Springboot cache redis integration method
The default is to use ConcurrentMapCache of ConcurrentMapCacheManager as the cache component.
When using ConcurrentMap, the data is saved in ConcurrentMap<object></object>.
In fact, during the development process, we often use some caching middleware.
For example, we often use redis, memcache, including the ehcache we use, etc. We all use some caching middleware.
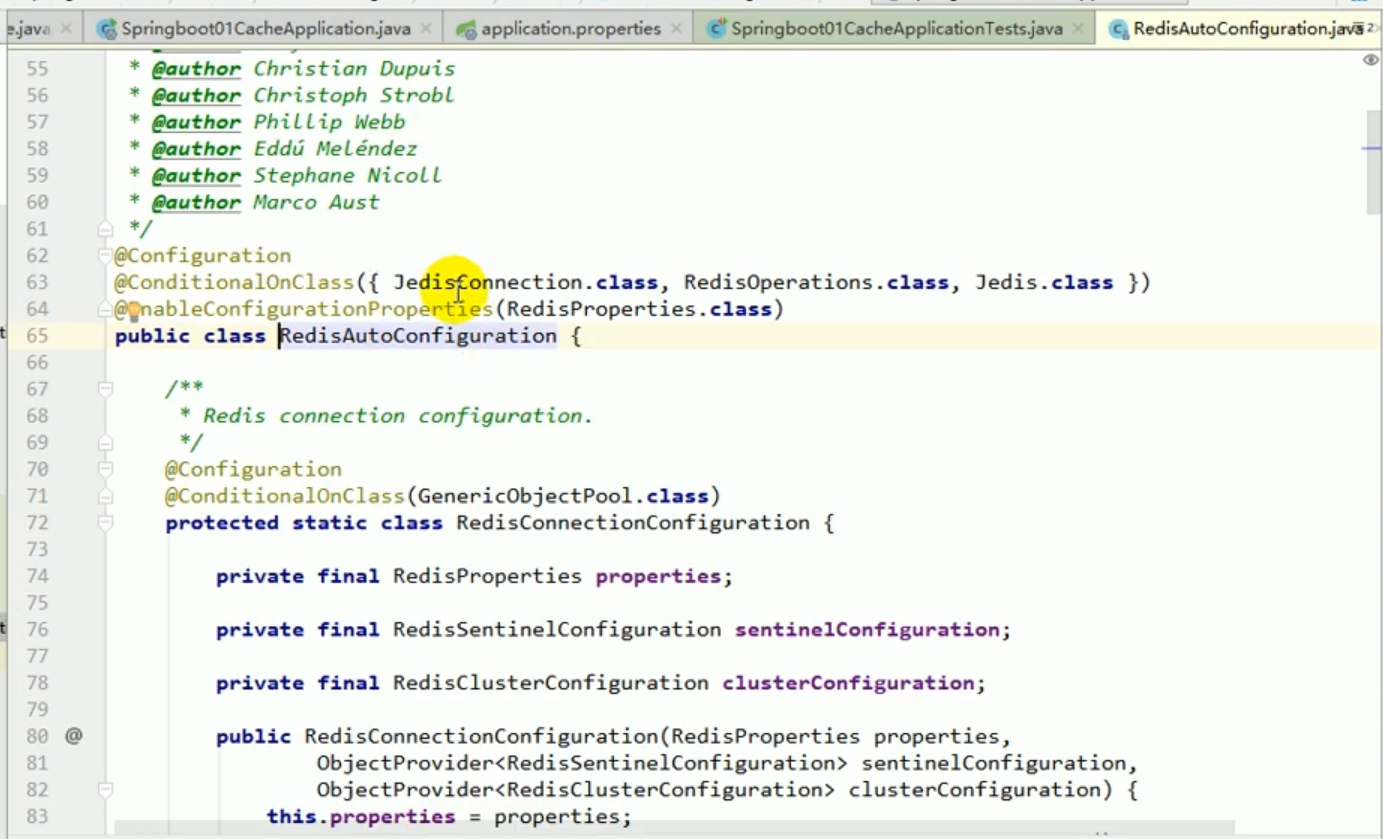
When we explained the principle before, we also discovered that springboot supports many cache configurations:
As shown in the figure below:
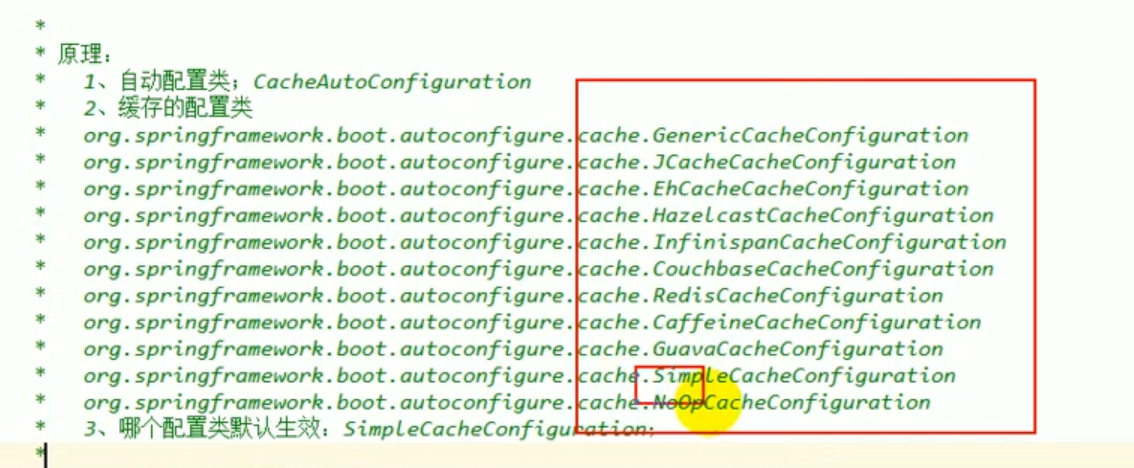
The default starting configuration is: SimpleCacheConfiguration.
When are other caches enabled?
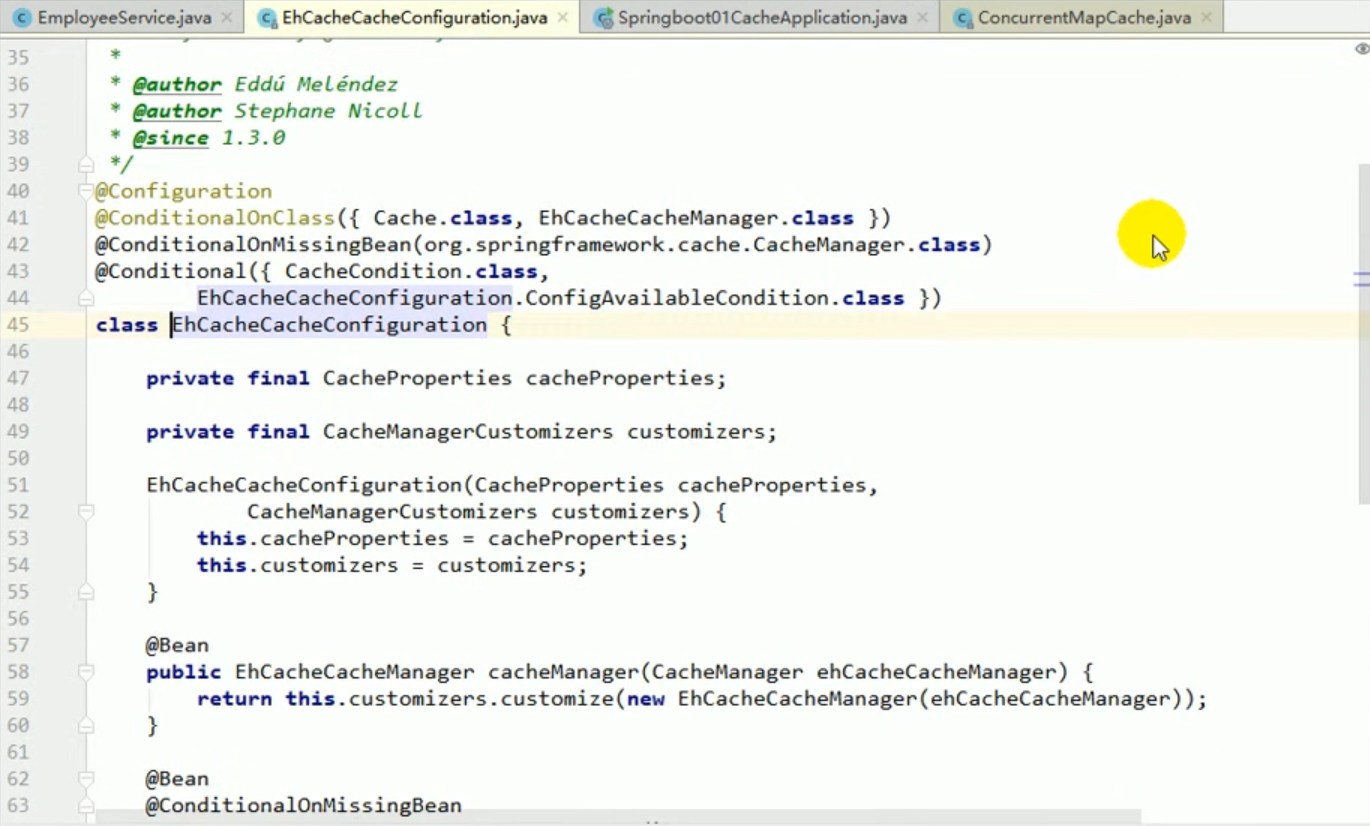
We can search for these configuration classes with ctrl n, and then go in and see their conditional conditions:
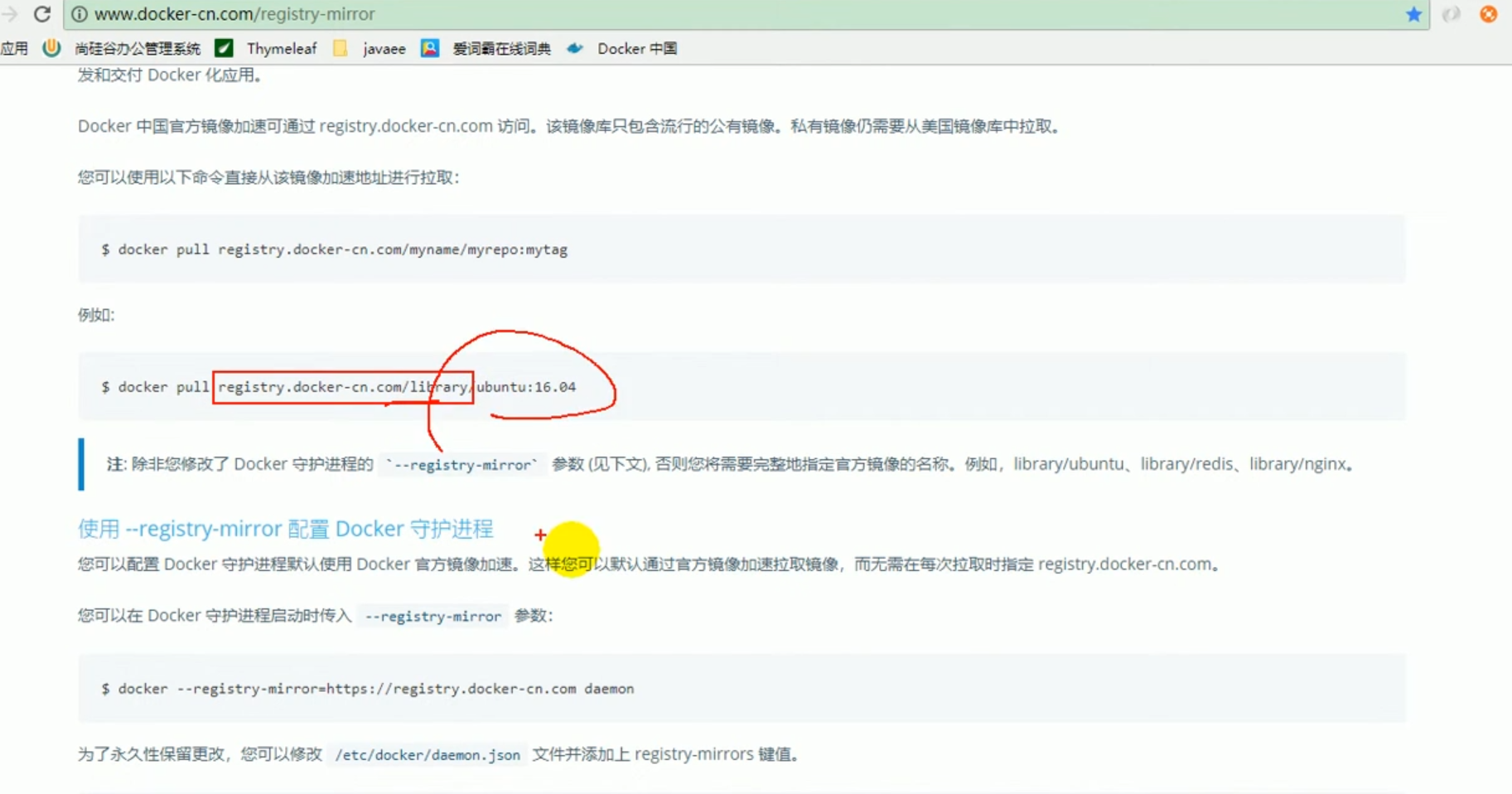
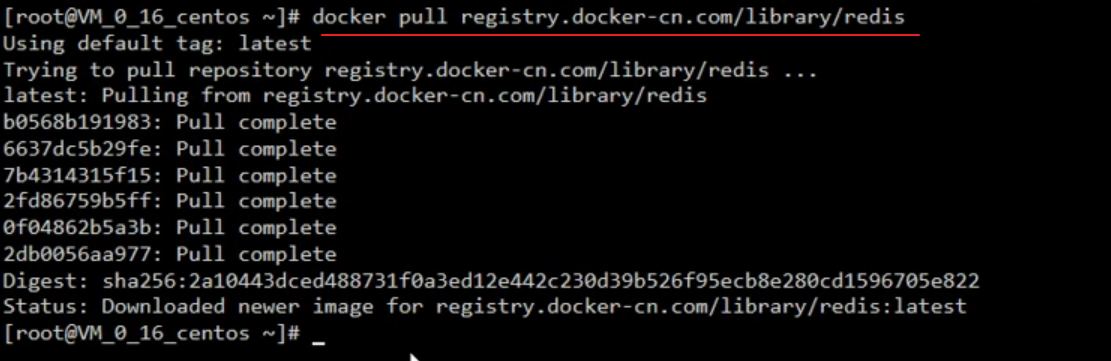
 Start the redis image
Start the redis image
docker run -d -p 6379:6379 --name myredis [REPOSITORY] docker ps
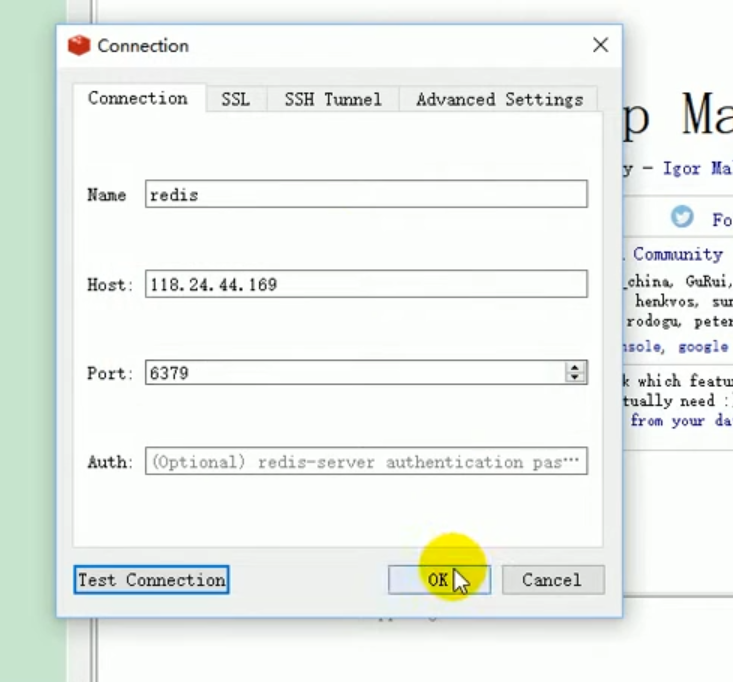
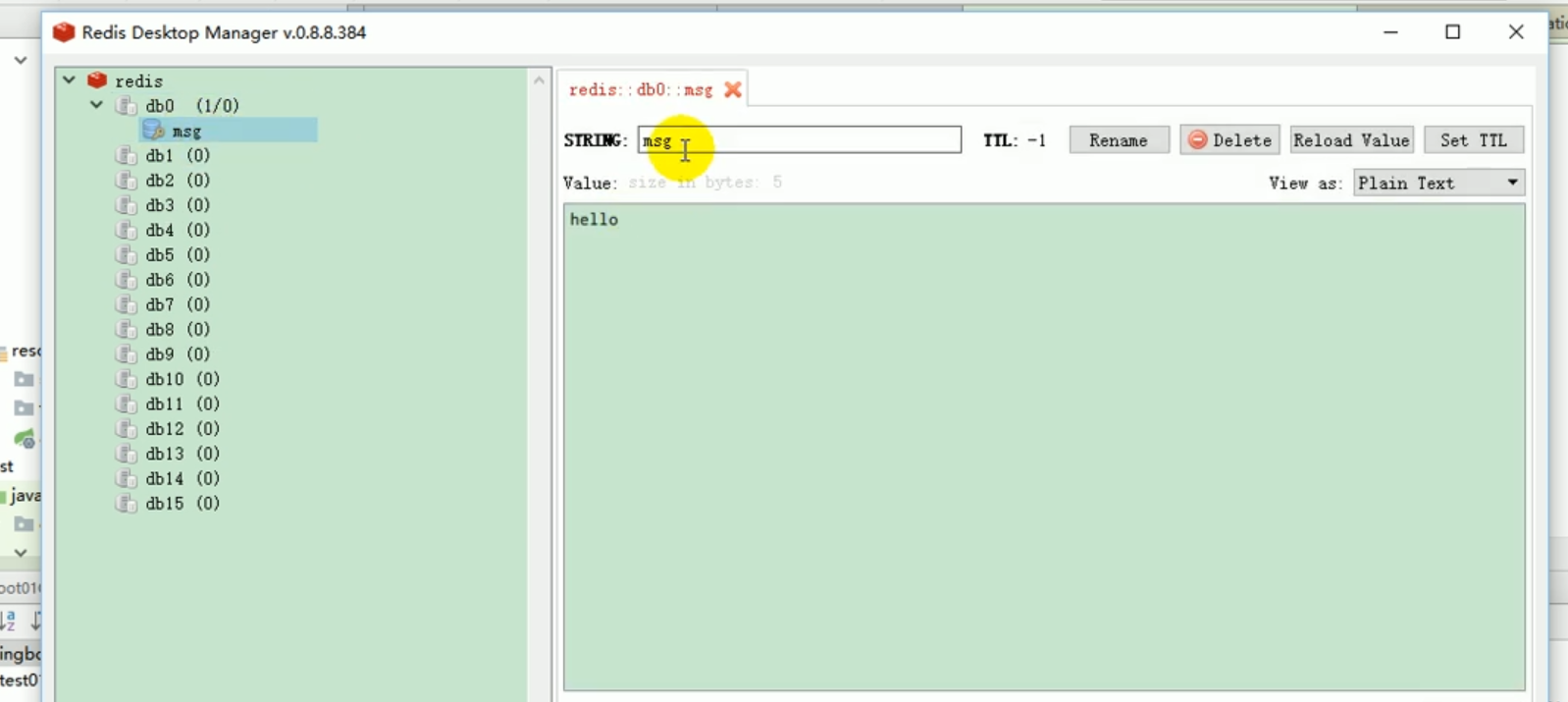
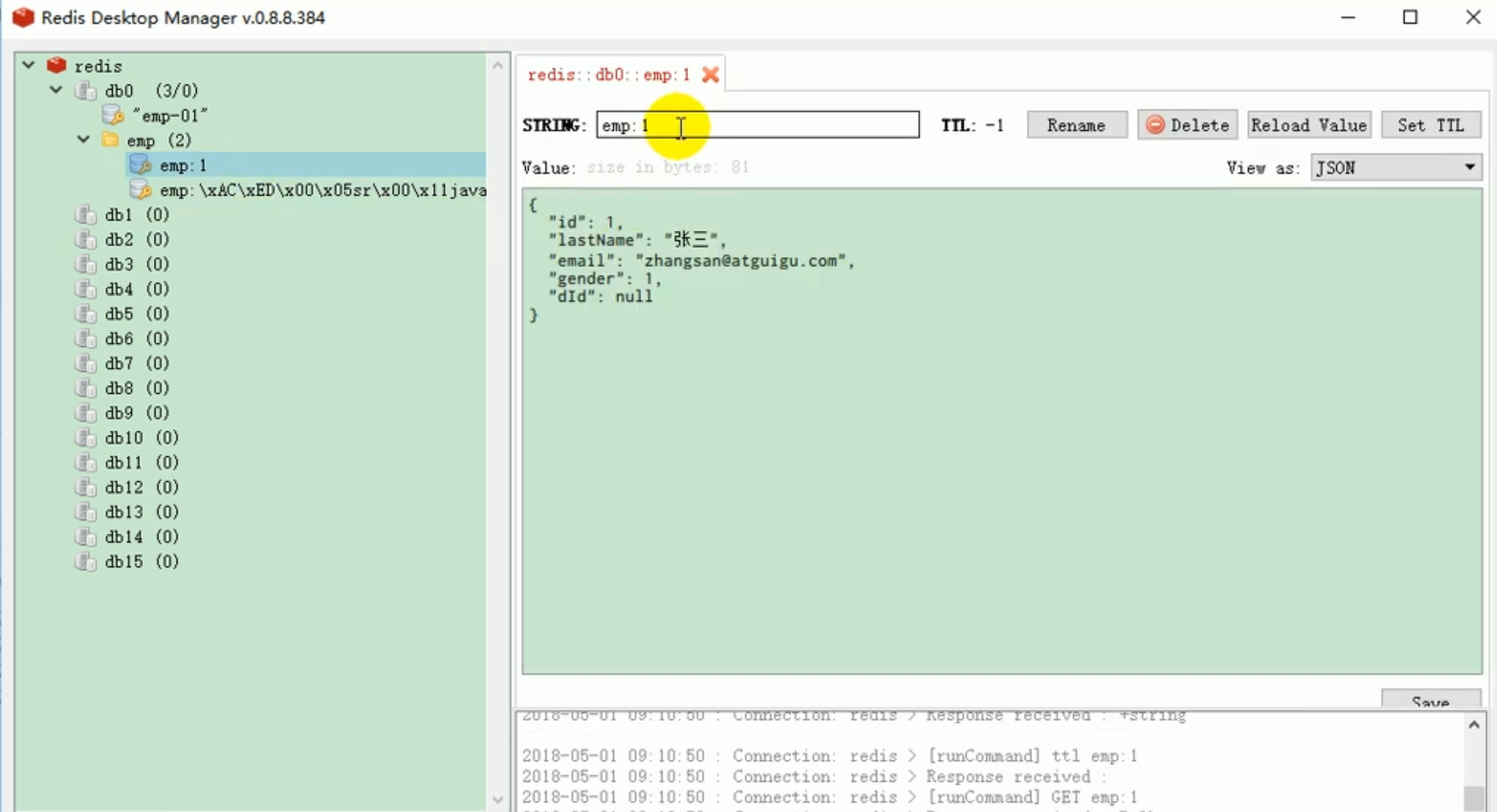
For testing, open the redis connection tool.
redis desktop manager
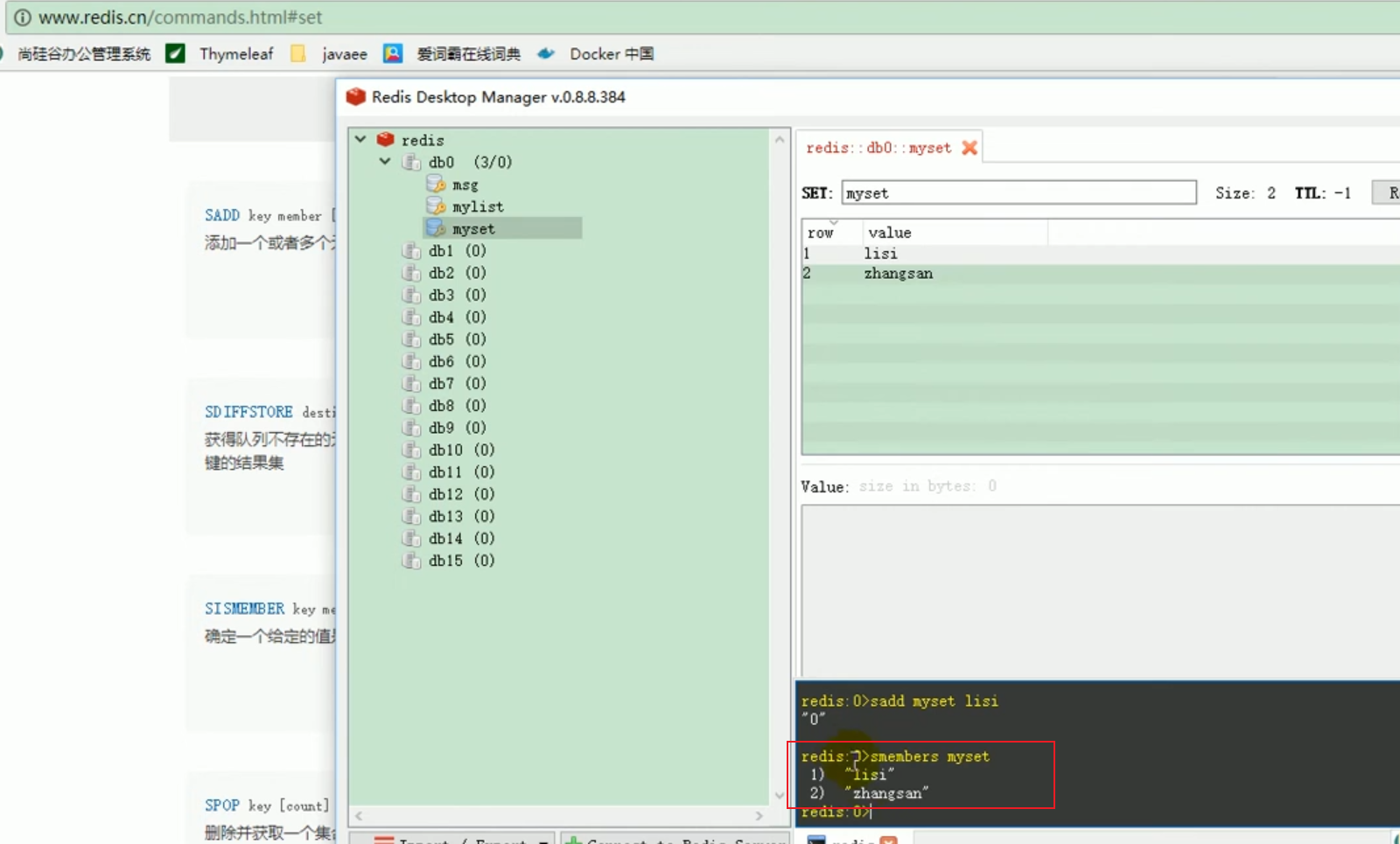
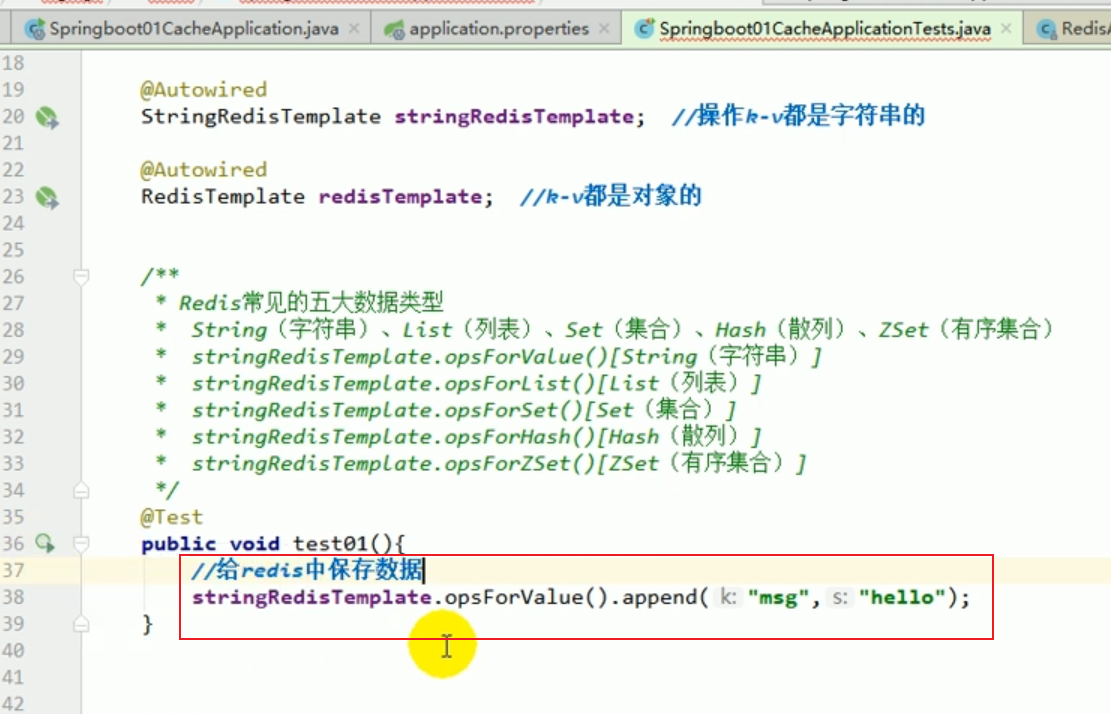
##Test redis common data operations
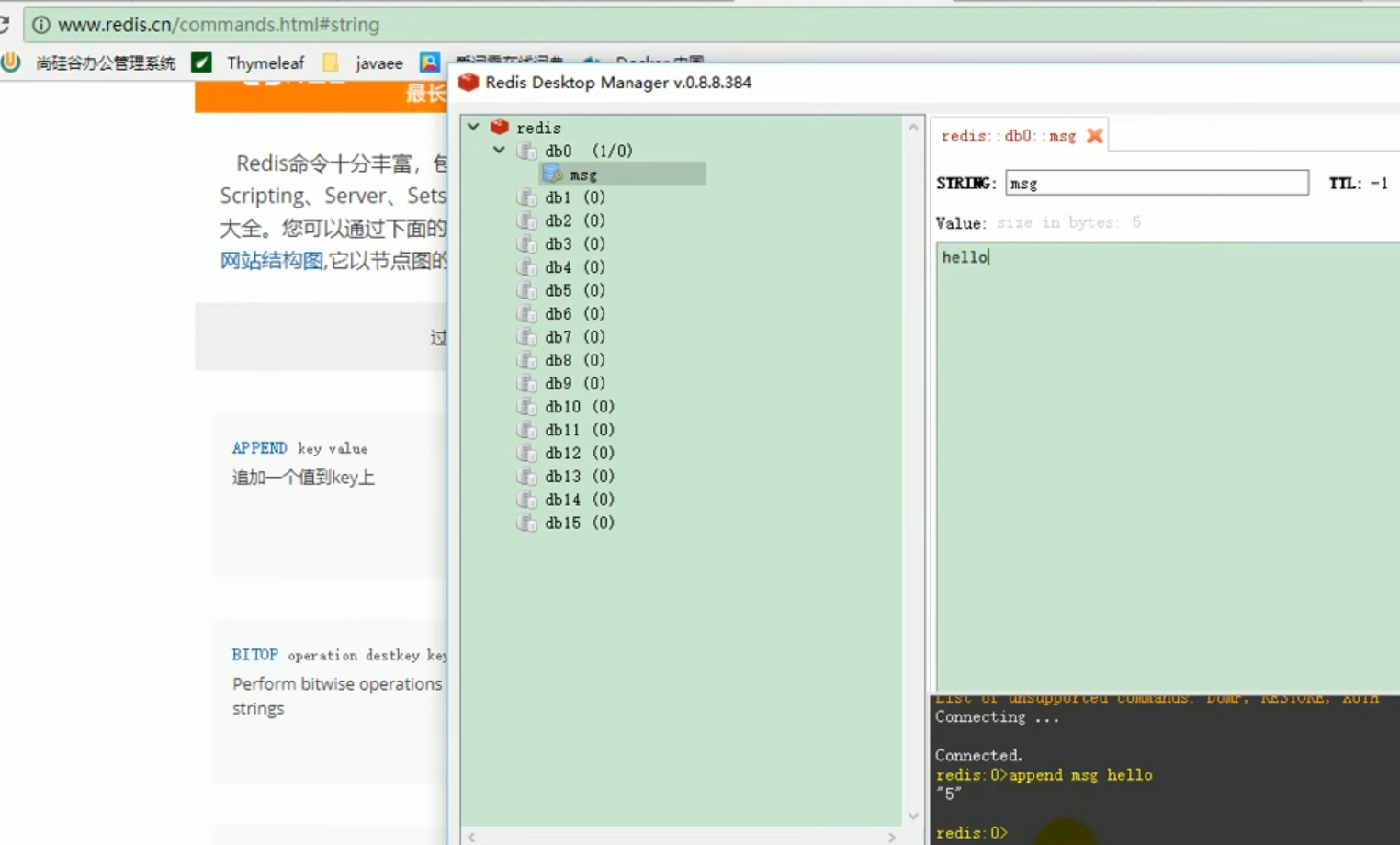
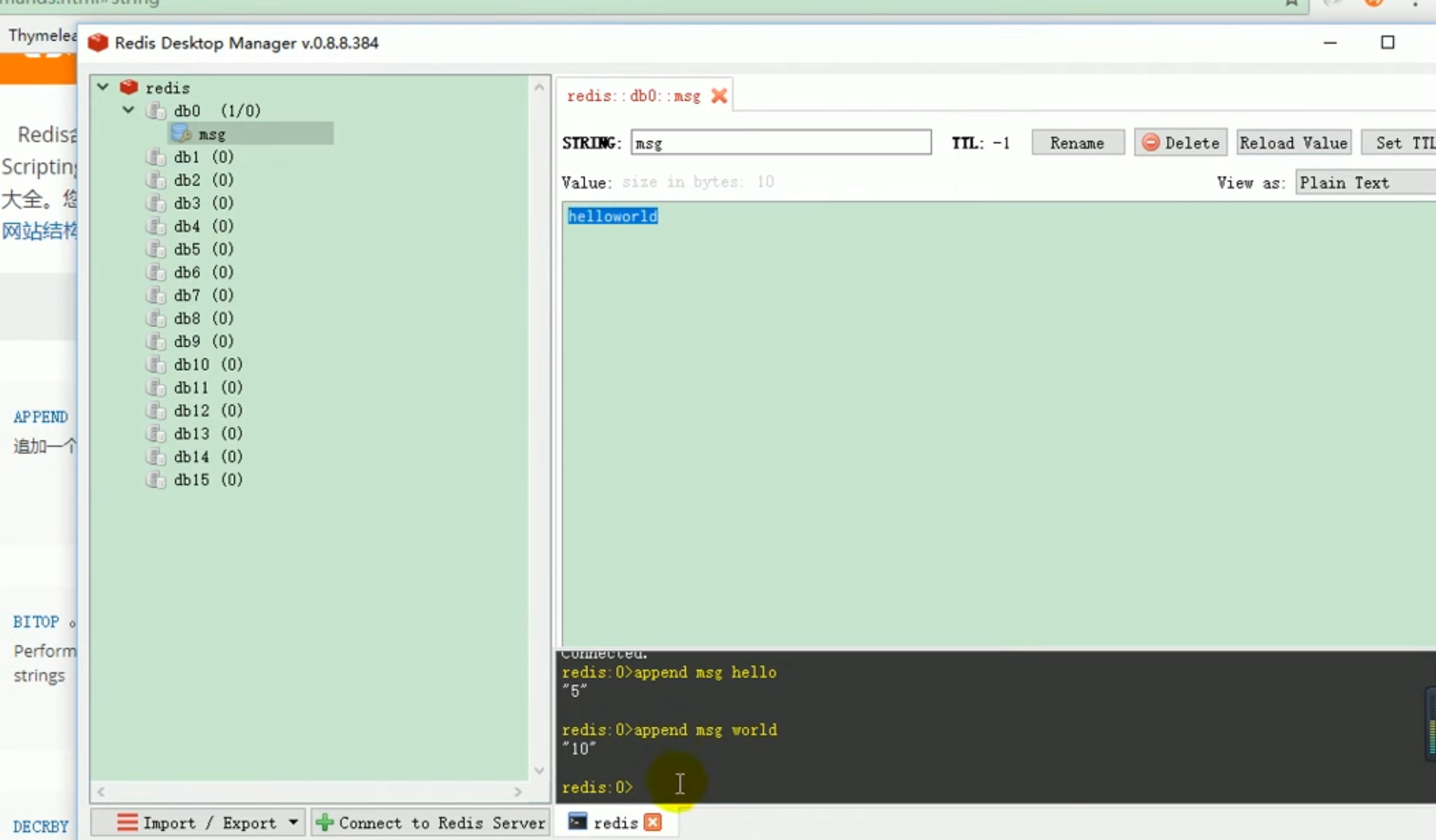
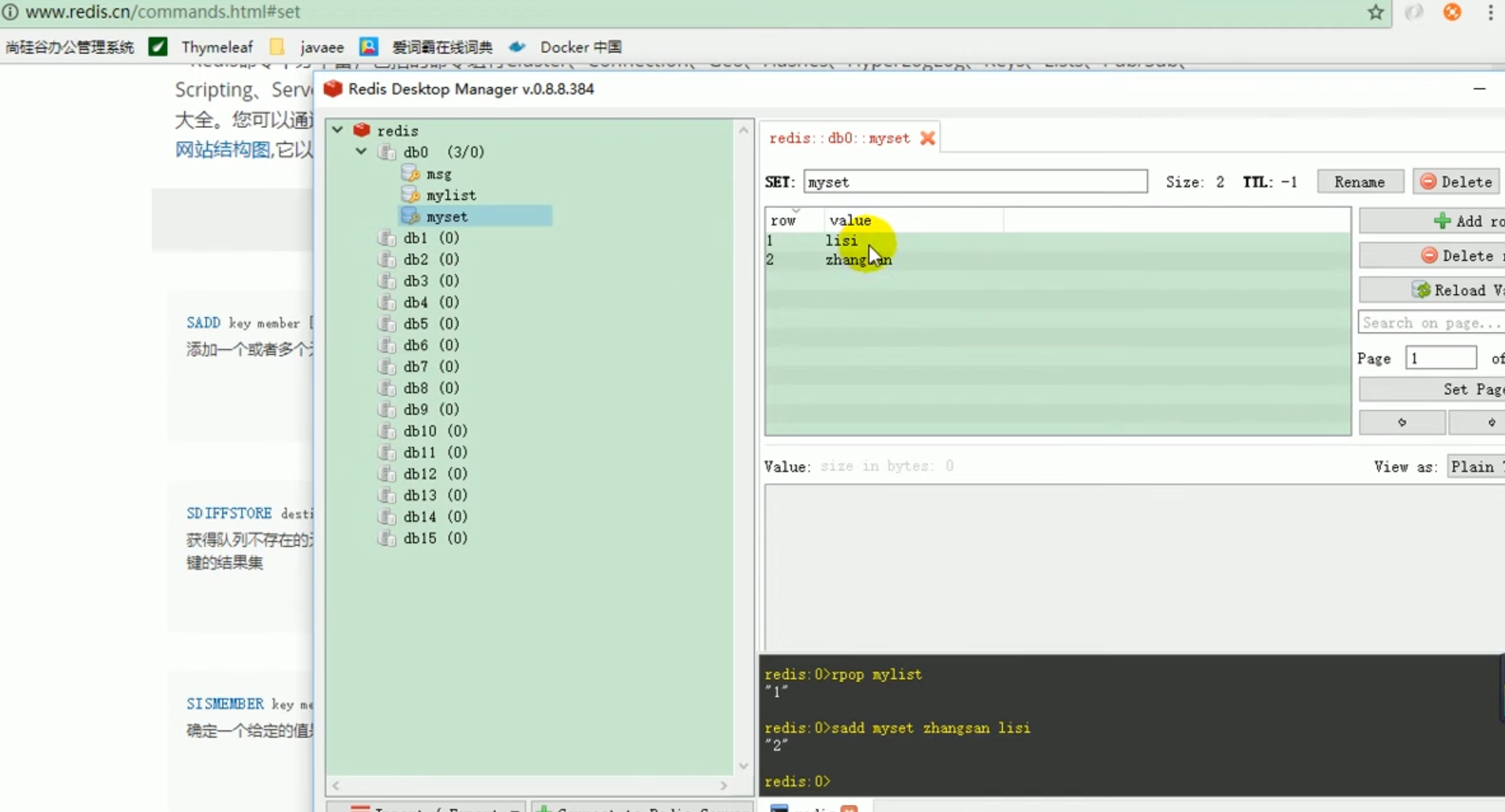
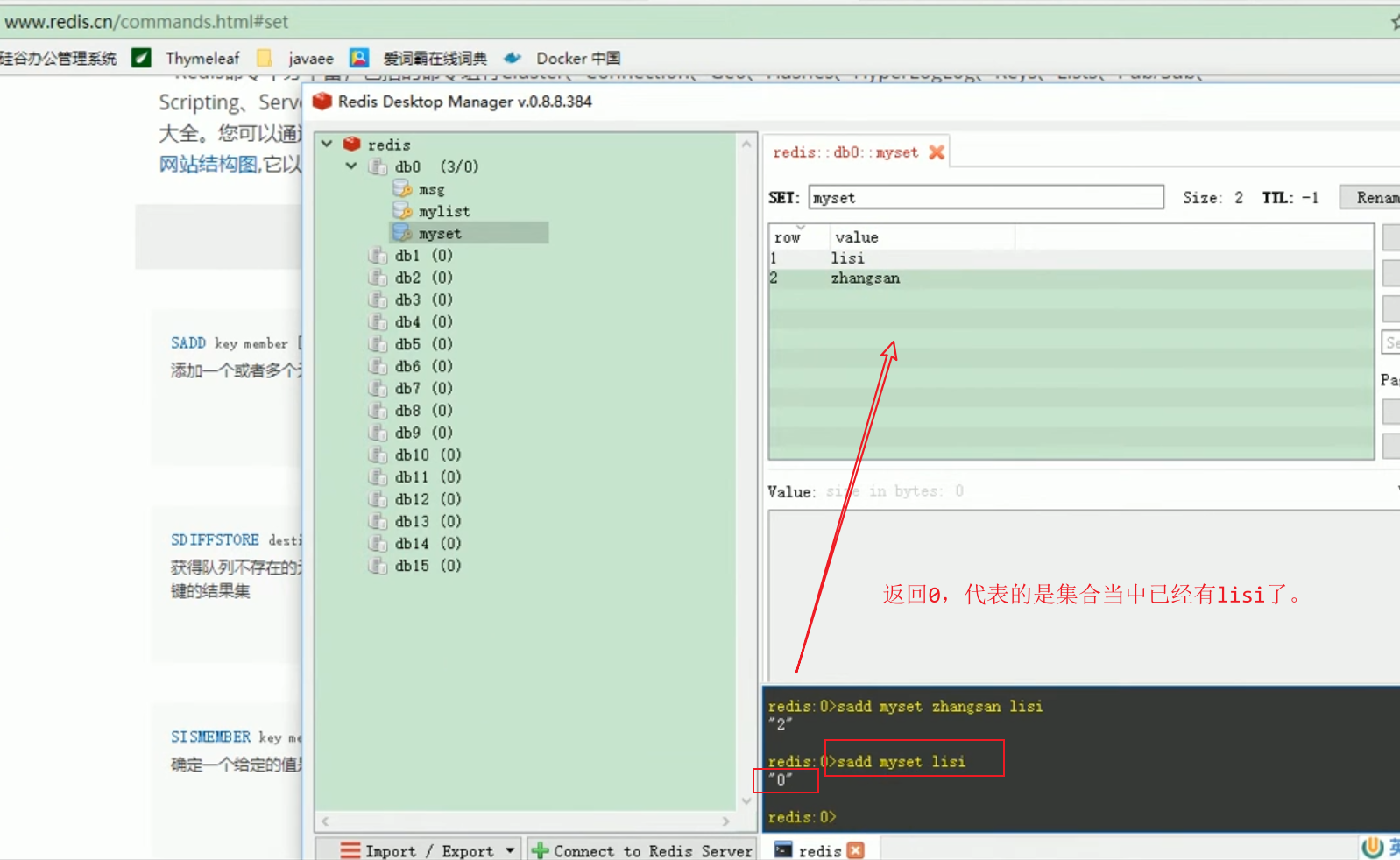
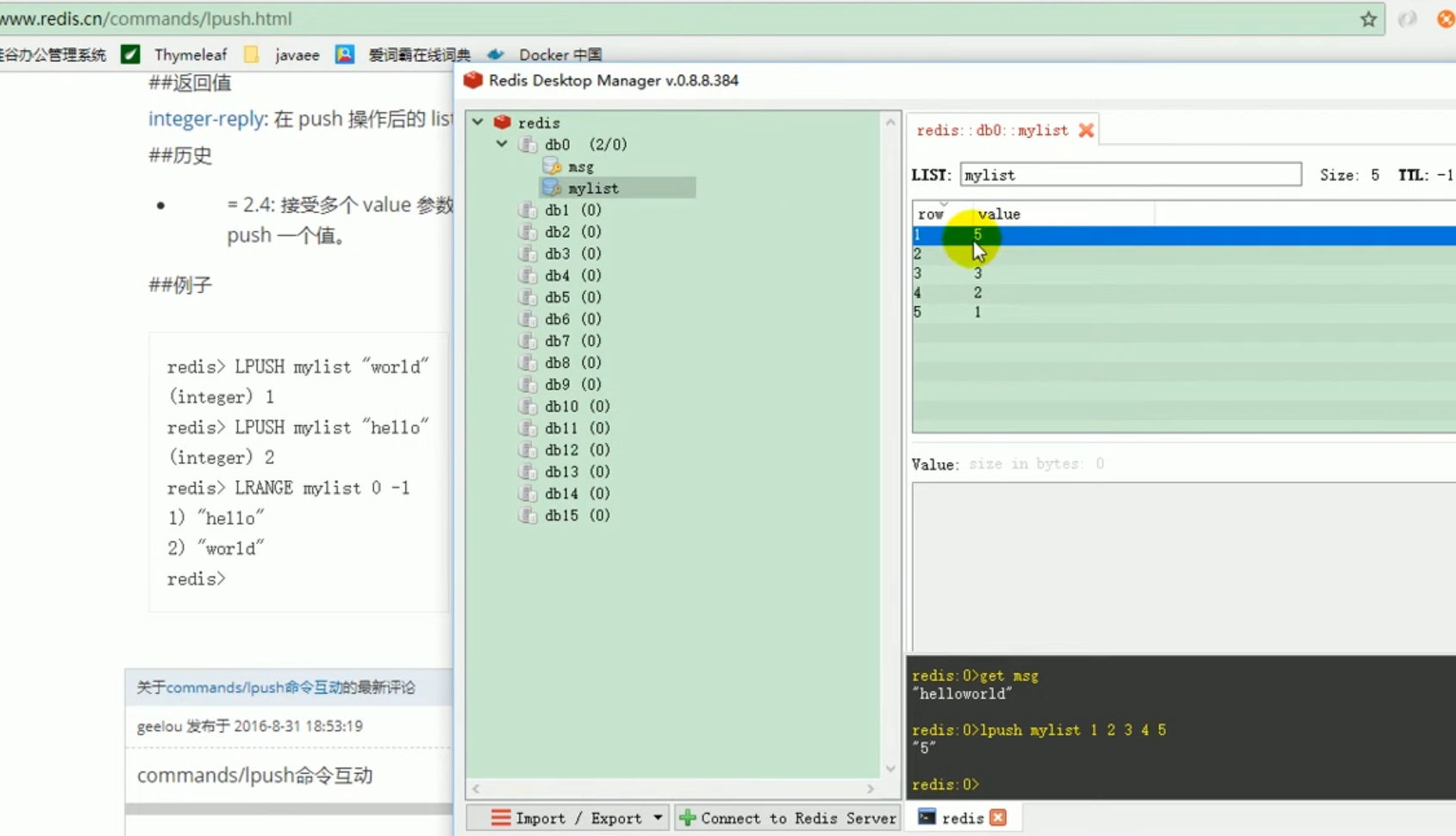 ##set operation of redis
##set operation of redis
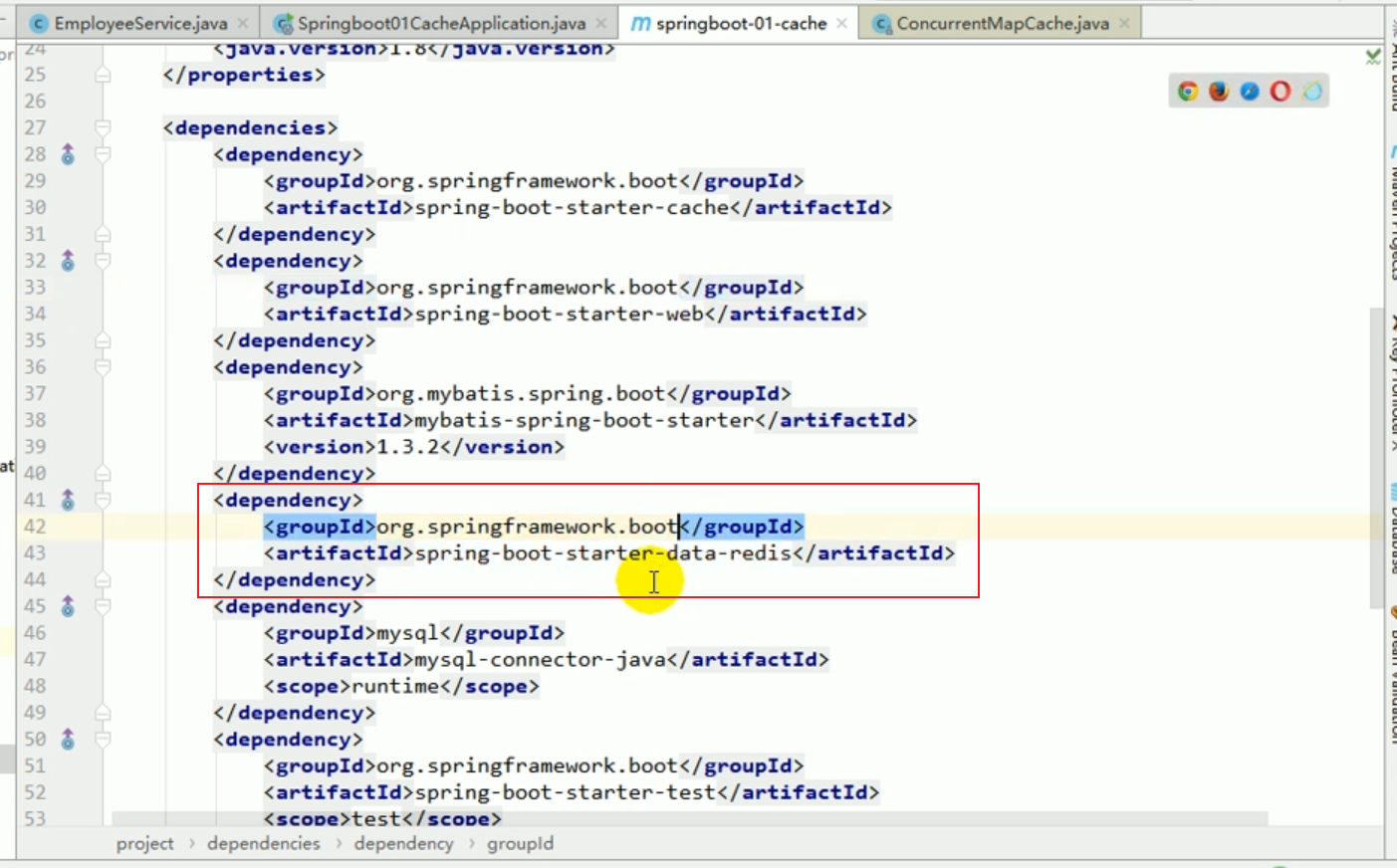
 Introducing the redis starter
Introducing the redis starter
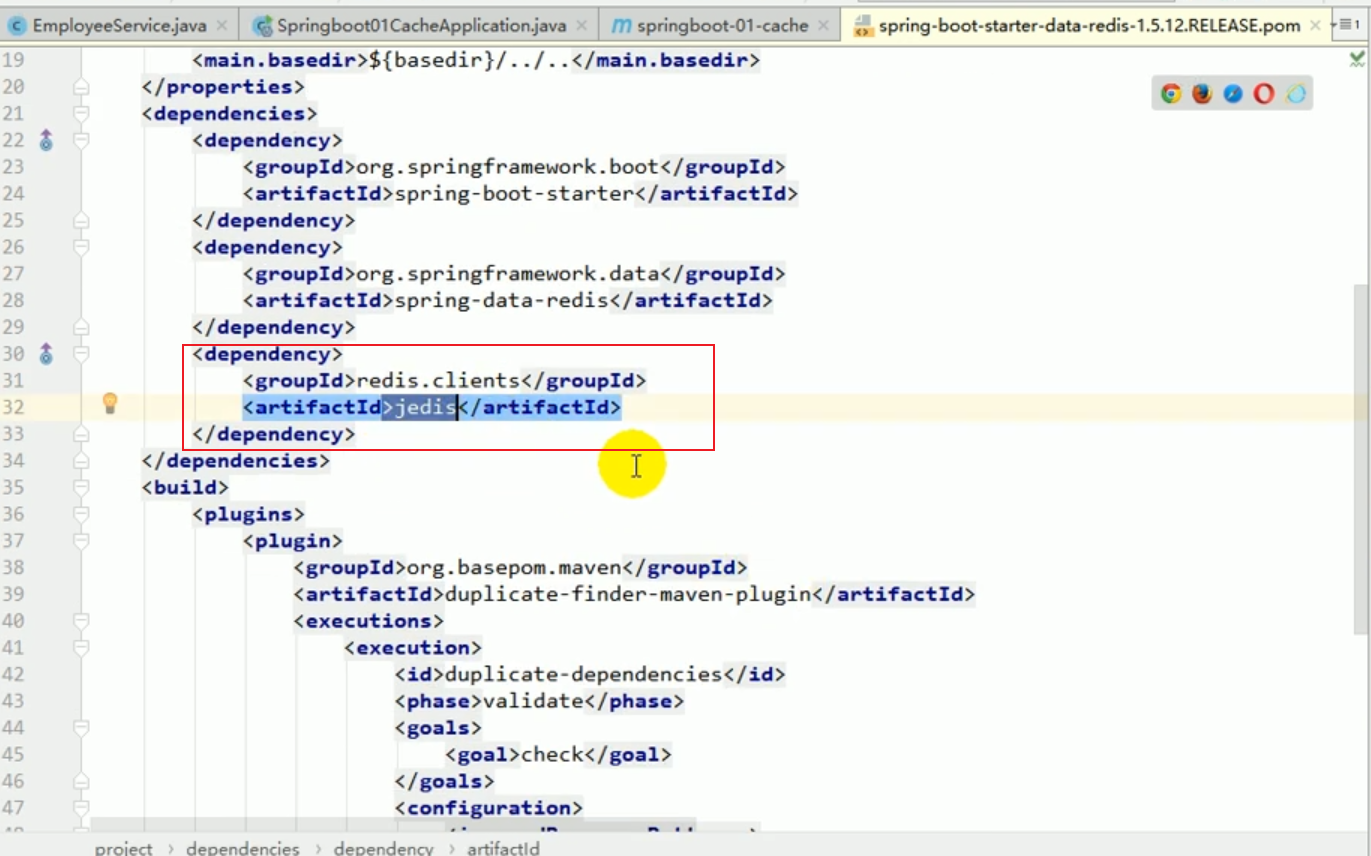
Configuring redis
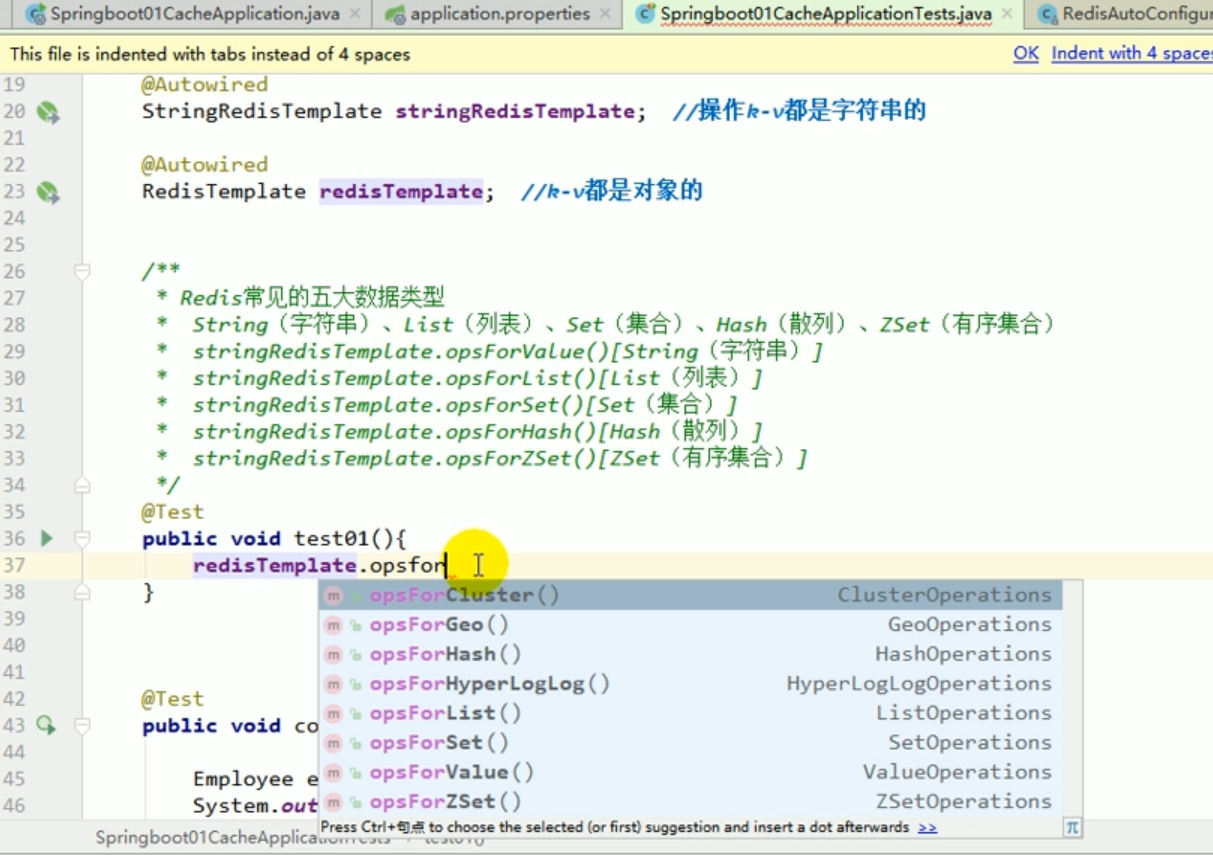
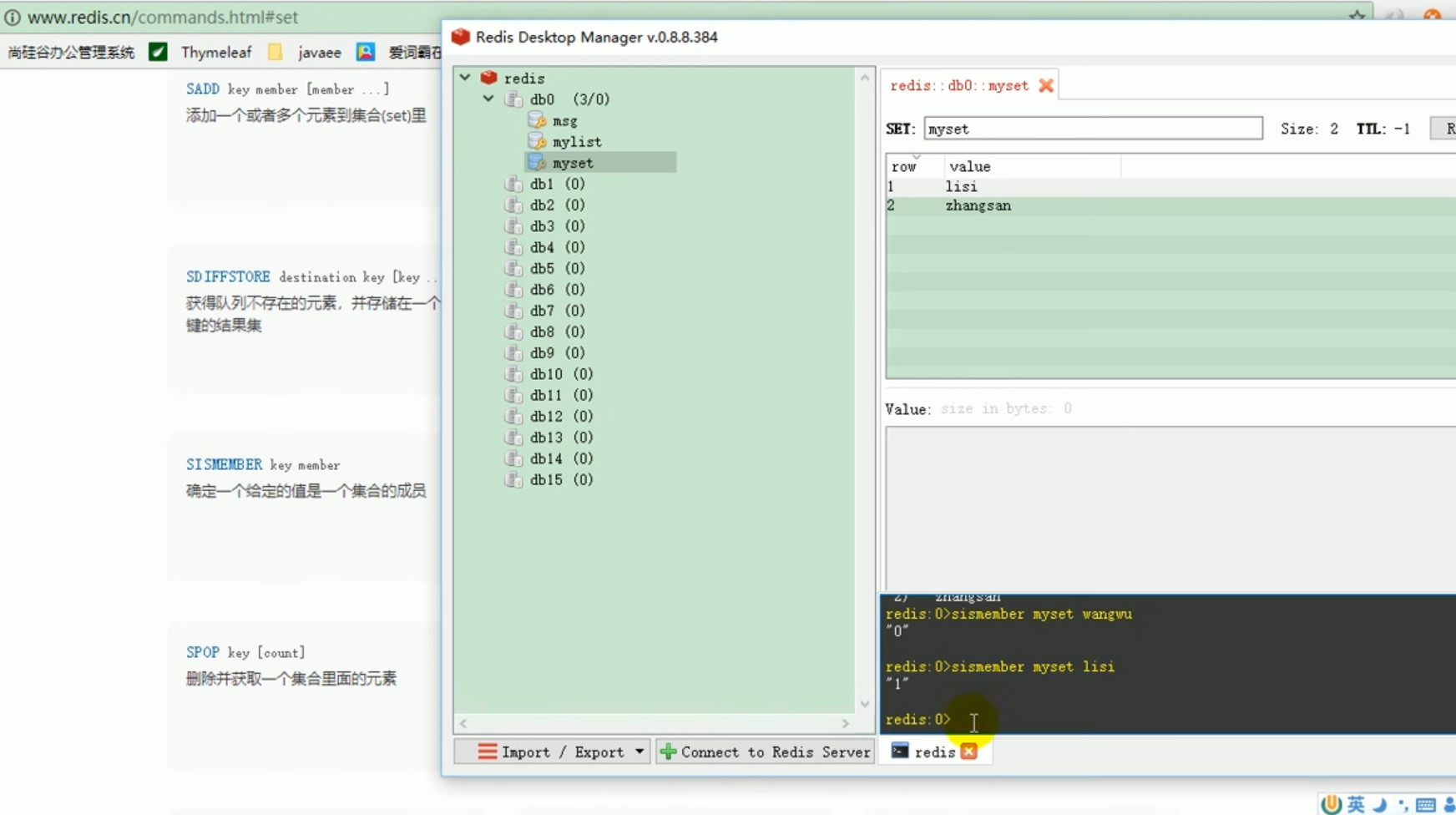
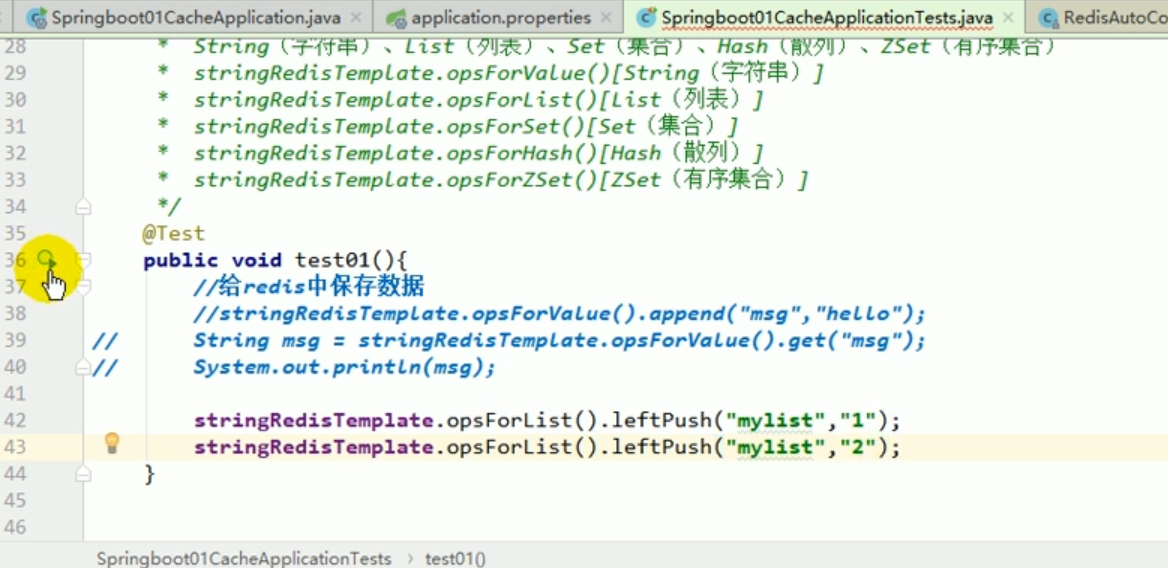
 ##redis operation list:
##redis operation list:
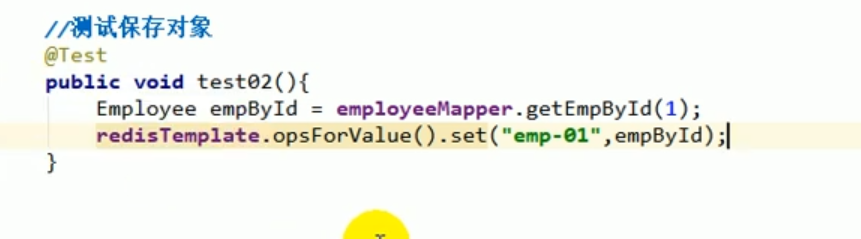
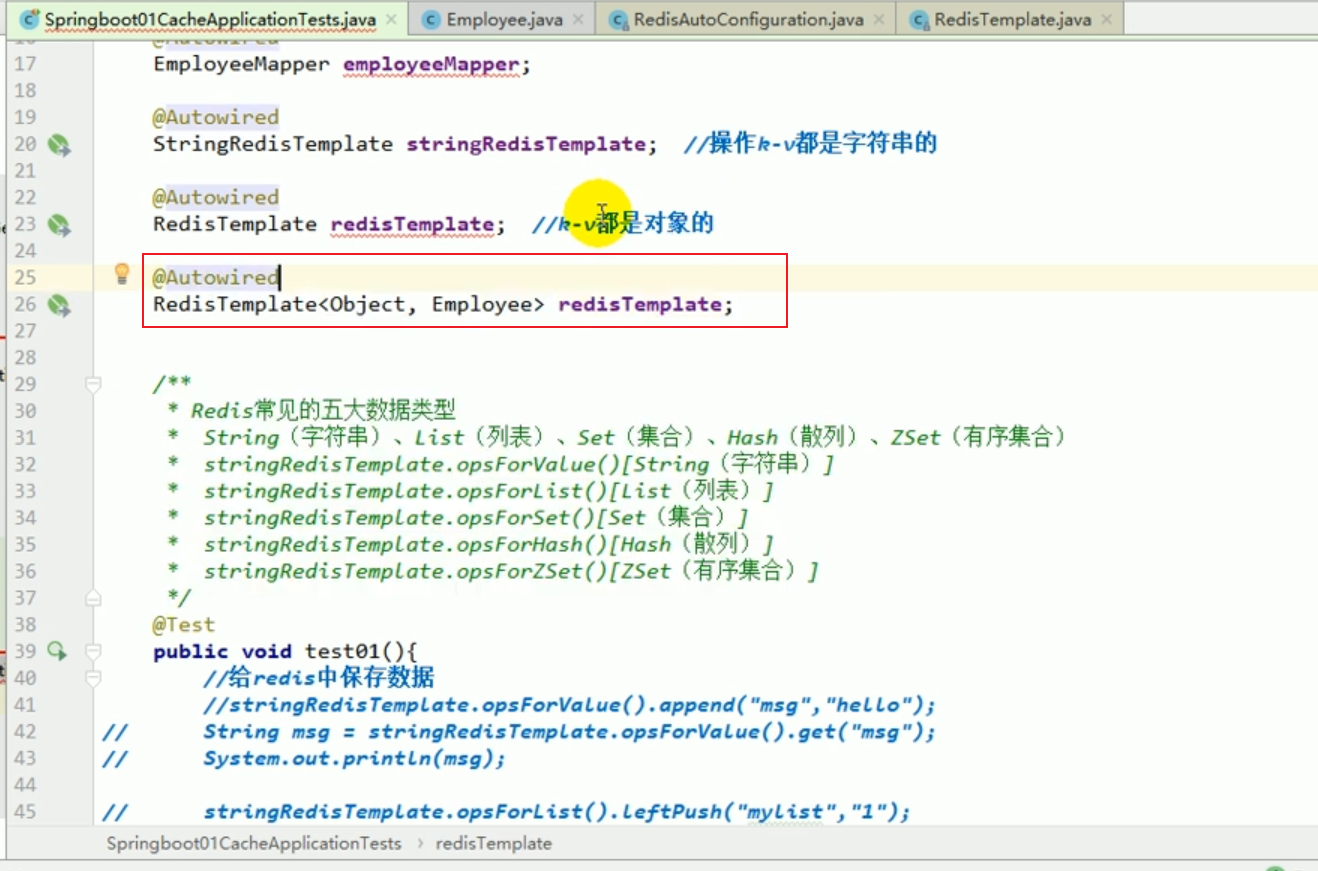
##redis test save object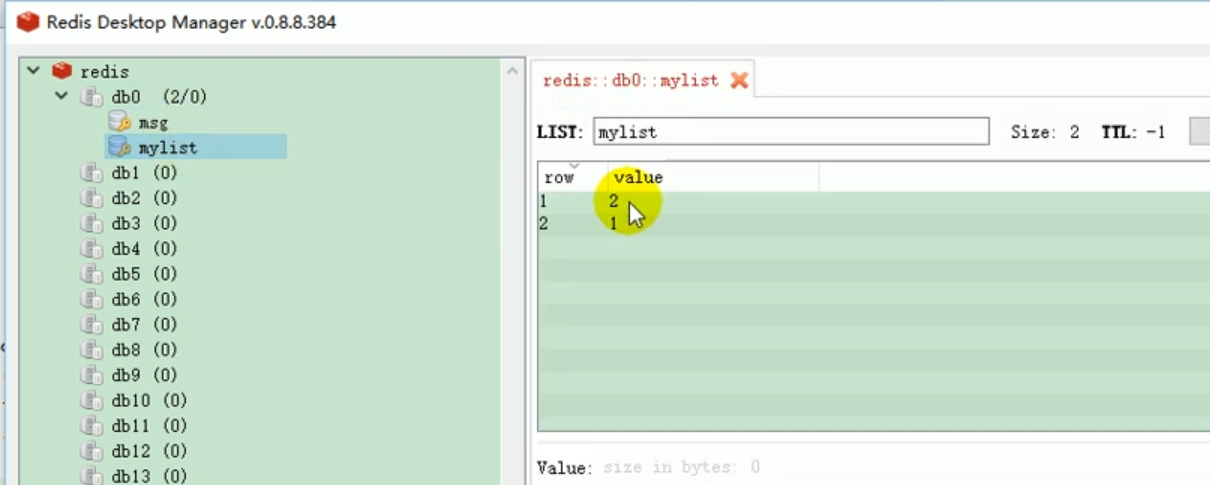
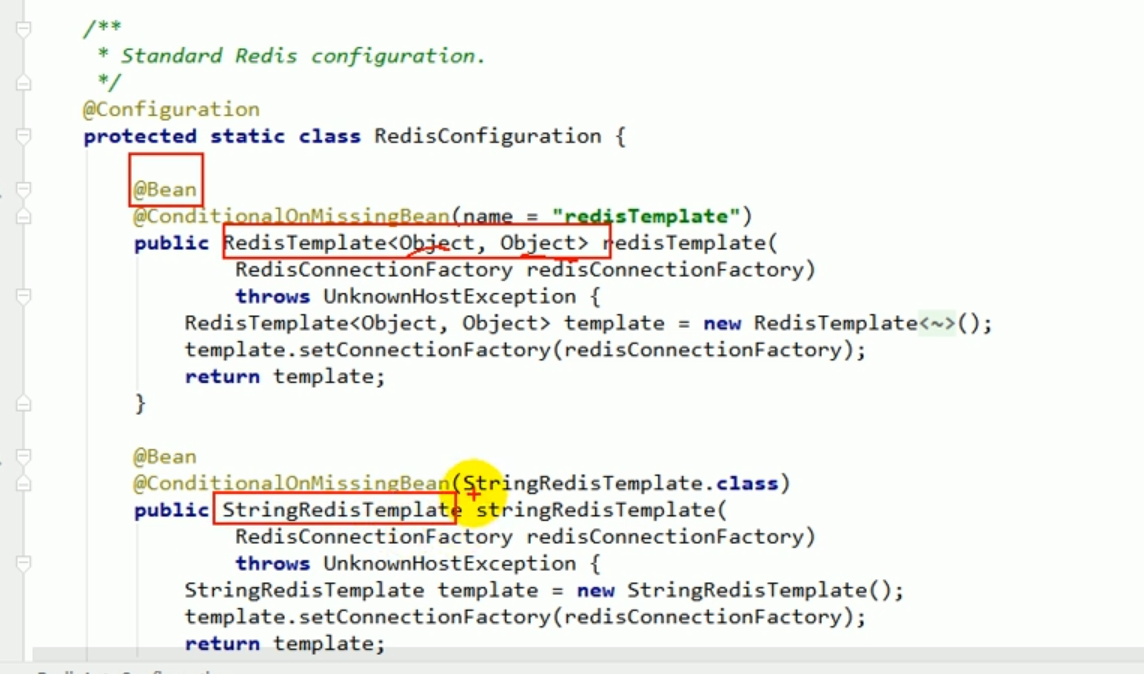
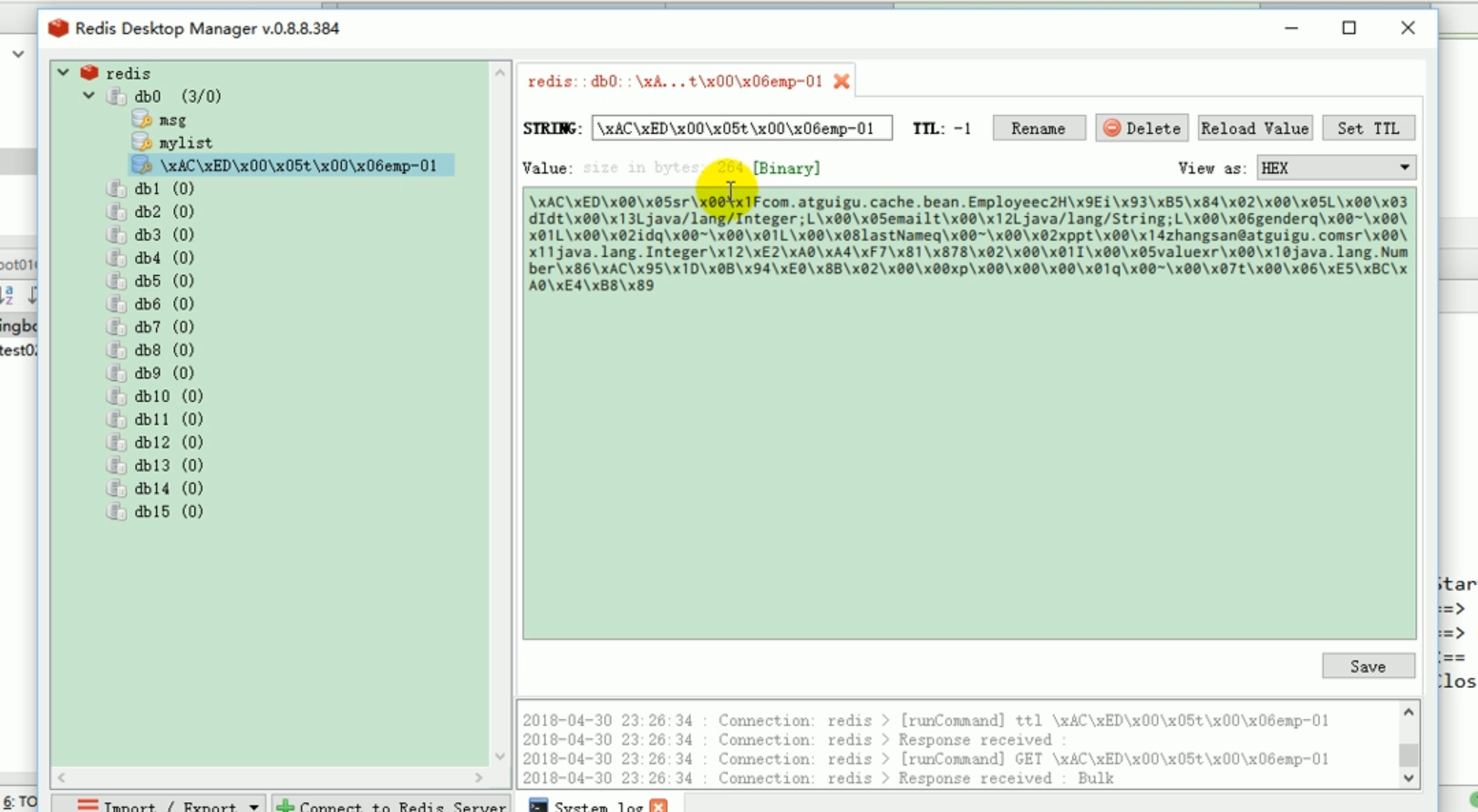 redisTemplate default serialization rules
redisTemplate default serialization rules

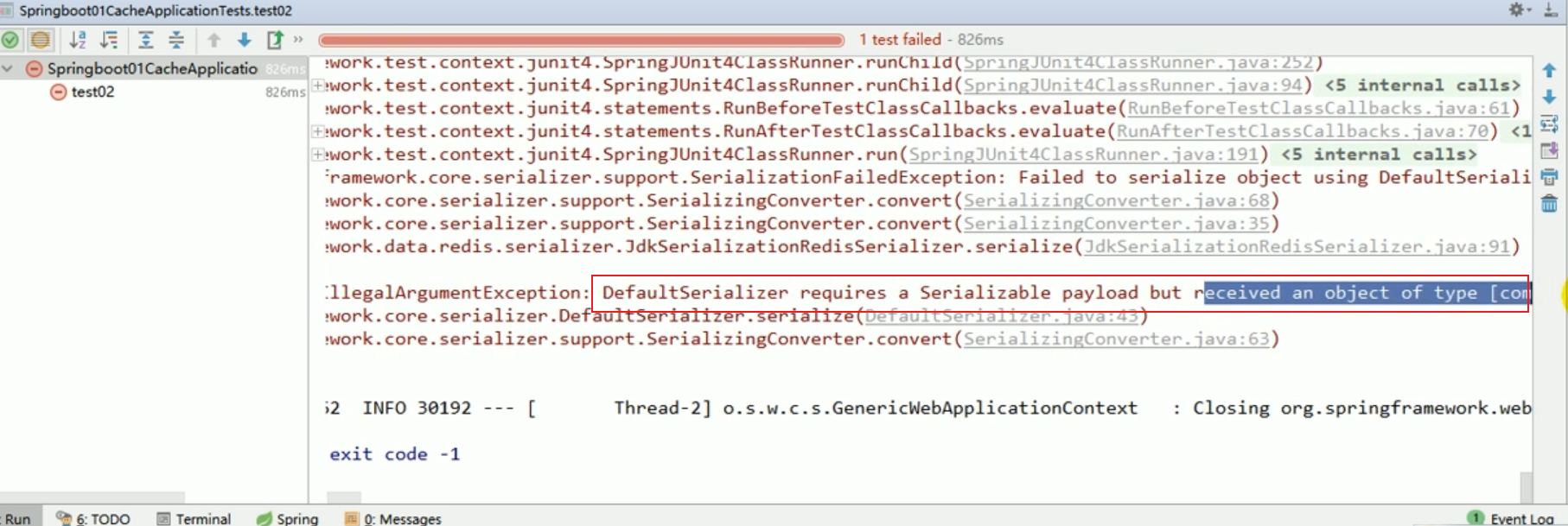
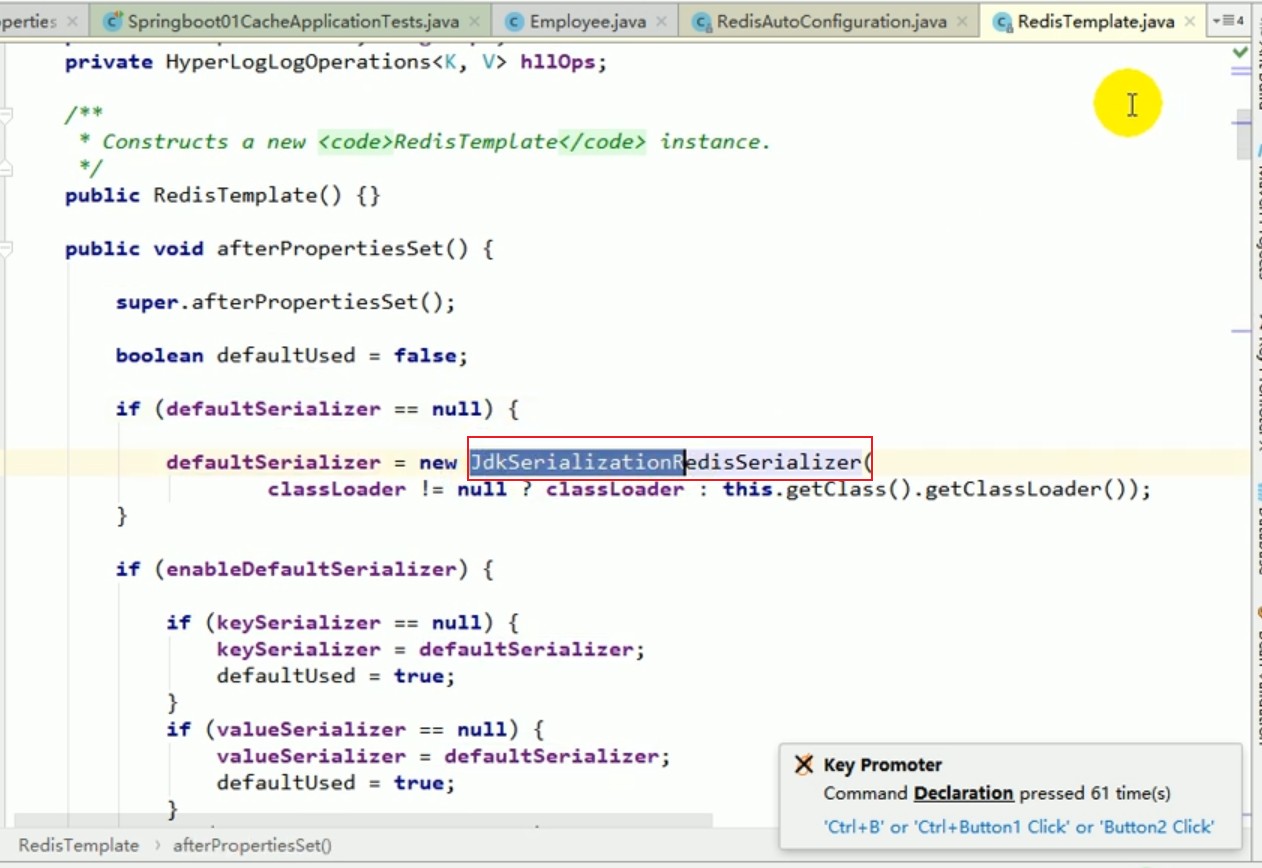 The default serializer is the JDK serializer used.
The default serializer is the JDK serializer used.
Let’s switch to the json serializer and that’s it.
redis configuration
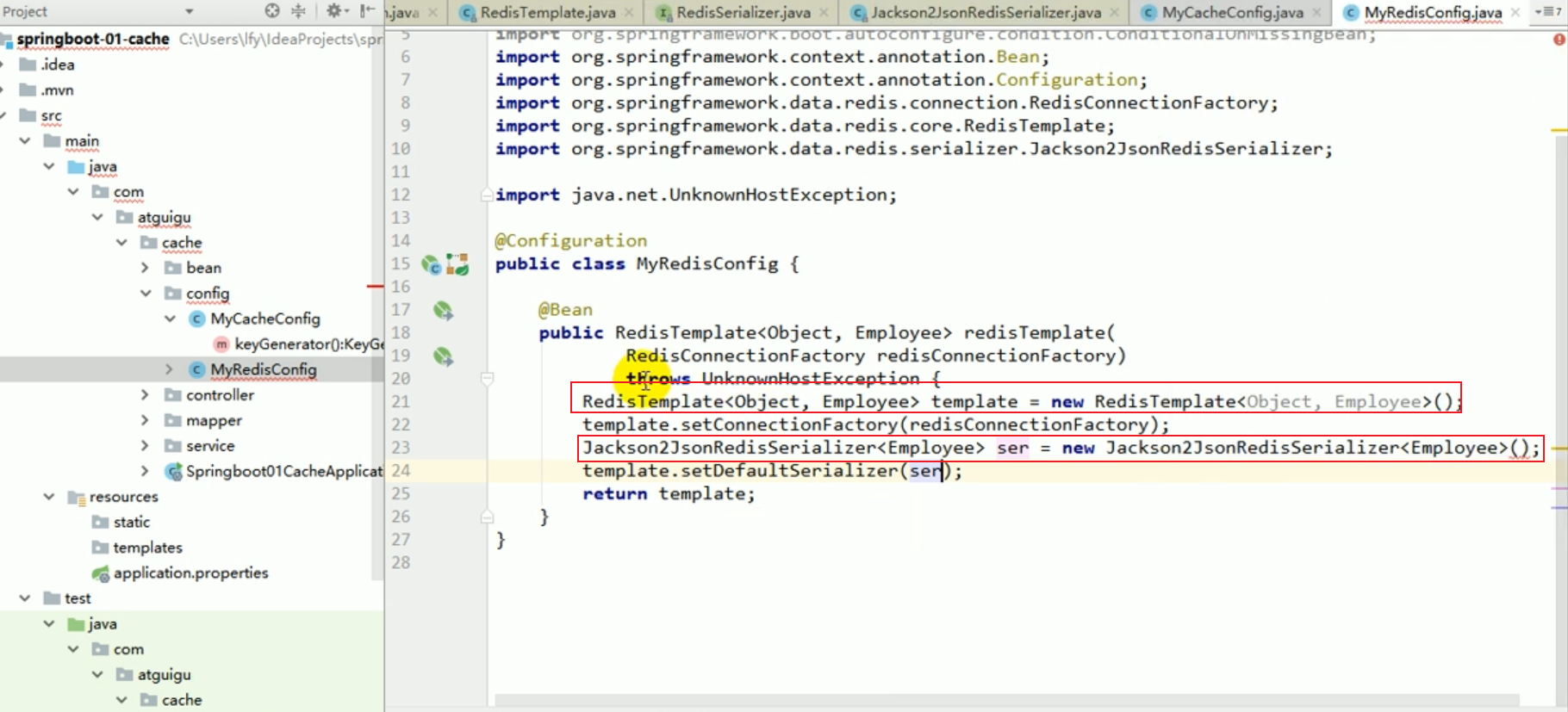
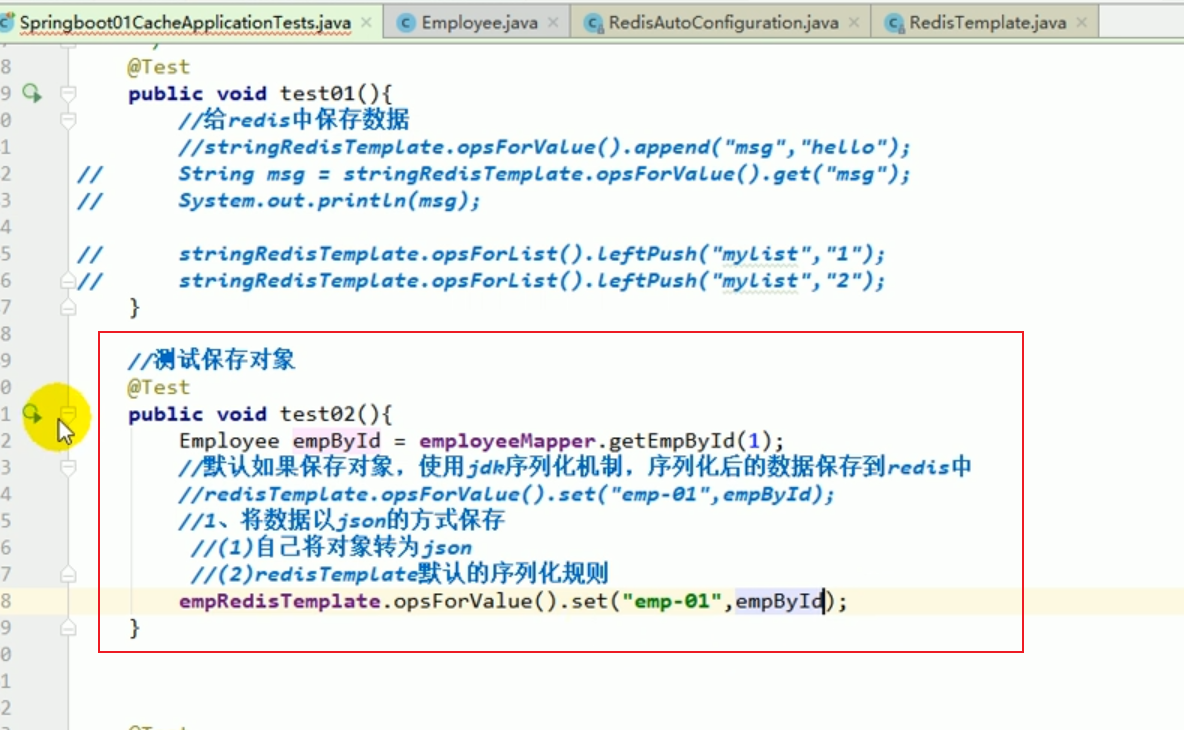
 This makes it clear that if we want to save the object later, we often need to modify the serializer.
This makes it clear that if we want to save the object later, we often need to modify the serializer.

We used ConCurrentMap's cache manager before.
This cache manager helps us create cache components.
The cache component actually performs CRUD work in the cache.
Now that we have introduced redis, what will happen?
We still set debug=true in application.properties so that the automatic configuration report can be turned on.
At this time, we restart our program and search in the console.
See which automatic configuration class is effective?
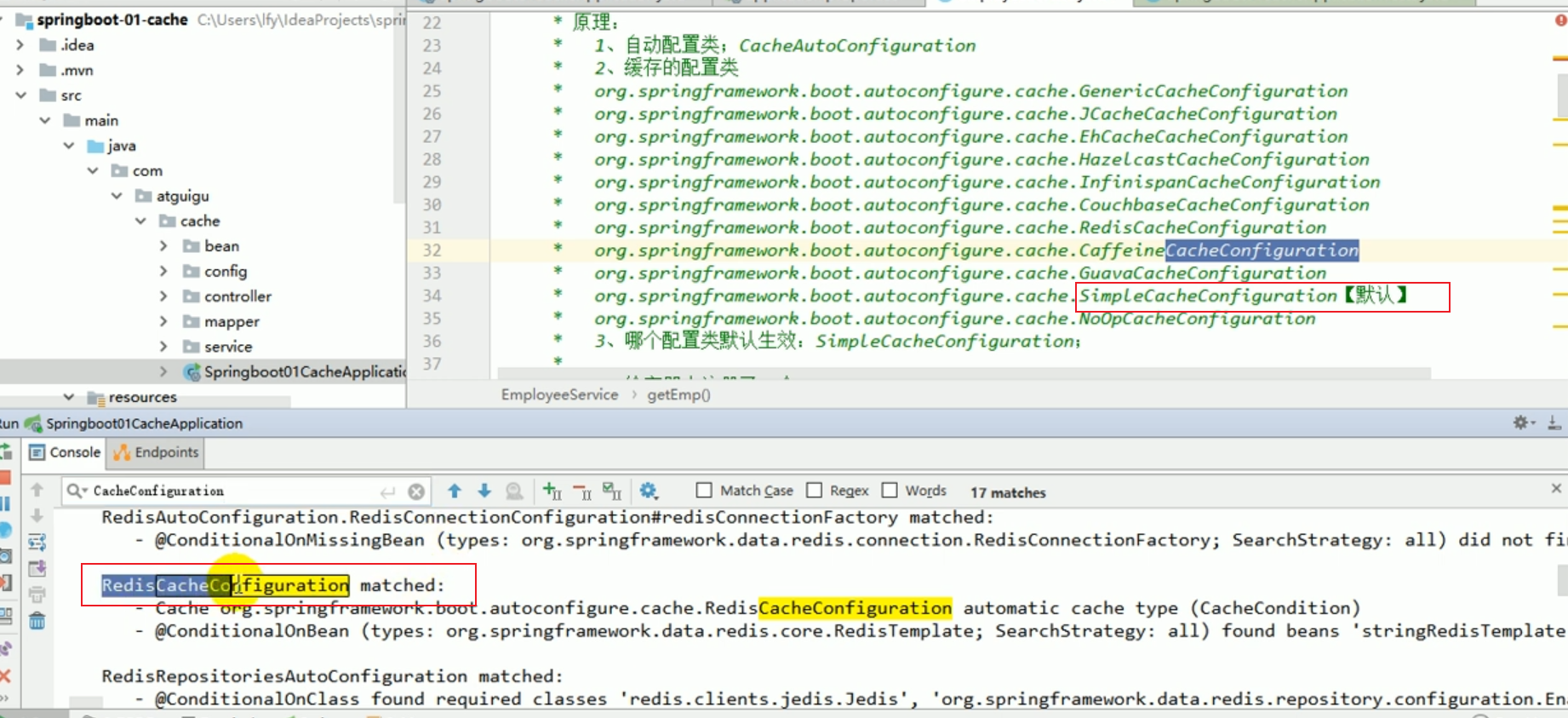
The original default enabled is: SimpleCacheConfiguration.
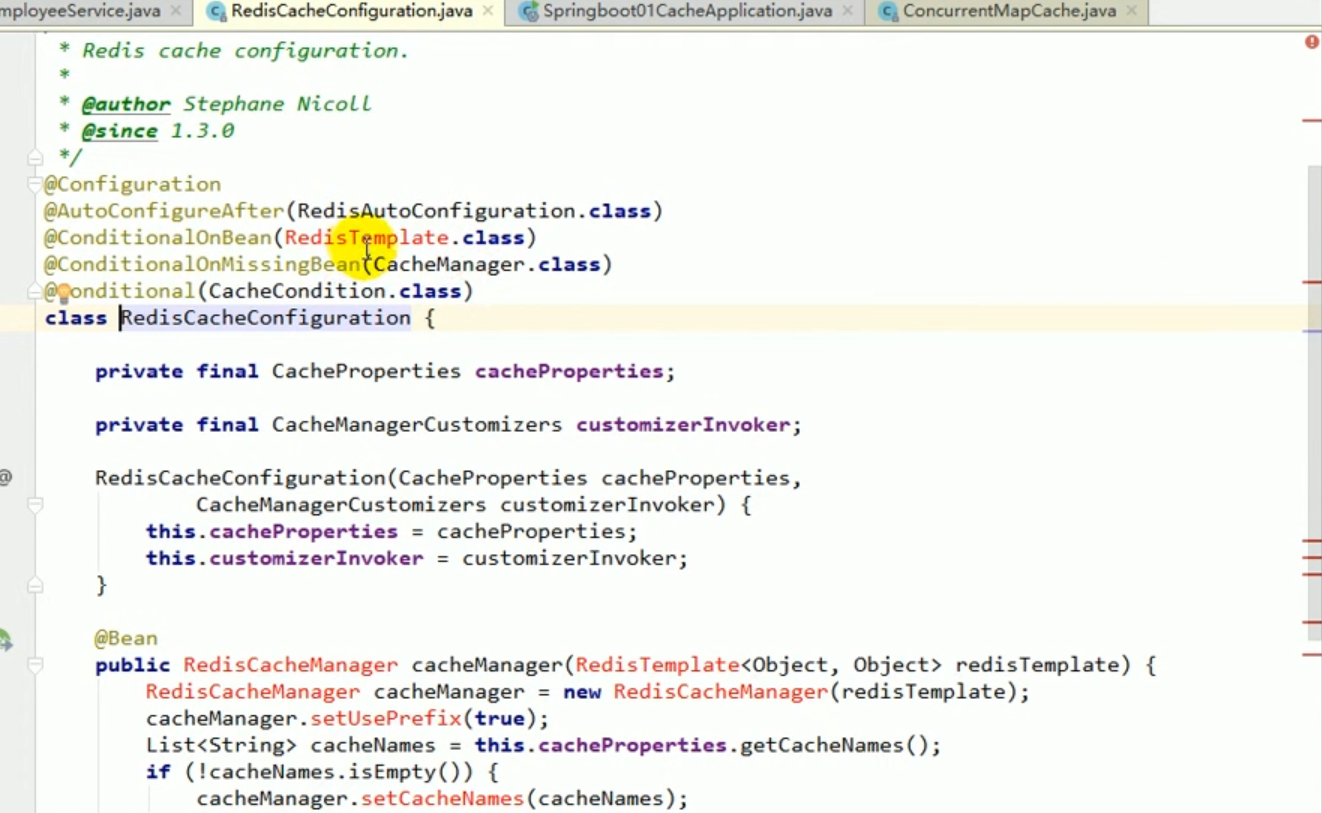
Now that we have introduced redis-related starters, the program starts RedisCacheConfiguration by default.

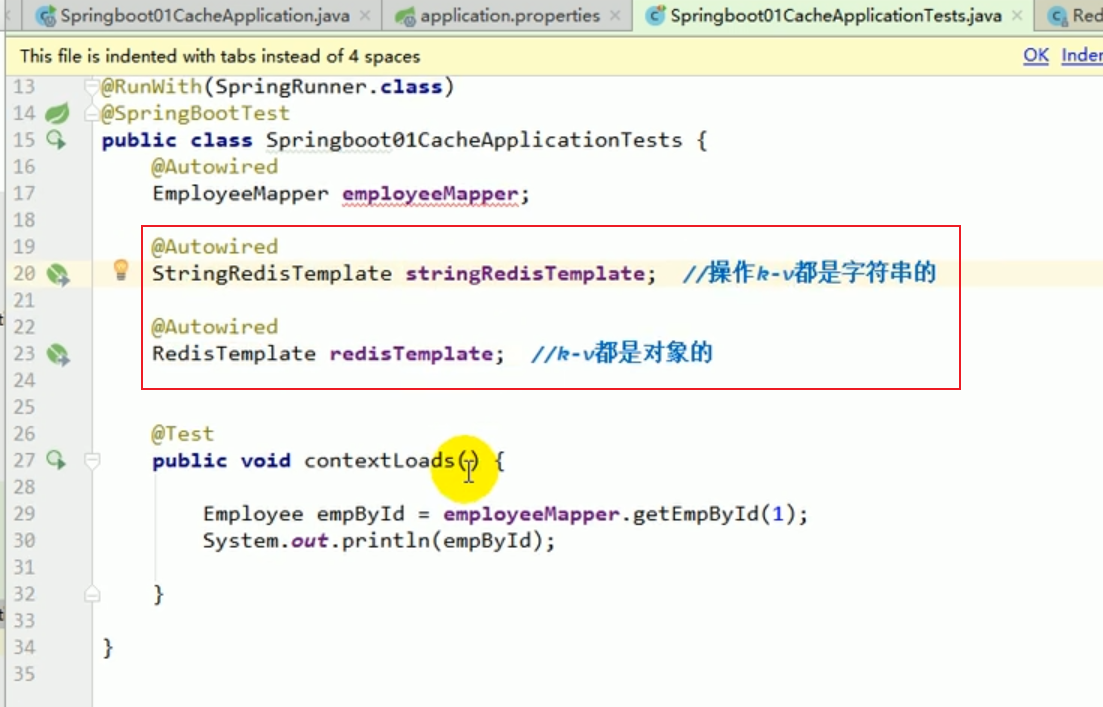
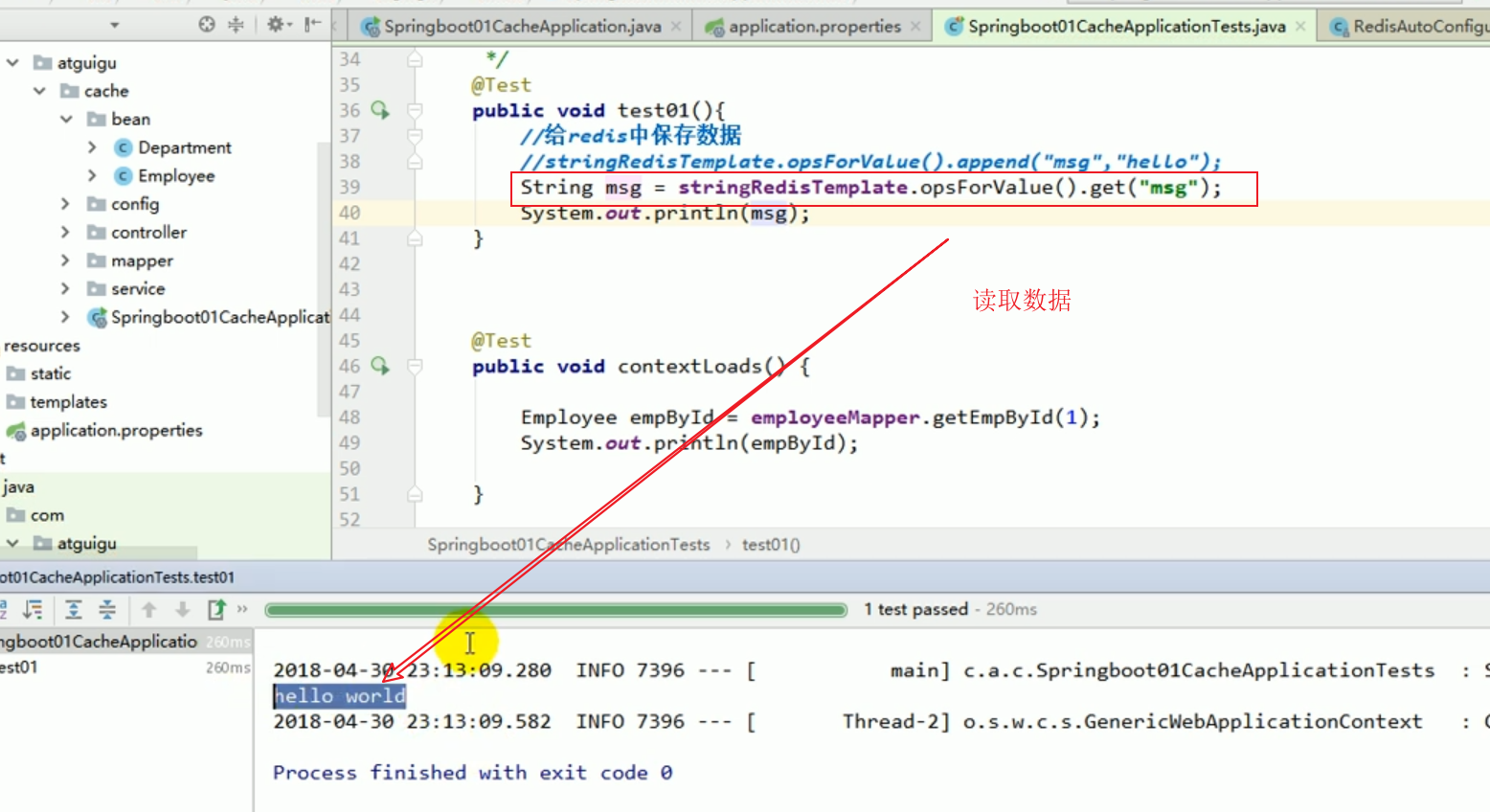
Just start the program and test it directly.
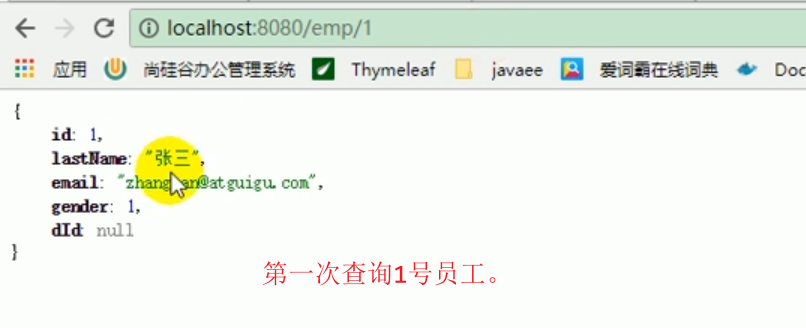
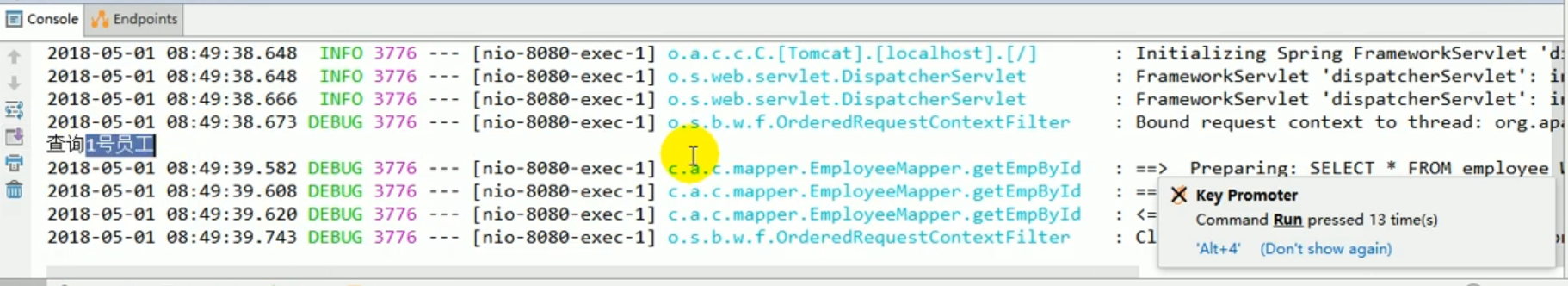
It means that when you query for the first time, you query the database.
When querying for the second time, there was no output from the console, indicating that the cache was queried.
The cache is only enabled by redis by default.
Then it must be in redis.
We can check it out:
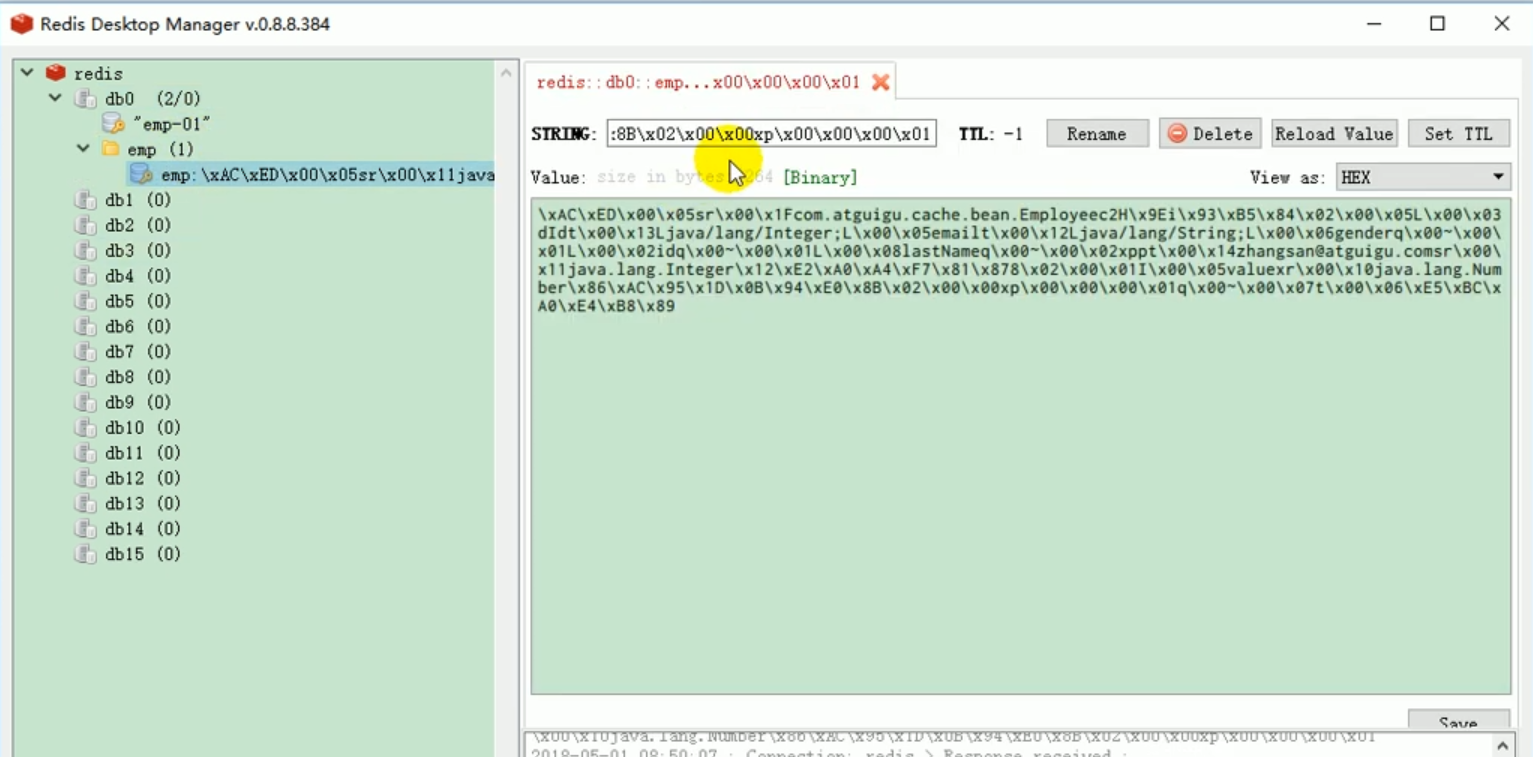
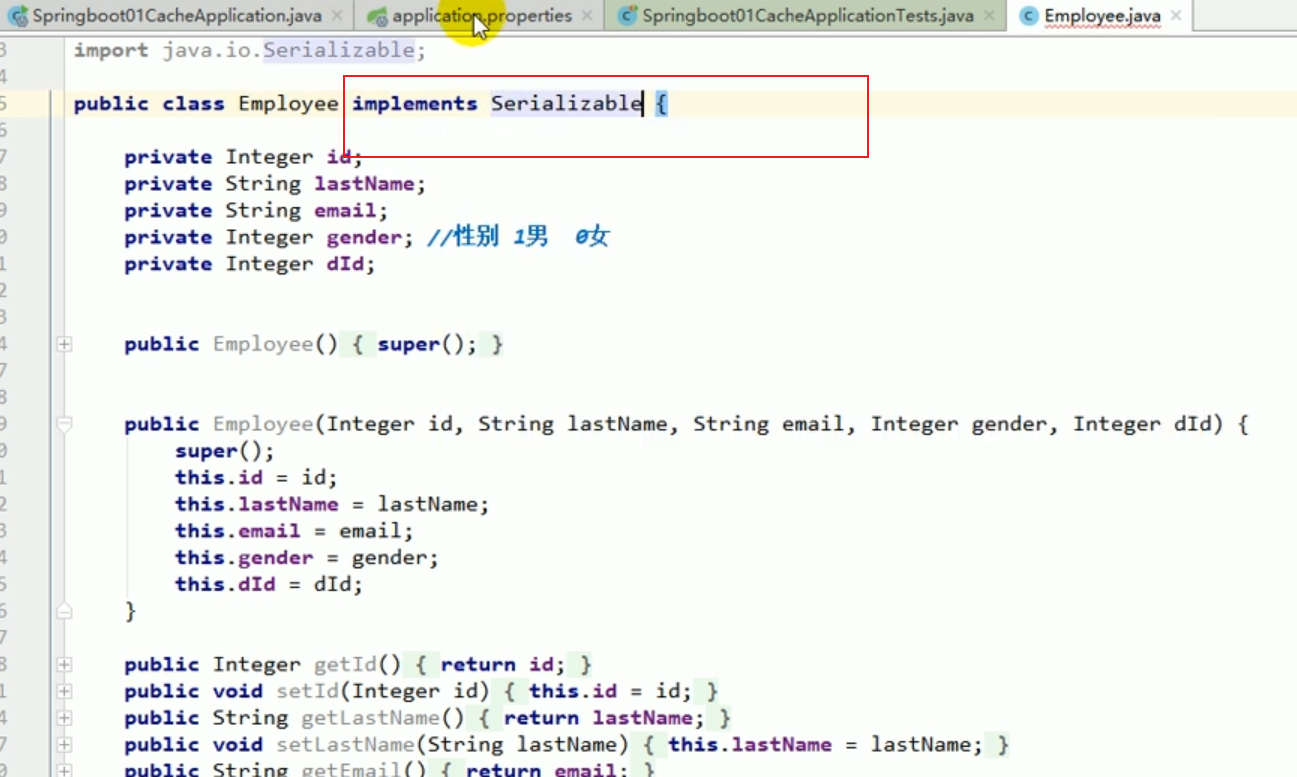
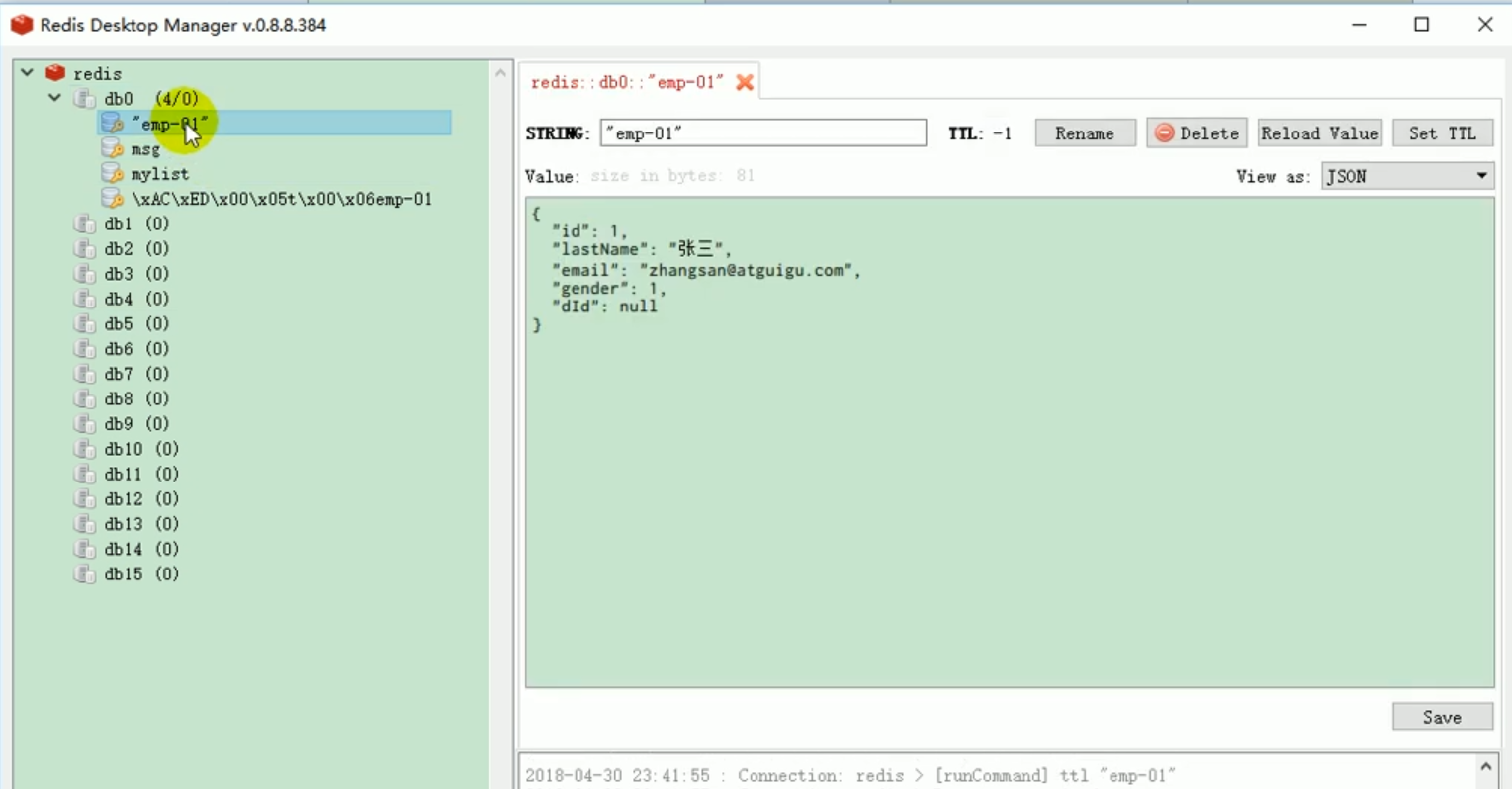
This illustrates a problem. When k and v are both objects, serialization is used to save the object by default. To save. We want redis to automatically save it as json.
What should we do?
Let’s first analyze the principles of these processes.
1. We have introduced the starter of redis, so our cachemanager has become rediscachemanager.
2. The rediscachemanager created by default passes in a redistemplate when operating our data. s things.
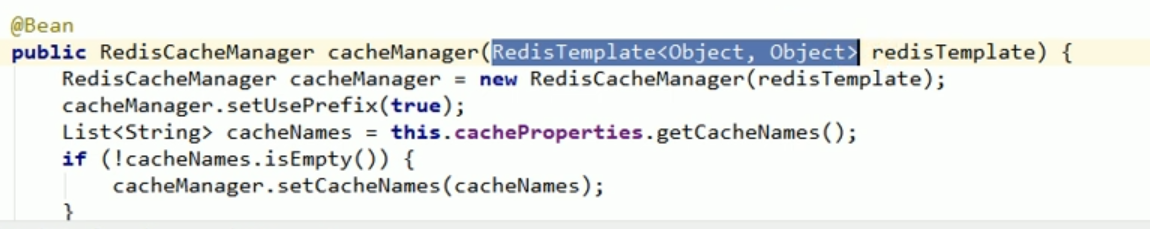
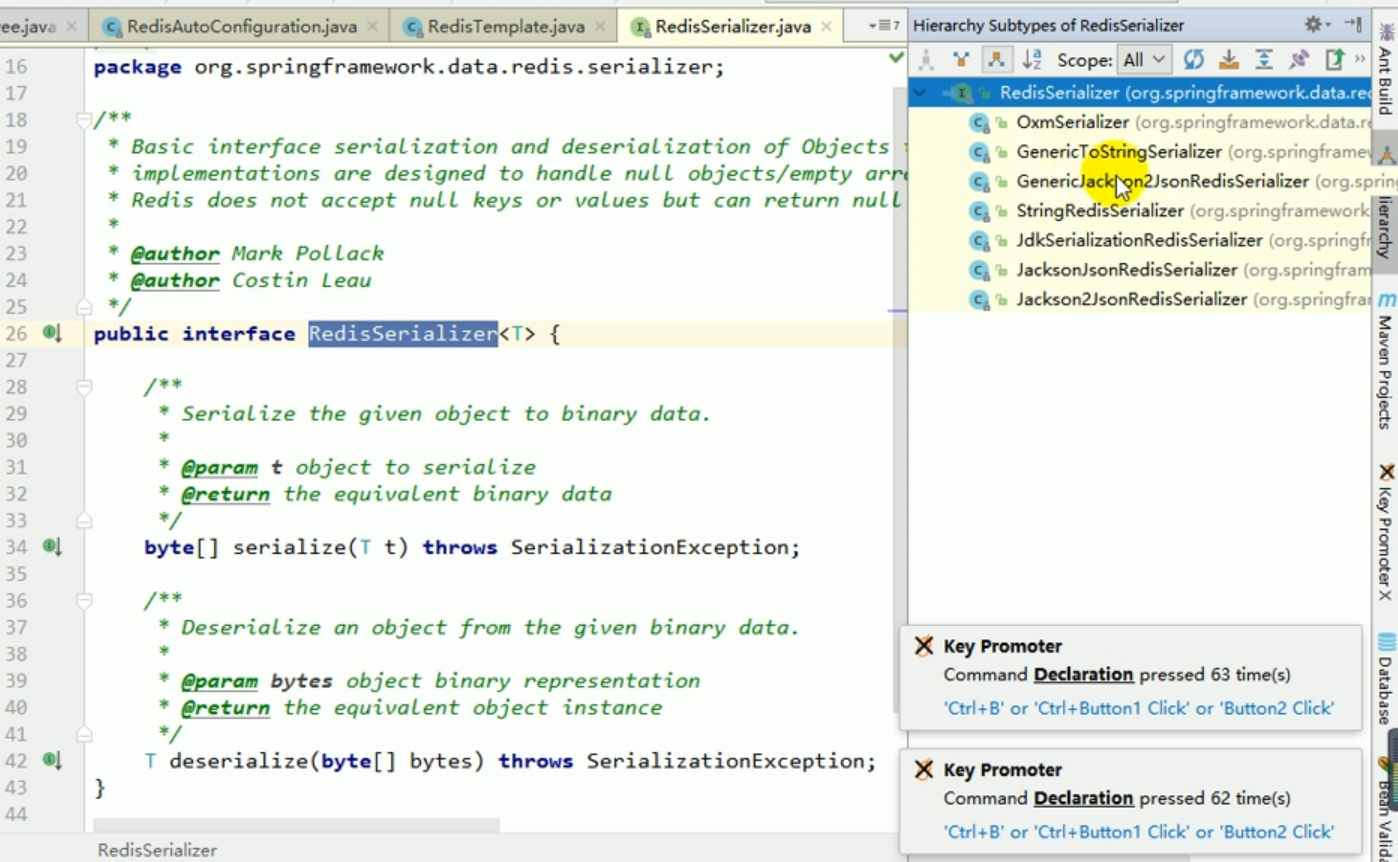
#3. This redistemplate was created for us by redisautoconfiguration. The default serialization mechanism used by this redistemplate is jdkserializationredisserializer. This is equivalent to the fact that the redisCacheManager that redis prevents us by default does not quite meet our requirements.
What should we do?
We should customize CacheManager.
Customized redisCacheManager
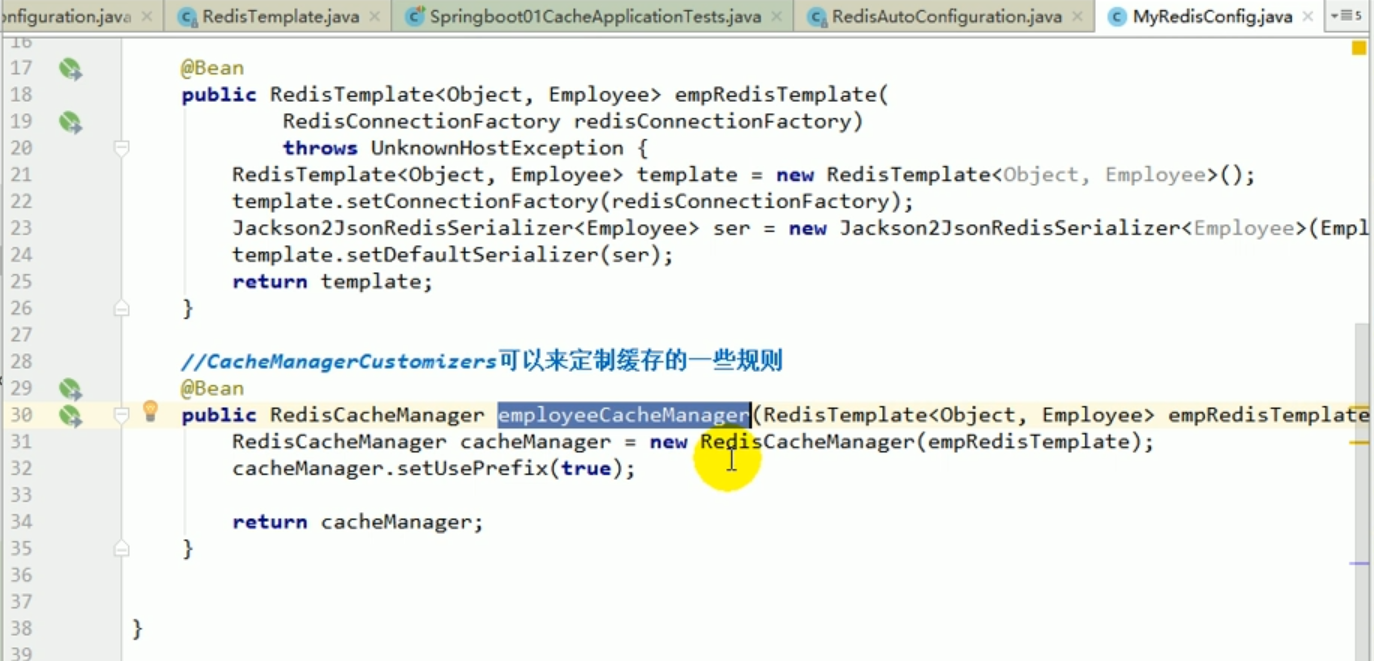
At this time, we start the project again to test. At this time, we can see the results in redis, which is We wanted it.
During Yunqiu’s next interview, she can ask those who want to come to the software park, do you know that when redis starter saves objects, redisTemplate What are the default serialization rules?
If we want to modify the default serialization rules when using redis, what should we do?
We can customize redisCacheManager, then customize redisTemplate, and pass in the json-related serializer in redisTemplate.
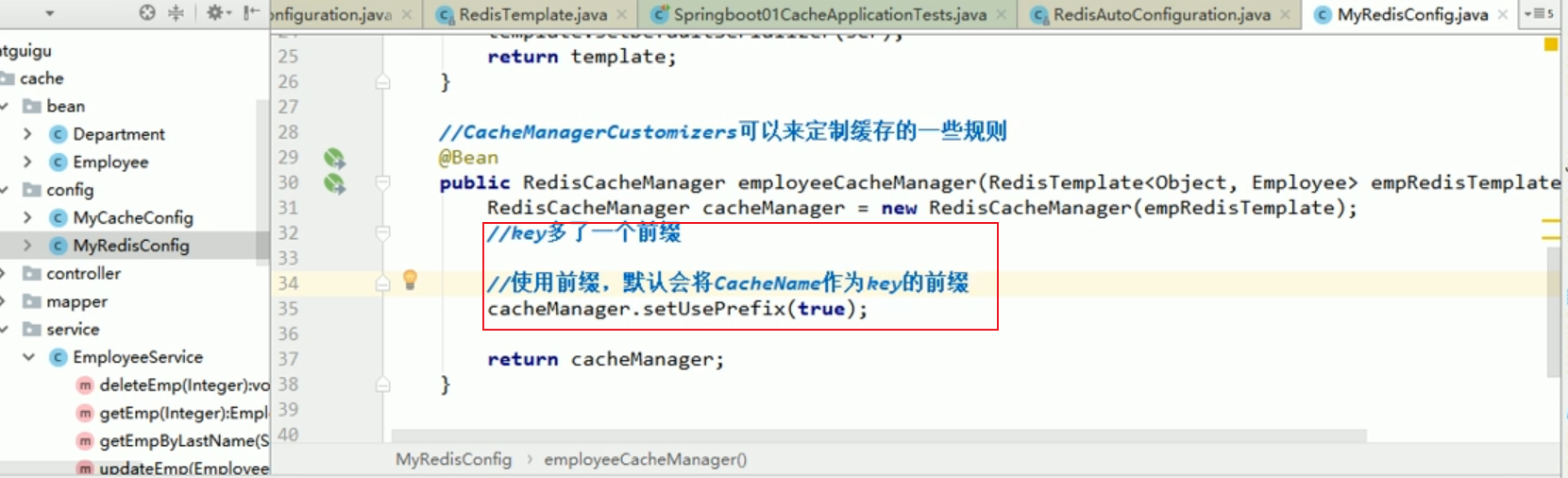
Small remaining problems
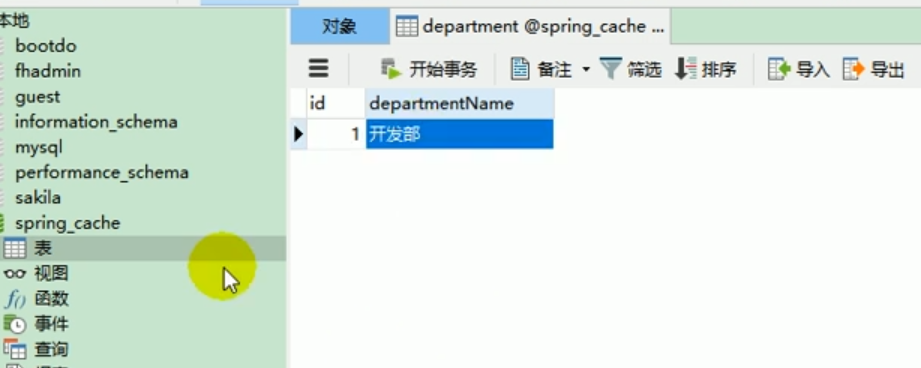
Database
We put a piece of data in the department table in the database:
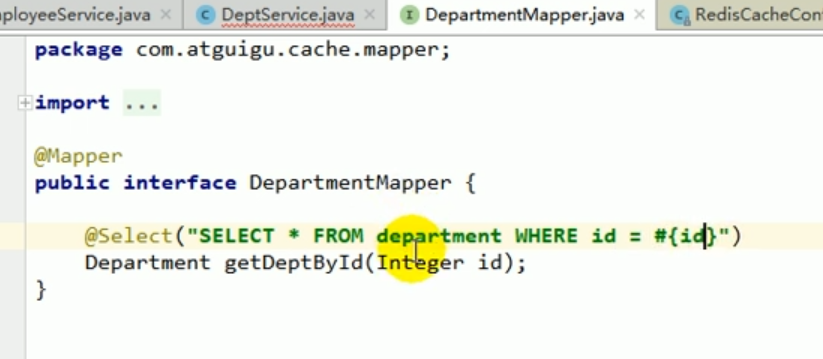
mapper
We write a mapper corresponding to the department operation.
service
Let’s write a corresponding service
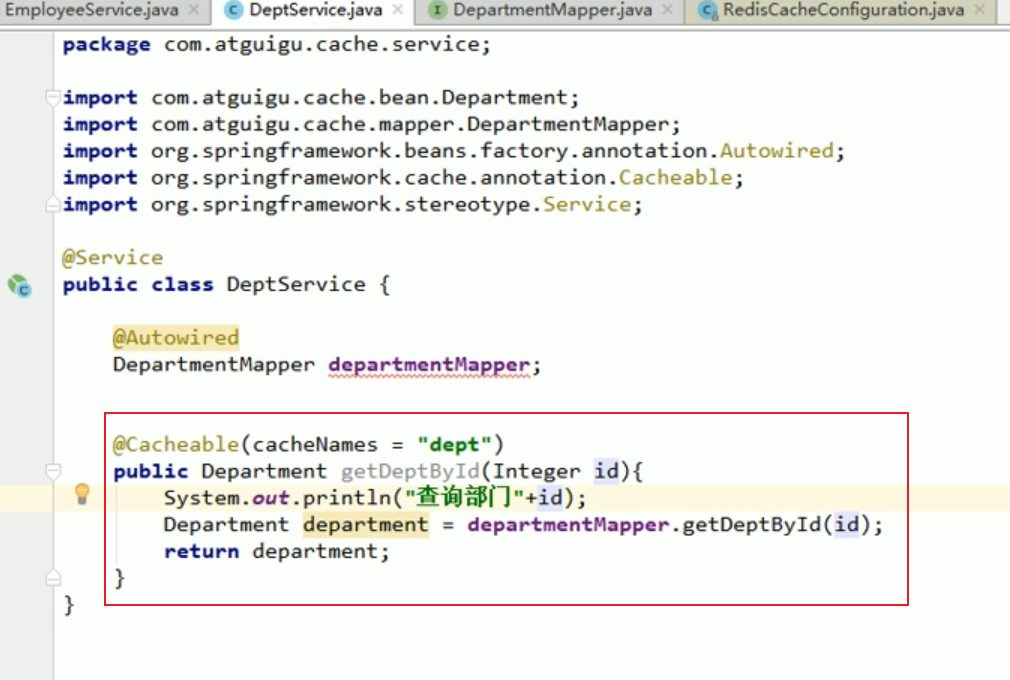
controller
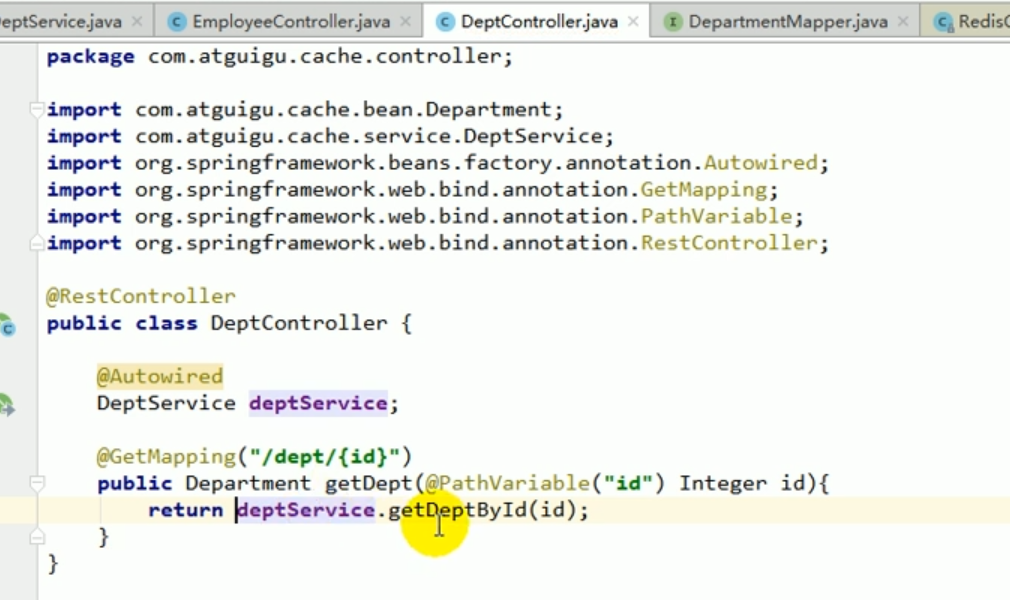
Start the project test
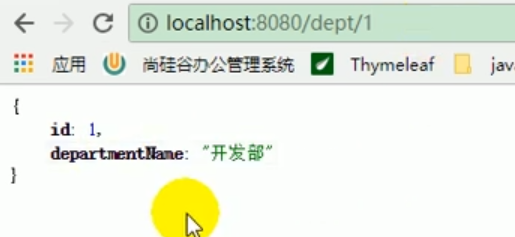
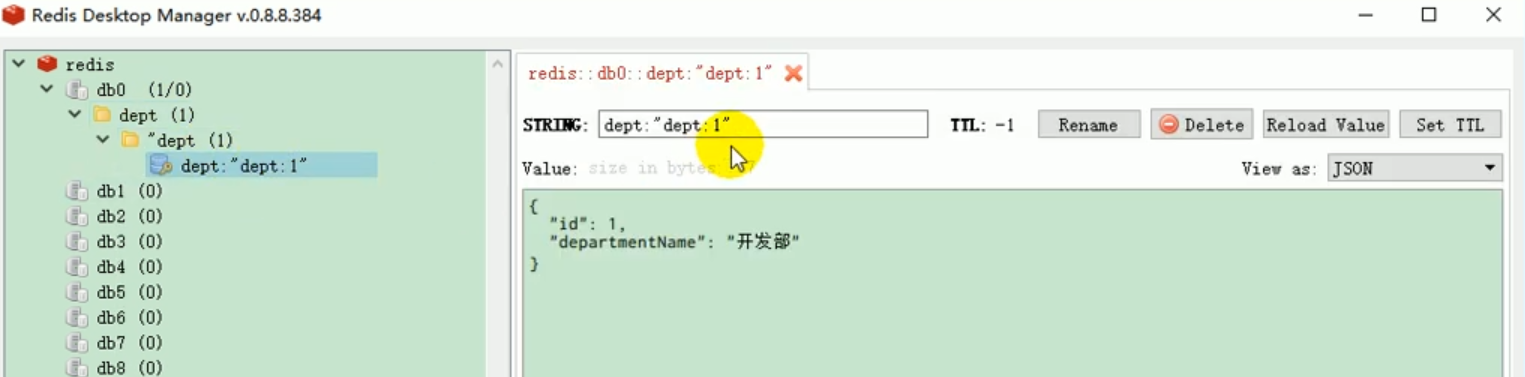
Then let’s see if there is data in redis?
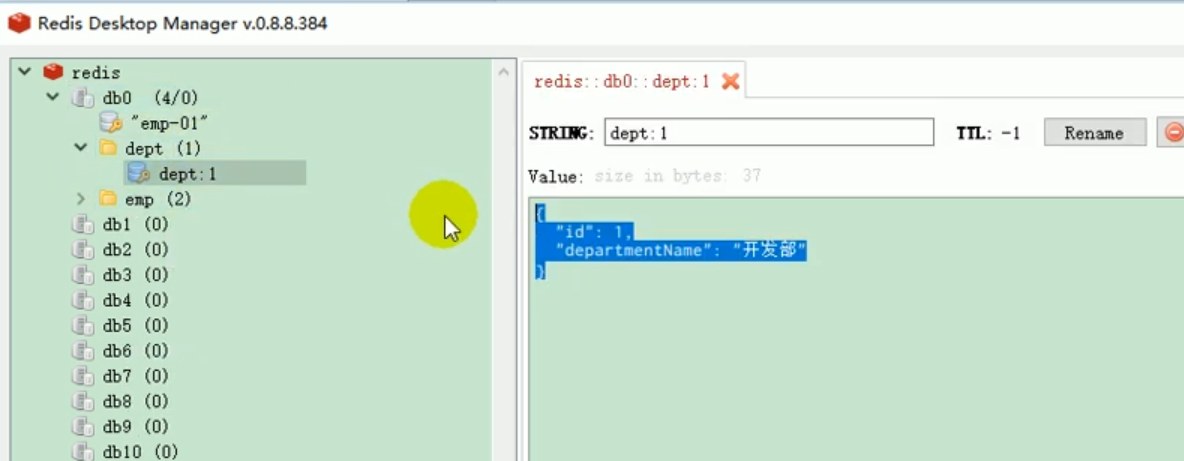
We have seen that there is dept-related data in redis.
When we query dept for the second time, we should cache redis.
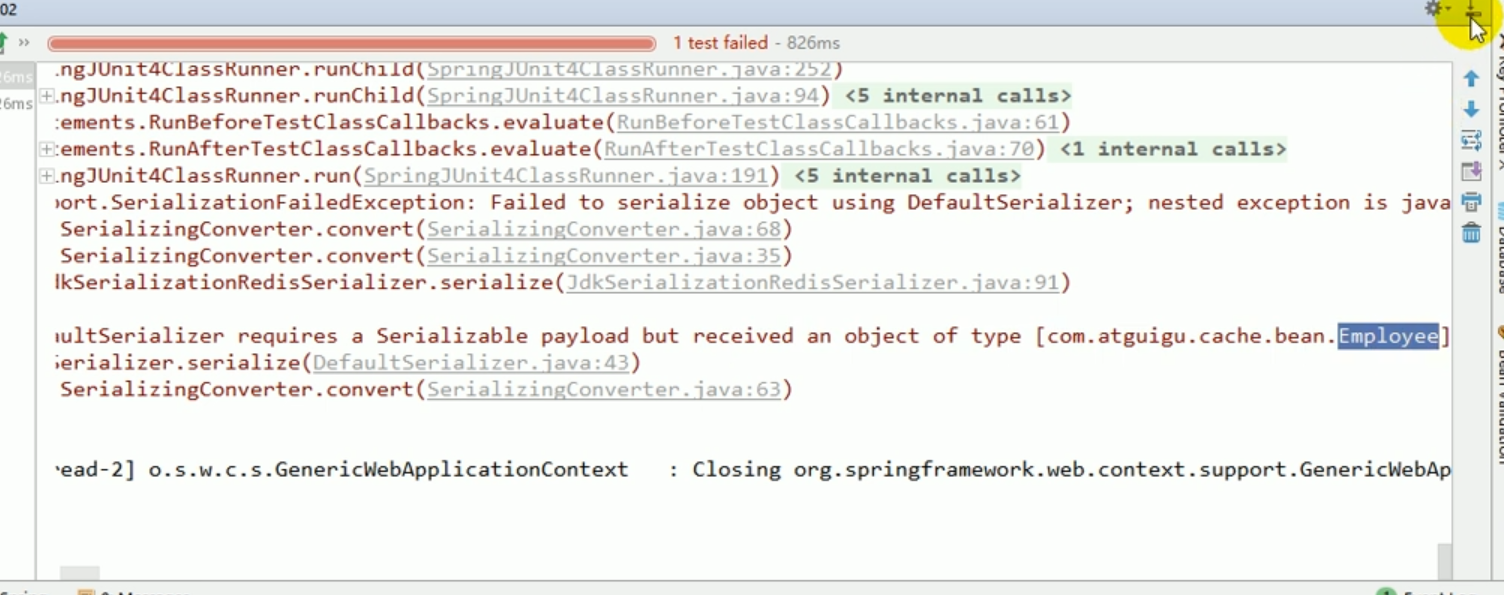
But when we checked for the second time, the following error occurred.
Error
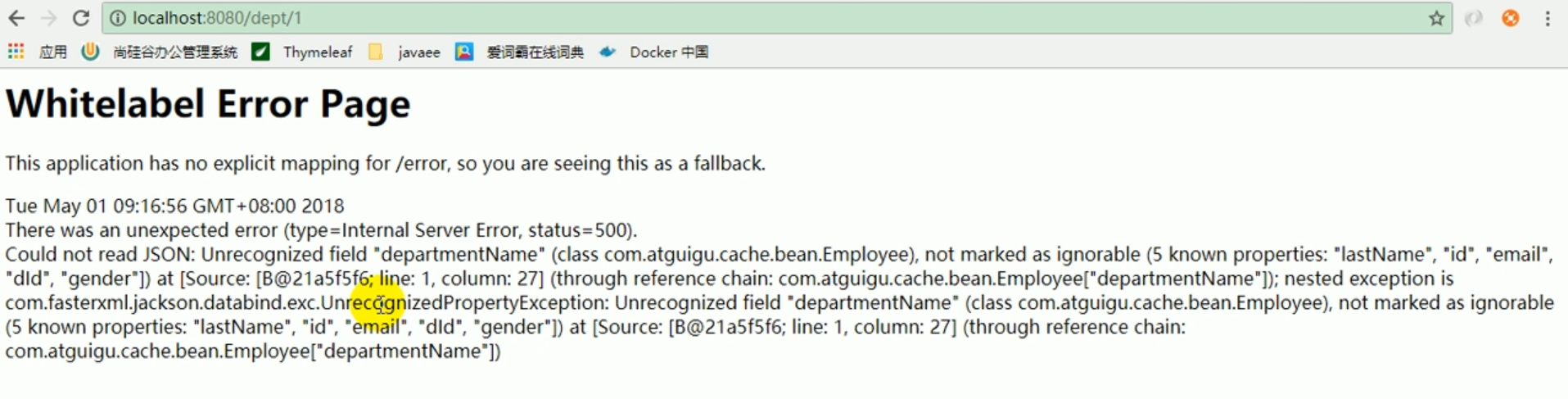
The error reported above means that json cannot be read.
Because it is necessary to convert the department's json object into the employee's json object, which is not possible.
This is because the redisCacheManager we placed is for operating employees.
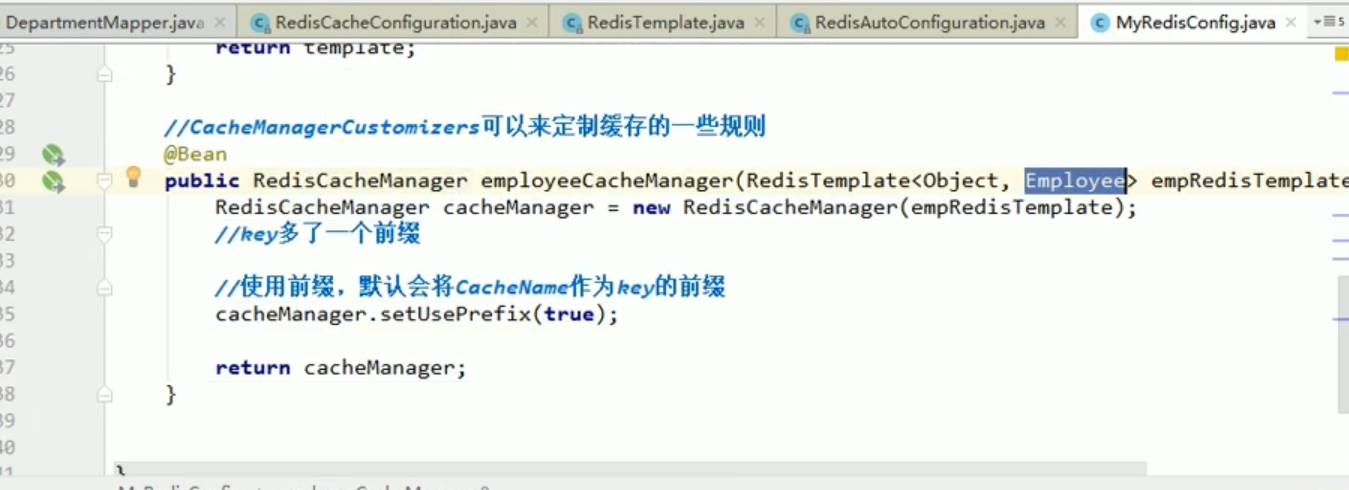
So, the effect we see now is very magical.
The cached data can be stored in redis.
But when we query from the cache for the second time, we cannot deserialize it back.
It turns out that what we store is dept's json data, and our cachemanager uses the employee's template to operate redis by default.
This thing can only deserialize employee data.
Solution to the error
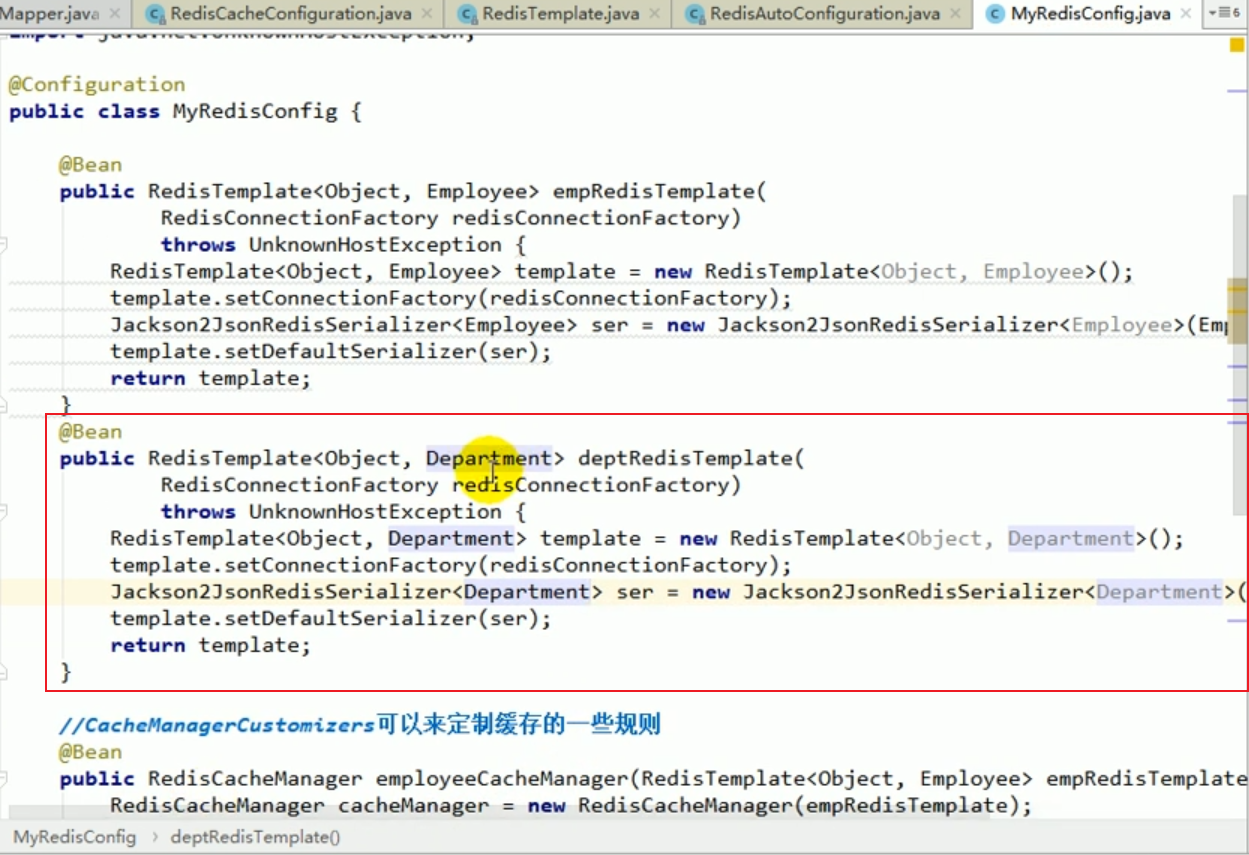
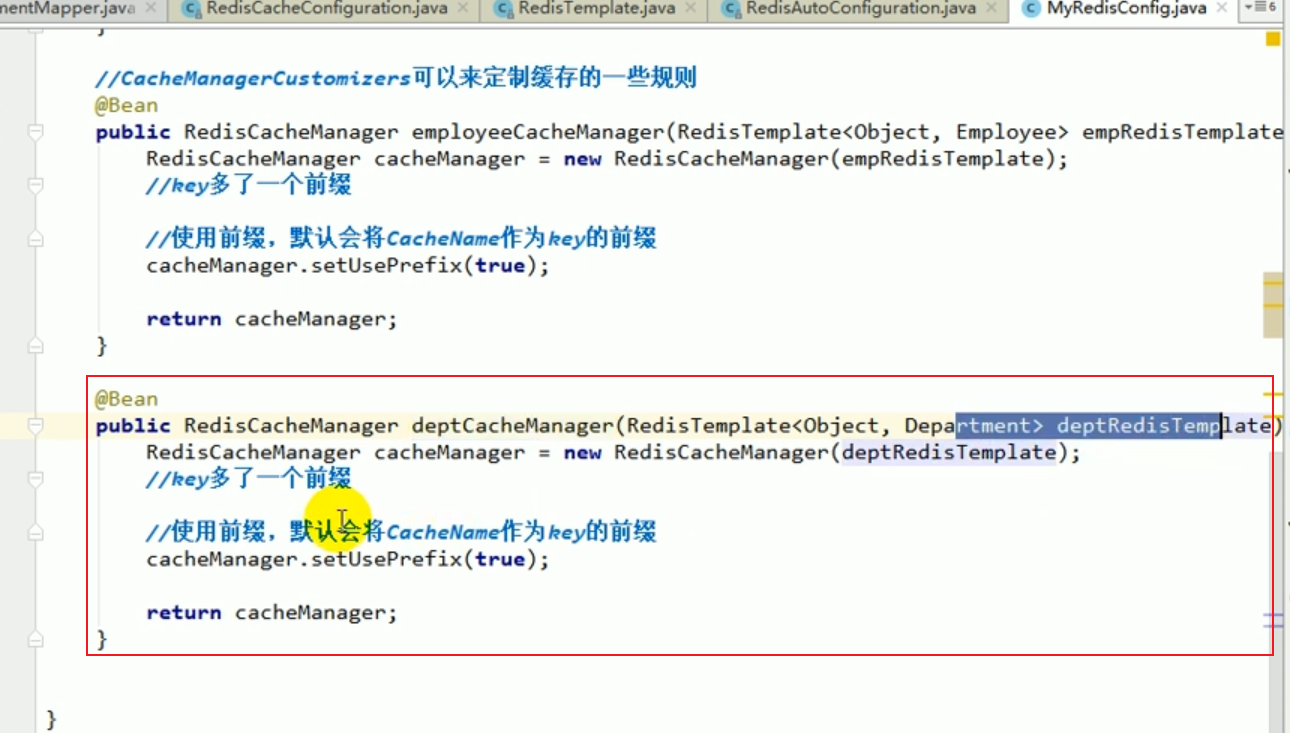
At this time, there are two redisCacheManagers. Which one should we use?
We can specify it in the service.
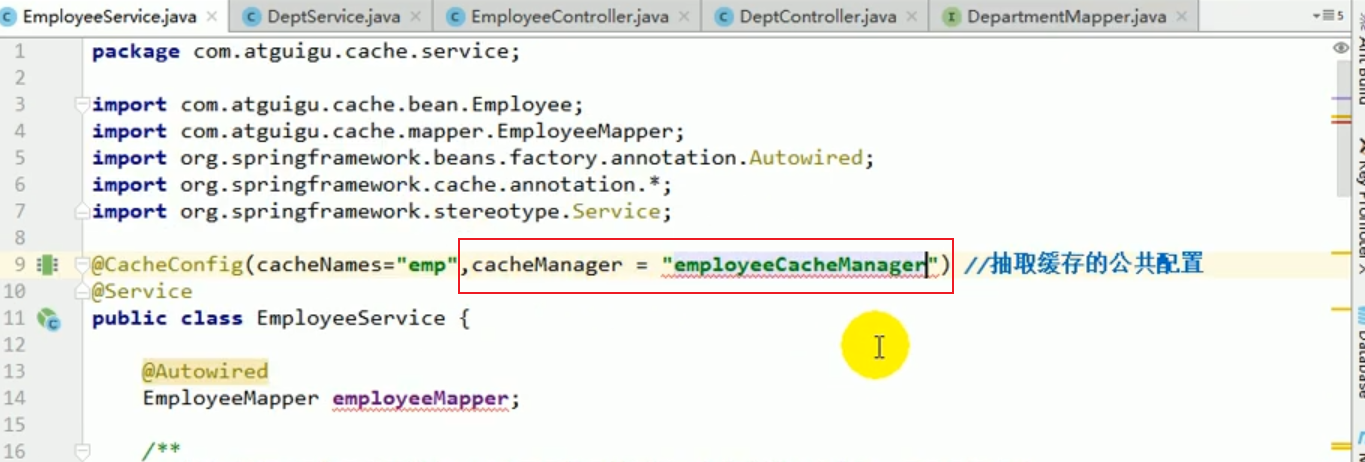
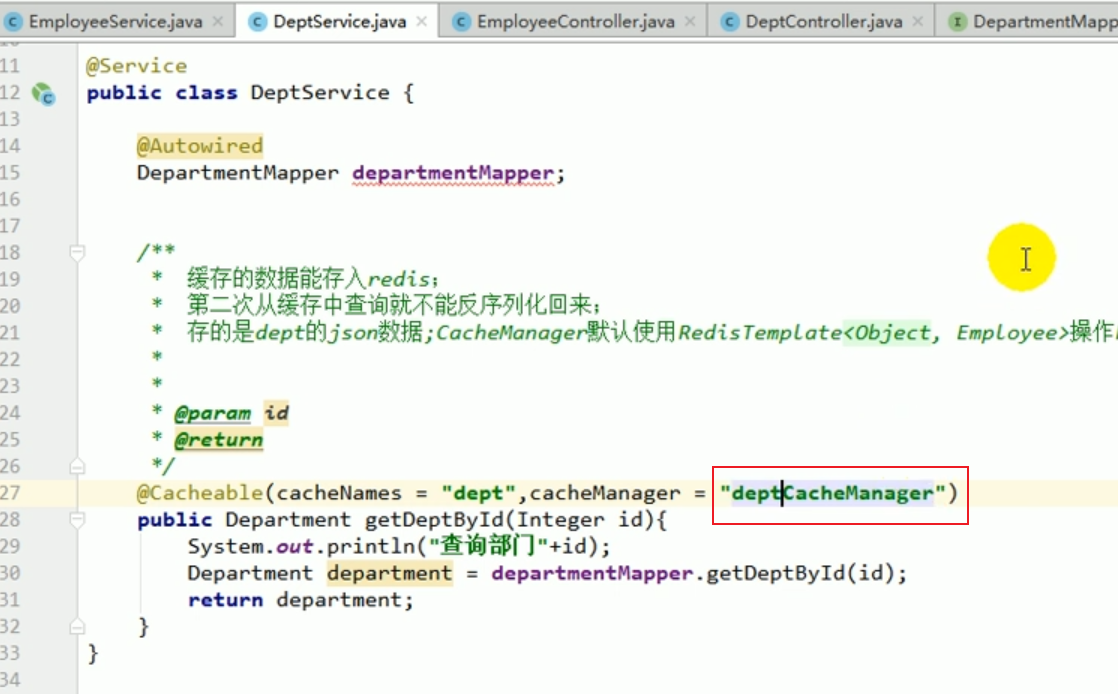
Then we restart the project, and the result is an error:
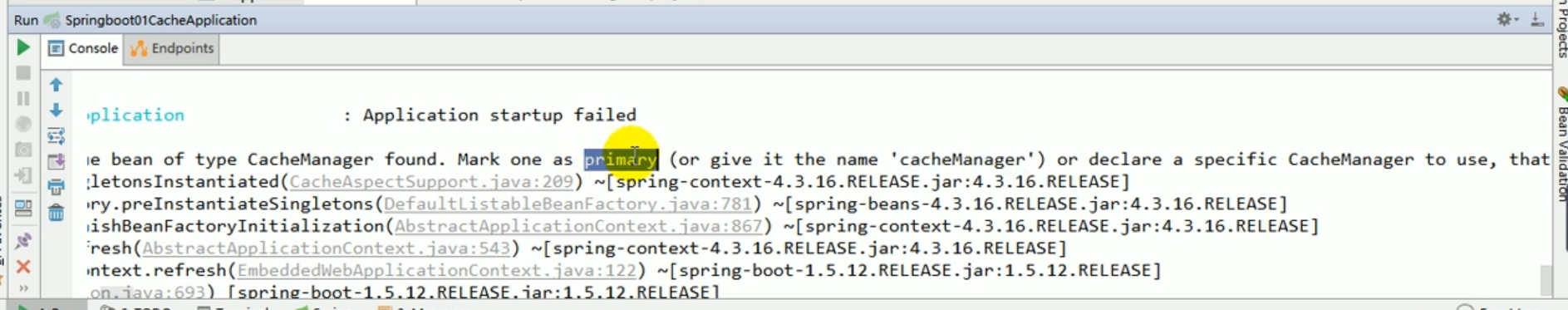
If , if we have multiple cacheManagers, we must use a certain cacheManager as our default configured cache manager.
For example, we can perform the following operations to fix the content of this startup error:
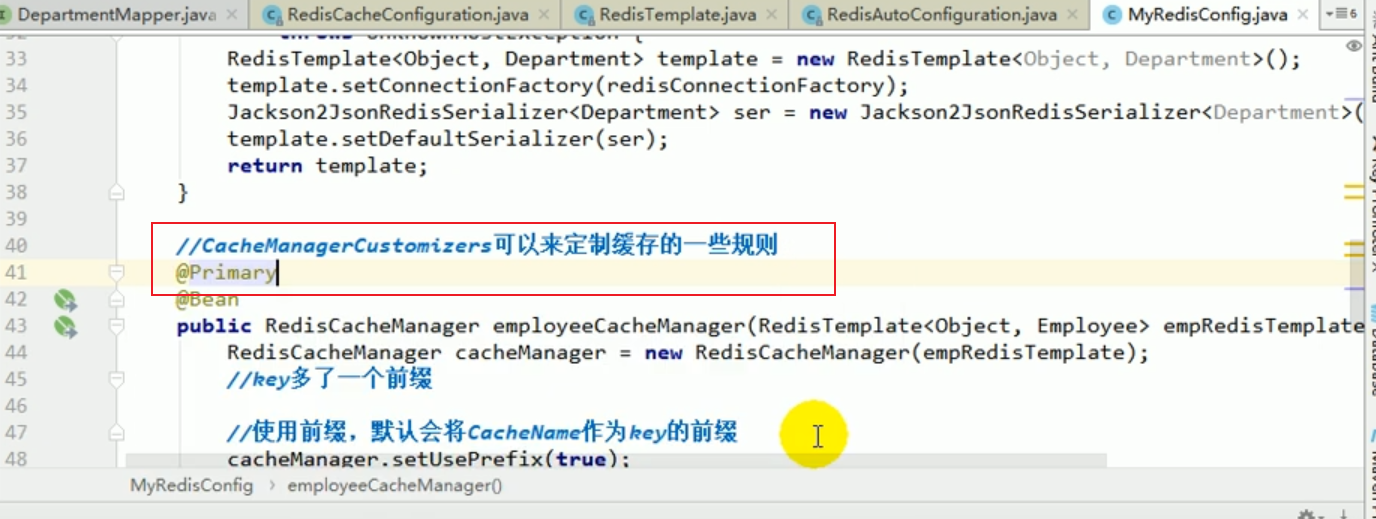
Restart for project testing
At this time, let’s see if we can deserialize and read our department information from redis normally and successfully when we perform the second department query?
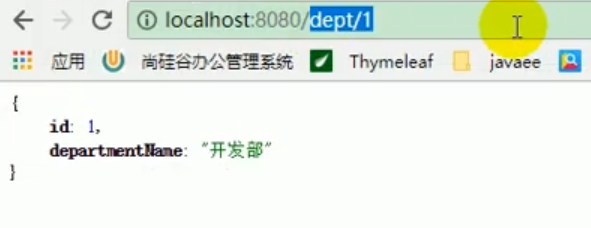
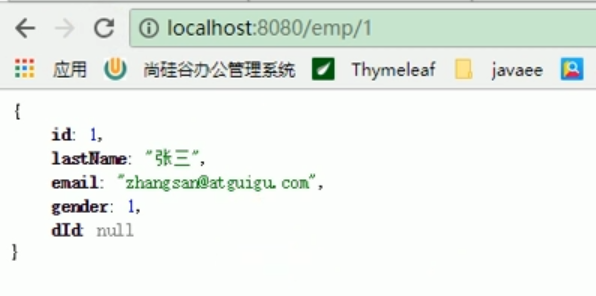
At this time, we discovered that whether it is an employee or a department, we can successfully deserialize and query it from redis .
This is perfect.
Coding method to operate the cache
What we said earlier is all using annotations to place data in the cache.
However, during development, we often encounter such situations.
That is, when our development reaches a certain stage, we need to put some data into the cache.
We need to use coding to operate the cache.
For example, after we query the department information, we want to put this information into redis.
We can inject the department’s cacheManager.
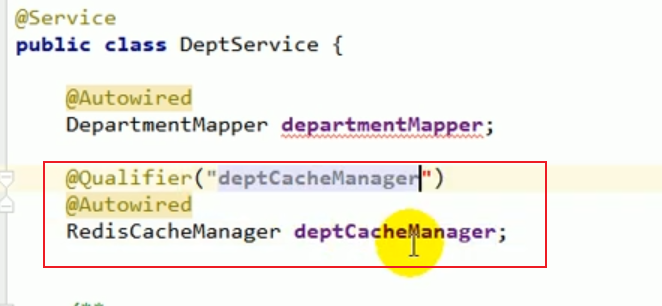
Then during the coding process, we can obtain the cache by operating this cacheManager,
Then, we can operate the cache component to increase the data. Delete, modify and check.
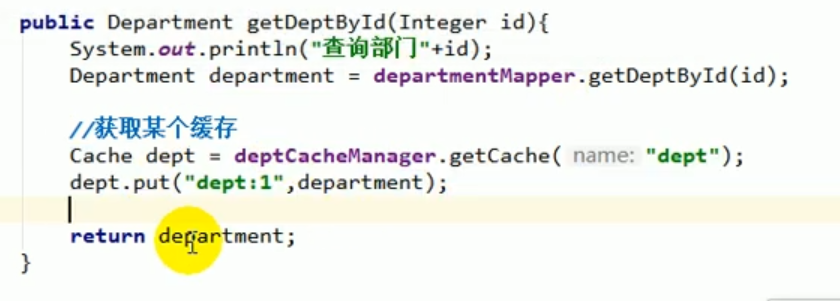
We tested the above code and started the project, and found that it was ok and successfully put data into redis:
The above is the detailed content of Springboot cache redis integration method. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1376
1376
 52
52
 How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
Redis cluster mode deploys Redis instances to multiple servers through sharding, improving scalability and availability. The construction steps are as follows: Create odd Redis instances with different ports; Create 3 sentinel instances, monitor Redis instances and failover; configure sentinel configuration files, add monitoring Redis instance information and failover settings; configure Redis instance configuration files, enable cluster mode and specify the cluster information file path; create nodes.conf file, containing information of each Redis instance; start the cluster, execute the create command to create a cluster and specify the number of replicas; log in to the cluster to execute the CLUSTER INFO command to verify the cluster status; make
 How to implement the underlying redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:21 PM
How to implement the underlying redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:21 PM
Redis uses hash tables to store data and supports data structures such as strings, lists, hash tables, collections and ordered collections. Redis persists data through snapshots (RDB) and append write-only (AOF) mechanisms. Redis uses master-slave replication to improve data availability. Redis uses a single-threaded event loop to handle connections and commands to ensure data atomicity and consistency. Redis sets the expiration time for the key and uses the lazy delete mechanism to delete the expiration key.
 How to view all keys in redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:15 PM
How to view all keys in redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:15 PM
To view all keys in Redis, there are three ways: use the KEYS command to return all keys that match the specified pattern; use the SCAN command to iterate over the keys and return a set of keys; use the INFO command to get the total number of keys.
 How to view the version number of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 05:57 PM
How to view the version number of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 05:57 PM
To view the Redis version number, you can use the following three methods: (1) enter the INFO command, (2) start the server with the --version option, and (3) view the configuration file.
 What to do if redis-server can't be found
Apr 10, 2025 pm 06:54 PM
What to do if redis-server can't be found
Apr 10, 2025 pm 06:54 PM
Steps to solve the problem that redis-server cannot find: Check the installation to make sure Redis is installed correctly; set the environment variables REDIS_HOST and REDIS_PORT; start the Redis server redis-server; check whether the server is running redis-cli ping.
 How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
Using the Redis directive requires the following steps: Open the Redis client. Enter the command (verb key value). Provides the required parameters (varies from instruction to instruction). Press Enter to execute the command. Redis returns a response indicating the result of the operation (usually OK or -ERR).
 How to use redis zset
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:27 PM
How to use redis zset
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:27 PM
Redis Ordered Sets (ZSets) are used to store ordered elements and sort by associated scores. The steps to use ZSet include: 1. Create a ZSet; 2. Add a member; 3. Get a member score; 4. Get a ranking; 5. Get a member in the ranking range; 6. Delete a member; 7. Get the number of elements; 8. Get the number of members in the score range.
 How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
The best way to understand Redis source code is to go step by step: get familiar with the basics of Redis. Select a specific module or function as the starting point. Start with the entry point of the module or function and view the code line by line. View the code through the function call chain. Be familiar with the underlying data structures used by Redis. Identify the algorithm used by Redis.




