What is the algorithm formula for Redis bloom filter size?
1. Introduction
Client: Does this key exist?
Server: Does not exist/don’t know
The Bloom filter is a relatively clever probabilistic data structure, and its essence is a data structure. It features efficient insertion and querying. But when we want to check whether a key exists in a certain structure, by using a Bloom filter, we can quickly learn that "this key must not exist or may exist." Compared with traditional data structures such as List, Set, and Map, it is more efficient and takes up less space, but the results it returns are probabilistic and inaccurate.
Bloom filters are only used to test membership in a collection. The classic Bloom filter example is to improve efficiency by reducing expensive disk (or network) lookups for non-existent keys. As we can see, a Bloom filter can search for a key in O(k) constant time, where k is the number of hash functions, and testing for the non-existence of a key will be very fast.
2. Application scenarios
2.1 Cache penetration
In order to improve access efficiency, we will put some data in the Redis cache. When performing data query, you can first obtain the data from the cache without reading the database. This can effectively improve performance.
When querying data, first determine whether there is data in the cache. If there is data, obtain the data directly from the cache.
But if there is no data, you need to get the data from the database and then put it into the cache. If a large number of accesses fail to hit the cache, it will put a lot of pressure on the database, causing the database to crash. Using Bloom filters, when accessing a non-existent cache, you can quickly return to avoid cache or DB crash.
2.2 Determine whether a certain data exists in massive data
HBase stores a very large amount of data. To determine whether a certain ROWKEYS or a certain column exists, use a Bloom filter. You can quickly get whether a certain data exists. But there is a certain misjudgment rate. But if a key does not exist, it must be accurate.
3. Problems with HashMap
To determine whether an element exists, the efficiency of using HashMap is very high. HashMap can achieve O(1) constant time complexity by mapping values to HashMap Keys.
However, if the amount of data stored is very large (for example: hundreds of millions of data), HashMap will consume a very large amount of memory. And it is simply impossible to read massive amounts of data into memory at once.
4. Understand the working principle diagram of Bloom filter
:
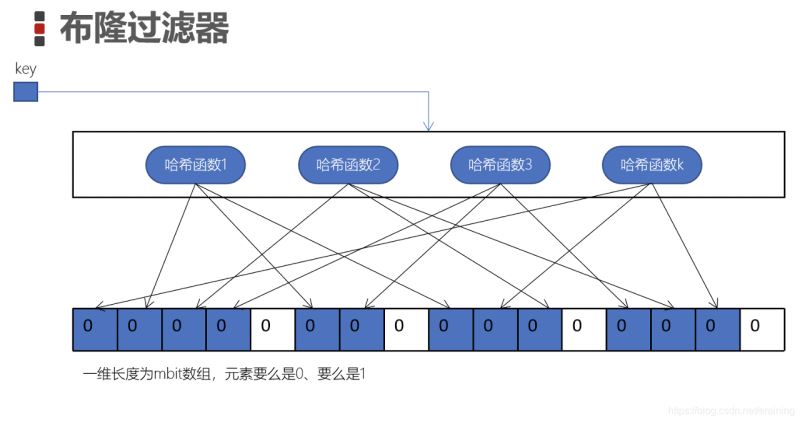
The Bloom filter is a bit array or a bit binary vector
The elements in this array are either 0 or 1
k hash functions are independent of each other, and the calculated result of each hash function is modulo the length m of the array , and set the corresponding bit to 1 (blue cell)
We set each key to the cell in this way, which is the "Bloom filter"
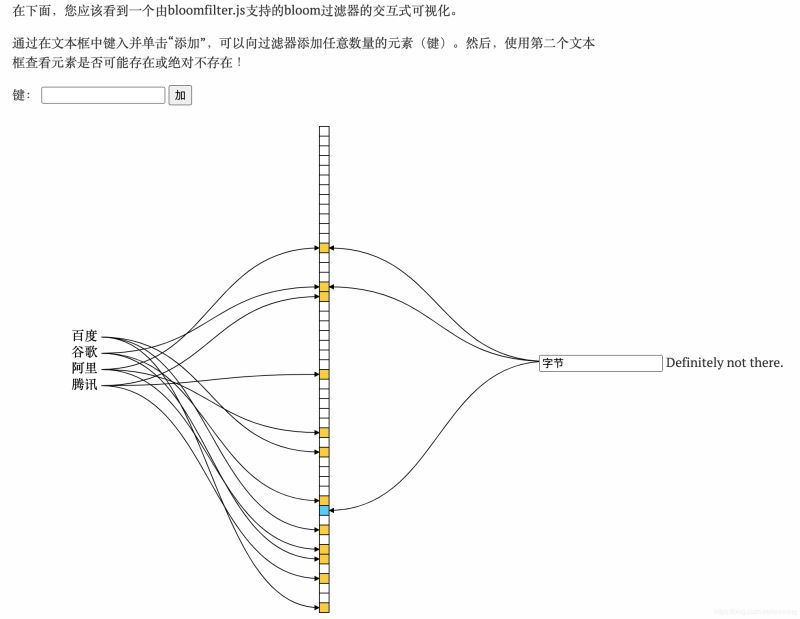
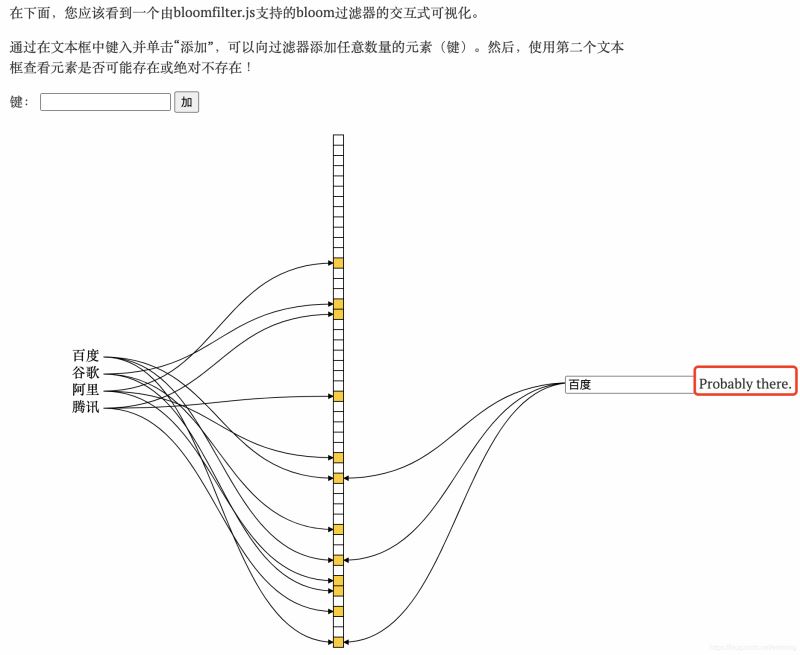
5. According to the cloth Long filter query element
Assume that a key is entered, we use the previous k hash functions to find the hash, and get k values
Determine whether the k values are all blue, if one is not Blue, then the key must not exist
If both are blue, then the key may exist (Bloom filter will cause misjudgment)
Because if there are many input objects and the set is relatively small, it will As a result, most positions in the collection will be painted blue. Then when a certain key is checked to be blue, a certain position happens to be set to blue. At this time, it will be mistakenly believed that the key is in the collection.
Example:
6. Can it be deleted?
Traditional bloom filters do not support deletion operations. However, a variant called Counting Bloom filter can be used to test whether the number of element counts is absolutely less than a certain threshold, and it supports element deletion. The principle and implementation of the article Counting Bloom Filter is written in great detail and you can read it in detail.
7. How to choose the number of hash functions and the length of the Bloom filter
Obviously, if the Bloom filter is too small, all bits will soon be 1, then any value can be queried All will return "may exist", which defeats the purpose of filtering. As the length of a Bloom filter increases, its false positive rate decreases.
In addition, the number of hash functions also needs to be weighed. The more the number, the faster the Bloom filter bit position is set to 1, and the lower the efficiency of the Bloom filter; but if there are too few If so, our false alarm rate will become higher.
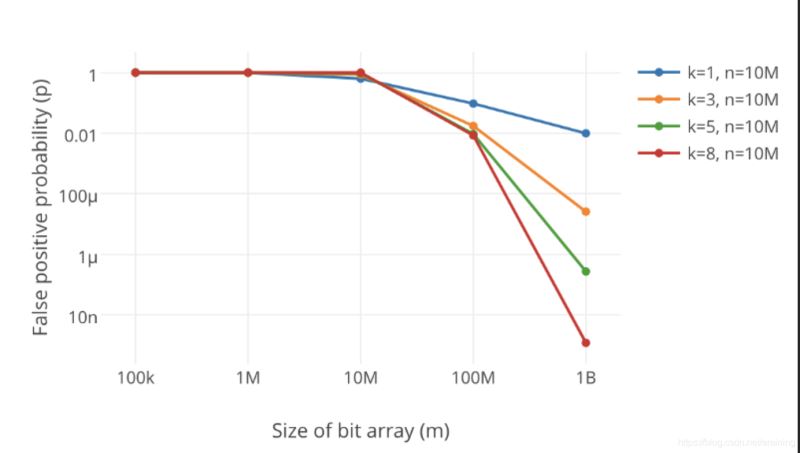
As can be seen from the above figure, increasing the number of hash functions k will greatly reduce the error rate p.
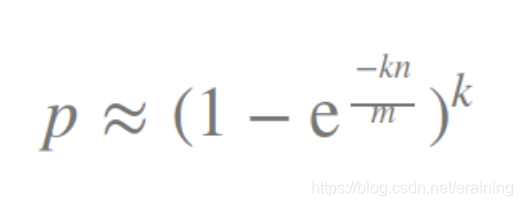
Don’t worry, actually we need to confirm the values of m and k. Then, if we specify the fault tolerance p and the number of elements n, these parameters can be calculated using the following formula:
We can calculate these parameters based on the size of the filter m, the number of hash functions k and the number of inserted elements n To calculate the false alarm rate p, the formula is as follows: Based on the above, how to choose the k and m values suitable for the business?
Formula:
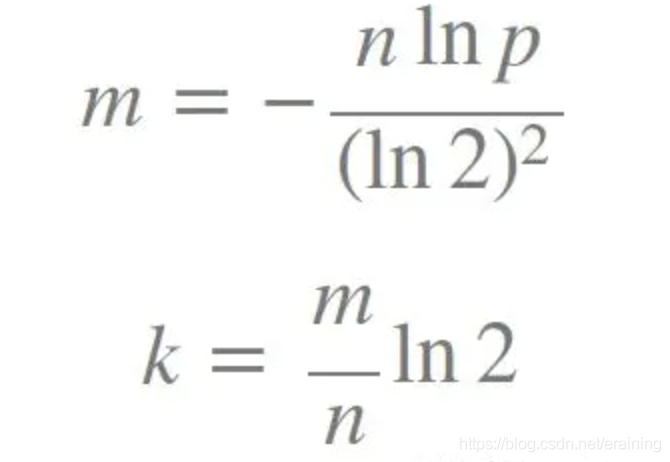
k is the number of hash functions, m is the Bloom filter length, n is the number of inserted elements, and p is the false positive rate.
As for how to derive this formula, I have published an article on Zhihu about it. If you are interested, you can read it. If you are not interested, just remember the formula above.
I would also like to mention another important point here. Since the only purpose of using a Bloom filter is to search faster, we can't use a slow hash function, right? Cryptographic hash functions (e.g. Sha-1, MD5) are not a good choice for bloom filters because they are a bit slow. So, better choices from faster hash function implementations are murmur, fnv family hashing, Jenkins hashing and HashMix.
More Application Scenarios
In the given example you have seen that we can use this to warn the user for entering a weak password.
You can use bloom filters to prevent users from visiting malicious websites.
Instead of querying a SQL database to check if a user with a specific email exists, you can first use the Bloom Bloom filter to do a cheap lookup check. If the email doesn't exist, great! If it does exist, you may have to make additional queries to the database. You can also do the same thing to search for "username already taken."
You can keep a Bloom filter based on the IP address of your website visitor to check whether the user of your website is a "returning user" or a "new user". A few false positives from “returning users” can’t hurt you, right?
You can also do spell checking by tracking dictionary words using Bloom filters.
The above is the detailed content of What is the algorithm formula for Redis bloom filter size?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1393
1393
 52
52
 1207
1207
 24
24
 How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
Redis cluster mode deploys Redis instances to multiple servers through sharding, improving scalability and availability. The construction steps are as follows: Create odd Redis instances with different ports; Create 3 sentinel instances, monitor Redis instances and failover; configure sentinel configuration files, add monitoring Redis instance information and failover settings; configure Redis instance configuration files, enable cluster mode and specify the cluster information file path; create nodes.conf file, containing information of each Redis instance; start the cluster, execute the create command to create a cluster and specify the number of replicas; log in to the cluster to execute the CLUSTER INFO command to verify the cluster status; make
 How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear Redis data: Use the FLUSHALL command to clear all key values. Use the FLUSHDB command to clear the key value of the currently selected database. Use SELECT to switch databases, and then use FLUSHDB to clear multiple databases. Use the DEL command to delete a specific key. Use the redis-cli tool to clear the data.
 How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
To read a queue from Redis, you need to get the queue name, read the elements using the LPOP command, and process the empty queue. The specific steps are as follows: Get the queue name: name it with the prefix of "queue:" such as "queue:my-queue". Use the LPOP command: Eject the element from the head of the queue and return its value, such as LPOP queue:my-queue. Processing empty queues: If the queue is empty, LPOP returns nil, and you can check whether the queue exists before reading the element.
 How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
Using the Redis directive requires the following steps: Open the Redis client. Enter the command (verb key value). Provides the required parameters (varies from instruction to instruction). Press Enter to execute the command. Redis returns a response indicating the result of the operation (usually OK or -ERR).
 How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
Using Redis to lock operations requires obtaining the lock through the SETNX command, and then using the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time. The specific steps are: (1) Use the SETNX command to try to set a key-value pair; (2) Use the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time for the lock; (3) Use the DEL command to delete the lock when the lock is no longer needed.
 How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
The best way to understand Redis source code is to go step by step: get familiar with the basics of Redis. Select a specific module or function as the starting point. Start with the entry point of the module or function and view the code line by line. View the code through the function call chain. Be familiar with the underlying data structures used by Redis. Identify the algorithm used by Redis.
 How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
Use the Redis command line tool (redis-cli) to manage and operate Redis through the following steps: Connect to the server, specify the address and port. Send commands to the server using the command name and parameters. Use the HELP command to view help information for a specific command. Use the QUIT command to exit the command line tool.
 How to configure Lua script execution time in centos redis
Apr 14, 2025 pm 02:12 PM
How to configure Lua script execution time in centos redis
Apr 14, 2025 pm 02:12 PM
On CentOS systems, you can limit the execution time of Lua scripts by modifying Redis configuration files or using Redis commands to prevent malicious scripts from consuming too much resources. Method 1: Modify the Redis configuration file and locate the Redis configuration file: The Redis configuration file is usually located in /etc/redis/redis.conf. Edit configuration file: Open the configuration file using a text editor (such as vi or nano): sudovi/etc/redis/redis.conf Set the Lua script execution time limit: Add or modify the following lines in the configuration file to set the maximum execution time of the Lua script (unit: milliseconds)




