
The data in the mysql database is stored on the disk in the form of files. By default, it is placed under /mysql/data (can be viewed through the datadir in my.cnf). One table mainly corresponds to three One file is frm to store the table structure, one is myd to store the table data, and the other is myi to store the table index. If the amount of data in a table is too large, then myd and myi will become very large, and searching for data will become very slow. At this time, we can use the partition function of mysql to physically correspond to this table. The three files are divided into many small blocks. In this way, when we search for a piece of data, we don’t have to search all of them. We only need to know which block the data is in, and then search in that block. When a table has a large amount of data, it may be necessary to spread the data across multiple disks to prevent one disk from being able to hold all the data.
Table partitioning is to split a table in the database into multiple smaller and easier-to-manage parts according to specific rules. Logically, there is only one table, but the bottom layer is composed of multiple physical partitions.
Table partitioning: refers to decomposing a table into multiple different tables through certain rules. For example, user order records are divided into multiple tables based on time. The difference between partitioning and table subdivision is that logically, partitioning is just one table, while table subdivision breaks one table into multiple tables.
(1). Compared with a single disk or file system partition, more data can be stored.
Generally, data that has no retention value can be easily purged by deleting the partitions associated with it. Sometimes, in order to easily add new data, you can create a new partition to specifically store these new data.
(3). Some queries can be greatly optimized. This is mainly because the data that satisfies a given WHERE statement can only be stored in one or more partitions, so that there is no need to search when searching. other remaining partitions. Because partitioning can be modified after the partitioned table is created, you can reorganize the data to improve the efficiency of commonly used queries if you have not done so when you first configure the partitioning scheme.
When queries involve aggregate functions such as SUM() and COUNT(), they can be easily processed in parallel. A simple example of such a query is "SELECT salesperson_id, COUNT (orders) as order_total FROM sales GROUP BY salesperson_id;". A "parallel" query means that the query can be executed on each partition simultaneously, and the final result simply aggregates the results from all partitions.
(5). Obtain greater query throughput by dispersing data queries across multiple disks.
(1). A table can only have a maximum of 1024 partitions.
In MySQL5.1, partition expressions can only be integers, or expressions that can return integers. Support for non-integer expression partitioning is provided in MySQL 5.5.
If a primary key or unique index column is included in the partition field, all primary key columns and unique index columns must be included. Either the partition field does not include the primary key and index columns, or it includes all primary key and index columns.
(4). Foreign key constraints cannot be used in partitioned tables.
(5) MySQL partitioning applies to all data and indexes in a table. You cannot partition table data but not indexes, you cannot partition indexes but not tables, and you cannot partition tables only. part of the data partition.
mysql> show variables like '%partition%'; +-------------------+-------+ | Variable_name | Value | +-------------------+-------+ | have_partitioning | YES | +-------------------+-------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
The value of have_partintioning is YES, indicating that partitioning is supported.
(1), RANGE partitioning: Allocate multiple rows to partitions based on column values belonging to a given continuous interval.
(2) LIST partitioning: Similar to partitioning by RANGE, the difference is that LIST partitioning is selected based on the column value matching a certain value in a discrete value set.
(3), HASH partition: The partition selected based on the return value of a user-defined expression, which is calculated using the column values of the rows to be inserted into the table. Any valid MySQL expression that produces a non-negative integer value can be included in this function.
(4) KEY partitioning: similar to HASH partitioning, the difference is that KEY partitioning only supports calculation of one or more columns, and the MySQL server provides its own hash function. There must be one or more columns containing integer values.
Note: In MySQL5.1 version, RANGE, LIST, and HASH partitions require that the partition key must be of type INT, or return INT type through expressions. When performing KEY partitioning, in addition to BLOB and TEXT type columns, other types of columns can also be used as partition keys.
Partition based on range. The range should be continuous but not overlapping. Use the PARTITION BY RANGE, VALUES LESS THAN keyword. If you do not use the COLUMNS keyword, the RANGE brackets must be an integer field name or a function that returns a definite integer.
drop table if exists employees;
create table employees(
id int not null,
fname varchar(30),
lname varchar(30),
hired date not null default '1970-01-01',
separated date not null default '9999-12-31',
job_code int not null default 0,
store_id int not null default 0
)engine=myisam default charset=utf8
partition by range(store_id)(
partition p0 values less than (6),
partition p1 values less than (11),
partition p2 values less than (16),
partition p3 values less than (21)
);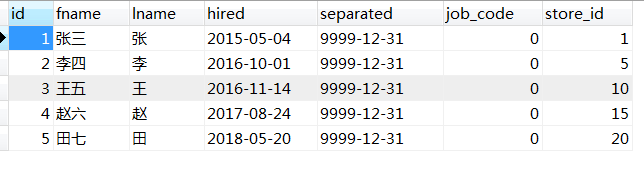
按照这种分区方案,在商店1到5工作的雇员相对应的所有行被保存在分区P0中,商店6到10的雇员保存在P1中,依次类推。注意,每个分区都是按顺序进行定义,从最低到最高。这是PARTITION BY RANGE 语法的要求。
对于包含数据(6,'亢八','亢','2018-06-24',13)的一个新行,可以很容易地确定它将插入到p2分区中。
insert into employees (id,fname,lname,hired,store_id) values(6,'亢八','亢','2018-06-24',13);
但是如果增加了一个编号为第21的商店(7,'周九','周','2018-07-24',21),将会发生什么呢?在这种方案下,由于没有规则把store_id大于20的商店包含在内,服务器将不知道把该行保存在何处,将会导致错误。
insert into employees (id,fname,lname,hired,store_id) values(7,'周九','周','2018-07-24',21); ERROR 1526 (HY000): Table has no partition for value 21
要避免这种错误,可以通过在CREATE TABLE语句中使用一个“catchall” VALUES LESS THAN子句,该子句提供给所有大于明确指定的最高值的值:
create table employees(
id int not null,
fname varchar(30),
lname varchar(30),
hired date not null default '1970-01-01',
separated date not null default '9999-12-31',
job_code int not null default 0,
store_id int not null default 0
)engine=myisam default charset=utf8
partition by range(store_id)(
partition p0 values less than (6),
partition p1 values less than (11),
partition p2 values less than (16),
partition p3 values less than (21),
partition p4 values less than MAXVALUE
);drop table if exists quarterly_report_status; create table quarterly_report_status( report_id int not null, report_status varchar(20) not null, report_updated timestamp not null default current_timestamp on update current_timestamp ) partition by range(unix_timestamp(report_updated))( partition p0 values less than (unix_timestamp('2008-01-01 00:00:00')), partition p1 values less than (unix_timestamp('2008-04-01 00:00:00')), partition p2 values less than (unix_timestamp('2008-07-01 00:00:00')), partition p3 values less than (unix_timestamp('2008-10-01 00:00:00')), partition p4 values less than (unix_timestamp('2009-01-01 00:00:00')), partition p5 values less than (unix_timestamp('2009-04-01 00:00:00')), partition p6 values less than (unix_timestamp('2009-07-01 00:00:00')), partition p7 values less than (unix_timestamp('2009-10-01 00:00:00')), partition p8 values less than (unix_timestamp('2010-01-01 00:00:00')), partition p9 values less than maxvalue );
添加COLUMNS关键字可定义非integer范围及多列范围,不过需要注意COLUMNS括号内只能是列名,不支持函数;多列范围时,多列范围必须呈递增趋势:
drop table if exists member; create table member( firstname varchar(25) not null, lastname varchar(25) not null, username varchar(16) not null, email varchar(35), joined date not null ) partition by range columns(joined)( partition p0 values less than ('1960-01-01'), partition p1 values less than ('1970-01-01'), partition p2 values less than ('1980-01-01'), partition p3 values less than ('1990-01-01'), partition p4 values less than maxvalue )
drop table if exists rc3; create table rc3( a int, b int ) partition by range columns(a,b)( partition p0 values less than (0,10), partition p1 values less than (10,20), partition p2 values less than (20,30), partition p3 values less than (30,40), partition p4 values less than (40,50), partition p5 values less than (maxvalue,maxvalue) )
drop table if exists staff; create table staff( id int not null, fname varchar(30), lname varchar(30), hired date not null default '1970-01-01', separated date not null default '9999-12-31', job_code int not null default 0, store_id int not null default 0 )engine=myisam default charset=utf8 partition by range(year(separated))( partition p0 values less than (1991), partition p1 values less than (1996), partition p2 values less than (2001), partition p4 values less than MAXVALUE );
只需删除分区,就能清除“旧的”数据。如果你使用上面最近的那个例子给出的分区方案,你只需简单地使用”alter table staff drop partition p0;”来删除所有在1991年前就已经停止工作的雇员相对应的所有行。对于有大量行的表,这比运行一个如”delete from staff WHERE year(separated) <= 1990;”这样的一个DELETE查询要有效得多。
(2)、想要使用一个包含有日期或时间值,或包含有从一些其他级数开始增长的值的列。
(3)、经常运行直接依赖于用于分割表的列的查询。例如,当执行一个如”select count(*) from staff where year(separated) = 200 group by store_id;”这样的查询时,MySQL可以很迅速地确定只有分区p2需要扫描,这是因为余下的分区不可能包含有符合该WHERE子句的任何记录。
根据具体数值分区,每个分区数值不重叠,使用PARTITION BY LIST、VALUES IN关键字。在不使用COLUMNS关键字的情况下,与Range分区类似,List括号内必须是整数字段名或返回确定整数的函数。
类似于按RANGE分区,区别在于LIST分区是基于列值匹配一个离散值集合中的某个值来进行选择。
LIST分区通过使用“PARTITION BY LIST(expr)”来实现,其中“expr”是某列值或一个基于某个列值、并返回一个整数值的表达式,然后通过“VALUES IN (value_list)”的方式来定义每个分区,其中“value_list”是一个通过逗号分隔的整数列表。
假定有20个音像店,分布在4个有经销权的地区,如下表所示:
====================
地区 商店ID 号
北区 3, 5, 6, 9, 17
东区 1, 2, 10, 11, 19, 20
4, 12, 13, 14, 18是西区的编号
中心区 7, 8, 15, 16
drop table if exists staff; create table staff( id int not null, fname varchar(30), lname varchar(30), hired date not null default '1970-01-01', separated date not null default '9999-12-31', job_code int not null default 0, store_id int not null default 0 ) partition by list(store_id)( partition pNorth values in (3,5,6,9,17), partition pEast values in (1,2,10,11,19,20), partition pWest values in (4,12,13,14,18), partition pCentral values in (7,8,15,16) );
这使得在表中增加或删除指定地区的雇员记录变得容易起来。例如,假定西区的所有音像店都卖给了其他公司。那么与在西区音像店工作雇员相关的所有记录(行)可以使用查询“ALTER TABLE staff DROP PARTITION pWest;”来进行删除,它与具有同样作用的DELETE(删除)“DELETE FROM staff WHERE store_id IN (4,12,13,14,18);”比起来,要有效得多。
如果试图插入列值(或分区表达式的返回值)不在分区值列表中的一行时,那么“INSERT”查询将失败并报错。
当插入多条数据出错时,如果表的引擎支持事务(Innodb),则不会插入任何数据;如果不支持事务,则出错前的数据会插入,后面的不会执行。
与Range分区相同,添加COLUMNS关键字可支持非整数和多列。
Hash分区主要用来确保数据在预先确定数目的分区中平均分布,Hash括号内只能是整数列或返回确定整数的函数,实际上就是使用返回的整数对分区数取模。
要使用HASH分区来分割一个表,要在CREATE TABLE 语句上添加一个“PARTITION BY HASH (expr)”子句,其中“expr”是一个返回一个整数的表达式。它可以仅仅是字段类型为MySQL整型的一列的名字。此外,你很可能需要在后面再添加一个“PARTITIONS num”子句,其中num是一个非负的整数,它表示表将要被分割成分区的数量。
如果没有包括一个PARTITIONS子句,那么分区的数量将默认为1
drop table if exists staff; create table staff( id int not null, fname varchar(30), lname varchar(30), hired date not null default '1970-01-01', separated date not null default '9999-12-31', job_code int not null default 0, store_id int not null default 0 ) partition by hash(store_id) partitions 4;
drop table if exists staff; create table staff( id int not null, fname varchar(30), lname varchar(30), hired date not null default '1970-01-01', separated date not null default '9999-12-31', job_code int not null default 0, store_id int not null default 0 ) partition by hash(year(hired)) partitions 4;
Hash分区也存在与传统Hash分表一样的问题,可扩展性差。MySQL也提供了一个类似于一致Hash的分区方法-线性Hash分区,只需要在定义分区时添加LINEAR关键字。
drop table if exists staff; create table staff( id int not null, fname varchar(30), lname varchar(30), hired date not null default '1970-01-01', separated date not null default '9999-12-31', job_code int not null default 0, store_id int not null default 0 ) partition by linear hash(year(hired)) partitions 4;
线性哈希功能,它与常规哈希的区别在于,线性哈希功能使用的一个线性的2的幂(powers-of-two)运算法则,而常规哈希使用的是求哈希函数值的模数。
Key分区与Hash分区很相似,只是Hash函数不同,定义时把Hash关键字替换成Key即可,同样Key分区也有对应与线性Hash的线性Key分区方法。
drop table if exists staff; create table staff( id int not null, fname varchar(30), lname varchar(30), hired date not null default '1970-01-01', separated date not null default '9999-12-31', job_code int not null default 0, store_id int not null default 0 ) partition by key(store_id) partitions 4;
在KEY分区中使用关键字LINEAR和在HASH分区中使用具有同样的作用,分区的编号是通过2的幂(powers-of-two)算法得到,而不是通过模数算法。
另外,当表存在主键或唯一索引时可省略Key括号内的列名,Mysql将按照主键-唯一索引的顺序选择,当找不到唯一索引时报错。
The above is the detailed content of What are the four partitioning methods of mysql table. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




