 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals
 AI
AI
 Artificial Intelligence and Cybersecurity Guard against Emerging Threats
Artificial Intelligence and Cybersecurity Guard against Emerging Threats
Artificial Intelligence and Cybersecurity Guard against Emerging Threats
Threats against technology are also growing exponentially with technology. Cybercrime is big business; hackers are using increasingly sophisticated methods to break into systems and steal data. Artificial intelligence may be the answer to defeating these evil forces. AI can help identify new threats as they emerge in real time and even predict future attacks by employing machine learning algorithms and predictive analytics.
Cybersecurity should be an organization’s top priority in protecting digital assets and consumer data. For security teams, AI can be a powerful tool for network visibility, anomaly detection, and threat automation.
Artificial intelligence is key to detecting emerging cyber threats
As cyber threats rapidly evolve and sophisticate, artificial intelligence (AI) has become key to identifying and stopping cyber threats. Artificial intelligence systems can analyze large amounts of data faster than humans to find new patterns that indicate cyberattacks.
AI-based cybersecurity systems continuously monitor network and user activity to establish a baseline of typical behavior. They can then look for anomalies that might point to an attack. For example, if a user suddenly downloads an unusually large amount of data or checks in from an unfamiliar location, AI systems can detect potentially dangerous behavior.
Artificial intelligence can identify new attack strategies that have never been used before by discovering links between huge data sets. This skill is critical when fraudsters try to quickly exploit new vulnerabilities. AI can also help detect zero-day attacks, which are entirely new vulnerabilities that have yet to be patched.
AI enables predictive analytics that, in addition to detection, can estimate the likelihood of specific types of attacks. When resources are prioritized, cybersecurity teams can strengthen defenses against the most pressing threats. AI can also automatically defend against typical attacks, freeing up security teams to focus on the most advanced threats.
Overall, artificial intelligence is expected to revolutionize cybersecurity by leveraging data and algorithms to detect new threats and support information security. When combined with human judgment and oversight, AI creates new risks, such as adversarial attacks designed to trick AI systems, but it is even more necessary to avoid today's cyber threats. Without artificial intelligence, the speed and scope of contemporary attacks could make progress in the cyber weapons race possible.
Machine learning algorithms can identify malware and phishing attempts
As cyber threats evolve, artificial intelligence and machine learning are fundamental technologies for cybersecurity. Machine learning algorithms can detect malware and phishing attempts by identifying trends and anomalies.
Large datasets containing good and bad code are used to train machine learning algorithms. After learning the characteristics of each type, algorithms can analyze new files or emails to determine whether they may be dangerous.
Malware Detection
To identify malware such as viruses, worms, and spyware, machine learning models examine attributes such as file structure, metadata, and code instructions. Traditional signature-based techniques are far less effective than algorithms at detecting variants of established malware families.
Phishing Detection
Machine learning analyzes emails and web pages to identify phishing behavior. Algorithms consider elements including text, formatting, sender information, links and images when determining whether a piece of content is authentic or an attempt to steal data or install malware. As phishing emails become more sophisticated and targeted, machine learning is essential.
Machine learning has greatly enhanced malware and phishing detection, although there are still some shortcomings. Over time, algorithms become smarter as they are exposed to more data. The use of artificial intelligence in cybersecurity must continue to evolve to keep up with new dangers, as cybercriminals also leverage machine learning to generate increasingly sophisticated threats. In general, machine learning is an effective technique that, when combined with human expertise, helps develop important defenses against cyberattacks.
Artificial intelligence helps with vulnerability management and patching
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are helping security teams keep up with the number of vulnerabilities. AI systems can analyze large amounts of data to identify vulnerabilities, prioritize risks, and determine the best remediation strategies.
AI Improves Vulnerability Discovery
Vast amounts of data from vulnerability databases, vendor recommendations, and open source platforms are combed through by AI using sophisticated data analysis techniques, including natural language processing. To identify potential risks faster and more accurately, AI can uncover patterns and connections that humans might miss. Because AI reduces the number of false positives they have to investigate, security teams can free up time to focus on the risks that matter most.
AI prioritizes vulnerabilities by risk level
Each vulnerability poses a different degree of danger. Artificial intelligence (AI) evaluates vulnerabilities based on factors such as Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) scores, exploitability, active malware activity targeting the vulnerability, and the assets affected by the issue. The AI then ranks the vulnerabilities so security teams can focus on the biggest threats first. Prioritization ensures security teams use their time and resources efficiently.
AI Optimization Patch Plan
Patching vulnerabilities requires a balance. To prevent outages, patches must be applied promptly and fully evaluated. AI can analyze large amounts of data to determine the best patching plan based on risk levels, dependencies, and operational impact. Artificial intelligence may find strategies to reduce business disruption while speeding up high-priority patching times. AI patches in a data-driven way, improving safety and productivity.
AI improves identity and access management
Artificial intelligence and machine learning enhance identity and access management (IAM) systems. IAM solutions authenticate users’ identities and control their access to systems, applications, and data. AI helps improve IAM in many ways:
Detecting Abnormal Behavior
AI systems can analyze large amounts of data to identify typical behavioral patterns of users and identify possible account compromises or insider threats Signs of unusual circumstances. AI can identify anomalous activity for further inquiry by tracking metrics such as login locations, access requests, and resource consumption.
Adaptive Authentication
AI analyzes user profiles, login locations, and access behaviors to assess risk and select the best authentication technology. The risk of a transaction or access request determines how much authentication is required, and AI makes this possible. A simple password may be enough for low-risk access. High-risk access may require multi-factor authentication such as biometrics.
Autoprovisioning and Deprovisioning
AI can help streamline the process of granting access to new users and removing them from those who leave the company or change jobs. AI systems can automatically provision and de-provision access to systems and data by checking job responsibilities, access requirements and termination checklists. This reduces the administrative burden and ensures that access rights are granted and revoked in a timely and legal manner.
Continuous Monitoring
IAM systems can leverage machine learning to continuously monitor user access and permissions to identify instances of unauthorized access, inactive accounts, and improper role separation. AI tools can examine entitlements and role data to identify and resolve issues, such as people with too much access or conflicting roles. Organizations can ensure compliance and least privilege through continuous monitoring.
IAM systems will continue to be improved through artificial intelligence and machine learning to increase threat detection, speed up procedures and enable risk-based adaptive access control. By leveraging AI, organizations can reduce risk, increase compliance, and improve access governance. Overall, AI will play a key role in assisting IAM systems in providing comprehensive protection against new cyber threats.
Artificial Intelligence Enhances Network Monitoring and Threat Detection
In many important areas, artificial intelligence and machine learning are improving network monitoring and threat detection. AI Systems Can analyze
Massive Amounts of Data can analyze large amounts of data to discover patterns and anomalies that point to potential risks. Artificial intelligence (AI) can detect signs of DDoS attacks, malware infections, unauthorized access, and other problems by applying machine learning algorithms to network data, logs, and events. AI discovers connections and insights that would be difficult for humans to discover on their own. AI detects emerging threatsWhile cybercriminals are always developing new attack strategies, AI systems can identify these new dangers in real time. AI systems constantly update their knowledge base to keep up with new attack methods. AI analyzes network activity and traffic, comparing it to established patterns and detecting any anomalies that could point to newly discovered zero-day vulnerabilities or other new threats. Artificial Intelligence Performs Predictive AnalyticsAI’s capabilities go far beyond tracking web activity. It can also perform predictive analytics to identify potential future hazards. To proactively protect networks and data, AI systems can anticipate new attacks that threat actors may launch next by spotting trends in their tactics, methods, and procedures (TTPs). Thanks to predictive AI, security teams can stay ahead of danger before it even arises. AI Augmented Human Security AnalystThe most effective cyber defense is achieved when artificial intelligence and human knowledge are combined. Even as AI improves network monitoring and threat identification, human analysts remain critical. AI systems can support human analysts by handling time-consuming, repetitive activities such as data correlation and analysis, freeing them up to focus on higher-order thinking. Additionally, AI provides alerts and recommendations to analysts for additional research and action. ###As cyber threats continue to increase in volume and sophistication, artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are becoming indispensable technologies for monitoring networks, detecting attacks, and protecting systems and data. To enable comprehensive and proactive cyber defense, AI improves threat visibility, identifies new attack techniques, predicts impending dangers, and simplifies the work of human analysts. By harnessing the power of AI, organizations can gain significant advantages against threat actors looking to penetrate their networks and data.
AI-Enhanced Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Solutions
SIEM systems can detect dangers and anomalies in real-time thanks to artificial intelligence, which analyzes large amounts of data to spot suspicious activity. AI algorithms can establish a baseline of typical network activity and user behavior to identify deviations that may indicate cyber threats. Thanks to real-time threat detection, security personnel can react quickly to contain and mitigate attacks.
Automatic Alert Classification
SIEM systems generate many alerts, but not all of them require immediate action. To prioritize the highest priority threats analyzed by security analysts, AI can help automatically classify warnings based on severity and risk. AI evaluates alerts based on the likelihood of real danger, suspicious activity detected, and the severity of the affected systems. For analysts, this reduces alert fatigue so they can focus on the most important risks.
Faster Threat Investigation
If a threat is discovered, AI speeds up the investigation process. These systems can combine information from multiple sources to piece together the full scope of an attack, identify affected systems, and identify the initial attack vector. AI can also recommend areas to look for more compromises and identify related issues. Thanks to this rapid threat hunting, security teams can quickly understand the full impact of an attack, and they can then take decisive action to eliminate dangers in their environment.
Continuous Tuning
With continuous tuning, AI-enabled SIEMs become smarter over time. The AI system monitors the comments and activity of security analysts as they review and react to alerts. The system uses this information to enhance its understanding of threats, improve the accuracy and priority of warnings, and enhance detection algorithms. AI also uses analyst reviews to select data sources to provide the most insightful information on various hazards. As a result of this adaptation process, SIEMs become better at identifying threats and taking action over time.
With an AI-enhanced SIEM system, organizations can keep up with growing data volumes and sophisticated cyber threats. AI improves threat detection, speeds up response times, reduces alert fatigue, and increases the overall effectiveness and efficiency of security operations. Therefore, organizations can improve their security posture and stay ahead of new threats by adopting AI.
Artificial intelligence can analyze user behavior to detect compromised accounts
Artificial intelligence systems can analyze user behavior and account activity to detect compromised accounts. By closely monitoring how you typically access and interact with your accounts and online services, AI can spot anomalies that might indicate your account has been hacked or accessed by unauthorized users.
Analyzing login patterns
When there is an abnormality in login, AI will check factors such as the device, location and time you frequently log in to. For example, if a login comes from an unknown device or unexpected location, AI can detect it as potentially suspicious and require further authentication to confirm your login identity. AI can also determine whether a login is from a location or device associated with fraud or hacking.
Detecting changes in usage patterns
The features or data you access, the length and frequency of your logins, and other factors. Once logged in, the AI tracks information about your typical account and online service usage. If AI detects significant changes in your usage and behavior patterns, it may indicate that an unauthorized person has accessed your account. For example, if your account suddenly experiences a lot of activity after being inactive for several months, or if you have access to sensitive information that is unusual for your account.
Analyzing Biometric and Behavioral Factors
The cognitive “fingerprint” of your interaction with technology is the behavioral factor. Some systems use biometrics, such as mouse movements or keystroke dynamics, to create a profile of your typing and clicking habits. If the system discovers that someone else has typed or clicked into your account before confirming your identity, it may lock access. For example, how quickly you read and respond to items on your screen can be used by AI to determine whether individuals using that account exhibit different behavioral traits.
Artificial intelligence (AI) and cybersecurity systems work together to analyze user accounts and look for compromised access by closely monitoring logins, usage, biometrics, and behavior. Artificial intelligence can help identify and quickly manage cyber threats, including account takeovers and identity theft. AI adds an extra layer of security by automatically identifying red flags that human security teams and individual users might miss.
AI-based password security check to check for weak or compromised passwords
AI-based password security check analyzes user passwords to determine if they are weak or have been compromised in a data breach. By leveraging machine learning and natural language processing, AI systems can check whether passwords have been exposed in previous breaches, contain common patterns that are easy to guess, or have similarities to the user's personal information.
Detect weak or commonly used passwords
AI systems can identify passwords if they contain identifiable patterns that are easy to guess, such as "123456", "password" or "qwerty". Additionally, they can determine whether a password is similar to the user's name, email address, birthday, or other private information. The technology uses machine learning methods to identify these types of weak or frequent passwords after being trained on millions of real-world passwords.
Check for known compromised passwords
Databases containing billions of passwords compromised in past data breaches and leaks are available to AI-powered password scanners. If a user's password appears on any of these hacked lists, they can immediately check to see if it exists. To help prevent account takeovers, the system will identify passwords as compromised when they match, requiring users to choose a new, different password.
Suggest strong and unique passwords
The system may provide users with various password suggestions. In addition to highlighting compromised or weak passwords, the AI-based password checker can also suggest new strong passwords for users. They provide random passwords that are at least 8-16 characters long, include a variety of letters, numbers, and symbols, and do not have any well-known patterns. These AI-generated passwords help users create different passwords for their accounts, which are difficult for thieves to decipher.
With the help of artificial intelligence and machine learning, password security may be significantly improved. Organizations are increasingly integrating an emerging cybersecurity technology called AI into password policies and authentication routines. Artificial intelligence systems can help users choose passwords that provide greater security for their accounts and personal information by leveraging massive data sets and algorithms to detect weak, popular or compromised passwords.
FAQ: How can artificial intelligence solve some of the biggest cybersecurity challenges?
Some of the biggest problems in cybersecurity can be solved with the help of artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies. Artificial intelligence (AI) systems can find vulnerabilities, identify emerging threats, and help organizations enhance their security posture by leveraging large amounts of data and computer power.
Detecting New Threats
In huge data sets, artificial intelligence is very good at finding anomalies and new patterns. By analyzing large amounts of network traffic data, AI systems can detect new viruses, phishing attempts, and other dangers that signature-based solutions may miss. AI can also compare data from many systems to detect multi-stage attacks.
Identify vulnerabilities
Artificial intelligence tools such as natural language processing can search code repositories, websites and other data sources to identify security vulnerabilities that hackers could exploit. Many software glitches, incorrect settings, and other vulnerabilities can be discovered using AI. Additionally, it can rank vulnerabilities according to risk, assisting security teams in focusing remediation efforts.
Strengthening Defenses
Artificial intelligence and machine learning help strengthen an organization’s security defenses with:
- Behavioral Analytics: Monitor changes in user behavior to look for account compromises or signs of an insider threat.
- Adaptive Authentication: Change access restrictions and authentication procedures based on risk factors such as location, access time, and previous behavior.
- Predictive Modeling: Predict the risks, vulnerabilities, and attacks most likely to target a company based on its specific risk profile.
- Auto-patching: Find and distribute software updates across systems to fix vulnerabilities as quickly as possible.
The future of cybersecurity will rely heavily on artificial intelligence, but human expertise remains critical. AI systems require large amounts of data to function properly, and this bias may be reflected in or even amplified by these systems. Teams responsible for cybersecurity must closely monitor AI systems, confirm their findings, and make correct judgments. When combined with human experience, artificial intelligence could become a powerful weapon against new cyber threats. In the field of network security, artificial intelligence cannot completely replace human judgment and decision-making.
Conclusion
As new technologies such as artificial intelligence transform our digital world, cyber risks are increasing rapidly. However, AI can also be used to detect and reduce these new hazards. Organizations using AI for cyber defense can identify threats faster, understand hackers’ methods and goals, and even predict upcoming attacks. Cybersecurity experts have the opportunity to outwit harmful actors and build stronger defenses with the help of artificial intelligence. While the future remains unknown, collaboration between AI and human experts is critical to protecting our globally connected society. By investing in and using AI cybersecurity solutions, organizations and individuals can feel more secure knowing their data and systems are secure.
The above is the detailed content of Artificial Intelligence and Cybersecurity Guard against Emerging Threats. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 Bytedance Cutting launches SVIP super membership: 499 yuan for continuous annual subscription, providing a variety of AI functions
Jun 28, 2024 am 03:51 AM
Bytedance Cutting launches SVIP super membership: 499 yuan for continuous annual subscription, providing a variety of AI functions
Jun 28, 2024 am 03:51 AM
This site reported on June 27 that Jianying is a video editing software developed by FaceMeng Technology, a subsidiary of ByteDance. It relies on the Douyin platform and basically produces short video content for users of the platform. It is compatible with iOS, Android, and Windows. , MacOS and other operating systems. Jianying officially announced the upgrade of its membership system and launched a new SVIP, which includes a variety of AI black technologies, such as intelligent translation, intelligent highlighting, intelligent packaging, digital human synthesis, etc. In terms of price, the monthly fee for clipping SVIP is 79 yuan, the annual fee is 599 yuan (note on this site: equivalent to 49.9 yuan per month), the continuous monthly subscription is 59 yuan per month, and the continuous annual subscription is 499 yuan per year (equivalent to 41.6 yuan per month) . In addition, the cut official also stated that in order to improve the user experience, those who have subscribed to the original VIP
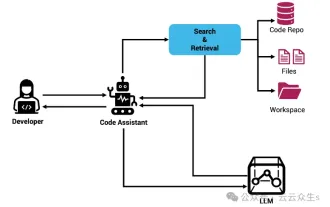 Context-augmented AI coding assistant using Rag and Sem-Rag
Jun 10, 2024 am 11:08 AM
Context-augmented AI coding assistant using Rag and Sem-Rag
Jun 10, 2024 am 11:08 AM
Improve developer productivity, efficiency, and accuracy by incorporating retrieval-enhanced generation and semantic memory into AI coding assistants. Translated from EnhancingAICodingAssistantswithContextUsingRAGandSEM-RAG, author JanakiramMSV. While basic AI programming assistants are naturally helpful, they often fail to provide the most relevant and correct code suggestions because they rely on a general understanding of the software language and the most common patterns of writing software. The code generated by these coding assistants is suitable for solving the problems they are responsible for solving, but often does not conform to the coding standards, conventions and styles of the individual teams. This often results in suggestions that need to be modified or refined in order for the code to be accepted into the application
 Can fine-tuning really allow LLM to learn new things: introducing new knowledge may make the model produce more hallucinations
Jun 11, 2024 pm 03:57 PM
Can fine-tuning really allow LLM to learn new things: introducing new knowledge may make the model produce more hallucinations
Jun 11, 2024 pm 03:57 PM
Large Language Models (LLMs) are trained on huge text databases, where they acquire large amounts of real-world knowledge. This knowledge is embedded into their parameters and can then be used when needed. The knowledge of these models is "reified" at the end of training. At the end of pre-training, the model actually stops learning. Align or fine-tune the model to learn how to leverage this knowledge and respond more naturally to user questions. But sometimes model knowledge is not enough, and although the model can access external content through RAG, it is considered beneficial to adapt the model to new domains through fine-tuning. This fine-tuning is performed using input from human annotators or other LLM creations, where the model encounters additional real-world knowledge and integrates it
 Seven Cool GenAI & LLM Technical Interview Questions
Jun 07, 2024 am 10:06 AM
Seven Cool GenAI & LLM Technical Interview Questions
Jun 07, 2024 am 10:06 AM
To learn more about AIGC, please visit: 51CTOAI.x Community https://www.51cto.com/aigc/Translator|Jingyan Reviewer|Chonglou is different from the traditional question bank that can be seen everywhere on the Internet. These questions It requires thinking outside the box. Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly important in the fields of data science, generative artificial intelligence (GenAI), and artificial intelligence. These complex algorithms enhance human skills and drive efficiency and innovation in many industries, becoming the key for companies to remain competitive. LLM has a wide range of applications. It can be used in fields such as natural language processing, text generation, speech recognition and recommendation systems. By learning from large amounts of data, LLM is able to generate text
 Five schools of machine learning you don't know about
Jun 05, 2024 pm 08:51 PM
Five schools of machine learning you don't know about
Jun 05, 2024 pm 08:51 PM
Machine learning is an important branch of artificial intelligence that gives computers the ability to learn from data and improve their capabilities without being explicitly programmed. Machine learning has a wide range of applications in various fields, from image recognition and natural language processing to recommendation systems and fraud detection, and it is changing the way we live. There are many different methods and theories in the field of machine learning, among which the five most influential methods are called the "Five Schools of Machine Learning". The five major schools are the symbolic school, the connectionist school, the evolutionary school, the Bayesian school and the analogy school. 1. Symbolism, also known as symbolism, emphasizes the use of symbols for logical reasoning and expression of knowledge. This school of thought believes that learning is a process of reverse deduction, through existing
 To provide a new scientific and complex question answering benchmark and evaluation system for large models, UNSW, Argonne, University of Chicago and other institutions jointly launched the SciQAG framework
Jul 25, 2024 am 06:42 AM
To provide a new scientific and complex question answering benchmark and evaluation system for large models, UNSW, Argonne, University of Chicago and other institutions jointly launched the SciQAG framework
Jul 25, 2024 am 06:42 AM
Editor |ScienceAI Question Answering (QA) data set plays a vital role in promoting natural language processing (NLP) research. High-quality QA data sets can not only be used to fine-tune models, but also effectively evaluate the capabilities of large language models (LLM), especially the ability to understand and reason about scientific knowledge. Although there are currently many scientific QA data sets covering medicine, chemistry, biology and other fields, these data sets still have some shortcomings. First, the data form is relatively simple, most of which are multiple-choice questions. They are easy to evaluate, but limit the model's answer selection range and cannot fully test the model's ability to answer scientific questions. In contrast, open-ended Q&A
 SOTA performance, Xiamen multi-modal protein-ligand affinity prediction AI method, combines molecular surface information for the first time
Jul 17, 2024 pm 06:37 PM
SOTA performance, Xiamen multi-modal protein-ligand affinity prediction AI method, combines molecular surface information for the first time
Jul 17, 2024 pm 06:37 PM
Editor | KX In the field of drug research and development, accurately and effectively predicting the binding affinity of proteins and ligands is crucial for drug screening and optimization. However, current studies do not take into account the important role of molecular surface information in protein-ligand interactions. Based on this, researchers from Xiamen University proposed a novel multi-modal feature extraction (MFE) framework, which for the first time combines information on protein surface, 3D structure and sequence, and uses a cross-attention mechanism to compare different modalities. feature alignment. Experimental results demonstrate that this method achieves state-of-the-art performance in predicting protein-ligand binding affinities. Furthermore, ablation studies demonstrate the effectiveness and necessity of protein surface information and multimodal feature alignment within this framework. Related research begins with "S
 SK Hynix will display new AI-related products on August 6: 12-layer HBM3E, 321-high NAND, etc.
Aug 01, 2024 pm 09:40 PM
SK Hynix will display new AI-related products on August 6: 12-layer HBM3E, 321-high NAND, etc.
Aug 01, 2024 pm 09:40 PM
According to news from this site on August 1, SK Hynix released a blog post today (August 1), announcing that it will attend the Global Semiconductor Memory Summit FMS2024 to be held in Santa Clara, California, USA from August 6 to 8, showcasing many new technologies. generation product. Introduction to the Future Memory and Storage Summit (FutureMemoryandStorage), formerly the Flash Memory Summit (FlashMemorySummit) mainly for NAND suppliers, in the context of increasing attention to artificial intelligence technology, this year was renamed the Future Memory and Storage Summit (FutureMemoryandStorage) to invite DRAM and storage vendors and many more players. New product SK hynix launched last year



