How to build a vue3 project from scratch
Instructions
Record the Vue3 project building process. The article is based on vue3.2.6 and vite2.51 versions, and uses the UI library Element plus, vue-router4, Layout layout encapsulation, axios request encapsulation, alias configuration, etc.
Start
1. Use the vscode development tool to install the vue3 plug-in Volar. In vue2 we use Vetur.
vue3 online code tool portal sfc.vuejs.org/
2. Execute initialization and installation commands:
npm init vite In this process of initializing vite, you can enter the project name, select the vue/react project and select the js/ts environment. Vue3 fully supports ts. This article uses js. npm install Install dependencies. Finally execute npm run dev to run the project.
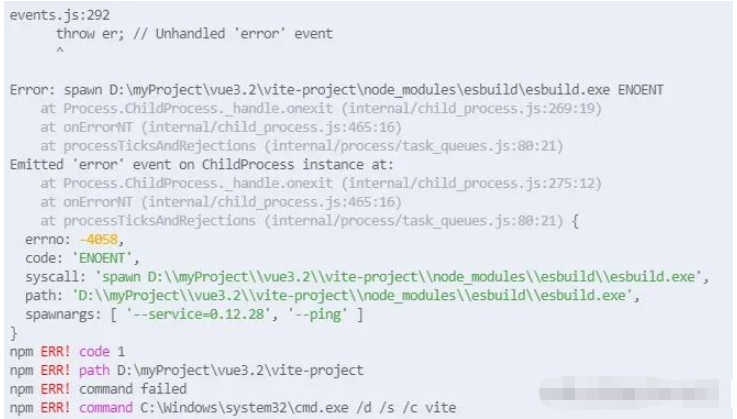
If the error message above appears when running the process, you can manually execute node node_modules/esbuild/install.js, and then execute npm run dev
3. Install vue-router
Executionnpm install vue-router@4, vue- corresponding to vue3 The versions of router and vuex are both 4.0. After executing the command to install, create src/router/index.js in the directory and write the following configuration:
import { createRouter, createWebHistory } from 'vue-router'
const routes = [
// ...
]
export default createRouter({
history: createWebHistory(),
routes,
})main.js uses
// ...+ import router from './router/index' createApp(App).use(router).mount('#app')
vue-router4. The writing method is somewhat different from the previous one. Difference hash mode createWebHashHistory history modecreateWebHistory, please check the official website for details.
4. Global styles and sass installation (using @ path requires configuring an alias, and there are corresponding instructions later)
Execute the commandnpm i sass -D, and then create src/styles/index.scss in the directory:
// @import './a.scss'; // 作为出口组织这些样式文件,同时编写一些全局样式
Introduce
import '@/styles/index.scss'
tips in mian.js: Use style penetration in vue3 ::deep(.className) or deep(.className)
5. Element plus on-demand introduction and global introduction
Executionnpm i element3 -S Command installation, if you can use most of the components inside, use the global import method, as follows:
// main.js import element3 from "element3"; import "element3/lib/theme-chalk/index.css"; createApp(App).use(router).use(element3).mount('#app')
If you only use a few components, you can load them on demand to optimize performance and create src/plugins/element3.js, as follows
// 按需引入 plugins/element3.js
import { ElButton, ElMenu, ElMenuItem } from 'element3'
import 'element3/lib/theme-chalk/button.css'
import 'element3/lib/theme-chalk/menu.css'
import 'element3/lib/theme-chalk/menu-item.css'
export default function (app) {
app.use(ElButton)
app.use(ElMenu)
app.use(ElMenuItem)
}
// main.js中引用
import element3 from '@/plugins/element3.js'
createApp(App).use(router).use(element3).mount('#app')6. Layout layout, create the file src/layout/index.vue
// src/layout/index.vue <template> <!-- 顶部导航 --> <Navbar /> <!-- 页面内容部分、路由出口 --> <AppMain /> <!-- 底部内容 --> <Footer /> </template> <script setup> import Navbar from './Navbar.vue' import AppMain from './AppMain.vue' import Footer from './Footer.vue' </script>
Design the layout according to your own needs, When using Layout, you need to pay attention to using Layout.vue as the parent route. The routing design is roughly as follows:
// src/router/index.js
import { createRouter, createWebHistory } from 'vue-router'
import Layout from '@/layout/index.vue'
import Home from '@/views/home/Home.vue'
import Test from '@/views/test/Test.vue'
const routes = [
{
path: '/',
component: Layout,
children: [{ path: '', component: Home }],
},
{
path: '/test',
component: Layout,
children: [{ path: '', component: Test }],
},
]
export default createRouter({
history: createWebHistory(),
routes,
})7. axios request encapsulation
Execute commandnpm i axios Install axios
Create a new src/utils/request.js and encapsulate axios in this file
import axios from 'axios'
// 可以导入element plus 的弹出框代替alert进行交互操作
// create an axios instance
const service = axios.create({
baseURL: import.meta.env.VITE_APP_BASEURL, // 使用设置好的全局环境
timeout: 30 * 1000, // request timeout
})
// request interceptor
service.interceptors.request.use(
(config) => {
// 此处可以执行处理添加token等逻辑
// config.headers["Authorization"] = getToken();
return config
},
(error) => {
console.log(error)
return Promise.reject(error)
}
)
// response interceptor
service.interceptors.response.use(
(response) => {
const res = response.data // 根据接口返回参数自行处理
if (res.code !== 200) {
if (res.code === 50000) {
// 根据状态码自行处理
alert('服务器内部出现异常,请稍后再试')
}
return Promise.reject(new Error(res.msg || 'Error'))
} else {
// 调用成功返回数据
return Promise.resolve(res)
}
},
(error) => {
console.log('err' + error) // 出现异常的处理
return Promise.reject(error)
}
)
export default serviceIn order to facilitate the management and maintenance of the API, you can create it in src/ Create a separate JS file for each module or page in the api directory. To provide an example here, create a file called src/api/home.js and write the code into it
// 引入封装好的 request.js
import request from '@/utils/request'
export function getList(query) {
return request({
url: '/list',
method: 'get',
params: query,
})
}Use
<script setup>
import { getList } from '@/api/home.js'
const query = { pagenum: 1 }
getList(query)
.then((res) => {
console.log(res) // 调用成功返回的数据
})
.error((err) => {
console.log(err) // 调用失败要执行的逻辑
})
</script>8 in home.vue. Environment variable related
Create three files in the project root directory.env.production Production environment.env.development Development environment.env. staging Test environment, add the following code respectively, in different compilation environments, automatically execute the code in the current environment when packaging
# .env.production VITE_APP_BASEURL=https://www.prod.api/
# .env.development VITE_APP_BASEURL=https://www.test.api/
# .env.staging VITE_APP_BASEURL=https://www.test.api/
Use:
console.log(import.meta.env.VITE_APP_BASEURL) // 在不同编译环境下控制台会输出不同的url路径
In package In .json, pass the --mode option flag to override the default mode used by the command
"scripts": {
"dev": "vite",
"build:stage": "vite build --mode staging",
"build:prod": "vite build --mode production",
"serve": "vite preview"
},In this way, the production environment is packaged and executed npm run build:prod , Test/pre-release environment packagingnpm run build:stage
##9. Alias configuration in vite
vite.config.js in the root directory File add codeimport { defineConfig } from 'vite'
import vue from '@vitejs/plugin-vue'
import { resolve } from 'path'
// https://vitejs.dev/config/
export default defineConfig({
plugins: [vue()],
resolve: {
alias: [{ find: '@', replacement: resolve(__dirname, 'src') }],
},
base: './',
})The above is the detailed content of How to build a vue3 project from scratch. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 vue3+vite: How to solve the error when using require to dynamically import images in src
May 21, 2023 pm 03:16 PM
vue3+vite: How to solve the error when using require to dynamically import images in src
May 21, 2023 pm 03:16 PM
vue3+vite:src uses require to dynamically import images and error reports and solutions. vue3+vite dynamically imports multiple images. If vue3 is using typescript development, require will introduce image errors. requireisnotdefined cannot be used like vue2 such as imgUrl:require(' .../assets/test.png') is imported because typescript does not support require, so import is used. Here is how to solve it: use awaitimport
 How to use tinymce in vue3 project
May 19, 2023 pm 08:40 PM
How to use tinymce in vue3 project
May 19, 2023 pm 08:40 PM
tinymce is a fully functional rich text editor plug-in, but introducing tinymce into vue is not as smooth as other Vue rich text plug-ins. tinymce itself is not suitable for Vue, and @tinymce/tinymce-vue needs to be introduced, and It is a foreign rich text plug-in and has not passed the Chinese version. You need to download the translation package from its official website (you may need to bypass the firewall). 1. Install related dependencies npminstalltinymce-Snpminstall@tinymce/tinymce-vue-S2. Download the Chinese package 3. Introduce the skin and Chinese package. Create a new tinymce folder in the project public folder and download the
 How to refresh partial content of the page in Vue3
May 26, 2023 pm 05:31 PM
How to refresh partial content of the page in Vue3
May 26, 2023 pm 05:31 PM
To achieve partial refresh of the page, we only need to implement the re-rendering of the local component (dom). In Vue, the easiest way to achieve this effect is to use the v-if directive. In Vue2, in addition to using the v-if instruction to re-render the local dom, we can also create a new blank component. When we need to refresh the local page, jump to this blank component page, and then jump back in the beforeRouteEnter guard in the blank component. original page. As shown in the figure below, how to click the refresh button in Vue3.X to reload the DOM within the red box and display the corresponding loading status. Since the guard in the component in the scriptsetup syntax in Vue3.X only has o
 How Vue3 parses markdown and implements code highlighting
May 20, 2023 pm 04:16 PM
How Vue3 parses markdown and implements code highlighting
May 20, 2023 pm 04:16 PM
Vue implements the blog front-end and needs to implement markdown parsing. If there is code, it needs to implement code highlighting. There are many markdown parsing libraries for Vue, such as markdown-it, vue-markdown-loader, marked, vue-markdown, etc. These libraries are all very similar. Marked is used here, and highlight.js is used as the code highlighting library. The specific implementation steps are as follows: 1. Install dependent libraries. Open the command window under the vue project and enter the following command npminstallmarked-save//marked to convert markdown into htmlnpmins
 How to solve the problem that after the vue3 project is packaged and published to the server, the access page displays blank
May 17, 2023 am 08:19 AM
How to solve the problem that after the vue3 project is packaged and published to the server, the access page displays blank
May 17, 2023 am 08:19 AM
After the vue3 project is packaged and published to the server, the access page displays blank 1. The publicPath in the vue.config.js file is processed as follows: const{defineConfig}=require('@vue/cli-service') module.exports=defineConfig({publicPath :process.env.NODE_ENV==='production'?'./':'/&
 How to select an avatar and crop it in Vue3
May 29, 2023 am 10:22 AM
How to select an avatar and crop it in Vue3
May 29, 2023 am 10:22 AM
The final effect is to install the VueCropper component yarnaddvue-cropper@next. The above installation value is for Vue3. If it is Vue2 or you want to use other methods to reference, please visit its official npm address: official tutorial. It is also very simple to reference and use it in a component. You only need to introduce the corresponding component and its style file. I do not reference it globally here, but only introduce import{userInfoByRequest}from'../js/api' in my component file. import{VueCropper}from'vue-cropper&
 How to use vue3+ts+axios+pinia to achieve senseless refresh
May 25, 2023 pm 03:37 PM
How to use vue3+ts+axios+pinia to achieve senseless refresh
May 25, 2023 pm 03:37 PM
vue3+ts+axios+pinia realizes senseless refresh 1. First download aiXos and pinianpmipinia in the project--savenpminstallaxios--save2. Encapsulate axios request-----Download js-cookienpmiJS-cookie-s//Introduce aixosimporttype{AxiosRequestConfig ,AxiosResponse}from"axios";importaxiosfrom'axios';import{ElMess
 How to use Vue3 reusable components
May 20, 2023 pm 07:25 PM
How to use Vue3 reusable components
May 20, 2023 pm 07:25 PM
Preface Whether it is vue or react, when we encounter multiple repeated codes, we will think about how to reuse these codes instead of filling a file with a bunch of redundant codes. In fact, both vue and react can achieve reuse by extracting components, but if you encounter some small code fragments and you don’t want to extract another file, in comparison, react can be used in the same Declare the corresponding widget in the file, or implement it through renderfunction, such as: constDemo:FC=({msg})=>{returndemomsgis{msg}}constApp:FC=()=>{return(




