 Operation and Maintenance
Operation and Maintenance
 Nginx
Nginx
 Cinnamon 5.8 desktop environment released: supports gesture operations, dark mode, new styles, etc.
Cinnamon 5.8 desktop environment released: supports gesture operations, dark mode, new styles, etc.
Cinnamon 5.8 desktop environment released: supports gesture operations, dark mode, new styles, etc.

On June 8, the Cinnamon 5.8 desktop environment has been released and is already available in the Arch Linux stable software repository, and now 9to5 Linux has introduced the new features.
Cinnamon 5.8 brings support for the XDG desktop portal, provides better compatibility for Flatpak applications as well as GNOME/libadwaita applications, and supports taking screenshots.
Additionally, the feature also brings global dark mode settings to apps that support it, with three options to choose from including light, black, and let the app decide.
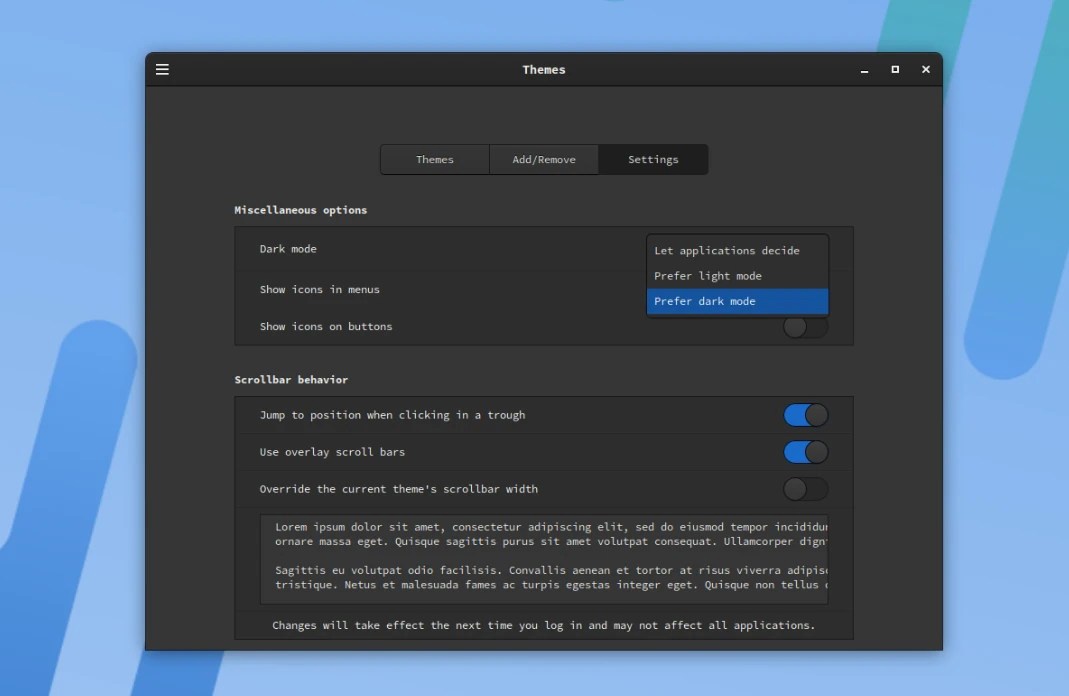
Another new feature in Cinnamon 5.8 is support for gestures on touchpads, touchscreens, and tablets for window management, workspace management, tiling, and media control.
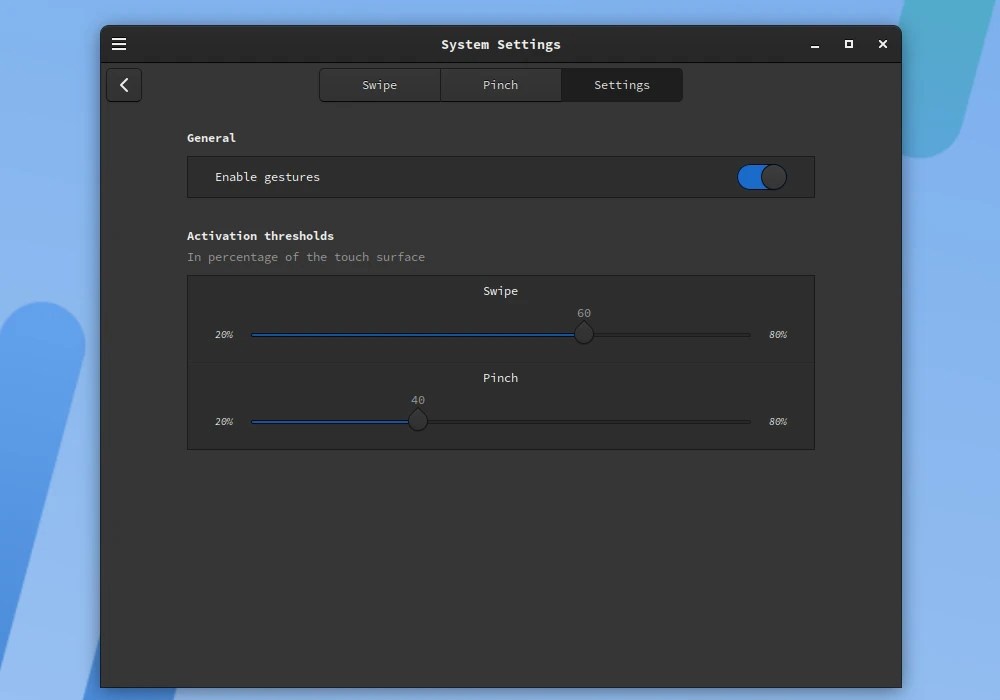
Cinnamon 5.8 also introduces the new concept of "styles" to make your desktop environment look better. For this purpose, each style comes with three modes, namely Mix, Dark and Light, and Accent Color. In blended mode, most applications are light-colored, while some desktop elements are dark for contrast.
Tooltips have been redesigned to be more consistent across various GTK versions (GTK2, GTK3) and Cinnamon, and they now also use accent colors. Tooltips in Cinnamon are now larger and rounder with larger margins, and there's some space between applets so they don't look crowded on the panel.
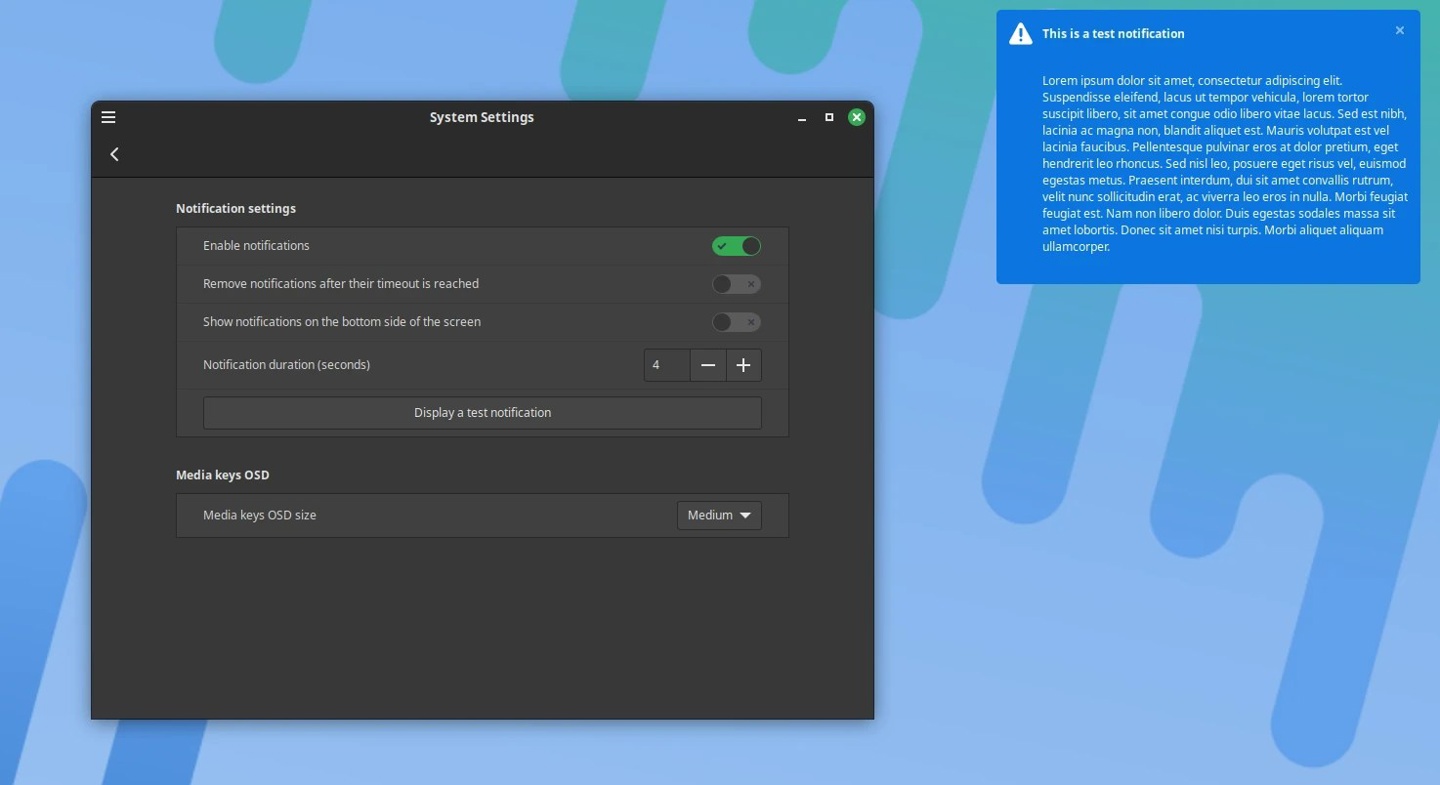
Notifications are also starting to use accent colors, and they now favor symbol icons whenever possible. Accent color options don't appear in the theme panels of distributions other than Linux Mint, but you can change them using advanced settings.
Cinnamon The default file manager Nemo has gained support for multi-threaded thumbnails. This is a performance improvement and Nemo is now generating Thumbnailing requires less CPU resources and can generate multiple thumbnails in parallel instead of generating each thumbnail one at a time. With this enhancement, your large folders now open faster.
Several Cinnamon applets have been improved, including the grouped window list and the sound applet. Additionally, the menu applet can now be resized using the mouse pointer, there are new buttons in settings that allow you to restore its original size, and menus can be edited faster via the applet's right-click context menu.
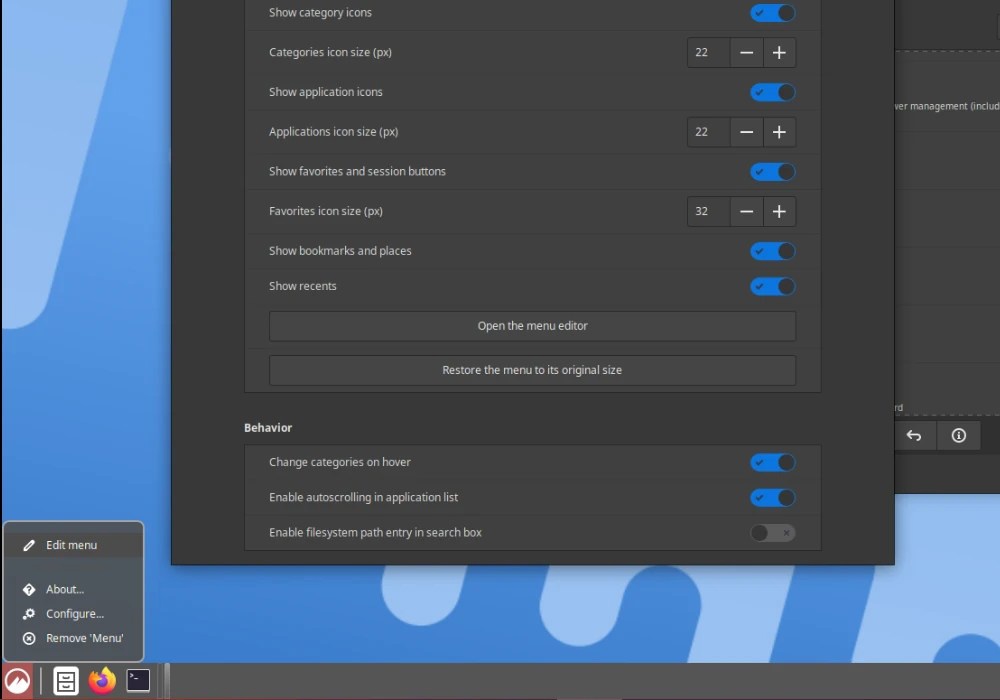
Among other things, Cinnamon 5.8 adds keyboard shortcuts for twisting the mouse pointer between monitors in a multi-monitor setup, adding the ability to twist the mouse pointer by clicking the middle mouse button Pasted the currently selected feature (enabled by default in Mouse and Touchpad settings) and added disabling low battery warnings for connected devices in Power Management settings.
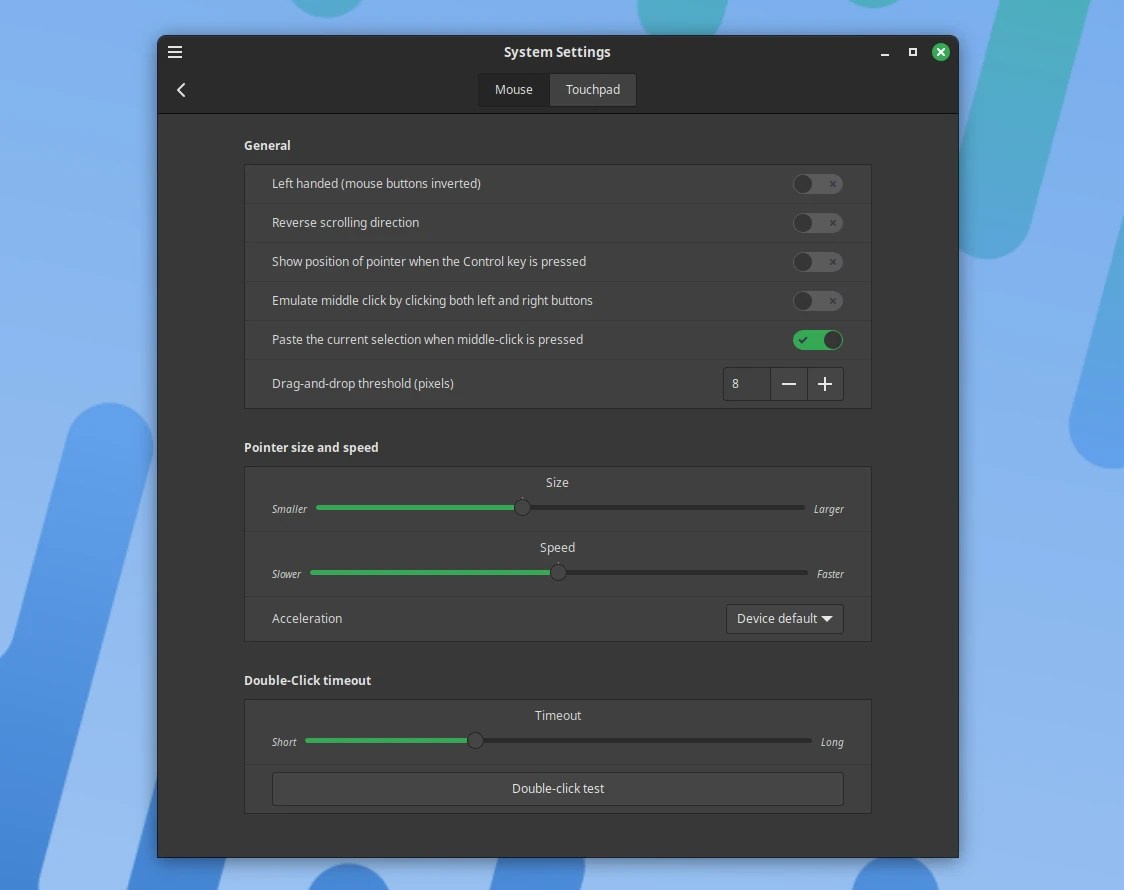
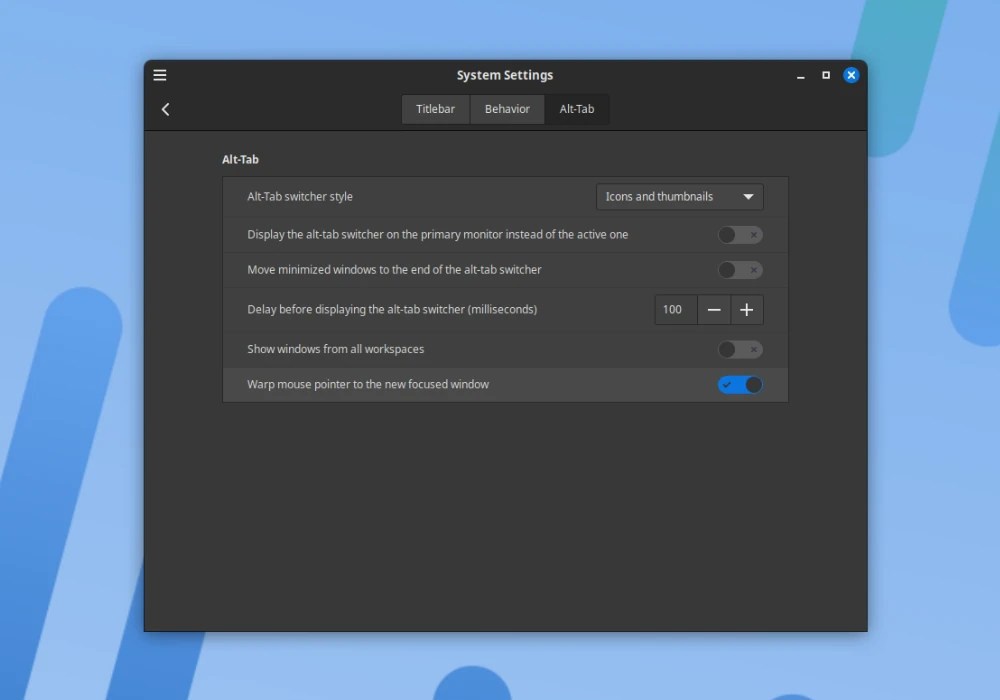
Cinnamon 5.8 also leverages the vga_switcheroo Linux subsystem for GPU offloading on laptops with mixed graphics and adds a new option in the Windows Alt Tab settings for Alt Tab After the operation is completed, adjust the mouse pointer to the newly focused window.
Cinnamon 5.8 comes with updated CJS (IT House Note: Cinnamon Javascript interpreter), which is based on GJS 1.74 and uses SpiderMonkey (libmozjs) 102, which will give Cinnamon Bring performance improvements.
As mentioned before, Cinnamon 5.8 has been launched in the Arch Linux stable repository and is expected to be launched in the repositories of other popular distributions soon. Cinnamon 5.8 will be the default desktop environment for the upcoming Linux Mint 21.2 “Victoria” distribution later this month.
The above is the detailed content of Cinnamon 5.8 desktop environment released: supports gesture operations, dark mode, new styles, etc.. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 How to start apache
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:06 PM
How to start apache
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:06 PM
The steps to start Apache are as follows: Install Apache (command: sudo apt-get install apache2 or download it from the official website) Start Apache (Linux: sudo systemctl start apache2; Windows: Right-click the "Apache2.4" service and select "Start") Check whether it has been started (Linux: sudo systemctl status apache2; Windows: Check the status of the "Apache2.4" service in the service manager) Enable boot automatically (optional, Linux: sudo systemctl
 What to do if the apache80 port is occupied
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:24 PM
What to do if the apache80 port is occupied
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:24 PM
When the Apache 80 port is occupied, the solution is as follows: find out the process that occupies the port and close it. Check the firewall settings to make sure Apache is not blocked. If the above method does not work, please reconfigure Apache to use a different port. Restart the Apache service.
 How to restart the apache server
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:12 PM
How to restart the apache server
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:12 PM
To restart the Apache server, follow these steps: Linux/macOS: Run sudo systemctl restart apache2. Windows: Run net stop Apache2.4 and then net start Apache2.4. Run netstat -a | findstr 80 to check the server status.
 How to learn Debian syslog
Apr 13, 2025 am 11:51 AM
How to learn Debian syslog
Apr 13, 2025 am 11:51 AM
This guide will guide you to learn how to use Syslog in Debian systems. Syslog is a key service in Linux systems for logging system and application log messages. It helps administrators monitor and analyze system activity to quickly identify and resolve problems. 1. Basic knowledge of Syslog The core functions of Syslog include: centrally collecting and managing log messages; supporting multiple log output formats and target locations (such as files or networks); providing real-time log viewing and filtering functions. 2. Install and configure Syslog (using Rsyslog) The Debian system uses Rsyslog by default. You can install it with the following command: sudoaptupdatesud
 How to solve the problem that apache cannot be started
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:21 PM
How to solve the problem that apache cannot be started
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:21 PM
Apache cannot start because the following reasons may be: Configuration file syntax error. Conflict with other application ports. Permissions issue. Out of memory. Process deadlock. Daemon failure. SELinux permissions issues. Firewall problem. Software conflict.
 Does the internet run on Linux?
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:03 AM
Does the internet run on Linux?
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:03 AM
The Internet does not rely on a single operating system, but Linux plays an important role in it. Linux is widely used in servers and network devices and is popular for its stability, security and scalability.
 How to fix apache vulnerability
Apr 13, 2025 pm 12:54 PM
How to fix apache vulnerability
Apr 13, 2025 pm 12:54 PM
Steps to fix the Apache vulnerability include: 1. Determine the affected version; 2. Apply security updates; 3. Restart Apache; 4. Verify the fix; 5. Enable security features.
 How to start nginx in Linux
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:51 PM
How to start nginx in Linux
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:51 PM
Steps to start Nginx in Linux: Check whether Nginx is installed. Use systemctl start nginx to start the Nginx service. Use systemctl enable nginx to enable automatic startup of Nginx at system startup. Use systemctl status nginx to verify that the startup is successful. Visit http://localhost in a web browser to view the default welcome page.



