem of reading and writing separation, and is relatively complicated to implement.
Recommendation:
If you monitor the same business, you can choose a Sentinel cluster to monitor multiple groups of Redis data nodes. Otherwise, choose a Sentinel cluster to monitor a group of Redis data nodes.
The recommended setting in the sentinel monitor configuration is half of the Sentinel nodes plus 1. When Sentinel is deployed in multiple IDCs, the number of Sentinels deployed in a single IDC is not recommended to exceed (Sentinel number – quorum).
Set parameters reasonably to prevent accidental cutting and control switching sensitivity control:
a. quorum
b. down-after-milliseconds 30000
c. failover-timeout 180000
d. maxclient
e. timeout
The server time of each deployed node must be synchronized as much as possible, otherwise the timing of the logs will be confused.
Redis recommends using pipeline and multi-keys operations to reduce the number of RTTs and improve request efficiency.
Configure the configuration center (zookeeper) by yourself to facilitate client access to the instance link.
4. Redis Cluster
Redis Cluster is a Redis distributed cluster solution launched by the community version. It mainly solves the needs of Redis distribution, such as when encountering single-machine memory, concurrency and traffic. When there is a bottleneck, Redis Cluster can achieve a good load balancing purpose.
The minimum configuration of the Redis Cluster cluster node is more than 6 nodes (3 masters and 3 slaves). The master node provides read and write operations, and the slave node serves as a backup node, does not provide requests, and is only used for failover.
Redis Cluster uses virtual slot partitioning. All keys are mapped to 0 to 16383 integer slots according to the hash function. Each node is responsible for maintaining a part of the slots and the key value data mapped by the slots.
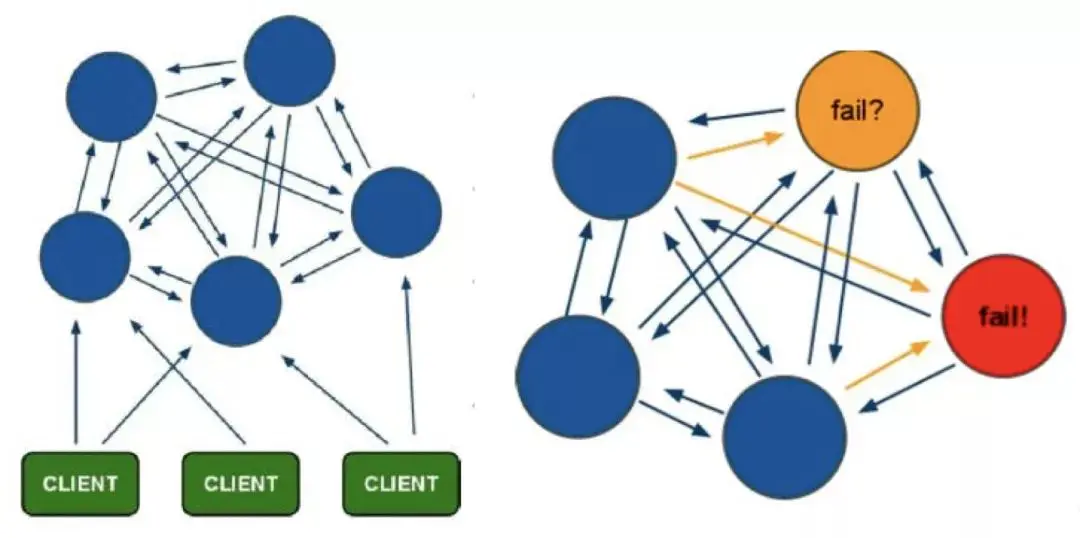
Advantages:
No central architecture;
Data is stored and distributed in multiple nodes according to slots, and data is shared between nodes , can dynamically adjust data distribution;
Scalability: can be linearly expanded to more than 1,000 nodes, and nodes can be dynamically added or deleted;
High availability: when some nodes are unavailable, the cluster is still available . By adding a Slave as a standby data copy, automatic failover can be achieved. Status information is exchanged between nodes through the gossip protocol, and the voting mechanism is used to complete the role promotion from Slave to Master;
Reduce operation and maintenance costs and improve system expansion performance and availability.
Disadvantages:
Client implementation is complex, and the driver requires the implementation of Smart Client, caching slots mapping information and updating it in a timely manner, which increases the difficulty of development. The immaturity of the client affects the stability of the business. At present, only JedisCluster is relatively mature, and the exception handling part is not yet perfect, such as the common "max redirect exception".
The node will be blocked due to some reasons (the blocking time is greater than clutser-node-timeout) and will be judged to be offline. This kind of failover is not necessary.
Data is replicated asynchronously, and strong consistency of data is not guaranteed.
When multiple businesses use the same cluster, hot and cold data cannot be distinguished based on statistics. Resource isolation is poor and mutual influence is easy to occur.
Slave acts as a "cold standby" in the cluster and cannot relieve read pressure. Of course, the utilization of Slave resources can be improved through the reasonable design of the SDK.
Key batch operation restrictions, such as using mset and mget, currently only support Keys with the same slot value to perform batch operations. For Keys mapped to different slot values, since Keys does not support cross-slot query, it is not user-friendly to perform operations such as mset, mget, and sunion.
Key transaction operation support is limited and only supports multi-key transaction operations on the same node. The transaction function cannot be used when multiple keys are distributed on different nodes.
You cannot map data containing large key value objects (such as hash, list, etc.) to different nodes, because in data partitioning, the key is the smallest granularity.
Does not support multiple database spaces. Redis in stand-alone mode can support up to 16 databases. In cluster mode, only 1 database space can be used, that is, db 0.
The replication structure only supports one level. The slave node can only replicate the master node, and the nested tree replication structure is not supported.
Avoid generating hot-keys, causing the main library node to become a shortcoming of the system.
Avoid generating big-key, which may lead to network card overload, slow query, etc.
The retry time should be greater than the cluster-node-time time.
Redis Cluster does not recommend using pipeline and multi-keys operations to reduce max redirect scenarios.
Share an interview guide "Java Core Knowledge Points Compilation.pdf" "covers JVM, locks, high concurrency, reflection, Spring principles, microservices, Zookeeper, databases, data structures, etc.", and also If you have Java208 interview questions (including answers), join (Java Advanced Architecture) 705127209 to get them for free!
5. Redis self-developed
Redis self-developed high-availability solutions are mainly reflected in the configuration center, fault detection and failover processing mechanisms, which usually need to be based on the actual online business of the enterprise. environment to customize.
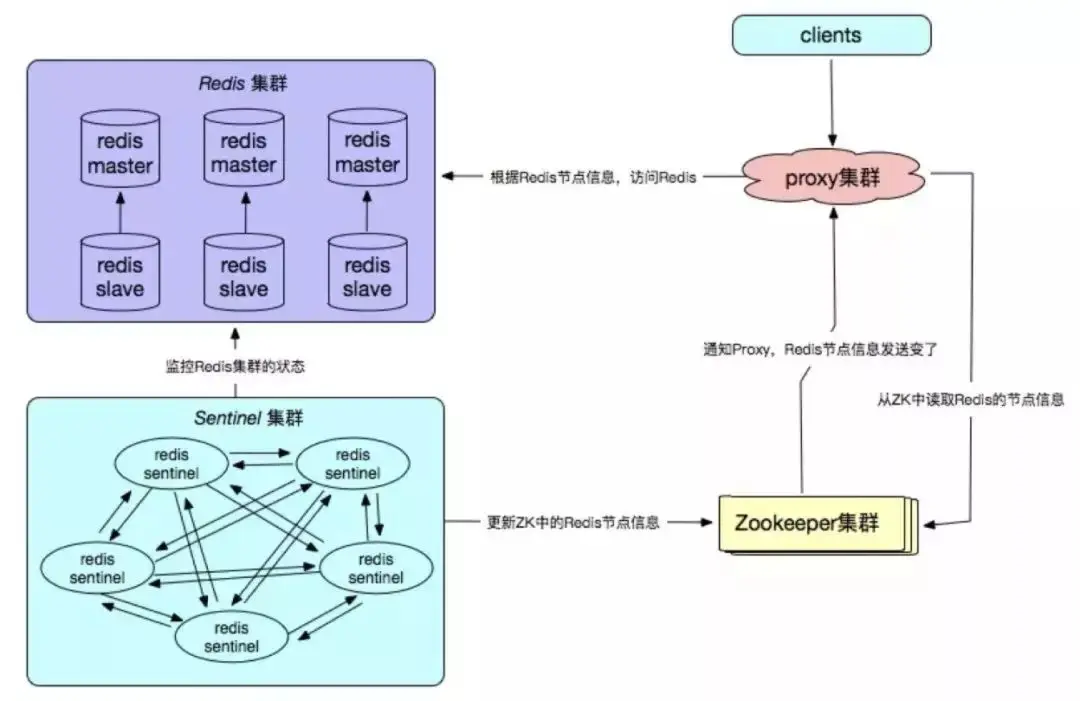
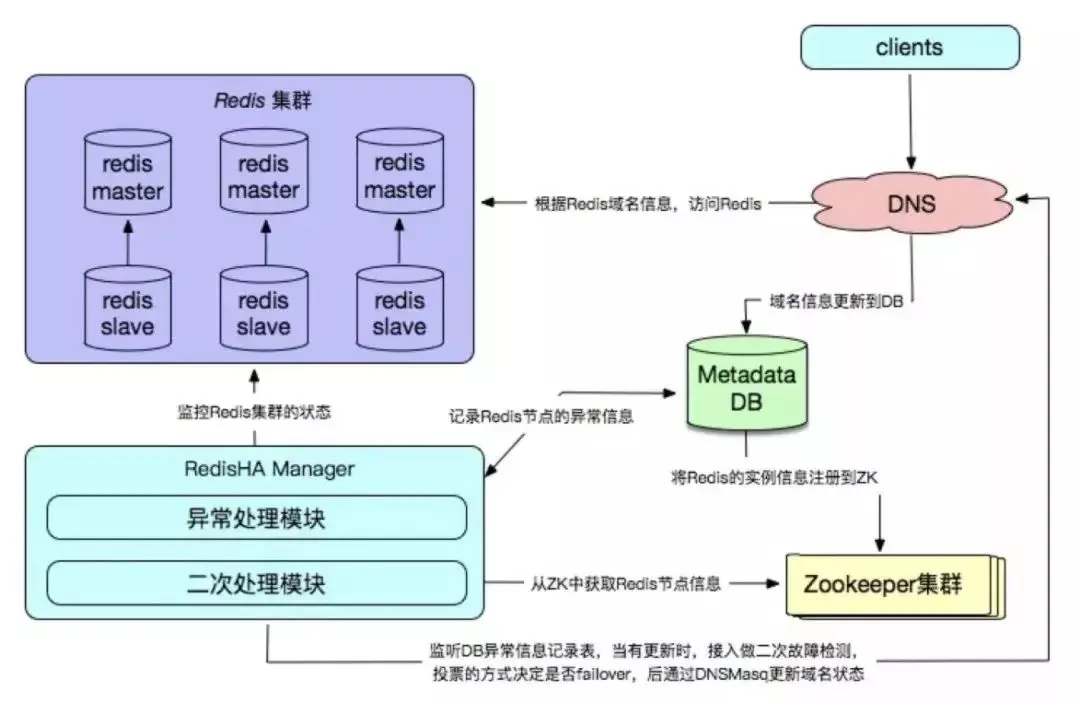
Advantages:
High reliability and high availability;
High autonomy and controllability;
Appropriate business Actual needs, good scalability and good compatibility.
Disadvantages:
Complex implementation and high development cost;
Requires the establishment of supporting peripheral facilities, such as monitoring, domain name services, databases for storing metadata information, etc.;
High maintenance costs.
The above is the detailed content of What are the common ways to use Redis?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
Redis cluster mode deploys Redis instances to multiple servers through sharding, improving scalability and availability. The construction steps are as follows: Create odd Redis instances with different ports; Create 3 sentinel instances, monitor Redis instances and failover; configure sentinel configuration files, add monitoring Redis instance information and failover settings; configure Redis instance configuration files, enable cluster mode and specify the cluster information file path; create nodes.conf file, containing information of each Redis instance; start the cluster, execute the create command to create a cluster and specify the number of replicas; log in to the cluster to execute the CLUSTER INFO command to verify the cluster status; make
 How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear Redis data: Use the FLUSHALL command to clear all key values. Use the FLUSHDB command to clear the key value of the currently selected database. Use SELECT to switch databases, and then use FLUSHDB to clear multiple databases. Use the DEL command to delete a specific key. Use the redis-cli tool to clear the data.
 How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
Using the Redis directive requires the following steps: Open the Redis client. Enter the command (verb key value). Provides the required parameters (varies from instruction to instruction). Press Enter to execute the command. Redis returns a response indicating the result of the operation (usually OK or -ERR).
 How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
To read a queue from Redis, you need to get the queue name, read the elements using the LPOP command, and process the empty queue. The specific steps are as follows: Get the queue name: name it with the prefix of "queue:" such as "queue:my-queue". Use the LPOP command: Eject the element from the head of the queue and return its value, such as LPOP queue:my-queue. Processing empty queues: If the queue is empty, LPOP returns nil, and you can check whether the queue exists before reading the element.
 How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
Using Redis to lock operations requires obtaining the lock through the SETNX command, and then using the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time. The specific steps are: (1) Use the SETNX command to try to set a key-value pair; (2) Use the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time for the lock; (3) Use the DEL command to delete the lock when the lock is no longer needed.
 How to implement the underlying redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:21 PM
How to implement the underlying redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:21 PM
Redis uses hash tables to store data and supports data structures such as strings, lists, hash tables, collections and ordered collections. Redis persists data through snapshots (RDB) and append write-only (AOF) mechanisms. Redis uses master-slave replication to improve data availability. Redis uses a single-threaded event loop to handle connections and commands to ensure data atomicity and consistency. Redis sets the expiration time for the key and uses the lazy delete mechanism to delete the expiration key.
 How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
The best way to understand Redis source code is to go step by step: get familiar with the basics of Redis. Select a specific module or function as the starting point. Start with the entry point of the module or function and view the code line by line. View the code through the function call chain. Be familiar with the underlying data structures used by Redis. Identify the algorithm used by Redis.
 How to make message middleware for redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:51 PM
How to make message middleware for redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:51 PM
Redis, as a message middleware, supports production-consumption models, can persist messages and ensure reliable delivery. Using Redis as the message middleware enables low latency, reliable and scalable messaging.




