
Problems with MySql Memcached architecture
Actual MySQL is suitable for massive data storage, and hotspot data is loaded into the cache through Memcached , to accelerate access, many companies have used such an architecture, but as the amount of business data continues to increase, and the number of visits continues to grow, we have encountered many problems:
1. MySQL needs to be continuously dismantled Memcached also needs to continue to expand as the database and tables are removed, and the expansion and maintenance work takes up a lot of development time.
2. Data consistency issues between Memcached and MySQL database.
3. Memcached data hit rate is low or the machine is down. A large number of accesses directly penetrate to the DB, which MySQL cannot support.
4. Cross-machine room cache synchronization problem.
Many NoSQL are blooming, how to choose
In recent years, many various NoSQL products have emerged in the industry, so how can we use these products correctly? , maximizing its strengths is a question that we need to study and think about in depth. In the final analysis, the most important thing is to understand the positioning of these products and understand the tradeoffs of each product, so as to maximize strengths and avoid weaknesses in practical applications. Generally speaking, these NoSQL is mainly used to solve the following problems
1. Small amount of data storage, high-speed read and write access. Such products ensure high-speed access by keeping all data in-momery, and at the same time provide the function of data landing. In fact, this is the main applicable scenario of Redis. [Related recommendations: Redis video tutorial]
2. Massive data storage, distributed system support, data consistency guarantee, and convenient addition/deletion of cluster nodes.
3. The most representative ideas in this regard are the two papers dynamo and bigtable. The former is a completely centerless design. Cluster information is transmitted between nodes through gossip, and the data ensures final consistency. The latter is a centralized solution design that ensures strong consistency through a distributed lock service, and data writing The memory and redo log are written first, and then regularly compat and merged to the disk, optimizing random writes into sequential writes to improve write performance.
4. Free mode structure, automatic sharding, etc. For example, some common document databases currently support schema-free, directly store json format data, and support auto-sharding and other functions, such as mongodb.
Redis is most suitable for all data in-momory scenarios. Although Redis also provides persistence functions, it is actually more of a disk-backed function, which is quite different from persistence in the traditional sense. , then you may have questions. It seems that Redis is more like an enhanced version of Memcached, so when to use Memcached and when to use Redis?
If you simply compare the difference between Redis and Memcached, most of them will Get the following views:
1. Redis not only supports simple k/v type data, but also provides storage of data structures such as list, set, zset, hash, etc.
2. Redis supports data backup, that is, data backup in master-slave mode.
3. Redis supports data persistence, which can keep data in memory on disk and can be loaded again for use when restarting.
Use a picture to understand how these different data types are described in Redis’s internal memory management:
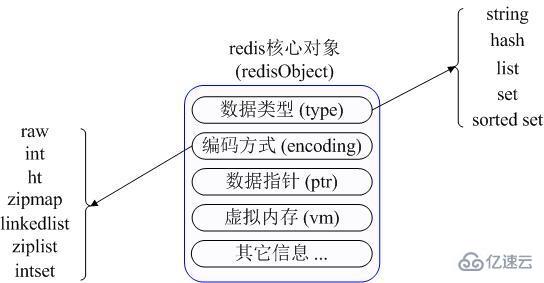
First, Redis uses a redisObject object internally to represent it. For all keys and values, the most important information of redisObject is shown in the figure above: type represents the specific data type of a value object, and encoding is the way different data types are stored inside redis. For example: type=string represents the value stored. An ordinary string, then the corresponding encoding can be raw or int. If it is int, it means that the actual redis internally stores and represents the string according to the numerical class. Of course, the premise is that the string itself can be represented by numerical values, such as :A string like "123" "456".
The vm field needs special explanation here. Only when the virtual memory function of Redis is turned on can this field actually allocate memory. This function is turned off by default. From the above figure, we can find that Redis uses redisObject to represent all key/value data, which is a waste of memory. Of course, these memory management costs are mainly to provide a unified management interface for different data types of Redis. The actual author also provides Various methods help us save memory usage as much as possible, which we will discuss in detail later.
Redis supports 5 data types: string (string), hash (hash), list (list), set (set) and zset (sorted set: ordered set) .
① string is the most basic type of redis. You can understand it as exactly the same type as Memcached. One key corresponds to one value. In fact, value is not only String, but also a number. The string type is binary safe. This means that the string of redis can contain any data. For example, jpg images or serialized objects. The string type is the most basic data type of Redis. The string type value can store up to 512MB.
Commonly used commands: get, set, incr, decr, mget, etc.
Application scenarios: String is the most commonly used data type, and ordinary key/value storage can be classified into this category, which means that the current functions of Memcached can be fully realized and more efficient. Redis also provides functions such as scheduled persistence, operation logs, and replication. In addition to providing the same get, set, incr, decr and other operations as Memcached, Redis also provides the following operations:
Get the string length
Append content to the string
Set and get a certain content of the string
Set and get a certain bit of the string (bit)
Set the contents of a series of strings in batches
Usage scenario: regular key-value caching application. Regular counts: number of Weibo posts, number of fans.
Implementation method: String is stored in redis as a string by default, which is referenced by redisObject. When encountering incr, decr and other operations, it will be converted into a numerical type for calculation. At this time, the encoding field of redisObject is int. .
redis 127.0.0.1:6379> SET name "runoob" "OK"redis 127.0.0.1:6379> GET name "runoob"
In the above example we used the SET and GET commands of Redis. The key is name and the corresponding value is runoob.
Note: A key can store up to 512MB.
② Redis hash is a collection of key-value (key => value) pairs. Redis hash is a mapping table of string type fields and values. Hash is particularly suitable for storing objects.
Commonly used commands: hget, hset, hgetall, etc.
Application scenario: Let’s give a simple example to describe the application scenario of Hash. For example, we want to store a user information object data, including the following information:
The user ID is the key to be searched, and the storage The value user object contains name, age, birthday and other information. If it is stored with an ordinary key/value structure, there are two main storage methods:
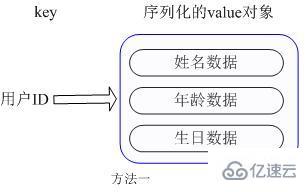
The first one The method uses the user ID as the search key, encapsulates other information into an object and stores it in a serialized manner. The disadvantage of this method is that it increases the overhead of serialization/deserialization, and when one of the information needs to be modified, The entire object needs to be retrieved, and the modification operation needs to protect concurrency, introducing complex issues such as CAS.
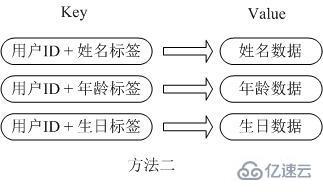
The second method is to store as many key-value pairs as there are members in the user information object, and use the name of the attribute corresponding to the user ID as a unique identifier to obtain it. Although serialization overhead and concurrency issues are eliminated for the value of the corresponding attribute, the user ID is stored repeatedly. If there is a large amount of such data, the memory waste is still very considerable.
Then the Hash provided by Redis solves this problem very well. The Hash of Redis actually stores the value internally as a HashMap, and provides an interface for direct access to the members of this Map, as shown below:
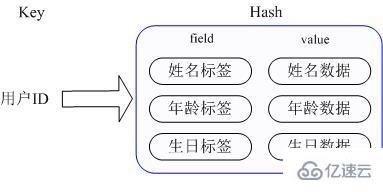
That is to say, the key is still the user ID, the value is a Map, the key of this Map is the attribute name of the member, and the value is the attribute value, so that the data can be modified and accessed You can directly use the key of its internal Map (the key of the internal Map is called field in Redis), that is, you can operate the corresponding attribute data through the key (user ID) field (attribute label). There is no need to store data repeatedly, and It will not cause problems with serialization and concurrent modification control, and solves the problem very well.
It should be noted here that Redis provides an interface (hgetall) to directly obtain all attribute data. However, if there are many members of the internal Map, it involves traversing the entire internal Map. Due to the Redis single-threaded model Because of this, this traversal operation may be time-consuming, and other client requests will not respond at all. This requires special attention.
Usage scenario: Store some change data, such as user information, etc.
Implementation method: As mentioned above, the corresponding value of Redis Hash is actually a HashMap. In fact, there are two different implementations. When the Hash has fewer members, Redis will use a one-dimensional array-like method to save memory. To compactly store, instead of using the real HashMap structure, the encoding of the corresponding value redisObject is zipmap. When the number of members increases, it will automatically be converted into a real HashMap, and the encoding is ht.
redis> HSET myhash field1 "Hello" field2 "World" "OK" redis> HGET myhash field1 "Hello" redis> HGET myhash field2 "World"
实例中我们使用了 Redis HMSET, HGET 命令,HMSET 设置了两个 field=>value 对, HGET 获取对应 field 对应的 value。每个 hash 可以存储 232 -1 键值对(40多亿)。
③ Redis list 列表是简单的字符串列表,按照插入顺序排序。你可以添加一个元素到列表的头部(左边)或者尾部(右边)。
常用命令:lpush(添加左边元素),rpush,lpop(移除左边第一个元素),rpop,lrange(获取列表片段,LRANGE key start stop)等。
应用场景:Redis list的应用场景非常多,也是Redis最重要的数据结构之一,比如twitter的关注列表,粉丝列表等都可以用Redis的list结构来实现。
List 就是链表,相信略有数据结构知识的人都应该能理解其结构。使用List结构,我们可以轻松地实现最新消息排行等功能。List的另一个应用就是消息队列,
可以利用List的PUSH操作,将任务存在List中,然后工作线程再用POP操作将任务取出进行执行。Redis还提供了操作List中某一段的api,你可以直接查询,删除List中某一段的元素。
实现方式:Redis list的实现为一个双向链表,即可以支持反向查找和遍历,更方便操作,不过带来了部分额外的内存开销,Redis内部的很多实现,包括发送缓冲队列等也都是用的这个数据结构。
Redis的list是每个子元素都是String类型的双向链表,可以通过push和pop操作从列表的头部或者尾部添加或者删除元素,这样List即可以作为栈,也可以作为队列。 获取越接近两端的元素速度越快,但通过索引访问时会比较慢。
使用场景:
消息队列系统:使用list可以构建队列系统,使用sorted set甚至可以构建有优先级的队列系统。比如:将Redis用作日志收集器,实际上还是一个队列,多个端点将日志信息写入Redis,然后一个worker统一将所有日志写到磁盘。
取最新N个数据的操作:记录前N个最新登陆的用户Id列表,超出的范围可以从数据库中获得。
//把当前登录人添加到链表里
ret = r.lpush("login:last_login_times", uid)
//保持链表只有N位
ret = redis.ltrim("login:last_login_times", 0, N-1)
//获得前N个最新登陆的用户Id列表
last_login_list = r.lrange("login:last_login_times", 0, N-1)比如微博:
我们在Redis中使用了常驻缓存来存储最新的微博ID,并且该缓存会一直更新。但是我们做了限制不能超过5000个ID,因此我们的获取ID函数会一直询问Redis。只有在start/count参数超出了这个范围的时候,才需要去访问数据库。我们的系统不会像传统方式那样“刷新”缓存,Redis实例中的信息永远是一致的。SQL数据库(或是硬盘上的其他类型数据库)只是在用户需要获取“很远”的数据时才会被触发,而主页或第一个评论页是不会麻烦到硬盘上的数据库了。
redis 127.0.0.1:6379> lpush runoob redis (integer) 1 redis 127.0.0.1:6379> lpush runoob mongodb (integer) 2 redis 127.0.0.1:6379> lpush runoob rabitmq (integer) 3 redis 127.0.0.1:6379> lrange runoob 0 10 1) "rabitmq" 2) "mongodb" 3) "redis" redis 127.0.0.1:6379>
列表最多可存储 232 - 1 元素 (4294967295, 每个列表可存储40多亿)。
④ Redis set是string类型的无序集合。集合是通过hashtable实现的,概念和数学中个的集合基本类似,可以交集,并集,差集等等,set中的元素是没有顺序的。所以添加,删除,查找的复杂度都是O(1)。
sadd 命令:添加一个 string 元素到 key 对应的 set 集合中,成功返回1,如果元素已经在集合中返回 0,如果 key 对应的 set 不存在则返回错误。
常用命令:sadd,spop,smembers,sunion 等。
应用场景:Redis set对外提供的功能与list类似是一个列表的功能,特殊之处在于set是可以自动排重的,当你需要存储一个列表数据,又不希望出现重复数据时,set是一个很好的选择,并且set提供了判断某个成员是否在一个set集合内的重要接口,这个也是list所不能提供的。
Set 就是一个集合,集合的概念就是一堆不重复值的组合。利用Redis提供的Set数据结构,可以存储一些集合性的数据。
可以将一个微博用户的所有关注者和粉丝分别存储为集合。Redis还为集合提供了求交集、并集、差集等操作,可以非常方便的实现如共同关注、共同喜好、二度好友等功能,对上面的所有集合操作,你还可以使用不同的命令选择将结果返回给客户端还是存集到一个新的集合中。
实现方式: set 的内部实现是一个 value永远为null的HashMap,实际就是通过计算hash的方式来快速排重的,这也是set能提供判断一个成员是否在集合内的原因。
使用场景:
①交集,并集,差集:(Set)
//book表存储book名称
set book:1:name ”The Ruby Programming Language”
set book:2:name ”Ruby on rail”
set book:3:name ”Programming Erlang”
//tag表使用集合来存储数据,因为集合擅长求交集、并集
sadd tag:ruby 1
sadd tag:ruby 2
sadd tag:web 2
sadd tag:erlang 3
//即属于ruby又属于web的书?
inter_list = redis.sinter("tag.web", "tag:ruby")
//即属于ruby,但不属于web的书?
inter_list = redis.sdiff("tag.ruby", "tag:web")
//属于ruby和属于web的书的合集?
inter_list = redis.sunion("tag.ruby", "tag:web")②获取某段时间所有数据去重值
这个使用Redis的set数据结构最合适了,只需要不断地将数据往set中扔就行了,set意为集合,所以会自动排重。
sadd key member
redis 127.0.0.1:6379> sadd runoob redis (integer) 1 redis 127.0.0.1:6379> sadd runoob mongodb (integer) 1 redis 127.0.0.1:6379> sadd runoob rabitmq (integer) 1 redis 127.0.0.1:6379> sadd runoob rabitmq (integer) 0 redis 127.0.0.1:6379> smembers runoob 1) "redis" 2) "rabitmq" 3) "mongodb"
注意:以上实例中 rabitmq 添加了两次,但根据集合内元素的唯一性,第二次插入的元素将被忽略。集合中最大的成员数为 232 - 1(4294967295, 每个集合可存储40多亿个成员)。
⑤ Redis zset 和 set 一样也是string类型元素的集合,且不允许重复的成员。
zadd 命令:添加元素到集合,元素在集合中存在则更新对应score。
常用命令:zadd,zrange,zrem,zcard等
使用场景:Redis sorted set的使用场景与set类似,区别是set不是自动有序的,而sorted set可以通过用户额外提供一个优先级(score)的参数来为成员排序,并且是插入有序的,即自动排序。当你需要一个有序的并且不重复的集合列表,那么可以选择sorted set数据结构,比如twitter 的public timeline可以以发表时间作为score来存储,这样获取时就是自动按时间排好序的。和Set相比,Sorted Set关联了一个double类型权重参数score,使得集合中的元素能够按score进行有序排列,redis正是通过分数来为集合中的成员进行从小到大的排序。zset的成员是唯一的,但分数(score)却可以重复。比如一个存储全班同学成绩的Sorted Set,其集合value可以是同学的学号,而score就可以是其考试得分,这样在数据插入集合的时候,就已经进行了天然的排序。另外还可以用Sorted Set来做带权重的队列,比如普通消息的score为1,重要消息的score为2,然后工作线程可以选择按score的倒序来获取工作任务。让重要的任务优先执行。
实现方式:Redis sorted set的内部使用HashMap和跳跃表(SkipList)来保证数据的存储和有序,HashMap里放的是成员到score的映射,而跳跃表里存放的是所有的成员,排序依据是HashMap里存的score,使用跳跃表的结构可以获得比较高的查找效率,并且在实现上比较简单。
zadd key score member
redis 127.0.0.1:6379> zadd runoob 0 redis (integer) 1 redis 127.0.0.1:6379> zadd runoob 0 mongodb (integer) 1 redis 127.0.0.1:6379> zadd runoob 0 rabitmq (integer) 1 redis 127.0.0.1:6379> zadd runoob 0 rabitmq (integer) 0 redis 127.0.0.1:6379> > ZRANGEBYSCORE runoob 0 1000 1) "mongodb" 2) "rabitmq" 3) "redis"
各个数据类型应用场景:
| 类型 | 简介 | 特性 | 场景 |
|---|---|---|---|
| String(字符串) | 二进制安全 | 可以包含任何数据,比如jpg图片或者序列化的对象,一个键最大能存储512M | --- |
| Hash(字典) | 键值对集合,即编程语言中的Map类型 | 适合存储对象,并且可以像数据库中update一个属性一样只修改某一项属性值(Memcached中需要取出整个字符串反序列化成对象修改完再序列化存回去) | 存储、读取、修改用户属性 |
| List(列表) | 链表(双向链表) | 增删快,提供了操作某一段元素的API | 1、最新消息排行等功能(比如朋友圈的时间线) 2、消息队列 |
| Set(集合) | 哈希表实现,元素不重复 | 1、添加、删除、查找的复杂度都是O(1) 2、为集合提供了求交集、并集、差集等操作 | 1、共同好友 2、利用唯一性,统计访问网站的所有独立ip 3、好友推荐时,根据tag求交集,大于某个阈值就可以推荐 |
| Sorted Set(有序集合) | 将Set中的元素增加一个权重参数score,元素按score有序排列 | 数据插入集合时,已经进行天然排序 | 1、排行榜 2、带权重的消息队列 |
Redis在很多方面与其他数据库解决方案不同:它使用内存提供主存储支持,而仅使用硬盘做持久性的存储;它的数据模型非常独特,用的是单线程。你可以在开发环境中使用Redis的功能,而不必切换到Redis。
转向Redis当然也是可取的,许多开发者从一开始就把Redis作为首选数据库;但设想如果你的开发环境已经搭建好,应用已经在上面运行了,那么更换数据库框架显然不那么容易。另外在一些需要大容量数据集的应用,Redis也并不适合,因为它的数据集不会超过系统可用的内存。所以如果你有大数据应用,而且主要是读取访问模式,那么Redis并不是正确的选择。
然而我喜欢Redis的一点就是你可以把它融入到你的系统中来,这就能够解决很多问题,比如那些你现有的数据库处理起来感到缓慢的任务。这些你就可以通过Redis来进行优化,或者为应用创建些新的功能。在本文中,我就想探讨一些怎样将Redis加入到现有的环境中,并利用它的原语命令等功能来解决 传统环境中碰到的一些常见问题。在这些例子中,Redis都不是作为首选数据库。
1、显示最新的项目列表
下面这个语句常用来显示最新项目,随着数据多了,查询毫无疑问会越来越慢。
SELECT * FROM foo WHERE ... ORDER BY time DESC LIMIT 10
在Web应用中,“列出最新的回复”之类的查询非常普遍,这通常会带来可扩展性问题。这令人沮丧,因为项目本来就是按这个顺序被创建的,但要输出这个顺序却不得不进行排序操作。
类似的问题就可以用Redis来解决。举个例子,我们的一个Web应用需要展示用户最新发布的20条评论。如果要查看更多的评论,可以单击最新评论旁边的“显示全部”链接。
我们假设数据库中的每条评论都有一个唯一的递增的ID字段。我们可以使用分页来制作主页和评论页,使用Redis的模板,每次新评论发表时,我们会将它的ID添加到一个Redis列表:
LPUSH latest.comments <ID>
我们将列表裁剪为指定长度,因此Redis只需要保存最新的5000条评论:
LTRIM latest.comments 0 5000
每次我们需要获取最新评论的项目范围时,我们调用一个函数来完成(使用伪代码):
FUNCTION get_latest_comments(start, num_items):
id_list = redis.lrange("latest.comments",start,start+num_items - 1)
IF id_list.length < num_items
id_list = SQL_DB("SELECT ... ORDER BY time LIMIT ...")
END
RETURN id_list
END这里我们做的很简单。在Redis中我们的最新ID使用了常驻缓存,这是一直更新的。由于我们设置了5000个ID的限制,因此获取ID函数会持续向Redis查询。只有在start/count参数超出了这个范围的时候,才需要去访问数据库。我们的系统不会像传统方式那样“刷新”缓存,Redis实例中的信息永远是一致的。SQL数据库(或是硬盘上的其他类型数据库)只是在用户需要获取“很远”的数据时才会被触发,而主页或第一个评论页是不会麻烦到硬盘上的数据库了。
2、删除与过滤
我们可以使用LREM来删除评论。如果删除操作很少,可以直接跳过评论入口并报告该评论已被删除。
redis 127.0.0.1:6379> LREM KEY_NAME COUNT VALUE
有些时候你想要给不同的列表附加上不同的过滤器。如果限制了过滤器的数量,你可以为每个不同的过滤器使用独立的Redis列表。Redis可以使用很少的内存来处理数百万条项目,因为每个列表只有5000个项目。
3、排行榜相关
另一个很普遍的需求是各种数据库的数据并非存储在内存中,因此在按得分排序以及实时更新这些几乎每秒钟都需要更新的功能上数据库的性能不够理想。
典型的比如那些在线游戏的排行榜,比如一个Facebook的游戏,根据得分你通常想要:
- 列出前100名高分选手
- 列出某用户当前的全球排名
这些操作对于Redis来说小菜一碟,即使你有几百万个用户,每分钟都会有几百万个新的得分。
模式是这样的,每次获得新得分时,我们用这样的代码:
ZADD leaderboard <score> <username>
你可能用userID来取代username,这取决于你是怎么设计的。
得到前100名高分用户很简单:ZREVRANGE leaderboard 0 99。
用户的全球排名也相似,只需要:ZRANK leaderboard
4、按照用户投票和时间排序
排行榜的一种常见变体模式就像Reddit或Hacker News用的那样,新闻按照类似下面的公式根据得分来排序:
score = points / time^alpha
随着用户投票,新闻会被逐渐展示出来,但时间的因素会逐渐使新闻消失。下面是我们的模式,当然算法由你决定。
模式是这样的,开始时先观察那些可能是最新的项目,例如首页上的1000条新闻都是候选者,因此我们先忽视掉其他的,这实现起来很简单。
每次新的新闻贴上来后,我们将ID添加到列表中,使用LPUSH + LTRIM,确保只取出最新的1000条项目。
这项后台任务会获取该列表,并连续计算其中每一篇新闻的最终得分。计算结果由ZADD命令按照新的顺序填充生成列表,老新闻则被清除。这里的关键思路是排序工作是由后台任务来完成的。
5、处理过期项目
另一种常用的项目排序是按照时间排序。我们使用unix时间作为得分即可。
模式如下:
我们会将每个新项目添加到排序集合中,这个集合在我们的非Redis数据库中。我们使用的是时间相关属性,包括current_time和time_to_live。
- 另一项后台任务使用ZRANGE…SCORES查询排序集合,取出最新的10个项目。如果发现unix时间已经过期,则在数据库中删除条目。
6、计数
Redis是一个很好的计数器,这要感谢INCRBY和其他相似命令。
我相信你曾许多次想要给数据库加上新的计数器,用来获取统计或显示新信息,但是最后却由于写入敏感而不得不放弃它们。
好了,现在使用Redis就不需要再担心了。有了原子递增(atomic increment),你可以放心的加上各种计数,用GETSET重置,或者是让它们过期。
例如这样操作:
INCR user:<id> EXPIRE user:<id> 60
你可以计算出最近用户在页面间停顿不超过60秒的页面浏览量,当计数达到比如20时,就可以显示出某些条幅提示,或是其它你想显示的东西。
7、特定时间内的特定项目
另一项对于其他数据库很难,但Redis做起来却轻而易举的事就是统计在某段特点时间里有多少特定用户访问了某个特定资源。比如我想要知道某些特定的注册用户或IP地址,他们到底有多少访问了某篇文章。
每次我获得一次新的页面浏览时我只需要这样做:
SADD page:day1:<page_id> <user_id>
当然你可能想用unix时间替换day1,比如time()-(time()%3600*24)等等。
想知道特定用户的数量吗?只需要使用
SCARD page:day1:<page_id>
需要测试某个特定用户是否访问了这个页面?
SISMEMBER page:day1:<page_id>
8、实时分析正在发生的情况,用于数据统计与防止垃圾邮件等
我们只做了几个例子,但如果你研究Redis的命令集,并且组合一下,就能获得大量的实时分析方法,有效而且非常省力。使用Redis原语命令,更容易实施垃圾邮件过滤系统或其他实时跟踪系统。
9、Pub/Sub
Redis的发布/订阅功能极为简单,稳定可靠且高效。支持模式匹配,能够实时订阅与取消频道。
10、队列
你应该已经注意到像list push和list pop这样的Redis命令能够很方便的执行队列操作了,但能做的可不止这些:比如Redis还有list pop的变体命令,能够在列表为空时阻塞队列。
现代的互联网应用大量地使用了消息队列(Messaging)。除了用于系统内部组件之间的通信,消息队列还被用于系统与其他服务之间的交互。消息队列的使用可以增加系统的可扩展性、灵活性和用户体验。非基于消息队列的系统,其运行速度取决于系统中最慢的组件的速度(注:短板效应)。而基于消息队列可以将系统中各组件解除耦合,这样系统就不再受最慢组件的束缚,各组件可以异步运行从而得以更快的速度完成各自的工作。
此外,当服务器处在高并发操作的时候,比如频繁地写入日志文件。可以利用消息队列实现异步处理。从而实现高性能的并发操作。
11、缓存
Redis的缓存部分值得写一篇新文章,我这里只是简单的说一下。Redis能够替代memcached,让你的缓存从只能存储数据变得能够更新数据,因此你不再需要每次都重新生成数据了。
The above is the detailed content of How to apply the 5 data types in Redis. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Commonly used database software
Commonly used database software
 What are the in-memory databases?
What are the in-memory databases?
 Which one has faster reading speed, mongodb or redis?
Which one has faster reading speed, mongodb or redis?
 How to use redis as a cache server
How to use redis as a cache server
 How redis solves data consistency
How redis solves data consistency
 How do mysql and redis ensure double-write consistency?
How do mysql and redis ensure double-write consistency?
 What data does redis cache generally store?
What data does redis cache generally store?
 What are the 8 data types of redis
What are the 8 data types of redis




