How to use Python async module
Coroutines, also known as micro-threads, are a technology for context switching in user mode. In short, it is actually a thread to implement code blocks to switch between executions
Python's support for coroutines is implemented through generators.
In the generator, we can not only iterate through the for loop, but also continuously call the next() function to obtain the next value returned by the yield statement. Python's yield can not only be used to return values, but can also receive parameters passed by the caller.
1. What is a generator
The mechanism called generator in Python is calculated while looping. By giving an algorithm and then calculating the true value during the call.
When you need to get the value from the generator, you can use next(), but generally use a for loop to get it.
generator implementation generator, use () to represent
such as: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5], generator method:
data = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] (x * x for x in len(data))
Function definition In some scenarios with complex logic, it is not appropriate to use the first method, so there is a way to define a type function, such as:
def num(x):
while (x < 10):
print(x * x)
x += 1
g = num(1)
for item in g:
print(item)When yield appears in the function, it becomes generator
def num(x):
while (x < 10):
yield x * x # 返回结果,下次从这个地方继续?
x += 1
g = num(1) # 返回的是generator对象
for item in g:
print(item)becomes a generator function, which is executed every time next() is called. It returns when encountering a yield statement. When executed again, execution continues from the yield statement returned last time.
2. Use asyncio to implement asynchronous io
Asynchronous io is implemented through event loops and coroutine functions
The event loop continuously monitors internal tasks and executes them if they exist; tasks Divided into executable and executing; the event loop determines the processing tasks. If the task list is empty, the event terminates.
import asyncio # 生成或获取事件循环对象loop;类比Java的Netty,我理解为开启一个selector loop = asyncio.get_event_loop() # 将协程函数(任务)提交到事件循环的任务列表中,协程函数执行完成之后终止。 # run_until_complete 会检查协程函数的运行状态,并执行协程函数 loop.run_until_complete( func() )
test demo
import asyncio
import time
async def test():
print("io等待")
await asyncio.sleep(1)
return 'hello'
async def hello():
print("Hello world")
r = await test()
print("hello again")
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
tasks = [hello(), hello()]
loop.run_until_complete(asyncio.wait(tasks))
loop.close()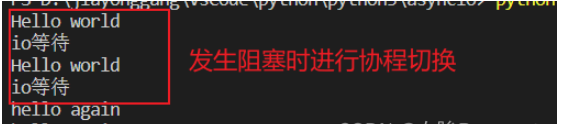
Coroutine function: a function modified by async def; compared to ordinary def, such as def func(), you can The value returned by the function is directly received; but for the coroutine function, a coroutine object is returned.
If you want to run the coroutine function, you need to hand this object to the event loop for processing.
# 测试协程
import asyncio
import time, datetime
# 异步函数不同于普通函数,调用普通函数会得到返回值
# 而调用异步函数会得到一个协程对象。我们需要将协程对象放到一个事件循环中才能达到与其他协程对象协作的效果
# 因为事件循环会负责处理子程 序切换的操作。
async def Print():
return "hello"
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
loop.run_until_complete(Print)await:
Usage: response = await Waitable object
Waitable object: Coroutine object, Future, Task object can be understood as IO waiting
response: The result of waiting await will suspend the current coroutine (task) when encountering an IO operation. When the current coroutine is suspended, the event loop can execute other coroutines (tasks). Note: Can wait If the object is a coroutine object, it becomes serial. If it is a Task object, the Task object runs concurrently. Multiple tasks can be added to the event loop list. You can use `asyncio.create_task()` to create a `Task` object, and the passed parameter is the coroutine object
import asyncio
import time, datetime
async def display(num):
pass
tasks = []
for num in range(10):
tasks.append(display(num)) # 生成任务列表
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
loop.run_until_complete(asyncio.wait(tasks))asnyc and await are new syntax, the old version is: @asyncio.coroutine and yield from
3. aiohttp
asyncio can implement single-threaded concurrent IO operations. If it is only used on the client side, it will not be very powerful. If asyncio is used on the server side, such as a web server, since HTTP connections are IO operations, single-threaded coroutine can be used to achieve high concurrency support for multiple users.
aiohttp is an HTTP framework based on asyncio.
You can send a request like requests get request
You can specify the parameters to be passed through the params parameter
async def fetch(session):
async with session.get("http://localhost:10056/test/") as response:
data = json.loads(await response.text())
print(data["data"])post request
Asynchronously execute two tasks
In a network request, a request is a session, and aiohttp uses ClientSession to manage the session
Use session.method to send a request
For the response information response, use status to get the response status code, and text() to get the response content; you can specify the encoding format in text(). Before waiting for the response result, you need to add the await keyword
async def init(num):
async with aiohttp.ClientSession() as session:
if num == 1:
time.sleep(5)
print("session begin", num)
async with session.post("http://localhost:10056/hello/", data=json.dumps({"data": "hello"})) as response:
print("client begin", num)
data = json.loads(await response.text())
print(data["data"])
print("session end", num)
print("other")
if __name__ == '__main__':
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
tasks = [init(1), init(2)]
loop.run_until_complete(asyncio.wait(tasks))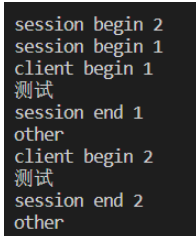
The above is the detailed content of How to use Python async module. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 The 2-Hour Python Plan: A Realistic Approach
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:04 AM
The 2-Hour Python Plan: A Realistic Approach
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:04 AM
You can learn basic programming concepts and skills of Python within 2 hours. 1. Learn variables and data types, 2. Master control flow (conditional statements and loops), 3. Understand the definition and use of functions, 4. Quickly get started with Python programming through simple examples and code snippets.
 Python: Exploring Its Primary Applications
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:41 AM
Python: Exploring Its Primary Applications
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:41 AM
Python is widely used in the fields of web development, data science, machine learning, automation and scripting. 1) In web development, Django and Flask frameworks simplify the development process. 2) In the fields of data science and machine learning, NumPy, Pandas, Scikit-learn and TensorFlow libraries provide strong support. 3) In terms of automation and scripting, Python is suitable for tasks such as automated testing and system management.
 How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
To read a queue from Redis, you need to get the queue name, read the elements using the LPOP command, and process the empty queue. The specific steps are as follows: Get the queue name: name it with the prefix of "queue:" such as "queue:my-queue". Use the LPOP command: Eject the element from the head of the queue and return its value, such as LPOP queue:my-queue. Processing empty queues: If the queue is empty, LPOP returns nil, and you can check whether the queue exists before reading the element.
 How to view server version of Redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 01:27 PM
How to view server version of Redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 01:27 PM
Question: How to view the Redis server version? Use the command line tool redis-cli --version to view the version of the connected server. Use the INFO server command to view the server's internal version and need to parse and return information. In a cluster environment, check the version consistency of each node and can be automatically checked using scripts. Use scripts to automate viewing versions, such as connecting with Python scripts and printing version information.
 How to start the server with redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:12 PM
How to start the server with redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:12 PM
The steps to start a Redis server include: Install Redis according to the operating system. Start the Redis service via redis-server (Linux/macOS) or redis-server.exe (Windows). Use the redis-cli ping (Linux/macOS) or redis-cli.exe ping (Windows) command to check the service status. Use a Redis client, such as redis-cli, Python, or Node.js, to access the server.
 How to set the Redis memory size according to business needs?
Apr 10, 2025 pm 02:18 PM
How to set the Redis memory size according to business needs?
Apr 10, 2025 pm 02:18 PM
Redis memory size setting needs to consider the following factors: data volume and growth trend: Estimate the size and growth rate of stored data. Data type: Different types (such as lists, hashes) occupy different memory. Caching policy: Full cache, partial cache, and phasing policies affect memory usage. Business Peak: Leave enough memory to deal with traffic peaks.
 What is the impact of Redis persistence on memory?
Apr 10, 2025 pm 02:15 PM
What is the impact of Redis persistence on memory?
Apr 10, 2025 pm 02:15 PM
Redis persistence will take up extra memory, RDB temporarily increases memory usage when generating snapshots, and AOF continues to take up memory when appending logs. Influencing factors include data volume, persistence policy and Redis configuration. To mitigate the impact, you can reasonably configure RDB snapshot policies, optimize AOF configuration, upgrade hardware and monitor memory usage. Furthermore, it is crucial to find a balance between performance and data security.
 Python vs. C : Applications and Use Cases Compared
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Python vs. C : Applications and Use Cases Compared
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Python is suitable for data science, web development and automation tasks, while C is suitable for system programming, game development and embedded systems. Python is known for its simplicity and powerful ecosystem, while C is known for its high performance and underlying control capabilities.




