 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals
 AI
AI
 To solve the biggest obstacle to the implementation of AI, has OpenAI found a way?
To solve the biggest obstacle to the implementation of AI, has OpenAI found a way?
To solve the biggest obstacle to the implementation of AI, has OpenAI found a way?
OpenAI seems to have found a solution to the "serious nonsense" of generative artificial intelligence.
On May 31, OpenAI announced on its official website that it had trained a model that can help eliminate common "illusions" and other common problems in generative AI.
OpenAI stated that reward models can be trained to detect hallucinations, and reward models are divided into outcome supervision (providing feedback based on the final result) or process supervision (providing feedback for each step in the thinking chain) model.
That is, process supervision rewards each correct step in reasoning, while outcome supervision simply rewards correct answers.
OpenAI said that in contrast, process supervision has an important advantage-It directly trains the model to produce human-approved thought chains:
Process supervision has several consistency advantages over outcome supervision. Each step is precisely supervised, so it rewards behavior that follows a consistent chain of thought model.
Process supervision is also more likely to produce explainable reasoning because it encourages the model to follow a human-approved process
Outcome monitoring can reward an inconsistent process and is often more difficult to review.
OpenAI tested both models on a mathematical dataset and found that the process supervision approach resulted in "significantly better performance."
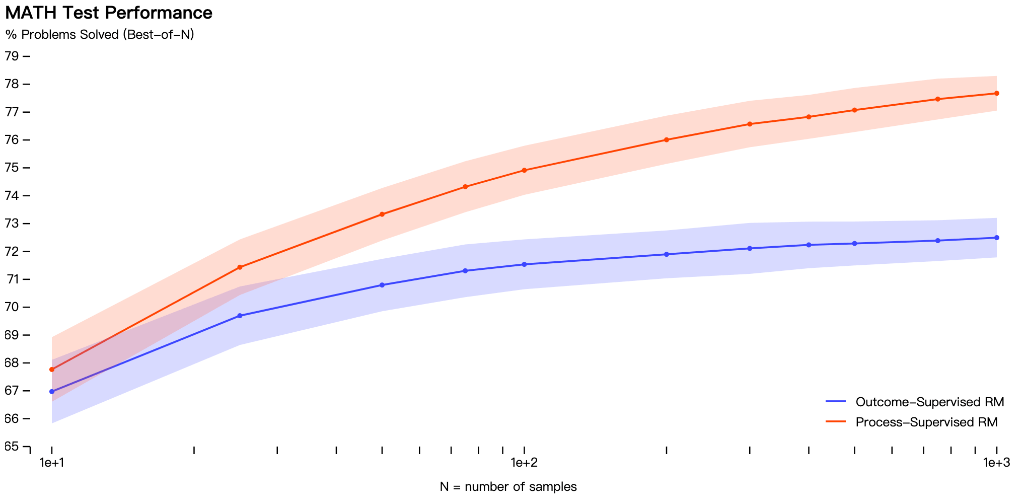
It is important to note, however, that so far the process supervision approach has only been tested in the mathematical domain, and more work is needed to see how it performs more generally.
In addition, OpenAI did not indicate how long it will take for this research to be applied to ChatGPT, which is still in the research stage.
While the initial results are good, OpenAI does mention that the safer approach incurs reduced performance, called an alignment tax.
Current results show that process supervision does not generate alignment taxes when dealing with mathematical problems, but the situation in general information is not known.
The “illusion” of generative AI
Since the advent of generative AI, accusations of fabricating false information and “generating hallucinations” have never disappeared. This is also one of the biggest problems with current generative AI models.
In February of this year, Google hastily launched the chatbot Bard in response to ChatGPT funded by Microsoft. However, it was found that common sense errors were made in the demonstration, causing Google's stock price to plummet.
There are many reasons that cause AI hallucinations. One of them is inputting data to trick the AI program into misclassifying.
For example, developers use data (such as images, text, or other types) to train artificial intelligence systems. If the data is changed or distorted, the application will interpret the input differently and produce incorrect results.
Illusions can occur in large language-based models like ChatGPT due to incorrect transformer decoding, causing the language model to potentially produce a story or narrative that is not illogical or ambiguous.
The above is the detailed content of To solve the biggest obstacle to the implementation of AI, has OpenAI found a way?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 I Tried Vibe Coding with Cursor AI and It's Amazing!
Mar 20, 2025 pm 03:34 PM
I Tried Vibe Coding with Cursor AI and It's Amazing!
Mar 20, 2025 pm 03:34 PM
Vibe coding is reshaping the world of software development by letting us create applications using natural language instead of endless lines of code. Inspired by visionaries like Andrej Karpathy, this innovative approach lets dev
 Top 5 GenAI Launches of February 2025: GPT-4.5, Grok-3 & More!
Mar 22, 2025 am 10:58 AM
Top 5 GenAI Launches of February 2025: GPT-4.5, Grok-3 & More!
Mar 22, 2025 am 10:58 AM
February 2025 has been yet another game-changing month for generative AI, bringing us some of the most anticipated model upgrades and groundbreaking new features. From xAI’s Grok 3 and Anthropic’s Claude 3.7 Sonnet, to OpenAI’s G
 How to Use YOLO v12 for Object Detection?
Mar 22, 2025 am 11:07 AM
How to Use YOLO v12 for Object Detection?
Mar 22, 2025 am 11:07 AM
YOLO (You Only Look Once) has been a leading real-time object detection framework, with each iteration improving upon the previous versions. The latest version YOLO v12 introduces advancements that significantly enhance accuracy
 Best AI Art Generators (Free & Paid) for Creative Projects
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:10 PM
Best AI Art Generators (Free & Paid) for Creative Projects
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:10 PM
The article reviews top AI art generators, discussing their features, suitability for creative projects, and value. It highlights Midjourney as the best value for professionals and recommends DALL-E 2 for high-quality, customizable art.
 Is ChatGPT 4 O available?
Mar 28, 2025 pm 05:29 PM
Is ChatGPT 4 O available?
Mar 28, 2025 pm 05:29 PM
ChatGPT 4 is currently available and widely used, demonstrating significant improvements in understanding context and generating coherent responses compared to its predecessors like ChatGPT 3.5. Future developments may include more personalized interactions and real-time data processing capabilities, further enhancing its potential for various applications.
 Which AI is better than ChatGPT?
Mar 18, 2025 pm 06:05 PM
Which AI is better than ChatGPT?
Mar 18, 2025 pm 06:05 PM
The article discusses AI models surpassing ChatGPT, like LaMDA, LLaMA, and Grok, highlighting their advantages in accuracy, understanding, and industry impact.(159 characters)
 How to Use Mistral OCR for Your Next RAG Model
Mar 21, 2025 am 11:11 AM
How to Use Mistral OCR for Your Next RAG Model
Mar 21, 2025 am 11:11 AM
Mistral OCR: Revolutionizing Retrieval-Augmented Generation with Multimodal Document Understanding Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems have significantly advanced AI capabilities, enabling access to vast data stores for more informed respons
 Top AI Writing Assistants to Boost Your Content Creation
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:11 PM
Top AI Writing Assistants to Boost Your Content Creation
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:11 PM
The article discusses top AI writing assistants like Grammarly, Jasper, Copy.ai, Writesonic, and Rytr, focusing on their unique features for content creation. It argues that Jasper excels in SEO optimization, while AI tools help maintain tone consist



