Redis distributed lock instance analysis
Distributed Lock Overview
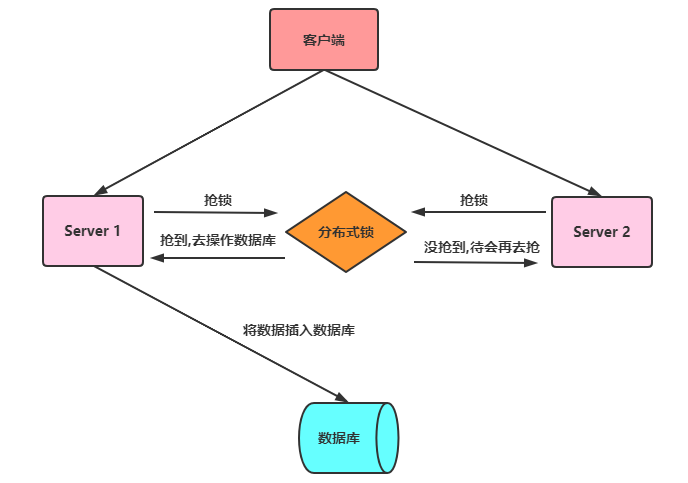
In a multi-threaded environment, in order to ensure that a code block can only be accessed by one thread at the same time, in Java we can generally use synchronized syntax and ReetrantLock to ensure that this is actually The above is a local lock method. But now companies are adopting distributed architecture. In a distributed environment, how to ensure that threads on different nodes execute simultaneously? Therefore, distributed locks are introduced, which are a way to control mutually exclusive access to shared resources between distributed systems. In a distributed system, multiple services are deployed on multiple machines. When a user on the client initiates a data insertion request, if there is no distributed lock mechanism guarantee, then the Multiple services may perform concurrent insertion operations, resulting in repeated insertion of data, which can cause problems for some businesses that do not allow redundant data. The distributed lock mechanism is to solve problems like this and ensure mutually exclusive access to shared resources between multiple services. If one service seizes the distributed lock and other services do not obtain the lock, no subsequent operations will be performed. The general meaning is as shown in the figure below:
 Characteristics of distributed locks
Characteristics of distributed locks
Distributed locks generally have the following characteristics:
- Mutual exclusivity: Only one thread can hold the lock at the same time
- Reentrancy: The same thread on the same node can acquire the lock again if it acquires it. Lock
- Lock timeout: supports lock timeout like the lock in J.U.C to prevent deadlock
- High performance and high availability: Lock and Unlocking needs to be efficient, and it also needs to ensure high availability to prevent distributed lock failure
- Have blocking and non-blocking properties: be able to wake up from the blocking state in time
- How to implement distributed locks
We generally implement distributed locks in the following ways:
- Based on database
- Based on Redis
- Based on zookeeper
- Problems with Redis ordinary distributed locks
Speaking of Redis Distributed locks, most people will think of:
setnx lua (redis guarantees that no other operations will be performed when executing Lua scripts, ensuring the atomicity of operations), or they may know set key value px milliseconds nx. The core implementation command of the latter method is as follows: <div class="code" style="position:relative; padding:0px; margin:0px;"><pre class='brush:php;toolbar:false;'>- 获取锁(unique_value可以是UUID等)
SET resource_name unique_value NX PX 30000
- 释放锁(lua脚本中,一定要比较value,防止误解锁)
if redis.call("get",KEYS[1]) == ARGV[1] then
return redis.call("del",KEYS[1])
else
return 0
end</pre><div class="contentsignin">Copy after login</div></div> This implementation method has three major points (which is also where the interview probability is very high):
The set command must use
In fact, the biggest disadvantage of this type of lock is that it only acts on one Redis node when locking, even if Redis guarantees it through sentinel High availability. If the master node switches master-slave for some reason, the lock will be lost:- set key value px milliseconds nx
value must be unique;;
- when releasing the lock To verify the value, you cannot misunderstand the lock;
RedlockObtained the lock on the Redis master node ;
In order to avoid the single point of failure problem, Redis author antirez proposed a more advanced distributed lock implementation method based on the distributed environment:- But the locked key has not yet been synchronized to the slave node;
- master fails, failover occurs, and the slave node is upgraded to master Node;
- caused the lock to be lost.
. Redlock is also the only way among all distributed lock implementations in Redis that can make the interviewer climax. Redis Advanced Distributed Lock: Redlock
The redlock algorithm proposed by antirez is roughly like this:
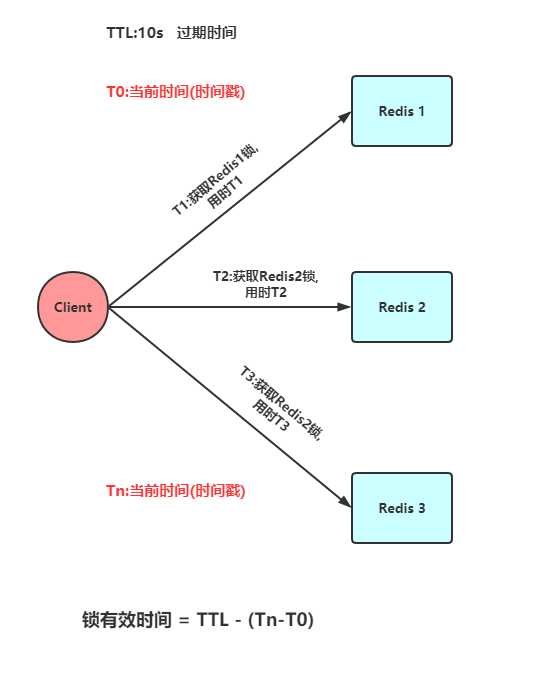
In the Redis distributed environment, we assume that there are N Redis masters . These nodes
are completely independent of each other, and there is no master-slave replication or other cluster coordination mechanism. We ensure that we will use the same method to acquire and release locks on N instances as under a Redis single instance. Now we assume that there are 5 Redis master nodes, and we need to run these Redis instances on 5 servers to ensure that they will not all go down at the same time. In order to obtain the lock, the client should perform the following operations:
- Get the current Unix time in milliseconds.
- Try to obtain locks from 5 instances in sequence, using the same key and
- unique value
(such as UUID). When requesting a lock from Redis, the client should set a network connection and response timeout, which should be less than the lock expiration time. For example, if your lock automatic expiration time TTL is 10 seconds, the timeout should be between 5-50 milliseconds. This can avoid the situation where the server-side Redis has hung up and the client is still waiting for the response result. If the server does not respond within the specified time, the client should try to obtain a lock from another Redis instance as soon as possible.
客户端使用当前时间减去开始获取锁时间(步骤1记录的时间)就得到获取锁使用的时间。当且仅当从大多数(N/2+1,这里是3个节点)的Redis节点都取到锁,并且使用的时间小于锁失效时间时,锁才算获取成功。
如果取到了锁,key的真正有效时间等于有效时间减去获取锁所使用的时间(步骤3计算的结果)。
如果因为某些原因,获取锁失败(没有在至少N/2+1个Redis实例取到锁或者取锁时间已经超过了有效时间),客户端应该在所有的Redis实例上进行解锁(即便某些Redis实例根本就没有加锁成功,防止某些节点获取到锁但是客户端没有得到响应而导致接下来的一段时间不能被重新获取锁)。
此处不讨论时钟漂移
Redlock源码
redisson已经有对redlock算法封装,接下来对其用法进行简单介绍,并对核心源码进行分析(假设5个redis实例)。
1. Redlock依赖
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.redisson/redisson -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.redisson</groupId>
<artifactId>redisson</artifactId>
<version>3.3.2</version>
</dependency>2. Redlock用法
首先,我们来看一下redission封装的redlock算法实现的分布式锁用法,非常简单,跟重入锁(ReentrantLock)有点类似:
Config config = new Config();
config.useSentinelServers().addSentinelAddress("127.0.0.1:6369","127.0.0.1:6379", "127.0.0.1:6389")
.setMasterName("masterName")
.setPassword("password").setDatabase(0);
RedissonClient redissonClient = Redisson.create(config);
// 还可以getFairLock(), getReadWriteLock()
RLock redLock = redissonClient.getLock("REDLOCK_KEY");
boolean isLock;
try {
isLock = redLock.tryLock();
// 500ms拿不到锁, 就认为获取锁失败。10000ms即10s是锁失效时间。
isLock = redLock.tryLock(500, 10000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
if (isLock) {
//TODO if get lock success, do something;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
} finally {
// 无论如何, 最后都要解锁
redLock.unlock();
}3. Redlock唯一ID
实现分布式锁的一个非常重要的点就是set的value要具有唯一性,redisson的value是怎样保证value的唯一性呢?答案是UUID+threadId。入口在redissonClient.getLock(“REDLOCK_KEY”),源码在Redisson.java和RedissonLock.java中:
protected final UUID id = UUID.randomUUID();
String getLockName(long threadId) {
return id + ":" + threadId;
}4. Redlock获取锁
获取锁的代码为redLock.tryLock()或者redLock.tryLock(500, 10000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS),两者的最终核心源码都是下面这段代码,只不过前者获取锁的默认租约时间(leaseTime)是LOCK_EXPIRATION_INTERVAL_SECONDS,即30s:
<T> RFuture<T> tryLockInnerAsync(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId, RedisStrictCommand<T> command) {
internalLockLeaseTime = unit.toMillis(leaseTime);
// 获取锁时向5个redis实例发送的命令
return commandExecutor.evalWriteAsync(getName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, command,
// 首先分布式锁的KEY不能存在,如果确实不存在,那么执行hset命令(hset REDLOCK_KEY uuid+threadId 1),并通过pexpire设置失效时间(也是锁的租约时间)
"if (redis.call('exists', KEYS[1]) == 0) then " +
"redis.call('hset', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); " +
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +
"return nil; " +
"end; " +
// 如果分布式锁的KEY已经存在,并且value也匹配,表示是当前线程持有的锁,那么重入次数加1,并且设置失效时间
"if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1) then " +
"redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); " +
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +
"return nil; " +
"end; " +
// 获取分布式锁的KEY的失效时间毫秒数
"return redis.call('pttl', KEYS[1]);",
// 这三个参数分别对应KEYS[1],ARGV[1]和ARGV[2]
Collections.<Object>singletonList(getName()), internalLockLeaseTime, getLockName(threadId));
}获取锁的命令中,
KEYS[1]就是Collections.singletonList(getName()),表示分布式锁的key,即REDLOCK_KEY;
ARGV[1]就是internalLockLeaseTime,即锁的租约时间,默认30s;
ARGV[2]就是getLockName(threadId),是获取锁时set的唯一值,即UUID+threadId:
5. Redlock释放锁
释放锁的代码为redLock.unlock(),核心源码如下:
protected RFuture<Boolean> unlockInnerAsync(long threadId) {
// 向5个redis实例都执行如下命令
return commandExecutor.evalWriteAsync(getName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, RedisCommands.EVAL_BOOLEAN,
// 如果分布式锁KEY不存在,那么向channel发布一条消息
"if (redis.call('exists', KEYS[1]) == 0) then " +
"redis.call('publish', KEYS[2], ARGV[1]); " +
"return 1; " +
"end;" +
// 如果分布式锁存在,但是value不匹配,表示锁已经被占用,那么直接返回
"if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[3]) == 0) then " +
"return nil;" +
"end; " +
// 如果就是当前线程占有分布式锁,那么将重入次数减1
"local counter = redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[3], -1); " +
// 重入次数减1后的值如果大于0,表示分布式锁有重入过,那么只设置失效时间,还不能删除
"if (counter > 0) then " +
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]); " +
"return 0; " +
"else " +
// 重入次数减1后的值如果为0,表示分布式锁只获取过1次,那么删除这个KEY,并发布解锁消息
"redis.call('del', KEYS[1]); " +
"redis.call('publish', KEYS[2], ARGV[1]); " +
"return 1; "+
"end; " +
"return nil;",
// 这5个参数分别对应KEYS[1],KEYS[2],ARGV[1],ARGV[2]和ARGV[3]
Arrays.<Object>asList(getName(), getChannelName()), LockPubSub.unlockMessage, internalLockLeaseTime, getLockName(threadId));
}Redis实现的分布式锁轮子
下面利用SpringBoot + Jedis + AOP的组合来实现一个简易的分布式锁。
1. 自定义注解
自定义一个注解,被注解的方法会执行获取分布式锁的逻辑
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
public @interface RedisLock {
/**
* 业务键
*
* @return
*/
String key();
/**
* 锁的过期秒数,默认是5秒
*
* @return
*/
int expire() default 5;
/**
* 尝试加锁,最多等待时间
*
* @return
*/
long waitTime() default Long.MIN_VALUE;
/**
* 锁的超时时间单位
*
* @return
*/
TimeUnit timeUnit() default TimeUnit.SECONDS;
}2. AOP拦截器实现
在AOP中我们去执行获取分布式锁和释放分布式锁的逻辑,代码如下:
@Aspect
@Component
public class LockMethodAspect {
@Autowired
private RedisLockHelper redisLockHelper;
@Autowired
private JedisUtil jedisUtil;
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(LockMethodAspect.class);
@Around("@annotation(com.redis.lock.annotation.RedisLock)")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) {
Jedis jedis = jedisUtil.getJedis();
MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature();
Method method = signature.getMethod();
RedisLock redisLock = method.getAnnotation(RedisLock.class);
String value = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
String key = redisLock.key();
try {
final boolean islock = redisLockHelper.lock(jedis,key, value, redisLock.expire(), redisLock.timeUnit());
logger.info("isLock : {}",islock);
if (!islock) {
logger.error("获取锁失败");
throw new RuntimeException("获取锁失败");
}
try {
return joinPoint.proceed();
} catch (Throwable throwable) {
throw new RuntimeException("系统异常");
}
} finally {
logger.info("释放锁");
redisLockHelper.unlock(jedis,key, value);
jedis.close();
}
}
}3. Redis实现分布式锁核心类
@Component
public class RedisLockHelper {
private long sleepTime = 100;
/**
* 直接使用setnx + expire方式获取分布式锁
* 非原子性
*
* @param key
* @param value
* @param timeout
* @return
*/
public boolean lock_setnx(Jedis jedis,String key, String value, int timeout) {
Long result = jedis.setnx(key, value);
// result = 1时,设置成功,否则设置失败
if (result == 1L) {
return jedis.expire(key, timeout) == 1L;
} else {
return false;
}
}
/**
* 使用Lua脚本,脚本中使用setnex+expire命令进行加锁操作
*
* @param jedis
* @param key
* @param UniqueId
* @param seconds
* @return
*/
public boolean Lock_with_lua(Jedis jedis,String key, String UniqueId, int seconds) {
String lua_scripts = "if redis.call('setnx',KEYS[1],ARGV[1]) == 1 then" +
"redis.call('expire',KEYS[1],ARGV[2]) return 1 else return 0 end";
List<String> keys = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> values = new ArrayList<>();
keys.add(key);
values.add(UniqueId);
values.add(String.valueOf(seconds));
Object result = jedis.eval(lua_scripts, keys, values);
//判断是否成功
return result.equals(1L);
}
/**
* 在Redis的2.6.12及以后中,使用 set key value [NX] [EX] 命令
*
* @param key
* @param value
* @param timeout
* @return
*/
public boolean lock(Jedis jedis,String key, String value, int timeout, TimeUnit timeUnit) {
long seconds = timeUnit.toSeconds(timeout);
return "OK".equals(jedis.set(key, value, "NX", "EX", seconds));
}
/**
* 自定义获取锁的超时时间
*
* @param jedis
* @param key
* @param value
* @param timeout
* @param waitTime
* @param timeUnit
* @return
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
public boolean lock_with_waitTime(Jedis jedis,String key, String value, int timeout, long waitTime,TimeUnit timeUnit) throws InterruptedException {
long seconds = timeUnit.toSeconds(timeout);
while (waitTime >= 0) {
String result = jedis.set(key, value, "nx", "ex", seconds);
if ("OK".equals(result)) {
return true;
}
waitTime -= sleepTime;
Thread.sleep(sleepTime);
}
return false;
}
/**
* 错误的解锁方法—直接删除key
*
* @param key
*/
public void unlock_with_del(Jedis jedis,String key) {
jedis.del(key);
}
/**
* 使用Lua脚本进行解锁操纵,解锁的时候验证value值
*
* @param jedis
* @param key
* @param value
* @return
*/
public boolean unlock(Jedis jedis,String key,String value) {
String luaScript = "if redis.call('get',KEYS[1]) == ARGV[1] then " +
"return redis.call('del',KEYS[1]) else return 0 end";
return jedis.eval(luaScript, Collections.singletonList(key), Collections.singletonList(value)).equals(1L);
}
}4. Controller层控制
定义一个TestController来测试我们实现的分布式锁
@RestController
public class TestController {
@RedisLock(key = "redis_lock")
@GetMapping("/index")
public String index() {
return "index";
}
}The above is the detailed content of Redis distributed lock instance analysis. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
Redis cluster mode deploys Redis instances to multiple servers through sharding, improving scalability and availability. The construction steps are as follows: Create odd Redis instances with different ports; Create 3 sentinel instances, monitor Redis instances and failover; configure sentinel configuration files, add monitoring Redis instance information and failover settings; configure Redis instance configuration files, enable cluster mode and specify the cluster information file path; create nodes.conf file, containing information of each Redis instance; start the cluster, execute the create command to create a cluster and specify the number of replicas; log in to the cluster to execute the CLUSTER INFO command to verify the cluster status; make
 How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear Redis data: Use the FLUSHALL command to clear all key values. Use the FLUSHDB command to clear the key value of the currently selected database. Use SELECT to switch databases, and then use FLUSHDB to clear multiple databases. Use the DEL command to delete a specific key. Use the redis-cli tool to clear the data.
 How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
To read a queue from Redis, you need to get the queue name, read the elements using the LPOP command, and process the empty queue. The specific steps are as follows: Get the queue name: name it with the prefix of "queue:" such as "queue:my-queue". Use the LPOP command: Eject the element from the head of the queue and return its value, such as LPOP queue:my-queue. Processing empty queues: If the queue is empty, LPOP returns nil, and you can check whether the queue exists before reading the element.
 How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
Using the Redis directive requires the following steps: Open the Redis client. Enter the command (verb key value). Provides the required parameters (varies from instruction to instruction). Press Enter to execute the command. Redis returns a response indicating the result of the operation (usually OK or -ERR).
 How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
Using Redis to lock operations requires obtaining the lock through the SETNX command, and then using the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time. The specific steps are: (1) Use the SETNX command to try to set a key-value pair; (2) Use the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time for the lock; (3) Use the DEL command to delete the lock when the lock is no longer needed.
 How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
The best way to understand Redis source code is to go step by step: get familiar with the basics of Redis. Select a specific module or function as the starting point. Start with the entry point of the module or function and view the code line by line. View the code through the function call chain. Be familiar with the underlying data structures used by Redis. Identify the algorithm used by Redis.
 How to solve data loss with redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:24 PM
How to solve data loss with redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:24 PM
Redis data loss causes include memory failures, power outages, human errors, and hardware failures. The solutions are: 1. Store data to disk with RDB or AOF persistence; 2. Copy to multiple servers for high availability; 3. HA with Redis Sentinel or Redis Cluster; 4. Create snapshots to back up data; 5. Implement best practices such as persistence, replication, snapshots, monitoring, and security measures.
 How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
Use the Redis command line tool (redis-cli) to manage and operate Redis through the following steps: Connect to the server, specify the address and port. Send commands to the server using the command name and parameters. Use the HELP command to view help information for a specific command. Use the QUIT command to exit the command line tool.




