 Operation and Maintenance
Operation and Maintenance
 Nginx
Nginx
 Nginx basic security knowledge: preventing SQL injection attacks
Nginx basic security knowledge: preventing SQL injection attacks
Nginx basic security knowledge: preventing SQL injection attacks
Nginx is a fast, high-performance, scalable web server, and its security is an issue that cannot be ignored in web application development. Especially SQL injection attacks, which can cause huge damage to web applications. In this article, we will discuss how to use Nginx to prevent SQL injection attacks to protect the security of web applications.
What is a SQL injection attack?
SQL injection attack is an attack method that exploits web application vulnerabilities. Attackers will inject malicious SQL code into the web application to obtain or destroy the data of the web application. SQL injection attacks can greatly undermine the security of web applications. If not handled in time, they may lead to immeasurable consequences such as data leakage and business losses.
How to prevent SQL injection attacks?
- Verify user input
When asking users to enter data, we should verify whether the data is legal. For example, if we expect the user to enter an integer, we need to validate the user input. If the user enters non-integer data, the input should be rejected and an error message returned.
- Hide server error information
Leakage of server error information may expose some important information of the server, including system version, framework version, etc. Attackers can use this information to launch attacks against web applications. Therefore, hiding server error messages is crucial.
You can add the following code to the Nginx configuration file to hide server error information:
server_tokens off;
- Use prepared statements
When processing dynamic SQL statements Sometimes, we should use prepared statements. Prepared statements are precompiled SQL statements that can avoid SQL injection attacks. In Nginx, we can use prepared statements using ngx_postgres and ngx_drizzle modules.
- Prohibit the use of specific characters
In Nginx, we can use the ngx_http_map_module module to prohibit the use of specific characters, such as single quotes, double quotes, etc. Prohibiting the use of specific characters can effectively prevent SQL injection attacks.
The following is a code example that prohibits the use of single quotes and double quotes:
http {
map $arg_name $invalid {
~' 1;
~" 1;
default 0;
}
server {
if ($invalid) {
return 404;
}
...
}
}- Use a firewall
Finally, we can use the Nginx configuration file Add WAF (Web Application Firewall) to prevent SQL injection attacks. A WAF is a firewall system that filters data between web applications and the Internet and blocks unsafe network traffic.
The following is a sample code for using ModSecurity WAF to prevent SQL injection attacks:
location / {
ModSecurityEnabled on;
ModSecurityConfig modsecurity.conf;
}Summary
SQL injection attacks pose a huge threat to the security of web applications. In Nginx, we can take a variety of methods to prevent SQL injection attacks, including validating user input, hiding server error messages, using prepared statements, prohibiting the use of specific characters, and using firewalls. These measures can effectively improve the security of web applications and avoid unnecessary losses.
The above is the detailed content of Nginx basic security knowledge: preventing SQL injection attacks. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1377
1377
 52
52
 How to allow external network access to tomcat server
Apr 21, 2024 am 07:22 AM
How to allow external network access to tomcat server
Apr 21, 2024 am 07:22 AM
To allow the Tomcat server to access the external network, you need to: modify the Tomcat configuration file to allow external connections. Add a firewall rule to allow access to the Tomcat server port. Create a DNS record pointing the domain name to the Tomcat server public IP. Optional: Use a reverse proxy to improve security and performance. Optional: Set up HTTPS for increased security.
 How to generate URL from html file
Apr 21, 2024 pm 12:57 PM
How to generate URL from html file
Apr 21, 2024 pm 12:57 PM
Converting an HTML file to a URL requires a web server, which involves the following steps: Obtain a web server. Set up a web server. Upload HTML file. Create a domain name. Route the request.
 How to deploy nodejs project to server
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:40 AM
How to deploy nodejs project to server
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:40 AM
Server deployment steps for a Node.js project: Prepare the deployment environment: obtain server access, install Node.js, set up a Git repository. Build the application: Use npm run build to generate deployable code and dependencies. Upload code to the server: via Git or File Transfer Protocol. Install dependencies: SSH into the server and use npm install to install application dependencies. Start the application: Use a command such as node index.js to start the application, or use a process manager such as pm2. Configure a reverse proxy (optional): Use a reverse proxy such as Nginx or Apache to route traffic to your application
 Can nodejs be accessed from the outside?
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:43 AM
Can nodejs be accessed from the outside?
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:43 AM
Yes, Node.js can be accessed from the outside. You can use the following methods: Use Cloud Functions to deploy the function and make it publicly accessible. Use the Express framework to create routes and define endpoints. Use Nginx to reverse proxy requests to Node.js applications. Use Docker containers to run Node.js applications and expose them through port mapping.
 How to deploy and maintain a website using PHP
May 03, 2024 am 08:54 AM
How to deploy and maintain a website using PHP
May 03, 2024 am 08:54 AM
To successfully deploy and maintain a PHP website, you need to perform the following steps: Select a web server (such as Apache or Nginx) Install PHP Create a database and connect PHP Upload code to the server Set up domain name and DNS Monitoring website maintenance steps include updating PHP and web servers, and backing up the website , monitor error logs and update content.
 How to use Fail2Ban to protect your server from brute force attacks
Apr 27, 2024 am 08:34 AM
How to use Fail2Ban to protect your server from brute force attacks
Apr 27, 2024 am 08:34 AM
An important task for Linux administrators is to protect the server from illegal attacks or access. By default, Linux systems come with well-configured firewalls, such as iptables, Uncomplicated Firewall (UFW), ConfigServerSecurityFirewall (CSF), etc., which can prevent a variety of attacks. Any machine connected to the Internet is a potential target for malicious attacks. There is a tool called Fail2Ban that can be used to mitigate illegal access on the server. What is Fail2Ban? Fail2Ban[1] is an intrusion prevention software that protects servers from brute force attacks. It is written in Python programming language
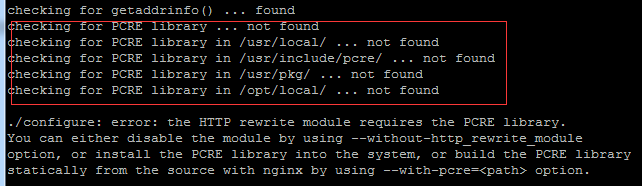 Come with me to learn Linux and install Nginx
Apr 28, 2024 pm 03:10 PM
Come with me to learn Linux and install Nginx
Apr 28, 2024 pm 03:10 PM
Today, I will lead you to install Nginx in a Linux environment. The Linux system used here is CentOS7.2. Prepare the installation tools 1. Download Nginx from the Nginx official website. The version used here is: 1.13.6.2. Upload the downloaded Nginx to Linux. Here, the /opt/nginx directory is used as an example. Run "tar-zxvfnginx-1.13.6.tar.gz" to decompress. 3. Switch to the /opt/nginx/nginx-1.13.6 directory and run ./configure for initial configuration. If the following prompt appears, it means that PCRE is not installed on the machine, and Nginx needs to
 Several points to note when building high availability with keepalived+nginx
Apr 23, 2024 pm 05:50 PM
Several points to note when building high availability with keepalived+nginx
Apr 23, 2024 pm 05:50 PM
After yum installs keepalived, configure the keepalived configuration file. Note that in the keepalived configuration files of master and backup, the network card name is the network card name of the current machine. VIP is selected as an available IP. It is usually used in high availability and LAN environments. There are many, so this VIP is an intranet IP in the same network segment as the two machines. If used in an external network environment, it does not matter whether it is on the same network segment, as long as the client can access it. Stop the nginx service and start the keepalived service. You will see that keepalived pulls the nginx service to start. If it cannot start and fails, it is basically a problem with the configuration files and scripts, or a prevention problem.



