
Correlated subquery execution process
If the execution of a subquery depends on an external query, it is usually because the table in the subquery uses an external table. And conditional correlation is performed, so every time an external query is executed, the subquery must be recalculated. Such a subquery is called a correlated subquery. As each row of the main query is executed, the correlated subqueries are executed in row-by-row order.
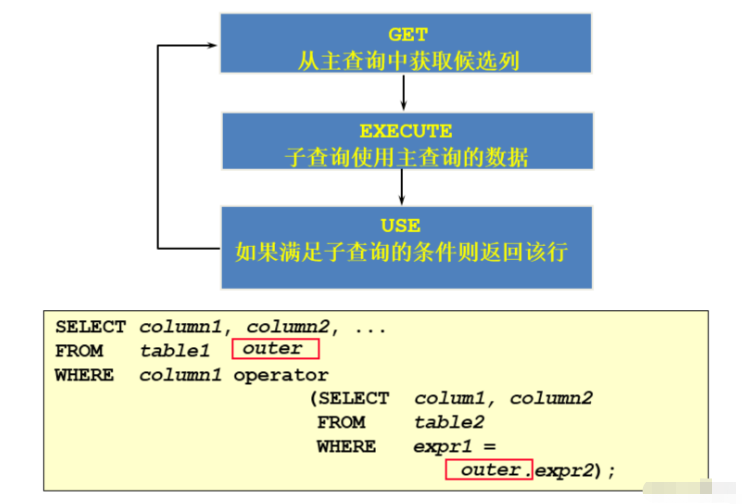
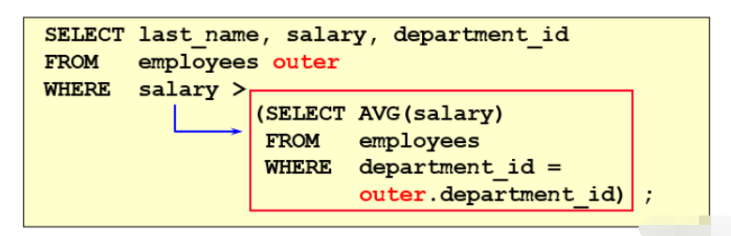
Description: Use the columns in the main query in the subquery
Title: Query the last_name, salary and sum of employees whose salary is greater than the average salary of the department Its department_id
Method 1: Related subquery
Use subquery in FROM
SELECT last_name,salary,e1.department_id FROM employees e1,(SELECT department_id,AVG(salary) dept_avg_sal FROM employees GROUP BY department_id) e2 WHERE e1.`department_id` = e2.department_id AND e2.dept_avg_sal < e1.`salary`;
from type subquery: subquery As part of from, the subquery must be quoted with (), and the subquery must be named
, and used as a "temporary virtual table".
Title: Query employee ID, salary, sorted by department_name
Use subquery in ORDER BY:
SELECT employee_id,salary FROM employees e ORDER BY ( SELECT department_name FROM departments d WHERE e.`department_id` = d.`department_id` );
Associated subqueries are usually used together with the EXISTS operator to check whether there are rows that meet the conditions in the subquery.
If there is no row that satisfies the condition in the subquery:
The condition returns FALSE
Continue to search in the subquery
If in the subquery There are rows that meet the condition:
Do not continue to search in the subquery
The condition returns TRUE
NOT EXISTS keyword indicates that if a certain condition does not exist, TRUE is returned, otherwise Return FALSE.
Title: Query the employee_id, last_name, job_id, department_id information of the company manager
SELECT employee_id, last_name, job_id, department_id FROM employees e1 WHERE EXISTS ( SELECT * FROM employees e2 WHERE e2.manager_id = e1.employee_id);
The subquery is actually a conditional judgment after querying through the unknown table, while the self-join is based on the known Its own data table
performs conditional judgment, so self-join processing is optimized in most DBMS.
The above is the detailed content of How to use MySQL subquery. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




