How Redis speeds up Spark
Apache Spark is increasingly becoming a model for next-generation big data processing tools.. By borrowing from open source algorithms and distributing processing tasks across clusters of compute nodes, Spark and Hadoop generation frameworks easily outperform both in the types of data analysis they can perform on a single platform and in the speed with which they can perform these tasks. over traditional frameworks. Spark uses memory to process data, making it significantly faster (up to 100 times faster) than disk-based Hadoop.
But with a little help, Spark can run even faster. If you combine Spark with Redis (a popular in-memory data structure storage technology), you can once again significantly improve the performance of processing analysis tasks. This is due to Redis' optimized data structure and its ability to minimize complexity and overhead when performing operations. Using connectors to connect to Redis' data structures and APIs can further speed up Spark.
How big is the speedup? If Redis is used in conjunction with Spark, it turns out that processing the data (in order to analyze the time series data described below) is faster than Spark simply using in-process memory or off-heap cache to store the data. 45 times – not 45% faster, but a full 45 times faster!
The importance of analytical transaction speed is growing as many companies need to enable analytics as fast as business transactions. As more and more decisions become automated, the analytics needed to drive those decisions should happen in real time. Apache Spark is an excellent general-purpose data processing framework; although it is not completely real-time, it is a big step towards making data useful in a more timely manner.
Spark uses Resilient Distributed Datasets (RDDs), which can be stored in volatile memory or in a persistent storage system like HDFS. All RDDs distributed across the nodes of the Spark cluster remain unchanged, but other RDDs can be created through transformation operations.
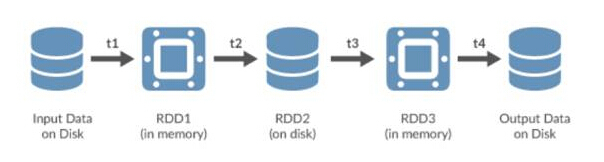
Spark RDD
RDD is an important abstract object in Spark. They represent a fault-tolerant way to efficiently present data to an iterative process. Using in-memory processing means that processing time will be reduced by orders of magnitude compared to using HDFS and MapReduce.
Redis is specially designed for high performance. Sub-millisecond latency is the result of optimized data structures that improve efficiency by allowing operations to be performed close to where the data is stored. This data structure not only efficiently utilizes memory and reduces application complexity, but also reduces network overhead, bandwidth consumption, and processing time. Redis supports multiple data structures, including strings, sets, sorted sets, hashes, bitmaps, hyperloglogs, and geospatial indexes. Redis data structures are like Lego bricks, providing developers with simple channels to implement complex functions.
To visually show how this data structure can simplify the processing time and complexity of applications, we might as well take the ordered set (Sorted Set) data structure as an example. An ordered set is basically a set of members ordered by score.
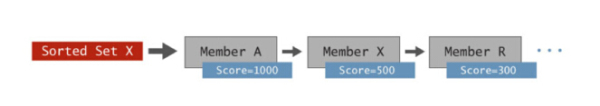
Redis sorted collection
You can store many types of data here, and they are automatically sorted by scores. Common data types stored in ordered collections include: time series data such as items (by price), product names (by quantity), stock prices, and sensor readings such as timestamps.
The charm of ordered collections lies in Redis's built-in operations, which allow range queries, intersection of multiple ordered collections, retrieval by member level and score, and more transactions to be executed simply with extreme speed. It can also be executed at scale. Not only do built-in operations save code that needs to be written, but in-memory execution reduces network latency and saves bandwidth, enabling high throughput with sub-millisecond latencies. If you use sorted sets to analyze time series data, you can often achieve performance improvements of several orders of magnitude compared to other in-memory key/value storage systems or disk-based databases.
The Spark-Redis connector was developed by the Redis team to improve Spark's analysis capabilities. This package enables Spark to use Redis as one of its data sources. Through this connector, Spark can directly access Redis's data structure, thereby significantly improving the performance of various types of analysis.

Spark Redis Connector
In order to demonstrate the benefits brought to Spark, the Redis team decided to use several different scenarios Execute time slice (range) queries to horizontally compare time series analysis in Spark. These scenarios include: Spark stores all data in in-heap memory, Spark uses Tachyon as an off-heap cache, Spark uses HDFS, and a combination of Spark and Redis.
The Redis team used Cloudera's Spark time series package to build a Spark-Redis time series package that uses Redis ordered collections to speed up time series analysis. In addition to providing all the data structures that allow Spark to access Redis, this package also performs two additional tasks
Automatically ensure that the Redis node is consistent with the Spark cluster, thereby ensuring that each Spark node uses local Redis data, thus optimizing latency.
Integrate with the Spark dataframe and data source API to automatically convert Spark SQL queries into the most efficient retrieval mechanism for data in Redis.
Simply put, this means that users do not have to worry about the operational consistency between Spark and Redis and can continue to use Spark SQL for analysis, while greatly improving query performance.
The time series data used in this horizontal comparison includes: randomly generated financial data and 1024 stocks per day for 32 years. Each stock is represented by its own ordered set, the score is the date, and the data members include the opening price, last price, last price, closing price, trading volume, and adjusted closing price. The following image depicts the data representation in a Redis sorted set used for Spark analysis:
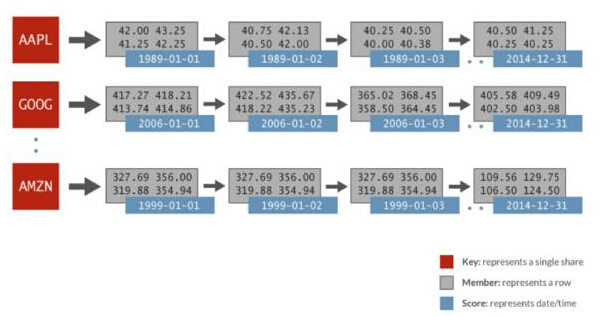
Spark Redis time series
in the above In the example, for the ordered set AAPL, there are scores represented for each day (1989-01-01), and multiple values for the whole day represented as a related row. Just use a simple ZRANGEBYSCORE command in Redis to do this: get all the values for a certain time slice, and therefore get all the stock prices in the specified date range. Redis can perform these types of queries faster than other key/value storage systems, up to 100 times faster.
This horizontal comparison confirms the performance improvement. It was found that Spark using Redis can perform time slice queries 135 times faster than Spark using HDFS, and 45 times faster than Spark using on-heap (process) memory or Spark using Tachyon as an off-heap cache. The figure below shows the average execution time compared for different scenarios:
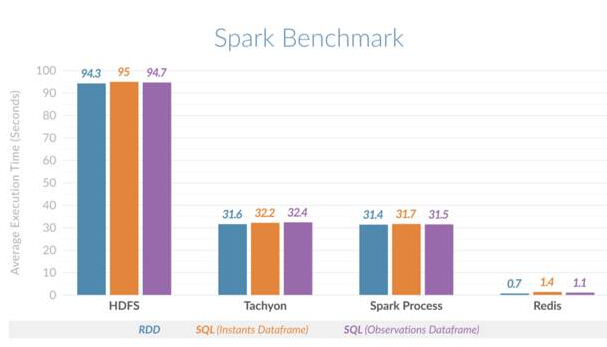
Spark Redis Horizontal Comparison
This guide will go step by step Guide you to install the standard Spark cluster and Spark-Redis package. Through a simple word counting example, it demonstrates how to integrate the use of Spark and Redis. After you have tried Spark and the Spark-Redis package, you can further explore more scenarios that utilize other Redis data structures.
While ordered sets are well suited for time series data, Redis’ other data structures (such as sets, lists, and geospatial indexes) can further enrich Spark analysis. Imagine this: a Spark process is trying to figure out which areas are suitable for launching a new product, taking into account factors such as crowd preferences and distance from the city center to optimize the launch effect. Imagine how data structures like geospatial indexes and collections with built-in analytics capabilities could significantly speed up this process. The Spark-Redis combination has great application prospects.
Spark provides a wide range of analysis capabilities, including SQL, machine learning, graph computing and Spark Streaming. Using Spark's in-memory processing capabilities only gets you up to a certain scale. However, with Redis, you can go one step further: not only can you improve performance by using Redis's data structure, but you can also expand Spark more easily, that is, by making full use of the shared distributed memory data storage mechanism provided by Redis to process hundreds of Thousands of records, or even billions of records.
This example of time series is just the beginning. Using Redis data structures for machine learning and graph analysis is also expected to bring significant execution time benefits to these workloads.
The above is the detailed content of How Redis speeds up Spark. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
Redis cluster mode deploys Redis instances to multiple servers through sharding, improving scalability and availability. The construction steps are as follows: Create odd Redis instances with different ports; Create 3 sentinel instances, monitor Redis instances and failover; configure sentinel configuration files, add monitoring Redis instance information and failover settings; configure Redis instance configuration files, enable cluster mode and specify the cluster information file path; create nodes.conf file, containing information of each Redis instance; start the cluster, execute the create command to create a cluster and specify the number of replicas; log in to the cluster to execute the CLUSTER INFO command to verify the cluster status; make
 How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear Redis data: Use the FLUSHALL command to clear all key values. Use the FLUSHDB command to clear the key value of the currently selected database. Use SELECT to switch databases, and then use FLUSHDB to clear multiple databases. Use the DEL command to delete a specific key. Use the redis-cli tool to clear the data.
 How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
To read a queue from Redis, you need to get the queue name, read the elements using the LPOP command, and process the empty queue. The specific steps are as follows: Get the queue name: name it with the prefix of "queue:" such as "queue:my-queue". Use the LPOP command: Eject the element from the head of the queue and return its value, such as LPOP queue:my-queue. Processing empty queues: If the queue is empty, LPOP returns nil, and you can check whether the queue exists before reading the element.
 How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
Using the Redis directive requires the following steps: Open the Redis client. Enter the command (verb key value). Provides the required parameters (varies from instruction to instruction). Press Enter to execute the command. Redis returns a response indicating the result of the operation (usually OK or -ERR).
 How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
Using Redis to lock operations requires obtaining the lock through the SETNX command, and then using the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time. The specific steps are: (1) Use the SETNX command to try to set a key-value pair; (2) Use the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time for the lock; (3) Use the DEL command to delete the lock when the lock is no longer needed.
 How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
The best way to understand Redis source code is to go step by step: get familiar with the basics of Redis. Select a specific module or function as the starting point. Start with the entry point of the module or function and view the code line by line. View the code through the function call chain. Be familiar with the underlying data structures used by Redis. Identify the algorithm used by Redis.
 How to solve data loss with redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:24 PM
How to solve data loss with redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:24 PM
Redis data loss causes include memory failures, power outages, human errors, and hardware failures. The solutions are: 1. Store data to disk with RDB or AOF persistence; 2. Copy to multiple servers for high availability; 3. HA with Redis Sentinel or Redis Cluster; 4. Create snapshots to back up data; 5. Implement best practices such as persistence, replication, snapshots, monitoring, and security measures.
 How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
Use the Redis command line tool (redis-cli) to manage and operate Redis through the following steps: Connect to the server, specify the address and port. Send commands to the server using the command name and parameters. Use the HELP command to view help information for a specific command. Use the QUIT command to exit the command line tool.




