
When querying data, if no sorting operation is used, by default SQL will arrange the query results in the order in which tuples are added.
To perform sorting operations in SQL, you can use the keyword ORDER BY.... After this keyword, you can add the keyword ASC (ascend) to indicate ascending order (from small to large), and DESC (descend) to indicate descending order (from large to small).
If ASC or DESC is not added after the ORDER BY... keyword to indicate ascending or descending order, SQL will default to ascending ASC order. As shown in the following code:
SELECT employee_id, last_name, salary FROM employees ORDER BY salary;
Query results:
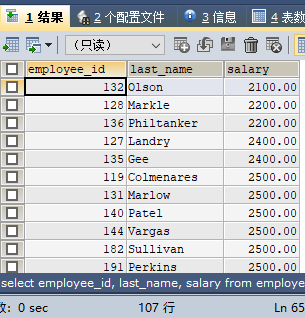
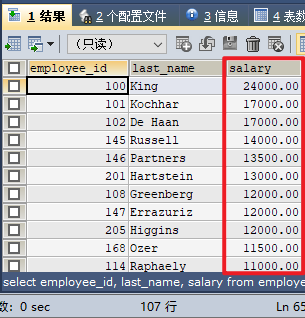
employees The employee's employee_id, last_name, salary and department_id information. And sort by salary from largest to smallest (descending order).
SELECT employee_id, last_name, salary FROM employees ORDER BY salary DESC;
annual_salary), or some field names are really too long, using short aliases can improve the efficiency of our programming. As shown in the following example:
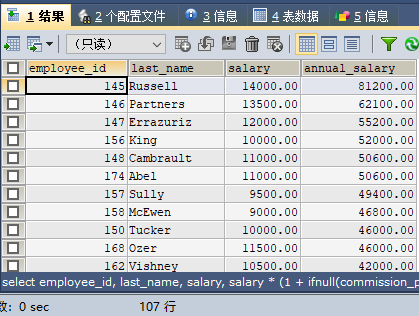
employee_id, last_name, and monthly salarysalary# of the employees in the employee table employees ## and annual salaryannual_salary information. And sorted by annual_salary from largest to smallest (descending order). <div class="code" style="position:relative; padding:0px; margin:0px;"><pre class='brush:php;toolbar:false;'>SELECT employee_id, last_name, salary,
salary * (1 + IFNULL(commission_pct, 0) * 12) AS "annual_salary"
FROM employees
ORDER BY annual_salary DESC;</pre><div class="contentsignin">Copy after login</div></div> Query results:
 [Note]
[Note]
Must be declared after FROM.
, not in WHERE. **If you use column aliases in WHERE, SQL will report an error. So why can’t column aliases in MySQL be used in WHERE? The reasons are as follows:
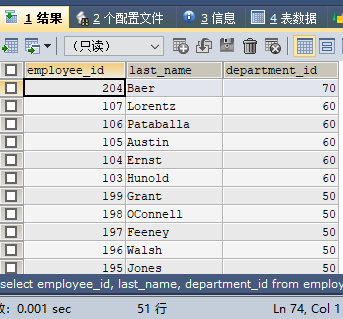
SELECT employee_id, last_name, department_id FROM employees WHERE department_id IN(50, 60, 70) ORDER BY department_id DESC;
 3. Second-level sorting
3. Second-level sorting
[Example 1] Query the employee ID
employee_id, name ## and so on. You can add a comma after The above is the detailed content of How to sort data in MySQL. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!last_name, of the employees in the employee table employees, Monthly salary salary and department ID department_id. And first sort by department ID department_id in descending order, and then sort by salary from large to small (descending order). SELECT employee_id, last_name, salary, department_id
FROM employees
ORDER BY department_id DESC, salary DESC;
 ORDER BY
ORDER BY




