Redis cache example code analysis
1. Introduction
1. Scenario
Since the data dictionary does not change very frequently, and the system accesses the data dictionary more frequently, it is necessary for us to store the data in the data dictionary. into the cache to reduce database pressure and increase access speed. Here, we use Redis as the distributed cache middleware of the system.
2. RedisTemplate
In the Spring Boot project, Spring Data Redis is integrated by default. Spring Data Redis provides a very convenient operation template for Redis, RedisTemplate, and can automatically manage the connection pool.
2. Introduction of Redis
1. Integrate Redis in the project
Add redis dependency in the service-base module. Spring Boot 2.0 and above connect to Redis through the commons-pool2 connection pool by default
<!-- spring boot redis缓存引入 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 缓存连接池-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-pool2</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- redis 存储 json序列化 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.datatype</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-datatype-jsr310</artifactId>
</dependency>2. Add Redis connection configuration
Add the following configuration to application.yml of service-core
#spring:
redis:
host: 192.168.100.100
port: 6379
database: 0
password: 123456 #Default is empty
timeout: 3000ms #Maximum waiting time, an exception will be thrown if it times out, otherwise the request will wait forever
lettuce:
pool:
max-active: 20 #Maximum number of connections, negative value means no limit, default is 8
max-wait: -1 #Maximum blocking waiting time, negative value means no limit, Default -1
max-idle: 8 #Maximum idle connection, default 8
min-idle: 0 #Minimum idle connection, default 0
3. Start Redis service
Connect to the Linux server remotely, here use redis on the centos virtual machine locally
#Start the service
cd /usr/local/redis-5.0.7
bin/redis- server redis.conf
3. Test RedisTemplate
1. Store value test
Create test class RedisTemplateTests
@SpringBootTest
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
public class RedisTemplateTests {
@Resource
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@Resource
private DictMapper dictMapper;
@Test
public void saveDict(){
Dict dict = dictMapper.selectById(1);
//向数据库中存储string类型的键值对, 过期时间5分钟
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("dict", dict, 5, TimeUnit.MINUTES);
}
}found that RedisTemplate defaults The JDK serialization method is used to store the key and value, which has poor readability
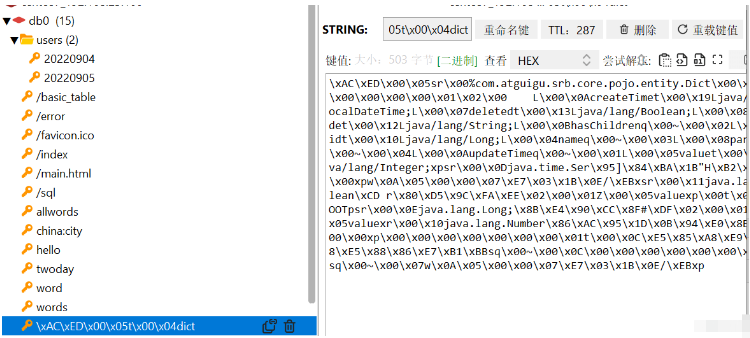
2. Add RedisConfig to the Redis configuration file
service-base. We You can configure the Redis serialization scheme in this configuration file
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig {
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate(LettuceConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) {
RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate = new RedisTemplate<>();
redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory);
//首先解决key的序列化方式
StringRedisSerializer stringRedisSerializer = new StringRedisSerializer();
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(stringRedisSerializer);
//解决value的序列化方式
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<Object> jackson2JsonRedisSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<>(Object.class);
//序列化时将类的数据类型存入json,以便反序列化的时候转换成正确的类型
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
//objectMapper.enableDefaultTyping(ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL);
objectMapper.activateDefaultTyping(LaissezFaireSubTypeValidator.instance, ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL);
// 解决jackson2无法反序列化LocalDateTime的问题
objectMapper.disable(SerializationFeature.WRITE_DATES_AS_TIMESTAMPS);
objectMapper.registerModule(new JavaTimeModule());
jackson2JsonRedisSerializer.setObjectMapper(objectMapper);
redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
return redisTemplate;
}
}Test again, the key uses string storage, and the value uses json storage
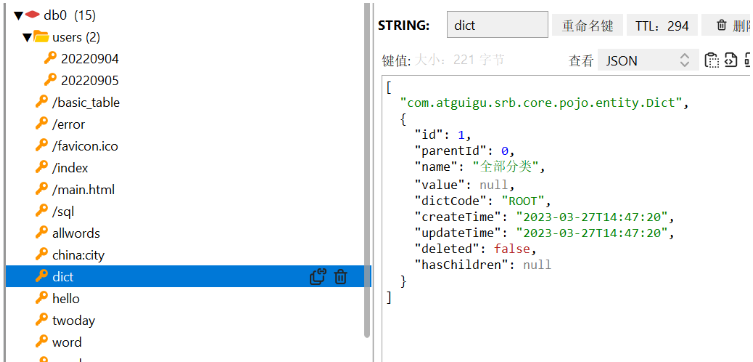
3. Value test
@Test
public void getDict(){
Dict dict = (Dict)redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("dict");
System.out.println(dict);
}4. Store the data dictionary in redis
DictServiceImpl
Note: When the redis server goes down, we should not throw an exception and execute it normally. The following process enables the business to run normally
@Resource
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@Override
public List<Dict> listByParentId(Long parentId) {
//先查询redis中是否存在数据列表
List<Dict> dictList = null;
try {
dictList = (List<Dict>)redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("srb:core:dictList:" + parentId);
if(dictList != null){
log.info("从redis中取值");
return dictList;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("redis服务器异常:" + ExceptionUtils.getStackTrace(e));//此处不抛出异常,继续执行后面的代码
}
log.info("从数据库中取值");
dictList = baseMapper.selectList(new QueryWrapper<Dict>().eq("parent_id", parentId));
dictList.forEach(dict -> {
//如果有子节点,则是非叶子节点
boolean hasChildren = this.hasChildren(dict.getId());
dict.setHasChildren(hasChildren);
});
//将数据存入redis
try {
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("srb:core:dictList:" + parentId, dictList, 5, TimeUnit.MINUTES);
log.info("数据存入redis");
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("redis服务器异常:" + ExceptionUtils.getStackTrace(e));//此处不抛出异常,继续执行后面的代码
}
return dictList;
}Summary of integrated redis:
(1) Import related dependencies;
(2) Configure redis connection information;
(3) Test connection, value test, and value storage test;
(4) Configure the serializer according to your own needs, otherwise the jdk serializer will be used by default.
redis business summary:
(1) First query whether there is corresponding cache information in redis, and if there is, it will be retrieved and returned directly without execution (2), if redis is connected for some reason If there is no downtime, print the error log at this time and continue to query the database;
(2) If not, query the database, store the data in redis and return the data.
The above is the detailed content of Redis cache example code analysis. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
Redis cluster mode deploys Redis instances to multiple servers through sharding, improving scalability and availability. The construction steps are as follows: Create odd Redis instances with different ports; Create 3 sentinel instances, monitor Redis instances and failover; configure sentinel configuration files, add monitoring Redis instance information and failover settings; configure Redis instance configuration files, enable cluster mode and specify the cluster information file path; create nodes.conf file, containing information of each Redis instance; start the cluster, execute the create command to create a cluster and specify the number of replicas; log in to the cluster to execute the CLUSTER INFO command to verify the cluster status; make
 How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear Redis data: Use the FLUSHALL command to clear all key values. Use the FLUSHDB command to clear the key value of the currently selected database. Use SELECT to switch databases, and then use FLUSHDB to clear multiple databases. Use the DEL command to delete a specific key. Use the redis-cli tool to clear the data.
 How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
Using the Redis directive requires the following steps: Open the Redis client. Enter the command (verb key value). Provides the required parameters (varies from instruction to instruction). Press Enter to execute the command. Redis returns a response indicating the result of the operation (usually OK or -ERR).
 How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
To read a queue from Redis, you need to get the queue name, read the elements using the LPOP command, and process the empty queue. The specific steps are as follows: Get the queue name: name it with the prefix of "queue:" such as "queue:my-queue". Use the LPOP command: Eject the element from the head of the queue and return its value, such as LPOP queue:my-queue. Processing empty queues: If the queue is empty, LPOP returns nil, and you can check whether the queue exists before reading the element.
 How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
Using Redis to lock operations requires obtaining the lock through the SETNX command, and then using the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time. The specific steps are: (1) Use the SETNX command to try to set a key-value pair; (2) Use the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time for the lock; (3) Use the DEL command to delete the lock when the lock is no longer needed.
 How to implement the underlying redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:21 PM
How to implement the underlying redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:21 PM
Redis uses hash tables to store data and supports data structures such as strings, lists, hash tables, collections and ordered collections. Redis persists data through snapshots (RDB) and append write-only (AOF) mechanisms. Redis uses master-slave replication to improve data availability. Redis uses a single-threaded event loop to handle connections and commands to ensure data atomicity and consistency. Redis sets the expiration time for the key and uses the lazy delete mechanism to delete the expiration key.
 How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
The best way to understand Redis source code is to go step by step: get familiar with the basics of Redis. Select a specific module or function as the starting point. Start with the entry point of the module or function and view the code line by line. View the code through the function call chain. Be familiar with the underlying data structures used by Redis. Identify the algorithm used by Redis.
 How to make message middleware for redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:51 PM
How to make message middleware for redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:51 PM
Redis, as a message middleware, supports production-consumption models, can persist messages and ensure reliable delivery. Using Redis as the message middleware enables low latency, reliable and scalable messaging.




