 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals
 AI
AI
 Google discloses its own 'AI+ software engineering' framework DIDACT: Thousands of developers have tested it internally, and they all say it is highly productive after using it
Google discloses its own 'AI+ software engineering' framework DIDACT: Thousands of developers have tested it internally, and they all say it is highly productive after using it
Google discloses its own 'AI+ software engineering' framework DIDACT: Thousands of developers have tested it internally, and they all say it is highly productive after using it
Any large-scale software is not fully conceived from the beginning, but is improved, edited, unit tested, repaired by developers, solved by code review, and solved again and again until it is satisfied and goes online. The code can be merged into the warehouse only after the requirements are met.
The knowledge of controlling the entire process is called Software Engineering.
Software engineering is not an independent process, but consists of developers, code reviewers, bug reporters, software architects and various development tools (such as compilers, unit tests, Connector, static analyzer).
Recently, Google announced its own DIDACT (Dynamic Integrated Developer ACTivity, dynamic integrated developer activity) framework, which uses AI technology to enhance software engineering and integrate software development The intermediate states are used as training data to assist developers in writing and modifying code, and understand the dynamics of software development in real time.
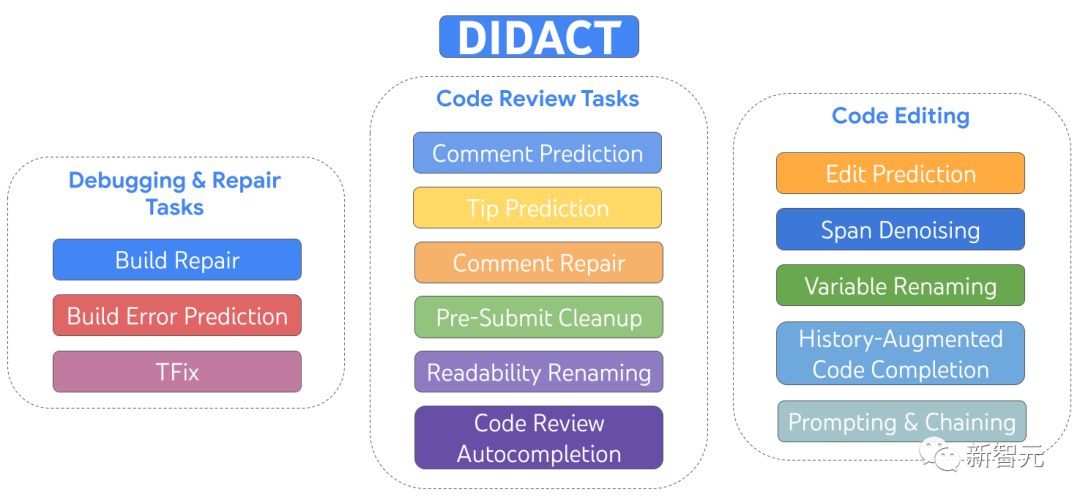
DIDACT is a multi-task model trained on development activities including editing, debugging, fixing and code review
The researchers built and deployed three DIDACT tools in-house, Annotation Parsing, Build Repair, and Tip Prediction, each integrated at different stages of the development workflow.
Software Engineering = Interaction Log
For decades, Google’s software engineering tool chain stored every operation related to code as a tool and development Logs of interactions between people.
In principle, users can use these records to replay in detail the key change process in the software development process, that is, how Google's code base was formed, including every code edit, Compilation, annotation, variable renaming, etc.
Google's development team will store the code in a monorepo (mono repository), which is a code repository that contains all tools and systems.
Software developers typically make code modifications in a local copy-on-write workspace managed by Clients in the Cloud (CitC) systems. experiment.
When a developer is ready to package a set of code changes together to achieve a certain task (such as fixing a bug), he or she needs to create a code change in Critique, Google's code review system. Changelist (CL).
Like common code review systems, developers communicate with peer reviewers about functionality and style, and then edit the CL to address issues raised during review comments.
Eventually, the reviewer declared the code "LGTM!" and merged the CL into the code base.
Of course, in addition to conversations with code reviewers, developers also need to maintain a large number of "dialogues" with other software engineering tools, including compilers, test frameworks, linkers, Static analyzers, fuzz testing tools, etc.
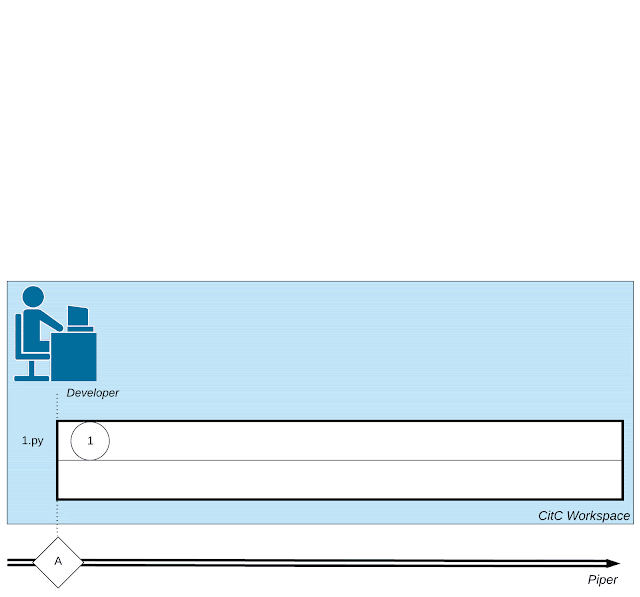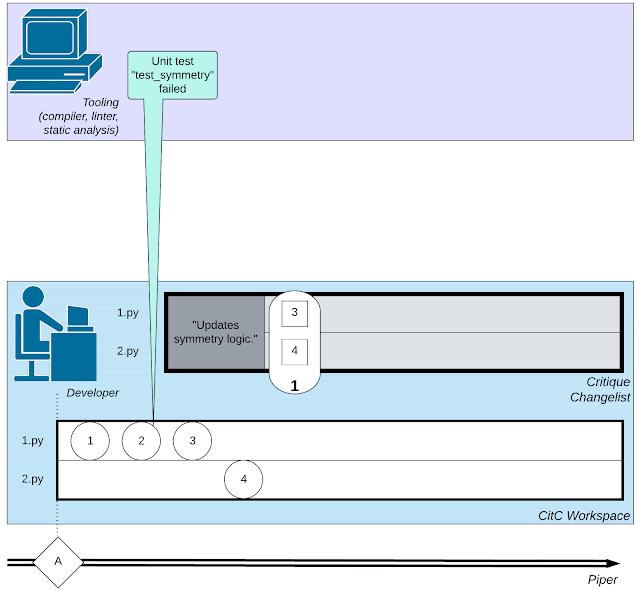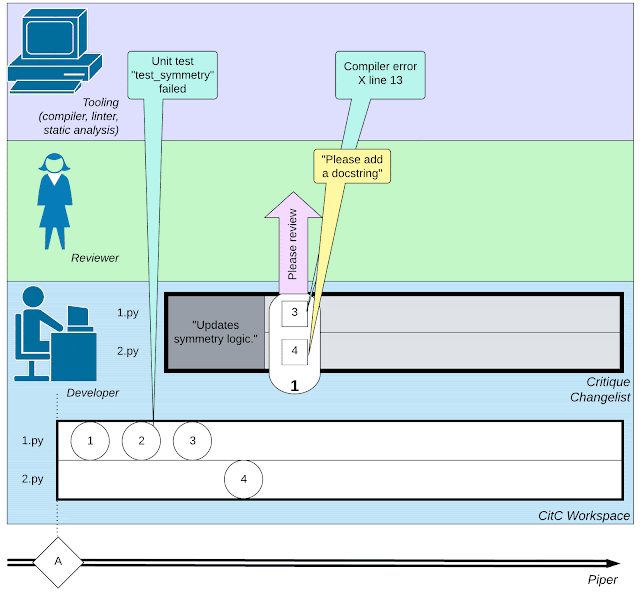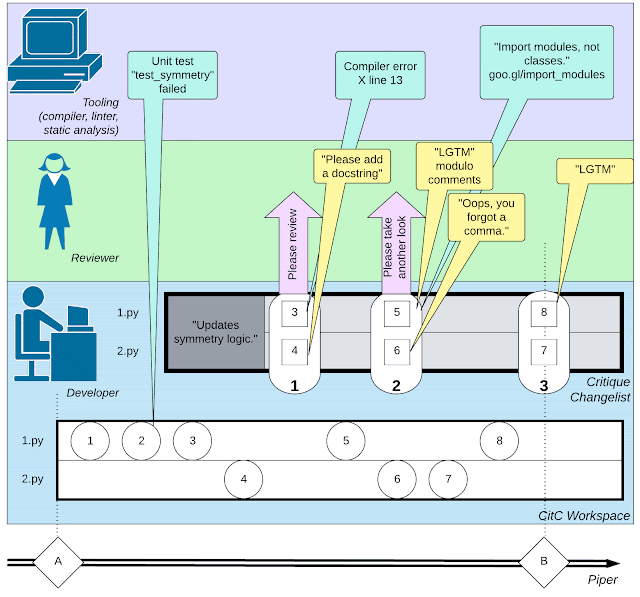
An illustration of the complex network of activities involved in software development: the activities of developers, interactions with code reviewers, and the use of tools such as compilers transfer.
Multi-task models in software engineering
DIDACT leverages the interaction between engineers and tools to empower machine learning models by suggesting or optimizing developers’ execution of software actions during engineering tasks to assist Google developers in participating in the software engineering process.
To this end, the researchers defined a number of tasks regarding individual developer activities: fixing broken builds, predicting code review comments, processing code review comments, renaming variables, editing files, etc. .
Then define a common form for each activity: get a certain State (code file), an Intent (annotation specific to an activity, such as code review annotation or compilation processor error) and generate an Action (an operation for processing the task).
Action is like a mini programming language that can be expanded into newly added activities, covering editing, adding comments, renaming variables, marking code errors, etc. It can also be called this The first language is DevScript.
The input prompts of the DIDACT model are tasks, code snippets and comments related to the task, and the output is development actions, such as editing or comments
Status- The definition form of Intent-Action (State-Intent-Action) can capture different tasks in a common way. More importantly, DevScript can express complex actions concisely without the need to output the entire state after the action occurs ( original code), making the model more efficient and interpretable.
For example, renaming may modify multiple places in the code file, but the model only needs to predict one renaming operation.
Assign a programmer to the AI model
DIDACT runs very well on personal auxiliary tasks. For example, the following example demonstrates the code of DIDACT after the function is completed. For cleanup work, first enter the code reviewer's final comments (marked human in the picture), and then predict the operations required to solve the problems raised in the comments (shown with diff).
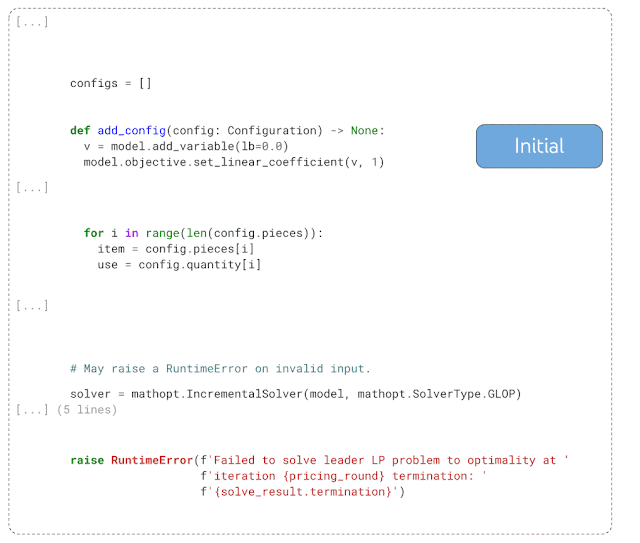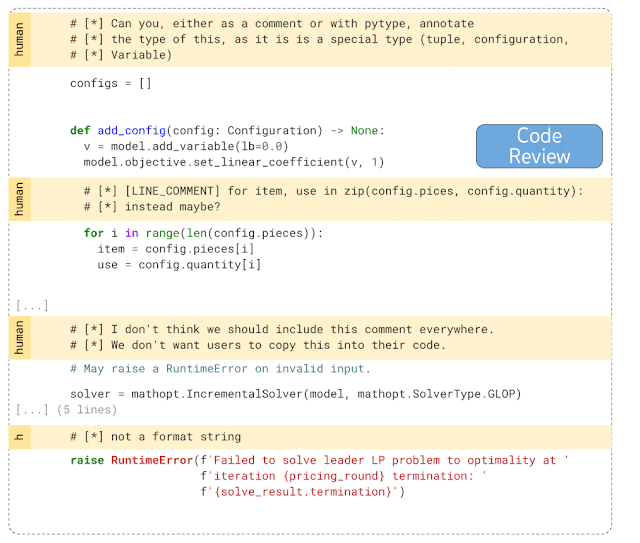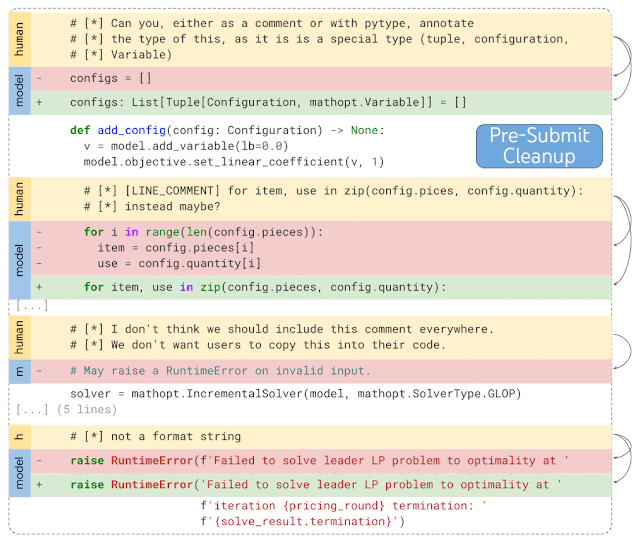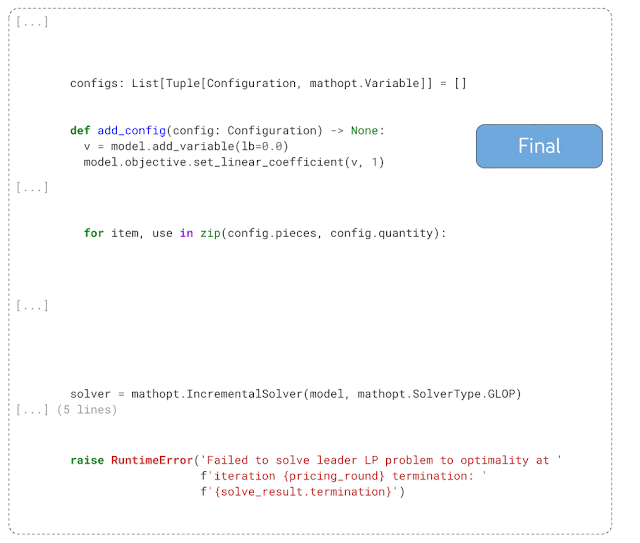
Given an initial snippet of code and the comments the code reviewer attached to the snippet, DIDACT's Pre-Submit Cleanup task generates a Editing operations (insertion and deletion of text)
The multi-modal nature of DIDACT also gives rise to some completely new behaviors that emerge with scale, one of which is history enhancement ( history augmentation), this capability can be enabled via prompts. Knowing what the developer has done recently allows the model to better predict what the developer should do next.
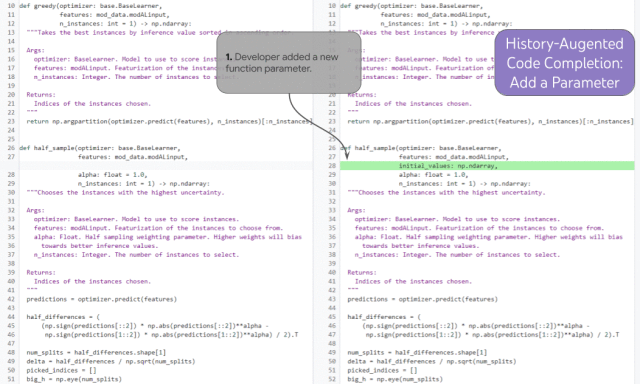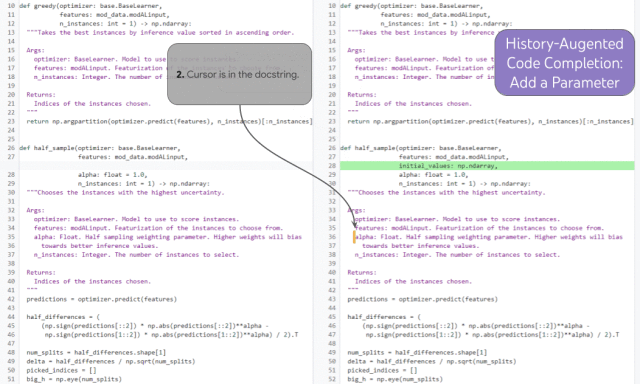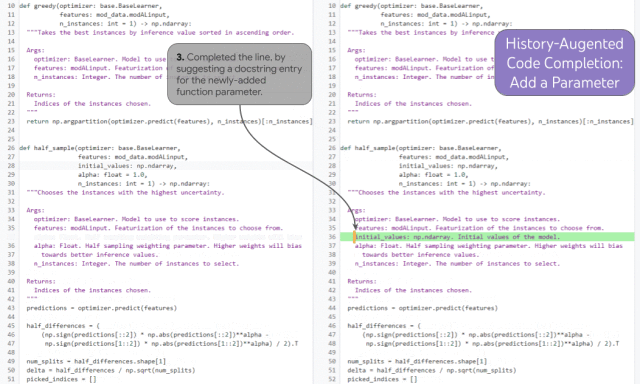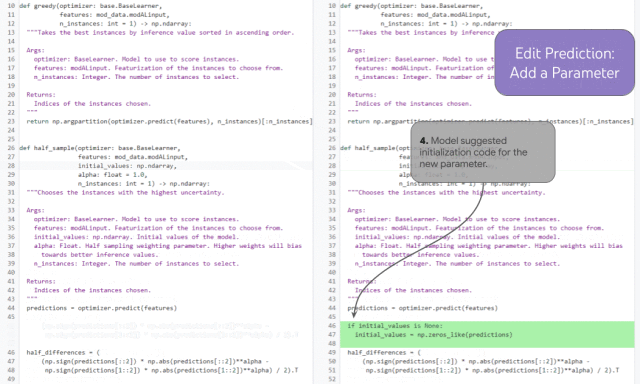
##Demonstration of historical enhanced code completion
The history enhanced code completion task can demonstrate this ability. In the example above, the developer added a new function parameter (1) and moved the cursor into the document (2). Based on the developer's editing history and cursor position, the model is able to accurately predict the docstring entry for the new parameter and complete the third step.
In the more difficult task of history-augmented edit prediction, the model is able to select the location of the next edit in a historically consistent manner.
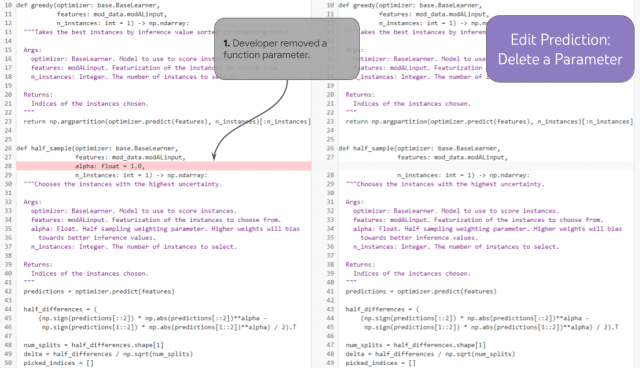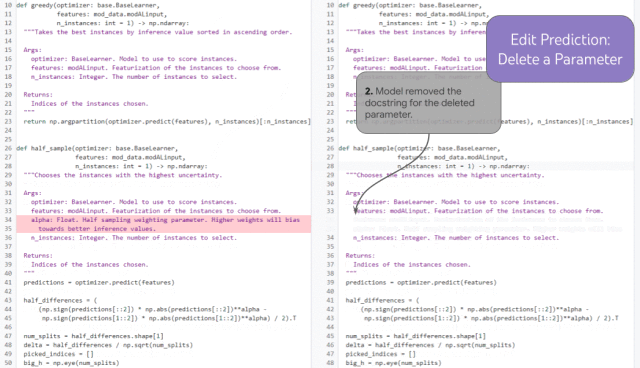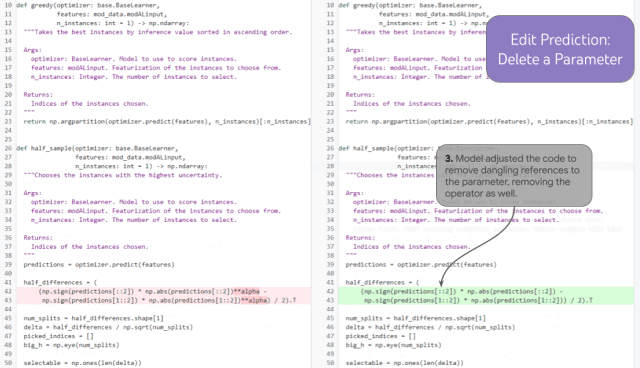
Demonstration of edit prediction over multiple chained iterations
If a developer removes a function parameter (1), the model can correctly predict an update to the docstring (2) that removes the parameter based on history (without requiring a human developer to manually place the cursor there), and in the syntax correctly (and arguably semantically) update the statement in function (3).
With the history, the model can clearly decide how to correctly continue the "editing code process", but without the history, the model has no way of knowing that the missing function parameters were intentional ( Because the developer was doing a longer editing operation to remove the parameter) or was it an unexpected situation (the model should re-add the parameter to fix the problem).
In addition, the model can also complete more tasks, such as starting from a blank file and requiring the model to continuously predict the next editing operations until a complete code is written. document.
Most importantly, the model assists in writing code in a step-by-step manner that is natural to developers:
Start by creating a complete working framework with imports, flags, and a basic main function; then gradually add new functionality, such as reading and writing results from files, and adding filtering of certain lines based on user-supplied regular expressions Function.
ConclusionDIDACT transforms Google’s software development process into training demos for machine learning developer assistants and uses these demo data to train models in a step-by-step manner Build code, interact with tools and code reviewers.
The DIDACT approach complements the great achievements of large-scale language models from Google and others to reduce workload, increase productivity, and improve the quality of software engineers' work.
The above is the detailed content of Google discloses its own 'AI+ software engineering' framework DIDACT: Thousands of developers have tested it internally, and they all say it is highly productive after using it. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 Centos shutdown command line
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:12 PM
Centos shutdown command line
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:12 PM
The CentOS shutdown command is shutdown, and the syntax is shutdown [Options] Time [Information]. Options include: -h Stop the system immediately; -P Turn off the power after shutdown; -r restart; -t Waiting time. Times can be specified as immediate (now), minutes ( minutes), or a specific time (hh:mm). Added information can be displayed in system messages.
 How to check CentOS HDFS configuration
Apr 14, 2025 pm 07:21 PM
How to check CentOS HDFS configuration
Apr 14, 2025 pm 07:21 PM
Complete Guide to Checking HDFS Configuration in CentOS Systems This article will guide you how to effectively check the configuration and running status of HDFS on CentOS systems. The following steps will help you fully understand the setup and operation of HDFS. Verify Hadoop environment variable: First, make sure the Hadoop environment variable is set correctly. In the terminal, execute the following command to verify that Hadoop is installed and configured correctly: hadoopversion Check HDFS configuration file: The core configuration file of HDFS is located in the /etc/hadoop/conf/ directory, where core-site.xml and hdfs-site.xml are crucial. use
 What are the backup methods for GitLab on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 05:33 PM
What are the backup methods for GitLab on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 05:33 PM
Backup and Recovery Policy of GitLab under CentOS System In order to ensure data security and recoverability, GitLab on CentOS provides a variety of backup methods. This article will introduce several common backup methods, configuration parameters and recovery processes in detail to help you establish a complete GitLab backup and recovery strategy. 1. Manual backup Use the gitlab-rakegitlab:backup:create command to execute manual backup. This command backs up key information such as GitLab repository, database, users, user groups, keys, and permissions. The default backup file is stored in the /var/opt/gitlab/backups directory. You can modify /etc/gitlab
 Centos install mysql
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:09 PM
Centos install mysql
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:09 PM
Installing MySQL on CentOS involves the following steps: Adding the appropriate MySQL yum source. Execute the yum install mysql-server command to install the MySQL server. Use the mysql_secure_installation command to make security settings, such as setting the root user password. Customize the MySQL configuration file as needed. Tune MySQL parameters and optimize databases for performance.
 How is the GPU support for PyTorch on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 06:48 PM
How is the GPU support for PyTorch on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 06:48 PM
Enable PyTorch GPU acceleration on CentOS system requires the installation of CUDA, cuDNN and GPU versions of PyTorch. The following steps will guide you through the process: CUDA and cuDNN installation determine CUDA version compatibility: Use the nvidia-smi command to view the CUDA version supported by your NVIDIA graphics card. For example, your MX450 graphics card may support CUDA11.1 or higher. Download and install CUDAToolkit: Visit the official website of NVIDIACUDAToolkit and download and install the corresponding version according to the highest CUDA version supported by your graphics card. Install cuDNN library:
 Detailed explanation of docker principle
Apr 14, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
Detailed explanation of docker principle
Apr 14, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
Docker uses Linux kernel features to provide an efficient and isolated application running environment. Its working principle is as follows: 1. The mirror is used as a read-only template, which contains everything you need to run the application; 2. The Union File System (UnionFS) stacks multiple file systems, only storing the differences, saving space and speeding up; 3. The daemon manages the mirrors and containers, and the client uses them for interaction; 4. Namespaces and cgroups implement container isolation and resource limitations; 5. Multiple network modes support container interconnection. Only by understanding these core concepts can you better utilize Docker.
 How to choose a GitLab database in CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 05:39 PM
How to choose a GitLab database in CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 05:39 PM
When installing and configuring GitLab on a CentOS system, the choice of database is crucial. GitLab is compatible with multiple databases, but PostgreSQL and MySQL (or MariaDB) are most commonly used. This article analyzes database selection factors and provides detailed installation and configuration steps. Database Selection Guide When choosing a database, you need to consider the following factors: PostgreSQL: GitLab's default database is powerful, has high scalability, supports complex queries and transaction processing, and is suitable for large application scenarios. MySQL/MariaDB: a popular relational database widely used in Web applications, with stable and reliable performance. MongoDB:NoSQL database, specializes in
 How to view GitLab logs under CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 06:18 PM
How to view GitLab logs under CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 06:18 PM
A complete guide to viewing GitLab logs under CentOS system This article will guide you how to view various GitLab logs in CentOS system, including main logs, exception logs, and other related logs. Please note that the log file path may vary depending on the GitLab version and installation method. If the following path does not exist, please check the GitLab installation directory and configuration files. 1. View the main GitLab log Use the following command to view the main log file of the GitLabRails application: Command: sudocat/var/log/gitlab/gitlab-rails/production.log This command will display product



