How to query and modify json data with Mysql
Query and modify json data
Use field->'$.json attribute' to query conditions
Use the json_extract function to query, json_extract(field, "$.json attributes")
To query based on the json array, use JSON_CONTAINS(field, JSON_OBJECT( 'json attribute', "content")): [{}]Query this form of json array
MySQL5.7 or above supports JSON operations and adds a JSON storage type
Generally, databases will use JSON type or TEXT type to store JSON type data
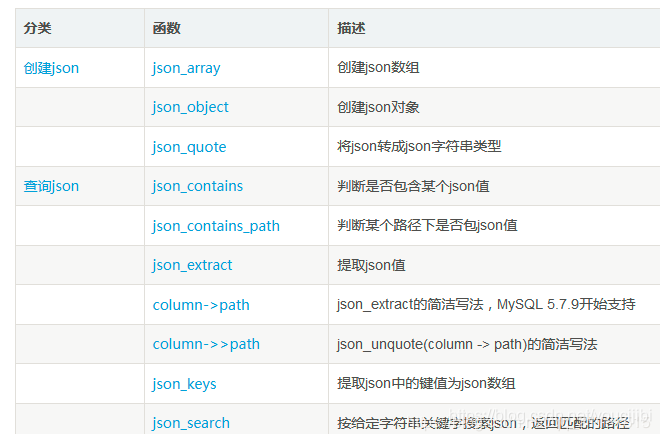
Several related functions
Example

I did not create the json field format here, but used text to store json.
Please note: If you want to use the JSON type, the data stored in the column must conform to the JSON format, otherwise an error will occur. 2) The JSON data type has no default value.
Insert json format data into this column:
{"age": "28", "pwd": "lisi", "name": "李四"}Query
1,
select * from `offcn_off_main` where json_extract(json_field,"$.name") = '李四'
2,
select * from `offcn_off_main` where json_field->'$.name' = '李四'
Use explain to see that the index cannot be used.
So it needs to be modified:
mysql does not natively support attribute indexing in json columns, but we can indirectly index certain items in json through mysql’s virtual columns. The principle of creating an index for an attribute is to create a virtual column for the attribute in json, and then create an index for the virtual column, thereby indirectly creating an index for the attribute.
In MySQL 5.7, two types of Generated Column are supported, namely Virtual Generated Column and Stored Generated Column. The former only saves the Generated Column in the data dictionary (metadata of the table) and does not store this column of data. Persist to disk; the latter will persist the Generated Column to disk instead of calculating it each time it is read. Obviously, the latter stores data that can be calculated from existing data, requires more disk space, and has no advantage over Virtual Column----(In fact, I think it still has an advantage, after all, it requires less query calculations. )
Therefore, in MySQL 5.7, the type of Generated Column is not specified, and the default is Virtual Column.
If you need Stored Generated Golumn, it may be more appropriate to create an index on Virtual Generated Column. Under normal circumstances, Virtual Generated Column is used, which is also the default method of MySQL.
The format is as follows:
fieldname <type> [ GENERATED ALWAYS ] AS ( <expression> ) [ VIRTUAL|STORED ] [ UNIQUE [KEY] ] [ [PRIMARY] KEY ] [ NOT NULL ] [ COMMENT <text> ]
So here I am:
ALTER TABLE 'off_main' `names_virtual` VARCHAR(20) GENERATED ALWAYS AS (`json_field` ->> '$.name') not null;
Please note: You can use the "»" operator to reference keys in JSON fields (KEY). In this example, the virtual field names_virtual has been defined as non-nullable. In actual work, it must be determined based on specific circumstances. Because JSON itself is a weakly structured data object. In other words, its structure is not fixed.
Add an index to the virtual field:
CREATE INDEX `names` ON `off_main`(`names_virtual`);
Note that if the virtual field is not added when the table is created, but added later, when adding the index, if the virtual field in some rows is null, But if it is set to not be null, then the index cannot be created successfully, and the prompt column can not be null.
After adding the index, please explain and you will see that the index is used, and the value of the virtual field will change with the The properties of the json field change automatically when modified.
Let’s take a look at the modification
update off_main set json_field = json_set(json_field,'$.phone', '132') WHERE id = 45 //同时修改多个 UPDATE offcn_off_main set json_field = json_set(json_field,'$.name',456,'$.age','bbb') WHERE id = 45
The json_set() method that exists will be overwritten, and the one that does not exist will be added.
Delete
UPDATE offcn_off_main set json_field = json_remove(json_field,'$.pwd','$.phone') WHERE id = 45
Insert
UPDATE offcn_off_main set json_field = json_insert(json_field,'$.pwd','111') WHERE id = 45
The difference between insert and update is that if the insert does not exist, it will be added, and if it exists, it will not be overwritten.
Mysql processes json Data
1. If the amount of data is small, copy the json data directly to the json field of mysql. If the data is too large, you can parse the json data through java and other background forms, and then write it to the database.
Query operation
select *,json->'$.features[0].geometry.rings' as rings from JSON;
Read part of the data from one table and store it in another table (one piece of data)
insert into DT_village(name, border) SELECT json->'$.features[0].attributes.CJQYMC',json->'$.features[0].geometry.rings' from JSON;
Read json data and write it to the database (at this time The method is executed in the form of a defined function, and the amount can be defined)
#清空数据库
TRUNCATE table DT_village;
#定义存储过程
delimiter //
DROP PROCEDURE IF EXISTS insert_test_val;
##num_limit 要插入数据的数量,rand_limit 最大随机的数值
CREATE PROCEDURE insert_test_val()
BEGIN
DECLARE i int default 0;
DECLARE a,b varchar(5000);
WHILE i<10 do
set a=CONCAT('$.features[',i,'].attributes.CJQYMC');
set b=CONCAT('$.features[',i,'].geometry.rings');
insert into DT_village(name, border) select
#json->'$.features[0].attributes.CJQYMC',json->'$.features[0].geometry.rings'
# (json->a),(json->b)
json_extract(json,a),json_extract(json,b)
from JSON;
set i = i + 1;
END WHILE;
END
//
#调用存储过程
call insert_test_val();Call the cursor to obtain a row in the jsosn data, and perform the insertion operation
delimiter //
drop procedure if exists StatisticStore;
CREATE PROCEDURE StatisticStore()
BEGIN
#创建接收游标数据的变量
declare j json;#存储json数据
DECLARE i int default 0; #创建总数变量,记录执行次数,控制循环
DECLARE a,b,c varchar(5000);#定义json数组中的某个数据的键值
#创建结束标志变量
declare done int default false;
#创建游标
declare cur cursor for select json from JSON where name = '1';
#指定游标循环结束时的返回值
declare continue HANDLER for not found set done = true;
#设置初始值
set a=CONCAT('$.features[',i,'].attributes.XZQDM');
set b=CONCAT('$.features[',i,'].attributes.XZQMC');
set c=CONCAT('$.features[',i,']');
#打开游标
open cur;
#开始循环游标里的数据
read_loop:loop
#根据游标当前指向的一条数据
fetch cur into j;
#判断游标的循环是否结束
if done then
leave read_loop;#跳出游标循环
end if;
#这里可以做任意你想做的操作
WHILE i<11 do
insert into dt_border(xzq_code,name,border) select
json_extract(j,a),json_extract(j,b),json_extract(j,c)
from JSON;
set i = i + 1;
END WHILE;
#结束游标循环
end loop;
#关闭游标
close cur;
#输出结果
select j,i;
END;
#调用存储过程
call StatisticStore();The above is the detailed content of How to query and modify json data with Mysql. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to use MySQL backup and restore in PHP?
Jun 03, 2024 pm 12:19 PM
How to use MySQL backup and restore in PHP?
Jun 03, 2024 pm 12:19 PM
Backing up and restoring a MySQL database in PHP can be achieved by following these steps: Back up the database: Use the mysqldump command to dump the database into a SQL file. Restore database: Use the mysql command to restore the database from SQL files.
 How to optimize MySQL query performance in PHP?
Jun 03, 2024 pm 08:11 PM
How to optimize MySQL query performance in PHP?
Jun 03, 2024 pm 08:11 PM
MySQL query performance can be optimized by building indexes that reduce lookup time from linear complexity to logarithmic complexity. Use PreparedStatements to prevent SQL injection and improve query performance. Limit query results and reduce the amount of data processed by the server. Optimize join queries, including using appropriate join types, creating indexes, and considering using subqueries. Analyze queries to identify bottlenecks; use caching to reduce database load; optimize PHP code to minimize overhead.
 How to insert data into a MySQL table using PHP?
Jun 02, 2024 pm 02:26 PM
How to insert data into a MySQL table using PHP?
Jun 02, 2024 pm 02:26 PM
How to insert data into MySQL table? Connect to the database: Use mysqli to establish a connection to the database. Prepare the SQL query: Write an INSERT statement to specify the columns and values to be inserted. Execute query: Use the query() method to execute the insertion query. If successful, a confirmation message will be output.
 How to create a MySQL table using PHP?
Jun 04, 2024 pm 01:57 PM
How to create a MySQL table using PHP?
Jun 04, 2024 pm 01:57 PM
Creating a MySQL table using PHP requires the following steps: Connect to the database. Create the database if it does not exist. Select a database. Create table. Execute the query. Close the connection.
 How to use MySQL stored procedures in PHP?
Jun 02, 2024 pm 02:13 PM
How to use MySQL stored procedures in PHP?
Jun 02, 2024 pm 02:13 PM
To use MySQL stored procedures in PHP: Use PDO or the MySQLi extension to connect to a MySQL database. Prepare the statement to call the stored procedure. Execute the stored procedure. Process the result set (if the stored procedure returns results). Close the database connection.
 How to fix mysql_native_password not loaded errors on MySQL 8.4
Dec 09, 2024 am 11:42 AM
How to fix mysql_native_password not loaded errors on MySQL 8.4
Dec 09, 2024 am 11:42 AM
One of the major changes introduced in MySQL 8.4 (the latest LTS release as of 2024) is that the "MySQL Native Password" plugin is no longer enabled by default. Further, MySQL 9.0 removes this plugin completely. This change affects PHP and other app
 The difference between oracle database and mysql
May 10, 2024 am 01:54 AM
The difference between oracle database and mysql
May 10, 2024 am 01:54 AM
Oracle database and MySQL are both databases based on the relational model, but Oracle is superior in terms of compatibility, scalability, data types and security; while MySQL focuses on speed and flexibility and is more suitable for small to medium-sized data sets. . ① Oracle provides a wide range of data types, ② provides advanced security features, ③ is suitable for enterprise-level applications; ① MySQL supports NoSQL data types, ② has fewer security measures, and ③ is suitable for small to medium-sized applications.
 How to delete data from MySQL table using PHP?
Jun 05, 2024 pm 12:40 PM
How to delete data from MySQL table using PHP?
Jun 05, 2024 pm 12:40 PM
PHP provides the following methods to delete data in MySQL tables: DELETE statement: used to delete rows matching conditions from the table. TRUNCATETABLE statement: used to clear all data in the table, including auto-incremented IDs. Practical case: You can delete users from the database using HTML forms and PHP code. The form submits the user ID, and the PHP code uses the DELETE statement to delete the record matching the ID from the users table.






