Example analysis of Redis timeout troubleshooting
During our work a few days ago, we suddenly received an alert that our Redis had crashed, and many people were discussing a certain Redis connection timeout. I thought there was a big problem at first, but who knew it would recover after a while. At that time, I logged into the server and checked the monitoring. Take a look at QPS for the first time:
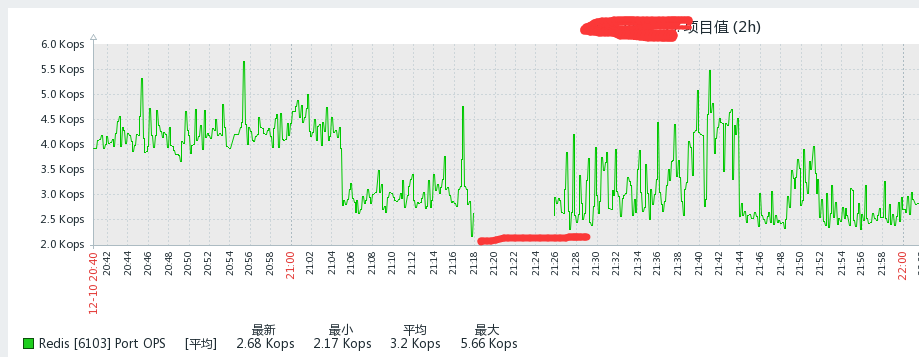
You can see that the QPS is not high, but why did the data not be obtained for a period of time? Then continue to look at the cpu usage of Redis:
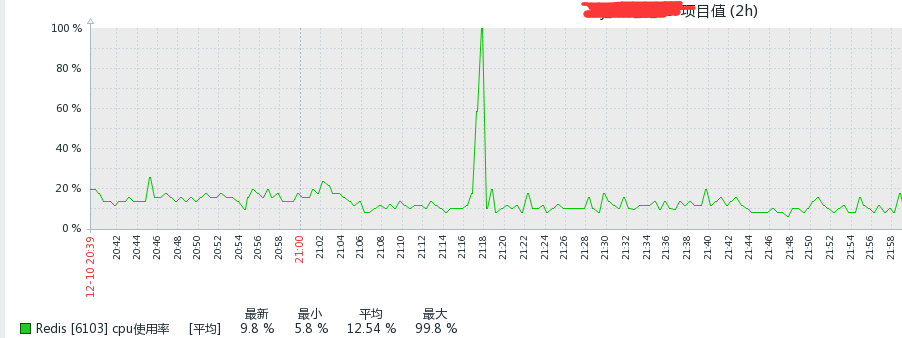
You can see that the cpu is saturated, which can also explain why the graph is broken, because redis is single-threaded, and after using 100% of the cpu, it cannot process other commands, and zabbix cannot execute info. The command is taken from qps. So we already know that the problem is caused by CPU saturation, so what is the reason? Then continue to check whether there are any slow logs during the period of high CPU usage:
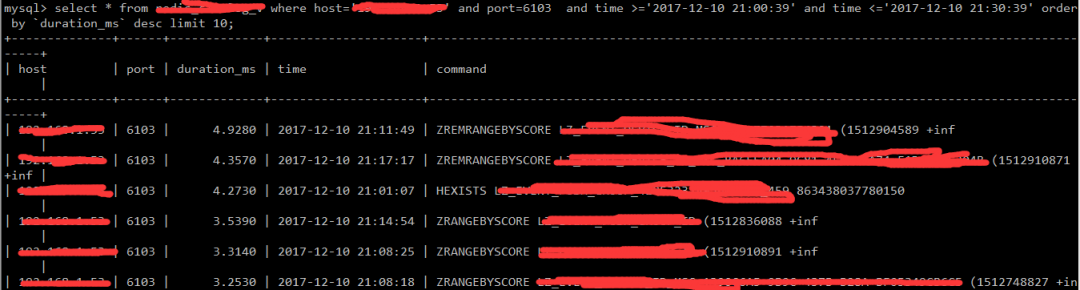
This does not appear to be the culprit of high CPU usage, so it is difficult to troubleshoot. This example is a master node and a slave node. Then let me take a look at the cpu usage of the slave library:
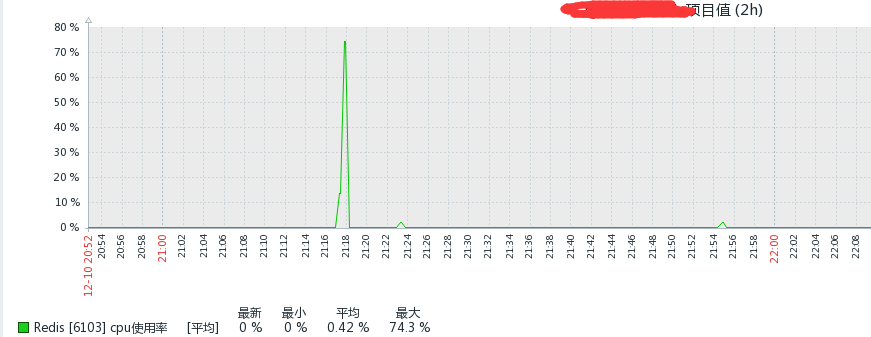
Damn it, what’s going on? How come the CPU that is not used by the slave library is also used at 74%? Isn't this scientific? Whatever, check if there are any slow logs from the slave library:
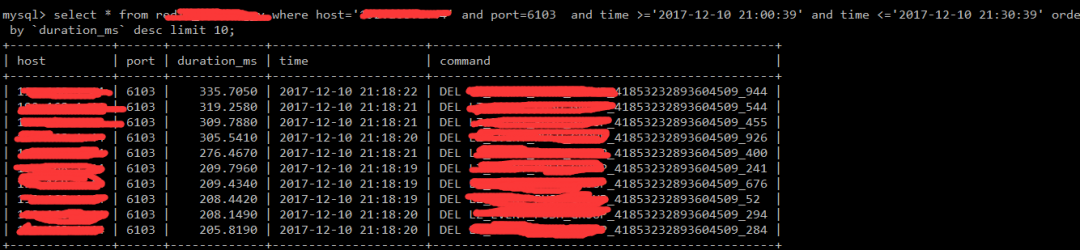
Damn it, what’s going on? No one is using the slave library. Check if it is read-only:
127.0.0.1:6103> CONFIG GET "slave-read-only" 1) "slave-read-only" 2) "yes" 127.0.0.1:6103>
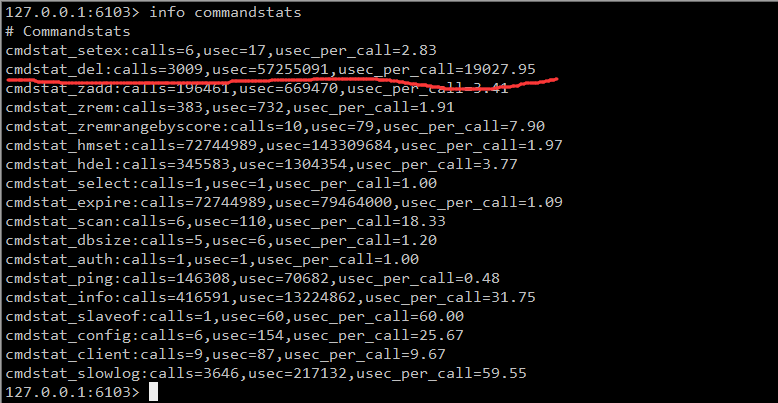
It seems to be read-only, which confused me. Finally, it suddenly occurred to me that the main library has a big key that has expired at this point, and the slow operation of the expired key in the main library will not record slow logs. The key expiration of the slave library is deleted by the main library initiating a DEL instruction. At this time, the slave library will record the slow log. From the slow log above, you can see that the maximum DEL operation is 335ms. No wonder there are application connection timeouts.
Use the command info commandstats again to see:
The above is the detailed content of Example analysis of Redis timeout troubleshooting. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
Redis cluster mode deploys Redis instances to multiple servers through sharding, improving scalability and availability. The construction steps are as follows: Create odd Redis instances with different ports; Create 3 sentinel instances, monitor Redis instances and failover; configure sentinel configuration files, add monitoring Redis instance information and failover settings; configure Redis instance configuration files, enable cluster mode and specify the cluster information file path; create nodes.conf file, containing information of each Redis instance; start the cluster, execute the create command to create a cluster and specify the number of replicas; log in to the cluster to execute the CLUSTER INFO command to verify the cluster status; make
 How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear Redis data: Use the FLUSHALL command to clear all key values. Use the FLUSHDB command to clear the key value of the currently selected database. Use SELECT to switch databases, and then use FLUSHDB to clear multiple databases. Use the DEL command to delete a specific key. Use the redis-cli tool to clear the data.
 How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
To read a queue from Redis, you need to get the queue name, read the elements using the LPOP command, and process the empty queue. The specific steps are as follows: Get the queue name: name it with the prefix of "queue:" such as "queue:my-queue". Use the LPOP command: Eject the element from the head of the queue and return its value, such as LPOP queue:my-queue. Processing empty queues: If the queue is empty, LPOP returns nil, and you can check whether the queue exists before reading the element.
 How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
Using the Redis directive requires the following steps: Open the Redis client. Enter the command (verb key value). Provides the required parameters (varies from instruction to instruction). Press Enter to execute the command. Redis returns a response indicating the result of the operation (usually OK or -ERR).
 How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
Using Redis to lock operations requires obtaining the lock through the SETNX command, and then using the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time. The specific steps are: (1) Use the SETNX command to try to set a key-value pair; (2) Use the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time for the lock; (3) Use the DEL command to delete the lock when the lock is no longer needed.
 How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
The best way to understand Redis source code is to go step by step: get familiar with the basics of Redis. Select a specific module or function as the starting point. Start with the entry point of the module or function and view the code line by line. View the code through the function call chain. Be familiar with the underlying data structures used by Redis. Identify the algorithm used by Redis.
 How to make message middleware for redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:51 PM
How to make message middleware for redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:51 PM
Redis, as a message middleware, supports production-consumption models, can persist messages and ensure reliable delivery. Using Redis as the message middleware enables low latency, reliable and scalable messaging.
 How to start the server with redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:12 PM
How to start the server with redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:12 PM
The steps to start a Redis server include: Install Redis according to the operating system. Start the Redis service via redis-server (Linux/macOS) or redis-server.exe (Windows). Use the redis-cli ping (Linux/macOS) or redis-cli.exe ping (Windows) command to check the service status. Use a Redis client, such as redis-cli, Python, or Node.js, to access the server.




