 Operation and Maintenance
Operation and Maintenance
 Linux Operation and Maintenance
Linux Operation and Maintenance
 What are the ways to check the host name in Linux?
What are the ways to check the host name in Linux?
What are the ways to check the host name in Linux?
linux查看主机名的方法有10种,分别是:1、使用hostnamectl;2、使用hostname;3、使用uname;4、使用nmcli;5、使用sysctl;6、使用cat /etc/hostname;7、使用cat /etc/hosts;8、通过ProcFS;9、使用nmtui;10、通过/etc/sysconfig/network查看即可。

本教程操作系统:linux5.18.14系统、Dell G3电脑。
1,查看主机名使用hostnamectl
hostnamectl 可用于查询和更改系统主机名和相关设置。运行 hostnamectl 命令以查看系统主机名,命令如下所示:
[root@localhost sharplee]# hostnamectl 或者 [root@localhost sharplee]# hostnamectl status
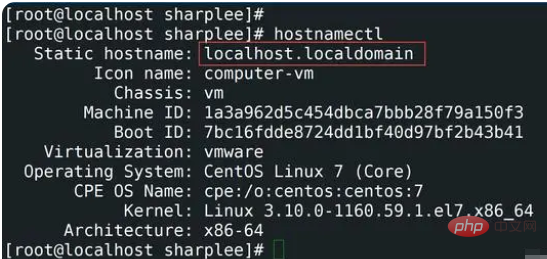
从上图可以看出当前的主机名是localhost.localdomain。
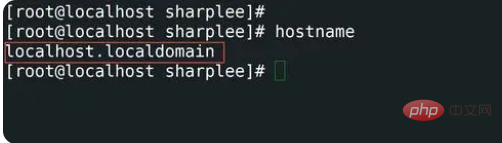
2,查看主机名使用hostname
主机名是用于设置或显示系统的当前主机、域或节点名。许多网络程序都使用这些名称来标识计算机。NIS/YP 也使用该域名,命令如下:
[root@localhost sharplee]#hostname
3,查看主机名使用uname
uname(含义是unix名称)是一个实用命令,它打印系统信息,如名称,版本和有关系统的其他详细信息,以及在其上运行的操作系统。命令如下:
[root@localhost sharplee]# uname -a | awk '{print $2}'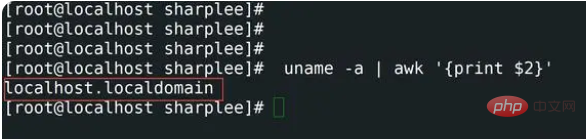
4,查看主机名使用nmcli
nmcli命令是主要用于网络管理控制以及网络状态报表。nmcli主要用于创建、显示、编辑、删除、激活和停用网络连接,以及控制和显示网络设备状态。命令如下:
[root@localhost sharplee]# nmcli general hostname
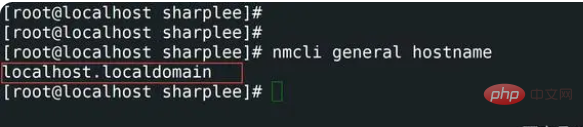
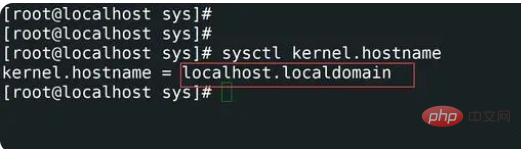
5,查看主机名使用sysctl
sysctl命令主要用于Linux运行时修改内核参数,可用的参数是 /proc/sys/ 下列出的参数。Procfs 是 Linux 中 sysctl 支持所必需的。您可以使用 sysctl 读取和写入 sysctl 数据。查看主机名命令如下所示。
[root@localhost sharplee]# sysctl kernel.hostname
通过上面五个命令可以查看主机名,接下来再来看一下后面的五个,后面五个主要用于补充说明以及扩展。
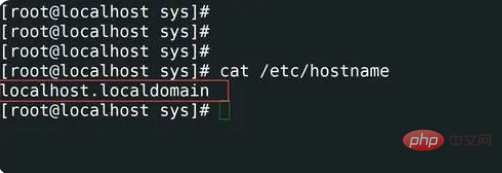
6,查看主机名使用cat /etc/hostname
通过查看/etc/hostname文件来查看主机名。命令如下所示。
[root@localhost sharplee]# cat /etc/hostname
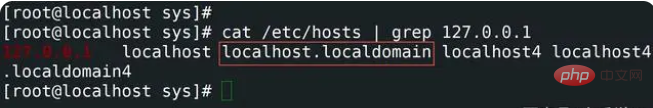
7,查看主机名使用cat /etc/hosts
通过查看 /etc/hosts 文件来查看主机名。 /etc/hosts 主要用于配置本机的dns映射关系,一般是ip地址主机名,用于ip和主机的映射关系。命令如下所示。
[root@localhost sharplee]# cat /etc/hosts | grep 127.0.0.1
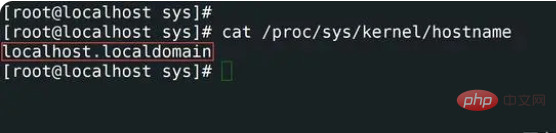
8,查看主机名通过ProcFS
proc 文件系统 (procfs) 是 Unix 操作系统中的一个特殊文件系统,它提供有关进程的信息和其他系统信息。它有时被称为进程信息伪文件系统。它不包含"真实"文件,而是运行时系统信息(例如系统内存,装载的设备,硬件配置等)。
[root@localhost sharplee]# cat /proc/sys/kernel/hostname
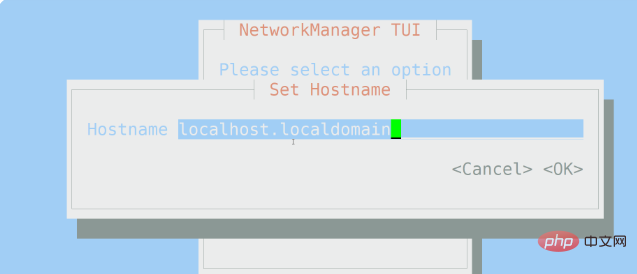
9,查看主机名使用nmtui
nmtui是一个基于图形化的应用程序,用于与NetworkManager进行交互。启动 nmtui 时,系统会提示用户选择要执行的活动,除非选择退出,不然的话回车进去都是选择默认的参数,进去之后可修改。
[root@localhost sharplee]#nmtui
10,查看主机名通过/etc/sysconfig/network
"/etc/sysconfig/network"文件指定对系统上的所有网络接口都有效的其他信息,该命令只能用于RHEL/CentOS 6 系统。Centos6以上的系统都不能使用。
[root@localhost sharplee]#$ cat /etc/sysconfig/network | grep -i hostname HOSTNAME=localhost.localdomain
通过以上10种方式可以看出,查看Linux主机名有很多种方式,但是小编在这里建议大家使用前五种通过命令的方式,这几种方式几乎涵盖了Linux中的任何系统类型。
The above is the detailed content of What are the ways to check the host name in Linux?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 How to start nginx in Linux
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:51 PM
How to start nginx in Linux
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:51 PM
Steps to start Nginx in Linux: Check whether Nginx is installed. Use systemctl start nginx to start the Nginx service. Use systemctl enable nginx to enable automatic startup of Nginx at system startup. Use systemctl status nginx to verify that the startup is successful. Visit http://localhost in a web browser to view the default welcome page.
 How to check whether nginx is started
Apr 14, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
How to check whether nginx is started
Apr 14, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
How to confirm whether Nginx is started: 1. Use the command line: systemctl status nginx (Linux/Unix), netstat -ano | findstr 80 (Windows); 2. Check whether port 80 is open; 3. Check the Nginx startup message in the system log; 4. Use third-party tools, such as Nagios, Zabbix, and Icinga.
 How to start nginx server
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
How to start nginx server
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
Starting an Nginx server requires different steps according to different operating systems: Linux/Unix system: Install the Nginx package (for example, using apt-get or yum). Use systemctl to start an Nginx service (for example, sudo systemctl start nginx). Windows system: Download and install Windows binary files. Start Nginx using the nginx.exe executable (for example, nginx.exe -c conf\nginx.conf). No matter which operating system you use, you can access the server IP
 How to solve nginx403 error
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:54 PM
How to solve nginx403 error
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:54 PM
The server does not have permission to access the requested resource, resulting in a nginx 403 error. Solutions include: Check file permissions. Check the .htaccess configuration. Check nginx configuration. Configure SELinux permissions. Check the firewall rules. Troubleshoot other causes such as browser problems, server failures, or other possible errors.
 How to solve nginx403
Apr 14, 2025 am 10:33 AM
How to solve nginx403
Apr 14, 2025 am 10:33 AM
How to fix Nginx 403 Forbidden error? Check file or directory permissions; 2. Check .htaccess file; 3. Check Nginx configuration file; 4. Restart Nginx. Other possible causes include firewall rules, SELinux settings, or application issues.
 How to solve nginx304 error
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:45 PM
How to solve nginx304 error
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:45 PM
Answer to the question: 304 Not Modified error indicates that the browser has cached the latest resource version of the client request. Solution: 1. Clear the browser cache; 2. Disable the browser cache; 3. Configure Nginx to allow client cache; 4. Check file permissions; 5. Check file hash; 6. Disable CDN or reverse proxy cache; 7. Restart Nginx.
 How to check whether nginx is started?
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:48 PM
How to check whether nginx is started?
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:48 PM
In Linux, use the following command to check whether Nginx is started: systemctl status nginx judges based on the command output: If "Active: active (running)" is displayed, Nginx is started. If "Active: inactive (dead)" is displayed, Nginx is stopped.
 How to clean nginx error log
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
How to clean nginx error log
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
The error log is located in /var/log/nginx (Linux) or /usr/local/var/log/nginx (macOS). Use the command line to clean up the steps: 1. Back up the original log; 2. Create an empty file as a new log; 3. Restart the Nginx service. Automatic cleaning can also be used with third-party tools such as logrotate or configured.



