How to master MySQL replication architecture

One master and multiple slaves replication architecture
In practical applications, most of the MySQL replication architecture patterns replicate one Master to one or more Slaves.
In scenarios where the main library read request pressure is very high, you can configure the one-master multi-slave replication architecture to achieve read-write separation, and separate a large number of data that do not have particularly high real-time requirements. Read requests are distributed to multiple slave libraries through load balancing (read requests with high real-time requirements can be read from the master library), reducing the reading pressure on the master library, as shown in the figure below.
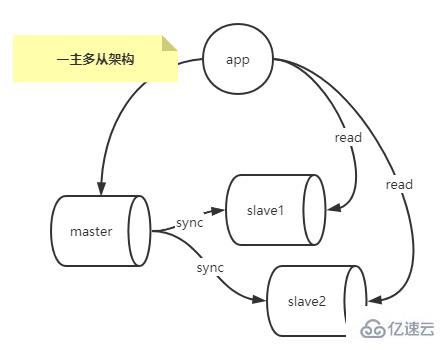
Disadvantages:
The master cannot be shut down, and it cannot receive write requests if it is shut down
Too many slaves will cause delays
Since the master needs to be shut down for routine maintenance, it is necessary to convert a slave into a master. Which one to choose is a problem?
When a slave becomes a master, there will be inconsistencies between the data of the current master and the previous master, and the previous master did not save the binlog file and pos location of the current master node.
Multi-master replication architecture
The multi-master replication architecture solves the single point of failure problem of the master in the single-master multi-slave replication architecture.
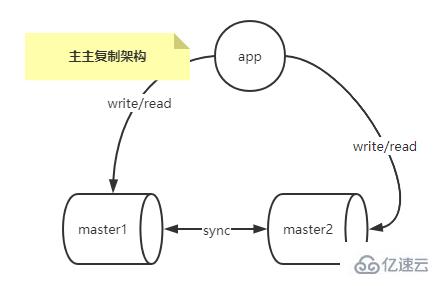
You can use a third-party tool, such as keepalived, to easily achieve IP drift, so that master downtime for maintenance will not affect write operations.
Cascade replication architecture
One master and many slaves. If there are too many slaves, the I/O pressure and network pressure of the master library will increase with the increase of slave libraries, because each The slave library will have an independent BINLOG Dump thread on the master library to send events, and the cascade replication architecture solves the additional I/O and network pressure on the master library in the scenario of one master and multiple slaves.
As shown below.
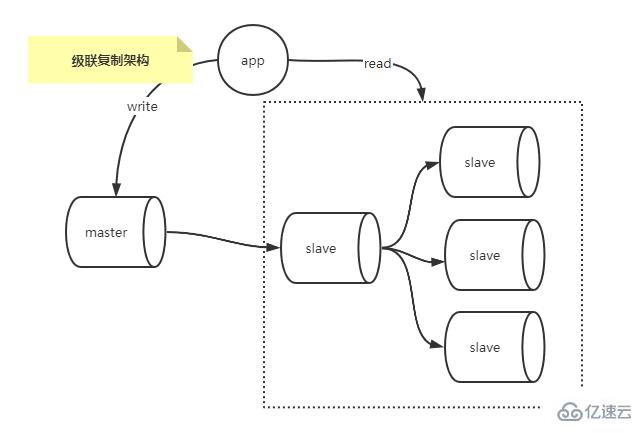
Compared with the one-master and multiple-slave architecture, cascade replication only copies from the master database to a small number of slave databases, and other slave databases then copy from these few slave databases. Copy the data, thus reducing the pressure on the main database Master.
Of course, there are also disadvantages: MySQL’s traditional replication is asynchronous. In the cascade replication scenario, the data in the master database has to undergo two replications before reaching other slave databases. The delay during this period is compared with the one-master and multiple-slave replication scenario. It's a big deal if it only goes through one copy next time.
By selecting the BLACKHOLE table engine on the secondary slave database, the delay of cascade replication can be reduced. As the name suggests, the BLACKHOLE engine is a "black hole" engine. The data written to the BLACKHOLE table will not be written to the disk. The BLACKHOLE table is always an empty table. INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE operations only record events in the BINLOG.
The following demonstrates the BLACKHOLE engine:
mysql> CREATE TABLE `user` (
-> `id` int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
-> `name` varchar(255) NOT NULL DEFAULT '',
-> `age` tinyint unsigned NOT NULL DEFAULT 0
-> )ENGINE=BLACKHOLE charset=utf8mb4;Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)mysql> INSERT INTO `user` (`name`,`age`) values("itbsl", "26");Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)mysql> select * from user;Empty set (0.00 sec)As you can see, there is no data in the user table whose storage engine is BLACKHOLE.
Combined architecture of multi-master and cascade replication
Combining multi-master and cascade replication architecture solves the problem of single-point master and the problem of slave cascade delay.
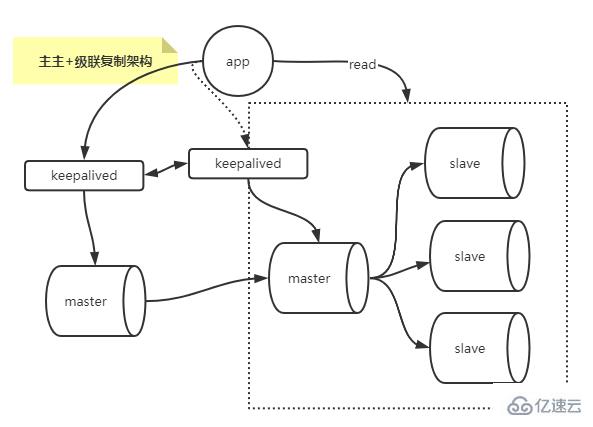
Building multi-master replication architecture
Host planning:
master1: docker, port 3314
master2: docker, port 3315
Configuration of master1
Configuration file my.cnf:
$ cat /home/mysql/docker-data/3315/conf/my.cnf [mysqld] character_set_server=utf8 init_connect='SET NAMES utf8' symbolic-links=0 lower_case_table_names=1 server-id=1403314 log-bin=mysql-bin binlog-format=ROW auto_increment_increment=2 # 几个主库,这里就配几 auto_increment_offset=1 # 每个主库的偏移量需要不一致 gtid_mode=ON enforce-gtid-consistency=true binlog-do-db=order # 要同步的数据库
Start docker:
$ docker run --name mysql3314 -p 3314:3306 --privileged=true -ti -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=root -e MYSQL_DATABASE=order -e MYSQL_USER=user -e MYSQL_PASSWORD=pass -v /home/mysql/docker-data/3314/conf:/etc/mysql/conf.d -v /home/mysql/docker-data/3314/data/:/var/lib/mysql -v /home/mysql/docker-data/3314/logs/:/var/log/mysql -d mysql:5.7
Add a user for replication and authorize:
mysql> GRANT REPLICATION SLAVE,FILE,REPLICATION CLIENT ON *.* TO 'repluser'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY '123456'; Query OK, 0 rows affected, 1 warning (0.01 sec) mysql> FLUSH PRIVILEGES; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
Start synchronization master1 (the user here comes from master2):
mysql> change master to master_host='172.23.252.98',master_port=3315,master_user='repluser',master_password='123456',master_auto_position=1; Query OK, 0 rows affected, 2 warnings (0.03 sec) mysql> start slave; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
Configuration of master2
The configuration of master2 is similar to master1.
The main difference is that there is an attribute in my.cnf that needs to be inconsistent:
auto_increment_offset=2 # 每个主库的偏移量需要不一致
Test:
Create a table in master2 and add data:
mysql> create table t_order(id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(20));
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> insert into t_order(name) values("A");
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> insert into t_order(name) values("B");
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from t_order;
+----+------+
| id | name |
+----+------+
| 2 | A |
| 4 | B |
+----+------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)It can be found that the step size of id in master2 is 2, and it starts to increase from 2.
Then query the data in master1 and add:
mysql> select * from t_order;
+----+------+
| id | name |
+----+------+
| 2 | A |
| 4 | B |
+----+------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> insert into t_order(name) values("E");
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from t_order;
+----+------+
| id | name |
+----+------+
| 2 | A |
| 4 | B |
| 5 | E |
+----+------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)You can find that the step size of id in master1 is 2, and it starts to increase from 1. Then query in master2 and you can find that the id is 5. The data shows that there is no problem with the master-master replication configuration.
Why are the offsets of the id increment in the two masters inconsistent? When the two masters receive the insertion request at the same time, it can ensure that the ID does not conflict. In fact, this can only ensure that the inserted data does not conflict, but cannot guarantee the data inconsistency caused by deletion and modification.
So in actual application scenarios, only one master can be exposed to the client to ensure data consistency.
MySQL high availability construction
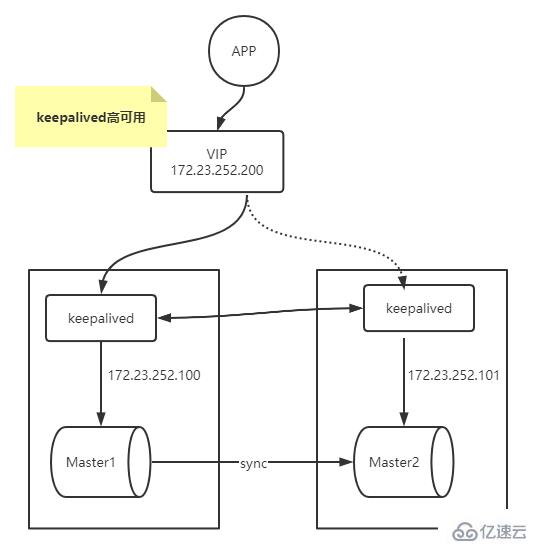
Here we use keepalived to transform the above multi-master replication architecture to achieve high availability of MySQL.
keepalived installation:
$ sudo apt-get install -y keepalived
keepalived.conf
$ cat /etc/keepalived/keepalived3314.conf! Configuration File for keepalived#简单的头部,这里主要可以做邮件通知报警等的设置,此处就暂不配置了;global_defs {
#notificationd LVS_DEVEL}#预先定义一个脚本,方便后面调用,也可以定义多个,方便选择;vrrp_script chk_haproxy {
script "/etc/keepalived/chkmysql.sh" #具体脚本路径
interval 2 #脚本循环运行间隔}#VRRP虚拟路由冗余协议配置vrrp_instance VI_1 { #VI_1 是自定义的名称;
state BACKUP #MASTER表示是一台主设备,BACKUP表示为备用设备【我们这里因为设置为开启不抢占,所以都设置为备用】
nopreempt #开启不抢占
interface eth0 #指定VIP需要绑定的物理网卡
virtual_router_id 11 #VRID虚拟路由标识,也叫做分组名称,该组内的设备需要相同
priority 130 #定义这台设备的优先级 1-254;开启了不抢占,所以此处优先级必须高于另一台
advert_int 1 #生存检测时的组播信息发送间隔,组内一致
authentication { #设置验证信息,组内一致
auth_type PASS #有PASS 和 AH 两种,常用 PASS
auth_pass asd #密码
}
virtual_ipaddress {
172.23.252.200 #指定VIP地址,组内一致,可以设置多个IP
}
track_script { #使用在这个域中使用预先定义的脚本,上面定义的
chk_haproxy }
#notify_backup "/etc/init.d/haproxy restart" #表示当切换到backup状态时,要执行的脚本
#notify_fault "/etc/init.d/haproxy stop" #故障时执行的脚本}/etc/keepalived/chkmysql.sh
$ cat /etc/keepalived/chkmysql.s.sh#!/bin/bashmysql -uroot -proot -P 3314 -e "show status;" > /dev/null 2>&1if [ $? == 0 ];then
echo "$host mysql login successfully"
exit 0else
echo "$host login failed"
killall keepalived exit 2fiThe above is the detailed content of How to master MySQL replication architecture. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 MySQL: Simple Concepts for Easy Learning
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:29 AM
MySQL: Simple Concepts for Easy Learning
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:29 AM
MySQL is an open source relational database management system. 1) Create database and tables: Use the CREATEDATABASE and CREATETABLE commands. 2) Basic operations: INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE and SELECT. 3) Advanced operations: JOIN, subquery and transaction processing. 4) Debugging skills: Check syntax, data type and permissions. 5) Optimization suggestions: Use indexes, avoid SELECT* and use transactions.
 How to open phpmyadmin
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
How to open phpmyadmin
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
You can open phpMyAdmin through the following steps: 1. Log in to the website control panel; 2. Find and click the phpMyAdmin icon; 3. Enter MySQL credentials; 4. Click "Login".
 MySQL: An Introduction to the World's Most Popular Database
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL: An Introduction to the World's Most Popular Database
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL is an open source relational database management system, mainly used to store and retrieve data quickly and reliably. Its working principle includes client requests, query resolution, execution of queries and return results. Examples of usage include creating tables, inserting and querying data, and advanced features such as JOIN operations. Common errors involve SQL syntax, data types, and permissions, and optimization suggestions include the use of indexes, optimized queries, and partitioning of tables.
 How to use single threaded redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:12 PM
How to use single threaded redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:12 PM
Redis uses a single threaded architecture to provide high performance, simplicity, and consistency. It utilizes I/O multiplexing, event loops, non-blocking I/O, and shared memory to improve concurrency, but with limitations of concurrency limitations, single point of failure, and unsuitable for write-intensive workloads.
 Why Use MySQL? Benefits and Advantages
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:17 AM
Why Use MySQL? Benefits and Advantages
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:17 AM
MySQL is chosen for its performance, reliability, ease of use, and community support. 1.MySQL provides efficient data storage and retrieval functions, supporting multiple data types and advanced query operations. 2. Adopt client-server architecture and multiple storage engines to support transaction and query optimization. 3. Easy to use, supports a variety of operating systems and programming languages. 4. Have strong community support and provide rich resources and solutions.
 MySQL's Place: Databases and Programming
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL's Place: Databases and Programming
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL's position in databases and programming is very important. It is an open source relational database management system that is widely used in various application scenarios. 1) MySQL provides efficient data storage, organization and retrieval functions, supporting Web, mobile and enterprise-level systems. 2) It uses a client-server architecture, supports multiple storage engines and index optimization. 3) Basic usages include creating tables and inserting data, and advanced usages involve multi-table JOINs and complex queries. 4) Frequently asked questions such as SQL syntax errors and performance issues can be debugged through the EXPLAIN command and slow query log. 5) Performance optimization methods include rational use of indexes, optimized query and use of caches. Best practices include using transactions and PreparedStatemen
 MySQL and SQL: Essential Skills for Developers
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:30 AM
MySQL and SQL: Essential Skills for Developers
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:30 AM
MySQL and SQL are essential skills for developers. 1.MySQL is an open source relational database management system, and SQL is the standard language used to manage and operate databases. 2.MySQL supports multiple storage engines through efficient data storage and retrieval functions, and SQL completes complex data operations through simple statements. 3. Examples of usage include basic queries and advanced queries, such as filtering and sorting by condition. 4. Common errors include syntax errors and performance issues, which can be optimized by checking SQL statements and using EXPLAIN commands. 5. Performance optimization techniques include using indexes, avoiding full table scanning, optimizing JOIN operations and improving code readability.
 Monitor Redis Droplet with Redis Exporter Service
Apr 10, 2025 pm 01:36 PM
Monitor Redis Droplet with Redis Exporter Service
Apr 10, 2025 pm 01:36 PM
Effective monitoring of Redis databases is critical to maintaining optimal performance, identifying potential bottlenecks, and ensuring overall system reliability. Redis Exporter Service is a powerful utility designed to monitor Redis databases using Prometheus. This tutorial will guide you through the complete setup and configuration of Redis Exporter Service, ensuring you seamlessly build monitoring solutions. By studying this tutorial, you will achieve fully operational monitoring settings




