Redis is written in ANSI C language and is an open source Key-Value database that can operate in memory and supports persistence. It has rich data structures, transaction functions, and ensures the atomicity of commands. In-memory database reads and writes are very fast, reaching a rate of 10w/s, so they are usually used in application scenarios such as rapid data changes, real-time communication, and caching. But in-memory databases usually have to consider the memory size of the machine.
Redis provides 16 logical databases (db0-db15). Each logical database is independent of each other. If not specified, the db0 database is used by default. When connecting in Python, you can select the second database by specifying the database, for example, using the command select 2.
String-string
List-list
Hash-Hash
Set-set
ZSet-ordered set
Bitmap-Bitmap
In python we use the redis-py library to operate the Redis database, which will be highlighted below.
Prerequisite: Redis database needs to be installed. If not installed, click here
pip3 install redis
First method: Normal
import redis redis_conn = redis.Redis(host='127.0.0.1', port= 6379, password= 'your pw', db= 0)
Second way: connection pool
import redis redis_pool = redis.ConnectionPool(host='127.0.0.1', port= 6379, password= 'your pw', db= 0) redis_conn = redis.Redis(connection_pool= redis_pool)
The character return value types in redis are all bytes type
In redis, a key corresponds to a value
1.String set sets a single key value
set(name, value, ex=None, px=None, nx =False, xx=False)
ex: Expiration time (seconds), redis will automatically delete it after the time is up
px: Expiration time (milliseconds), redis will automatically delete it after the time is up. Just choose one of ex and px
nx: If set to True, the current set operation will only be executed if name does not exist
xx: If set to True, the current set operation will be executed only if name exists
redis_conn.set('name_2', 'Zarten_2')
2.String get gets a single value
v = redis_conn.get('name_1') print(v)
3.String mset sets multiple key values
mset(*args, **kwargs)
redis_conn.mset(name_1= 'Zarten_1', name_2= 'Zarten_2')
or
name_dict = {
'name_4' : 'Zarten_4',
'name_5' : 'Zarten_5'
}
redis_conn.mset(name_dict)4.String mget gets multiple values
mget(keys, *args)
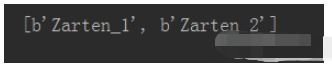
m = redis_conn.mget('name_1', 'name_2') #m = redis_conn.mget(['name_1', 'name_2']) 也行 print(m)
##5.String getset gives existing Set a new value for the key and return the original value
getset(name, value)When the given key does not exist, its new value will be set, but the return value For Nonev = redis_conn.getset('name_1', 'hi')
6.String setrange Modifies the value of a key according to the index
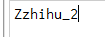
setrange(name, offset, value)Return value is: the modified string lengthlength = redis_conn.setrange('name_2', 1, 'zhihu') print(length)
7.String getrange obtains part of the value of a key based on the index
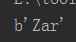
If the given key does not exist, a null value b'' is returned getrange(key, start, end)v = redis_conn.getrange('name_4', 0, 2)
strlen(name)
When the given key does not exist, the return value is 0
length = redis_conn.strlen('name_2')
Similarly: Decrement, decr(name, amount=1)
The value corresponding to the given key must be an integer or a string value. Otherwise, an error will be reported. The default auto-increment range is 1
incr(name, amount=1)
The return value is: modified value, int type
redis_conn.set('num_2', 2) #redis_conn.set('num_2', '2') 都行 v = redis_conn.incr('num_2')
incrbyfloat(name, amount=1.0)
The return value is: floating point type float
v = redis_conn.incrbyfloat('num_2')
append(key, value)
If the given key does not exist, set the new value
The return value is the modified value The length of the string
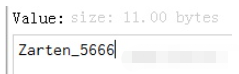
length = redis_conn.append('name_5', '666')
The result is:
 List list
List list
lpush(name, *values)
When there are multiple value values, from left to Add to the left of the list from right to left, the type can be different
When the given key does not exist, create a new list
Return value: the size of the list
v = redis_conn.lpush('Zarten', 1,2,3,4,5) #v = redis_conn.lpush('Zarten', 6)
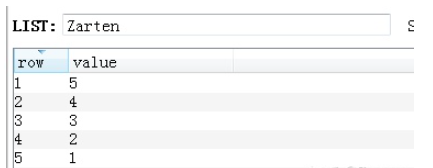
lpushx(name, value)
Only when the key exists , was added. If the key does not exist, it will not be added and the list will not be created
返回值为:列表大小
v = redis_conn.lpushx('Zarten_1', 'hehe')
14.List llen 获取所给键的列表大小
llen(name)
v = redis_conn.llen('Zarten')
15.List linsert 在列表中间插入新值
linsert(name, where, refvalue, value)
name:键名
where:位置,前面(BEFORE)或后面(AFTER)
refvalue:指定哪个值的前后插入
value:插入的新值
返回值:插入后列表的长度,若返回-1,则refvalue不存在
插入前的数据:
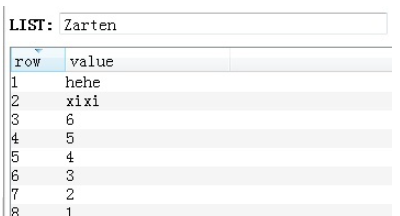
v = redis_conn.linsert('Zarten', 'AFTER', 6, 'b')
插入后的数据:
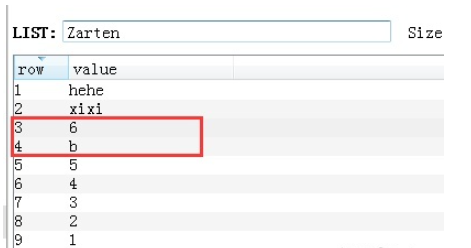
16.List lset 列表中通过索引赋值
lset(name, index, value)
返回值:成功 True 否则 False
v = redis_conn.lset('Zarten', 2, 'cc')
17.List lindex 通过索引获取列表值
lindex(name, index)
v = redis_conn.lindex('Zarten', 2)
18.List lrange 列表中获取一段数据
lrange(name, start, end)
返回值:List类型的一段数据
v = redis_conn.lrange('Zarten', 2, 5)
19.List lpop 删除左边的第一个值 rpop(右边)
lpop(name)
返回值:被删除元素的值
v = redis_conn.rpop('Zarten')
20.List lrem 删除列表中N个相同的值
lrem(name, value, num=0)
name:键名
value:需删除的值
num:删除的个数 整数表示从左往右 负数表示从右往左 例如:2 -2
返回值:返回删除的个数
v = redis_conn.lrem('Zarten', 'hehe', -2)
21.List ltrim 删除列表中范围之外的所有值
ltrim(name, start, end)
返回值:成功 True
v = redis_conn.ltrim('Zarten', 5, 10)
22.List blpop 删除并返回列表最左边的值 brpop(最右边)
blpop(keys, timeout=0)
keys:给定的键
timeout:等待超时时间,默认为0,表示一直等待
返回值:tuple类型 形如: (键名, 删除的值) (b'Zarten', b'hehe')
v = redis_conn.blpop('Zarten')
23.List rpoplpush 一个列表中最右边值取出后添加到另一个列表的最左边 brpoplpush阻塞版本
rpoplpush(src, dst)
brpoplpush(src, dst, timeout=0)为rpoplpush的阻塞版本,timeout为0时,永远阻塞
返回值:取出的元素值
v = redis_conn.rpoplpush('Zarten', 'Zhihu')
内部存储为各个键值对
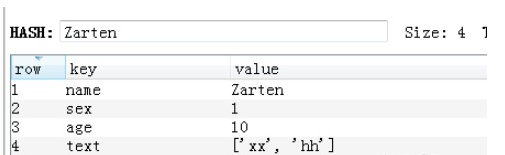
24.Hash hset 哈希中添加一个键值对
hset(name, key, value)
key存在,则修改,否则添加
返回值:返回添加成功的个数 int
v = redis_conn.hset('Zarten', 'age', 10)
25.Hash hmset 设置哈希中的多个键值对
hmset(name, mapping)
mapping:dict 类型
返回值:成功 True
v = redis_conn.hmset('Zarten', {'sex':1, 'tel':'123'})26.Hash hmget 获取哈希中多个键值对
hmget(name, keys, *args)
返回值:值的列表 list 形如: [b'1', b'123']
v = redis_conn.hmget('Zarten', ['sex', 'tel']) #v = redis_conn.hmget('Zarten', 'sex', 'tel') 也ok
27.Hash hget 获取指定key的值
hget(name, key)
v = redis_conn.hget('Zarten', 'age')
28.Hash hgetall 获取哈希中所有的键值对
hgetall(name)
返回值:dict类型
v = redis_conn.hgetall('Zarten')
29.Hash hlen 获取哈希中键值对的个数
hlen(name)
v = redis_conn.hlen('Zarten')
30.Hash hkeys 获取哈希中所有的键key
hkeys(name)
返回值:list类型
v = redis_conn.hkeys('Zarten')
31.Hash hvals 获取哈希中所有的值value
hvals(name)
返回值:list类型
v = redis_conn.hvals('Zarten')
32.Hash hexists 检查哈希中是否有某个键key
hexists(name, key)
返回值:有 True ;否则 False
v = redis_conn.hexists('Zarten', 'b')
33.Hash hdel 删除哈希中键值对(key-value)
hdel(self, name, *keys)
返回值:int 删除的个数
v = redis_conn.hdel('Zarten', 'age')
34.Hash hincrby 自增哈希中key对应的value值(必须整数数值类型)
hincrby(name, key, amount=1)
若所给的key不存在则创建,amount默认增加1,可以为负数
返回值:int 增加后的数值
v = redis_conn.hincrby('Zarten', 'sex', -3)
35.Hash hincrbyfloat 自增浮点数 同上hincrby
hincrbyfloat(name, key, amount=1.0)
36.Hash expire 设置整个键的过期时间
expire(name, time)
time:秒,时间一到,立马自动删除
v = redis_conn.expire('Zarten', 10)
37.Hash hscan 增量迭代获取哈希中的数据
hscan(name, cursor=0, match=None, count=None)
name:redis的name
cursor:游标(基于游标分批取获取数据)
match:匹配指定key,默认None 表示所有的key
count:每次分片最少获取个数,默认None表示采用Redis的默认分片个数
返回值:tuple 类型 ;(扫描位置,所有dict数据)
v = redis_conn.hscan('Zarten')
38.Hash hscan_iter 返回hscan的生成器
hscan_iter(name, match=None, count=None)
参照上面函数hscan
v = redis_conn.hscan_iter('Zarten')
for i in v:
print(type(i), i)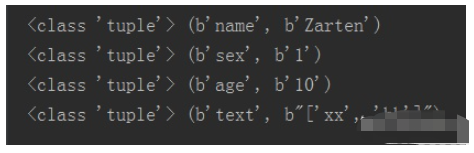
集合中的元素不重复,一般用于过滤元素
39.Set sadd 添加元素到集合中
sadd(name, *values)
若插入已有的元素,则自动不插入
v = redis_conn.sadd('Zarten', 'apple', 'a', 'b', 'c')
40.Set scard 返回集合中元素的个数
scard(name)
v = redis_conn.scard('Zarten')
41.Set smembers 获取集合中的所有元素
smembers(name)
返回值:set类型,形如: {b'a', b'apple', b'c', b'b'}
v = redis_conn.smembers('Zarten')
42.Set srandmember 随机获取一个或N个元素
srandmember(name, number=None)
name:键名
number:一个或N个,默认返回一个。若返回N个,则返回List类型
返回值:返回一个值或一个列表
v = redis_conn.srandmember('Zarten', 2)
43.Set sismember 判断某个值是否在集合中
sismember(name, value)
返回值:True 在 False 不在
v = redis_conn.sismember('Zarten', 'appl')
44.Set spop 随机删除并返回集合中的元素
spop(name)
v = redis_conn.spop('Zarten')
45.Set srem 删除集合中的一个或多个元素
srem(name, *values)
返回值:返回删除的个数 int
v = redis_conn.srem('Zarten', 'c', 'a')
46.Set smove 将一个集合中的值移动到另一个集合中
smove(src, dst, value)
若value不存在时,返回False
返回值:成功 True
v = redis_conn.smove('Zarten', 'Fruit', 'apple')
47.Set sdiff 返回在一个集合中但不在其他集合的所有元素(差集)
sdiff(keys, *args)
在keys集合中,不在其他集合中的元素
返回值:set类型 {b'2', b'4', b'3', b'1'}
v = redis_conn.sdiff('Zarten', 'Fruit')
48.Set sdiffstore 上面的sdiff的返回值(差集)保存在另一个集合中
sdiffstore(dest, keys, *args)
在keys集合中,不在其他集合中的元素保存在dest集合中
dest:新的集合,设置的新集合,旧集合会被覆盖
返回值:int 返回作用的个数
v = redis_conn.sdiffstore('Left', 'Zarten', 'Fruit')
49.Set sinter 返回一个集合与其他集合的交集
sinter(keys, *args)
返回值:set类型
v = redis_conn.sinter('Zarten', 'Fruit')
50.Set sinterstore 返回一个集合与其他集合的交集,并保存在另一个集合中
sinterstore(dest, keys, *args)
dest:另一个集合,设置新集合,旧集合元素会被覆盖
v = redis_conn.sinterstore('Left', 'Zarten', 'Fruit')
51.Set sunion 返回一个集合与其他集合的并集
sunion(keys, *args)
v = redis_conn.sunion('Zarten', 'Fruit')
52.Set sunionstore 返回一个集合与其他集合的并集,并保存在另一个集合中
sunionstore(dest, keys, *args)
dest:另一个集合,设置新集合,旧集合元素会被覆盖
返回值:新集合元素个数
v = redis_conn.sunionstore('Left', 'Zarten', 'Fruit')
有序集合比集合多了一个分数的字段,可对分数升序降序
53.Zset zadd 有序集合中添加元素
zadd(name, *args, **kwargs)
添加元素时需指定元素的分数
返回值:返回添加的个数
2种方式如下:
v = redis_conn.zadd('Zarten', 'a', 3, 'b', 4) #v = redis_conn.zadd('Zarten', c= 5, d= 6)
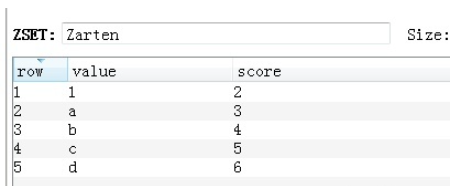
54.Zset zcard 返回有序集合中元素个数
zcard(name)
v = redis_conn.zcard('Zarten')
55.Zset zcount 返回有序集合中分数范围内的元素个数
zcount(name, min, max)
包含min max
返回值:个数 int
v = redis_conn.zcount('Zarten', 3, 5)
56.Zset zscore 返回有序集合中指定某个值的分数
zscore(name, value)
返回值:float 类型的分数;形如: -5.0
v = redis_conn.zscore('Zarten', 'zhi')
57.Zset zincrby 增加有序集合中某个值的分数
zincrby(name, value, amount=1)
value:若存在,则增加其amount分数;若不存在,则增加新值以及对应的分数
amount:增加的值,可以为负数
返回值:增加后的分数 float类型 ;形如: -5.0
v = redis_conn.zincrby('Zarten', 'zhi', -5)
58.Zset zrem 删除有序集合中的某个或多个值
zrem(name, *values)
返回值:返回删除的个数
v = redis_conn.zrem('Zarten', 'zhi', 'a')
59.Zset zremrangebyrank 删除有序集合元素根据排序范围
zremrangebyrank(name, min, max)
返回值:删除个数 int
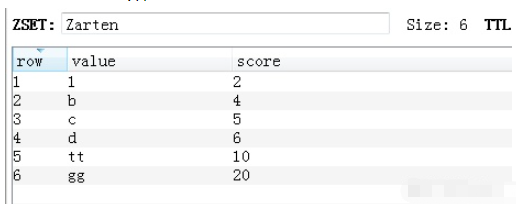
v = redis_conn.zremrangebyrank('Zarten', 1, 3)
删除后如下图:
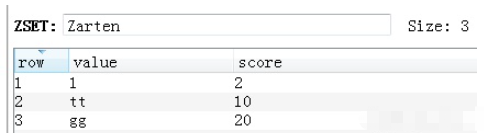
60.Zset zremrangebyscore 删除有序集合根据分数范围
zremrangebyscore(name, min, max)
返回值:删除个数 int
v = redis_conn.zremrangebyscore('Zarten', 8, 15)
61.Zset zrank 返回某个值在有序集合中的分数排名(从小到大) zrevrank(从大到小)
zrank(name, value)
返回值:value在name中的分数排名值,分数从小到大排名,从0开始
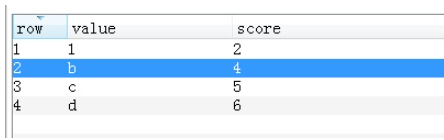
v = redis_conn.zrank('Zarten', 'b')
返回值如下图:
62.Zset zrange 返回有序集合分数排序的一段数据
zrange(name, start, end, desc=False, withscores=False, score_cast_func=float)
name:redis的name
start:有序集合索引起始位置(非分数)
end:有序集合索引结束位置(非分数)
desc:排序规则,默认按照分数从小到大排序
withscores:是否获取元素的分数,默认只获取元素的值
score_cast_func:对分数进行数据转换的函数
返回值:list类型 [(b'tt', 10.0), (b'd', 6.0), (b'c', 5.0)]
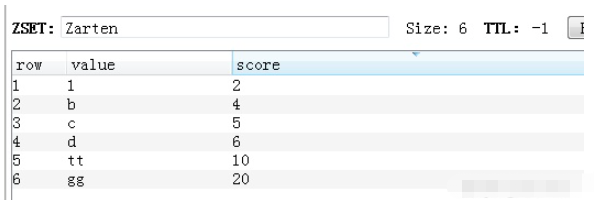
v = redis_conn.zrange('Zarten', 1, 3, True, True, score_cast_func=float)
结果如图:
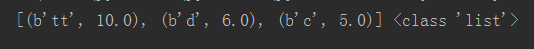
bitmap中存放二进制的位0和1,类似位数组。典型应用是基于redis的布隆过滤器。
属于String字符串数据结构,固bit 映射被限制在 512 MB 之内(2^32)
63.Bitmap setbit 设置位图的值
setbit(name, offset, value)
name:redis键名
offset:偏移量,大于等于0。当偏移伸展时,空白位置以0填充
value:二进制值 0或1
v = redis_conn.setbit('Zarten_2', 100, 1)
64.Bitmap getbit 返回位图指定偏移量的值
getbit(name, offset)
返回0或1
v = redis_conn.getbit('Zarten_2', 101)
65.Bitmap bitcount 返回位图中二进制为1的总个数
bitcount(key, start=None, end=None)
start end指定开始和结束的位,默认整个位图
v = redis_conn.bitcount('Zarten_2', 100, 1000)
全局函数对任何数据结构都适用
66.全局函数 delete 删除redis中一个或多个键的所有数据
delete(*names)
返回值:int 删除的个数
v = redis_conn.delete('name', 'name_1')
67.全局函数 exists 判断redis中是否存在某个键
exists(name)
返回值:存在True;反之False
v = redis_conn.exists('name')
68.全局函数 rename 重命名redis中键名
rename(src, dst)
返回值:成功True
v = redis_conn.rename('name_2', 'name_100')
69.全局函数 move 移动redis中某个键所有数据到某个db中
move(name, db)
返回值:成功True
v = redis_conn.move('name_100', 12)
70.全局函数 randomkey 随机获取redis中某个键名
randomkey()
返回值:形如: b'name_55'
v = redis_conn.randomkey()
71.全局函数 type 查看redis中某个键数据结构类型
type(name)
返回值:字符串(字节形式) 形如: b'hash'
none (key不存在)
string (字符串)
list (列表)
set (集合)
zset (有序集)
hash (哈希表)
v = redis_conn.type('name_4')
The above is the detailed content of How to use Python to operate Redis database. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




