 Operation and Maintenance
Operation and Maintenance
 Safety
Safety
 Why should I spend the time before retirement struggling with the operation and maintenance knowledge automation system?
Why should I spend the time before retirement struggling with the operation and maintenance knowledge automation system?
Why should I spend the time before retirement struggling with the operation and maintenance knowledge automation system?
My team has been doing system optimization since 2003. At the invitation of HP SERVICE, I joined their Haier system optimization team in 2003 and was responsible for the optimization of Oracle database. This was my first time to participate in the optimization of a large-scale system. Even at that time, I didn't know where to start optimizing a large-scale after-sales service system. I went to Qingdao to participate in this optimization project with a book by Levi's. Through this project, I gained a preliminary understanding of the optimization of Oracle databases. Later, I helped HP complete the performance evaluation of the CAF platform used in Huawei's SCM system, and recommended to the decision-makers to stop the project in time to avoid greater waste of funds, because the project could no longer be optimized. Later, HP adopted my suggestion and closed the project based on the CAF platform. Huawei also re-selected Oracle EBS as the basis of the SCM system and ERP system. Since then, our team has grown in size, done more and more optimization projects, and trained a group of experts in system optimization.
In 2011, we began to help the State Grid with system optimization. Under the leadership of experts, the first few projects achieved particularly good results. The customer wanted us to expand the scope of optimization and developed a large-scale optimization project that required nearly a hundred DBAs. We recruited dozens of DBAs from many partners to participate in this project. In order to ensure the quality of the project, we conducted multiple centralized trainings for the entire team. However, in the end, the results of this project were very unsatisfactory. The main reason is that the abilities of DBAs are uneven, and most of them have not participated in large-scale optimization projects. Since that project, I have also been thinking about the problems of the traditional operation and maintenance model that relies on people and experts, hoping to find a way to make the experience of experts play a greater role. This is my original intention to develop D-SMART, an operation and maintenance knowledge automation system. In order to build a knowledge automation system, the degree of digitization in Yunzhong must be improved. However, the degree of digitalization of IT operations and maintenance in traditional industries is very low. There are several main reasons for this.
Limited resources: Many companies may not have enough resources to invest in R&D and implementation of intelligent operation and maintenance systems, or may think that investing resources in other aspects is more rewarding.
Cultural factors: Some businesses may prefer to rely on human experience rather than automated systems, perhaps because they lack trust in automated systems, or they may believe that expert judgment is more reliable than machines in an emergency.
Technical limitations: Some companies may lack the necessary technical infrastructure to support intelligent operation and maintenance systems, which may require higher costs to upgrade equipment and systems.
Lack of awareness: Some enterprises may not be aware of the potential advantages of digital operations, or may not have enough knowledge and understanding of how to implement digital operations.
Although traditional industries have various cognitive deficiencies in digital operation and maintenance, with the development of technology and the increasing importance of digitalization, intelligent operation and maintenance will become a trend in future information system operation and maintenance, and also An inevitable direction.
Reflecting on our work experience in system optimization and operation and maintenance over the years, inexperienced technical personnel are an important factor leading to poor optimization results. Optimization work requires professional knowledge and skills rather than relying solely on experience. More systematic training may be needed to ensure that all personnel involved in optimization efforts have the necessary skills and knowledge. In addition, the effect of optimization work is also affected by multiple factors, such as system design, data quality and optimization work process.
With the continuous development of technology, many intelligent algorithms and methods are now available, which can greatly improve operation and maintenance efficiency and reduce human errors. Operation and maintenance knowledge automation tools can provide intelligent analysis and automated operations to help DBAs better manage and optimize the system. If the enterprise has sufficient resources, it can consider introducing these tools and systems to improve operation and maintenance efficiency. The "operation and maintenance knowledge automation system" combines big data analysis, artificial intelligence and other technologies, as well as expert experience and work accumulation, to build a comprehensive operation and maintenance knowledge system, which can help improve the efficiency and quality of operation and maintenance work. Through monitoring indicator systems, health models, operation and maintenance knowledge maps, anomaly detection algorithms and other technologies, the "operation and maintenance knowledge automation system" can automatically analyze and solve system performance problems, and at the same time provide intelligent optimization suggestions and decision-making support for Provides strong support for the enterprise's operation and maintenance work.
In fact, the most important purpose of D-SMART system development is to summarize our team’s more than 20 years of experience in IT operation and maintenance and system optimization, so that the experts in the team can accumulate experience over the years. experience into a digital knowledge base that can be automated. And through continuous iteration of the knowledge base, operation and maintenance knowledge can be continuously accumulated and accumulated in the platform, thereby continuously improving the ability of automated analysis.
The research and development of this system does not only rely on the R&D team. The research and development of knowledge tools is completely completed by the DBA without the help of ordinary operation and maintenance personnel. This is because ordinary R&D personnel do not understand IT operations, databases, and performance optimization. Only DBAs who have done operation and maintenance work can more accurately turn experts' ideas into automated tools.
The starting point of the D-SMART system is the indicator system. I think indicators are part of expert experience, and they are a very important part. Only indicators recognized by experts can be fully interpreted. At present, many database monitoring software provide many indicators that operation and maintenance personnel cannot correctly interpret. Even if these indicators are abnormal, they may not be discovered. In other words, if abnormal indicators are discovered, they cannot sense where the problem is in the system. The indicator data sorted out by experts are single and can be interpreted by experts, so each indicator will be marked by experts and given a specific label.
The second step of D-SMART is to complete the accurate collection of indicators. Accurate collection of data for each indicator is very critical for an intelligent operation and maintenance system. It is critical to ensure that every data accurately reflects the true state of the database. After a lot of data is collected, it needs to be processed before it can be turned into usable indicators. These processing algorithms also reflect the experience of experts. Through this step, the D-SMART system continuously obtains a digital model of the database's operating status.
The third step is to conduct automated modeling analysis on the collected indicators and log data. We use the health model to determine whether the running status of the database is normal and whether there are risks; we use the performance model to understand the overall performance status of the database; we use the load model to understand the current load situation of the database; we use the fault model to discover possible hidden dangers in the database and provide timely alarms.
The fourth step is to use the collected data to automatically complete various inspection tasks. For example, during daily inspection, the system will automatically analyze the data collected the previous day at midnight every day, discover the risks and hidden dangers, and generate a daily inspection report. Every month or every week, you can customize tasks to automatically analyze the recently collected data and generate inspection reports. This kind of inspection can analyze comprehensive data and has richer data than the traditional method of manual data collection and manual analysis. Algorithms that automate analysis are also more efficient.
Using this data, you can also do a lot of valuable analysis work, such as capacity prediction, performance optimization, special audits, etc. At the same time, using the standardized indicator system, we can also build digital communication between first-line operations and second- and third-line operations. Through a complete indicator set, we can provide third-line operations with a panoramic view of database operation as comprehensively as possible, truly eliminating the need for On site, experts can know everything about the world.
A while ago, my mother, who is over 80 years old, made sure to celebrate my birthday. She has been running around for many years and has not celebrated a birthday for more than ten years. When I put the candles, I realized that I was already 54 years old after my birthday, and there was not much time left before retirement. I want to digitize the experience accumulated over the years as much as possible while I can still do something now, so that I can keep it, so that there will be no regrets.
The above is the detailed content of Why should I spend the time before retirement struggling with the operation and maintenance knowledge automation system?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
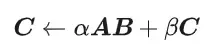 CUDA's universal matrix multiplication: from entry to proficiency!
Mar 25, 2024 pm 12:30 PM
CUDA's universal matrix multiplication: from entry to proficiency!
Mar 25, 2024 pm 12:30 PM
General Matrix Multiplication (GEMM) is a vital part of many applications and algorithms, and is also one of the important indicators for evaluating computer hardware performance. In-depth research and optimization of the implementation of GEMM can help us better understand high-performance computing and the relationship between software and hardware systems. In computer science, effective optimization of GEMM can increase computing speed and save resources, which is crucial to improving the overall performance of a computer system. An in-depth understanding of the working principle and optimization method of GEMM will help us better utilize the potential of modern computing hardware and provide more efficient solutions for various complex computing tasks. By optimizing the performance of GEMM
 Huawei's Qiankun ADS3.0 intelligent driving system will be launched in August and will be launched on Xiangjie S9 for the first time
Jul 30, 2024 pm 02:17 PM
Huawei's Qiankun ADS3.0 intelligent driving system will be launched in August and will be launched on Xiangjie S9 for the first time
Jul 30, 2024 pm 02:17 PM
On July 29, at the roll-off ceremony of AITO Wenjie's 400,000th new car, Yu Chengdong, Huawei's Managing Director, Chairman of Terminal BG, and Chairman of Smart Car Solutions BU, attended and delivered a speech and announced that Wenjie series models will be launched this year In August, Huawei Qiankun ADS 3.0 version was launched, and it is planned to successively push upgrades from August to September. The Xiangjie S9, which will be released on August 6, will debut Huawei’s ADS3.0 intelligent driving system. With the assistance of lidar, Huawei Qiankun ADS3.0 version will greatly improve its intelligent driving capabilities, have end-to-end integrated capabilities, and adopt a new end-to-end architecture of GOD (general obstacle identification)/PDP (predictive decision-making and control) , providing the NCA function of smart driving from parking space to parking space, and upgrading CAS3.0
 Always new! Huawei Mate60 series upgrades to HarmonyOS 4.2: AI cloud enhancement, Xiaoyi Dialect is so easy to use
Jun 02, 2024 pm 02:58 PM
Always new! Huawei Mate60 series upgrades to HarmonyOS 4.2: AI cloud enhancement, Xiaoyi Dialect is so easy to use
Jun 02, 2024 pm 02:58 PM
On April 11, Huawei officially announced the HarmonyOS 4.2 100-machine upgrade plan for the first time. This time, more than 180 devices will participate in the upgrade, covering mobile phones, tablets, watches, headphones, smart screens and other devices. In the past month, with the steady progress of the HarmonyOS4.2 100-machine upgrade plan, many popular models including Huawei Pocket2, Huawei MateX5 series, nova12 series, Huawei Pura series, etc. have also started to upgrade and adapt, which means that there will be More Huawei model users can enjoy the common and often new experience brought by HarmonyOS. Judging from user feedback, the experience of Huawei Mate60 series models has improved in all aspects after upgrading HarmonyOS4.2. Especially Huawei M
 Differences and similarities of cmd commands in Linux and Windows systems
Mar 15, 2024 am 08:12 AM
Differences and similarities of cmd commands in Linux and Windows systems
Mar 15, 2024 am 08:12 AM
Linux and Windows are two common operating systems, representing the open source Linux system and the commercial Windows system respectively. In both operating systems, there is a command line interface for users to interact with the operating system. In Linux systems, users use the Shell command line, while in Windows systems, users use the cmd command line. The Shell command line in Linux system is a very powerful tool that can complete almost all system management tasks.
 C++ program optimization: time complexity reduction techniques
Jun 01, 2024 am 11:19 AM
C++ program optimization: time complexity reduction techniques
Jun 01, 2024 am 11:19 AM
Time complexity measures the execution time of an algorithm relative to the size of the input. Tips for reducing the time complexity of C++ programs include: choosing appropriate containers (such as vector, list) to optimize data storage and management. Utilize efficient algorithms such as quick sort to reduce computation time. Eliminate multiple operations to reduce double counting. Use conditional branches to avoid unnecessary calculations. Optimize linear search by using faster algorithms such as binary search.
 Huawei will launch the Xuanji sensing system in the field of smart wearables, which can assess the user's emotional state based on heart rate
Aug 29, 2024 pm 03:30 PM
Huawei will launch the Xuanji sensing system in the field of smart wearables, which can assess the user's emotional state based on heart rate
Aug 29, 2024 pm 03:30 PM
Recently, Huawei announced that it will launch a new smart wearable product equipped with Xuanji sensing system in September, which is expected to be Huawei's latest smart watch. This new product will integrate advanced emotional health monitoring functions. The Xuanji Perception System provides users with a comprehensive health assessment with its six characteristics - accuracy, comprehensiveness, speed, flexibility, openness and scalability. The system uses a super-sensing module and optimizes the multi-channel optical path architecture technology, which greatly improves the monitoring accuracy of basic indicators such as heart rate, blood oxygen and respiration rate. In addition, the Xuanji Sensing System has also expanded the research on emotional states based on heart rate data. It is not limited to physiological indicators, but can also evaluate the user's emotional state and stress level. It supports the monitoring of more than 60 sports health indicators, covering cardiovascular, respiratory, neurological, endocrine,
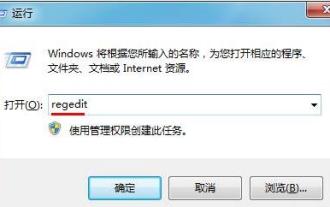 How to optimize the startup items of WIN7 system
Mar 26, 2024 pm 06:20 PM
How to optimize the startup items of WIN7 system
Mar 26, 2024 pm 06:20 PM
1. Press the key combination (win key + R) on the desktop to open the run window, then enter [regedit] and press Enter to confirm. 2. After opening the Registry Editor, we click to expand [HKEY_CURRENT_USERSoftwareMicrosoftWindowsCurrentVersionExplorer], and then see if there is a Serialize item in the directory. If not, we can right-click Explorer, create a new item, and name it Serialize. 3. Then click Serialize, then right-click the blank space in the right pane, create a new DWORD (32) bit value, and name it Star
 Vivox100s parameter configuration revealed: How to optimize processor performance?
Mar 24, 2024 am 10:27 AM
Vivox100s parameter configuration revealed: How to optimize processor performance?
Mar 24, 2024 am 10:27 AM
Vivox100s parameter configuration revealed: How to optimize processor performance? In today's era of rapid technological development, smartphones have become an indispensable part of our daily lives. As an important part of a smartphone, the performance optimization of the processor is directly related to the user experience of the mobile phone. As a high-profile smartphone, Vivox100s's parameter configuration has attracted much attention, especially the optimization of processor performance has attracted much attention from users. As the "brain" of the mobile phone, the processor directly affects the running speed of the mobile phone.



