 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals
 AI
AI
 Journal·See | Capturing the latest developments in the field of artificial intelligence? Save Applied Artificial Intelligence to your favorites
Journal·See | Capturing the latest developments in the field of artificial intelligence? Save Applied Artificial Intelligence to your favorites
Journal·See | Capturing the latest developments in the field of artificial intelligence? Save Applied Artificial Intelligence to your favorites
The emergence of ChatGPT is a breakthrough development of great historical significance in AI research. The seemingly omnipotent ChatGPT has had many positive impacts on human society, but it has also brought about thought-provoking conflicts. How to avoid the risks and negative impacts caused by the rise of artificial intelligence is an issue that policy makers and professionals in the field of artificial intelligence need to think about and discuss in depth.
This issue of "Journal·See" brings you Applied Artificial Intelligence, a high-quality journal in the field of artificial intelligence. In addition to introducing journals, we have also selected for you highly cited articles in the past three years and highly read articles in 2022 for you to read
- A framework based on transfer learning to classify pests on tomato plants
- Universal Learning Equilibrium Optimizer: A New Feature Selection Method for Biological Data Classification
- Review: A survey of 2D image semantic segmentation architecture based on deep learning
- Review: The new threat of artificial intelligence-driven cyberattacks
Applied Artificial Intelligence is the official publication of the Austrian Society for Cybernetic Research, aiming to address issues in applied research and artificial intelligence applications, while providing a platform for the exchange of views and ideas for influential research in the field of artificial intelligence. The journal focuses on the following areas, including but not limited to the progress of artificial intelligence systems in solving management, industry, engineering, administrative and educational work; the evaluation of existing artificial intelligence systems and tools, focusing on comparative research and user experience; the impact of artificial intelligence on economics , social and cultural influences.
This journal has been included in SCIE, Scopus, CSA, INSPECs, PsycINFO and other databases.

Journal homepage: http://985.so/m1ug4
Impact factor
According to JCR, the impact factor of Applied Artificial Intelligence in 2021 is 2.777, in
Computer: Ranking 82/145 in the field of artificial intelligence
Engineering: Electronics and Electrical Field Ranking 134/276
CiteScore
According to Scopus, Applied Artificial Intelligence’s
CiteScore (2021) is 3.0
CiteScoreTracker (2022) is 3.7
Ranked 151/269 in Computer Science: Artificial Intelligence
Editorial Team
The chief editor of Applied Artificial Intelligence is Professor Robert Trappl from the Austrian Institute of Artificial Intelligence and the University of Vienna. Among the deputy editor team, Professor Liu Peide from Shandong University of Finance and Economics is from China. In addition, the editorial team is composed of experts and scholars from many countries.
Editor
Professor Robert Trappl

Professor Robert Trappl is the head of the Austrian Institute of Artificial Intelligence. He is also an honorary professor of medical cybernetics and artificial intelligence at the Brain Research Center of the Medical University of Vienna. He has served as a full professor of the Department of Medical Cybernetics and Artificial Intelligence of the University of Vienna and Department chair for 30 years.
Deputy Editor from China
Professor Liu Peide

Professor Liu Peide is the dean of the School of Management Science and Engineering of Shandong University of Finance and Economics, the director of the Marine Economics and Management Research Center of Shandong University of Finance and Economics, and an outstanding teacher in China.
His main research directions are: decision theory and optimization methods; marine economy and management; big data business analysis.
In-Journal News
Currently, Applied Artificial Intelligence is soliciting papers on the following topics.
Theme 1: Multiagent Systems in the Era of Trustworthy Artificial Intelligence
Reliable multi-agent system in the era of artificial intelligence
Deadline for submission: August 23, 2023
Topic 2: Artificial Intelligence Applications in Industry 4.0
Artificial Intelligence in Industry 4.0
Deadline for submission: August 31, 2023
Topic 3: Explainable Machine Learning Operational Applied Research and Applications for Improved Decision-Making
Explainable machine learning application research and applications to improve decision-making
Deadline for submission: October 30, 2023
Author Distribution
According to JCR, among the countries that have published articles on Applied Artificial Intelligence in the past three years, the top three countries are:
- India
- China
- Iran
For article recommendations, you can go to [TandF Academic] to read: http://985.so/m1ug6
刊内高被引文章

Full article: Transfer Learning-Based Framework for Classification of Pest in Tomato Plants (tandfonline.com)
基于迁移学习的框架,为番茄植株上的害虫分类
作者:Gayatri Pattnaik et al.
 The concept of transfer learning
The concept of transfer learning
文章摘要:
Pest in the plant is a major challenge in the agriculture sector. Hence, early and accurate detection and classification of pests could help in precautionary measures while substantially reducing economic losses. Recent developments in deep convolutional neural network (CNN) have drastically improved the accuracy of image recognition systems. In this paper, we have presented a transfer learning of pre-trained deep CNN-based framework for classification of pest in tomato plants. The dataset for this study has been collected from online sources that consist of 859 images categorized into 10 classes. This study is first of its kind where: (i) dataset with 10 classes of tomato pest are involved; (ii) an exhaustive comparison of the performance of 15 pre-trained deep CNN models has been presented on tomato pest classification. The experimental results show that the highest classification accuracy of 88.83% has been obtained using DenseNet169 model. Further, the encouraging results of transfer learning-based models demonstrate its effectiveness in pest detection and classification tasks.

Full article: General Learning Equilibrium Optimizer: A New Feature Selection Method for Biological Data Classification (tandfonline.com)
通用学习均衡优化器:一种新的用于生物数据分类的特征选择方法
作者:Jingwei Too & Seyedali Mirjalili
Basic concept of general learning strategy
文章摘要:
Finding relevant information from biological data is a critical issue for the study of disease diagnosis, especially when an enormous number of biological features are involved. Intentionally, the feature selection can be an imperative preprocessing step before the classification stage. Equilibrium optimizer (EO) is a recently established metaheuristic algorithm inspired by the principle of dynamic source and sink models when measuring the equilibrium states. In this research, a new variant of EO called general learning equilibrium optimizer (GLEO) is proposed as a wrapper feature selection method. This approach adopts a general learning strategy to help the particles to evade the local areas and improve the capability of finding promising regions. The proposed GLEO aims to identify a subset of informative biological features among a large number of attributes. The performance of the GLEO algorithm is validated on 16 biological datasets, where nine of them represent high dimensionality with a smaller number of instances. The results obtained show the excellent performance of GLEO in terms of fitness value, accuracy, and feature size in comparison with other metaheuristic algorithms.
刊内2022年高阅读量文章

Full article: A Survey on Deep Learning-based Architectures for Semantic Segmentation on 2D Images (tandfonline.com)
综述:基于深度学习的2D图像语义分割体系架构的调查
作者:Irem Ulku & Erdem Akagündüz
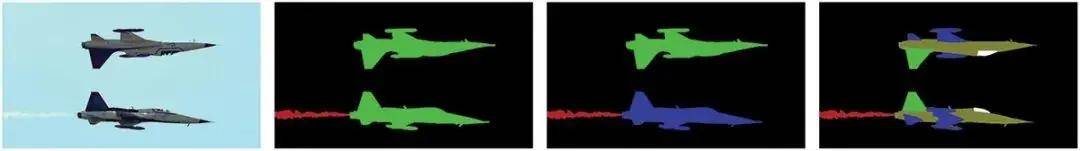
A sample image and its annotation for object, instance and parts segmentations separately, from left to right
文章摘要:
Semantic segmentation is the pixel-wise labeling of an image. Boosted by the extraordinary ability of convolutional neural networks (CNN) in creating semantic, high-level and hierarchical image features; several deep learning-based 2D semantic segmentation approaches have been proposed within the last decade. In this survey, we mainly focus on the recent scientific developments in semantic segmentation, specifically on deep learning-based methods using 2D images. We started with an analysis of the public image sets and leaderboards for 2D semantic segmentation, with an overview of the techniques employed in performance evaluation. In examining the evolution of the field, we chronologically categorized the approaches into three main periods, namely pre-and early deep learning era, the fully convolutional era, and the post-FCN era. We technically analyzed the solutions put forward in terms of solving the fundamental problems of the field, such as fine-grained localization and scale invariance. Before drawing our conclusions, we present a table of methods from all mentioned eras, with a summary of each approach that explains their contribution to the field. We conclude the survey by discussing the current challenges of the field and to what extent they have been solved.

Full article: The Emerging Threat of Ai-driven Cyber Attacks: A Review (tandfonline.com)
综述:人工智能驱动的网络攻击的新威胁
作者:Blessing Guembe et al.
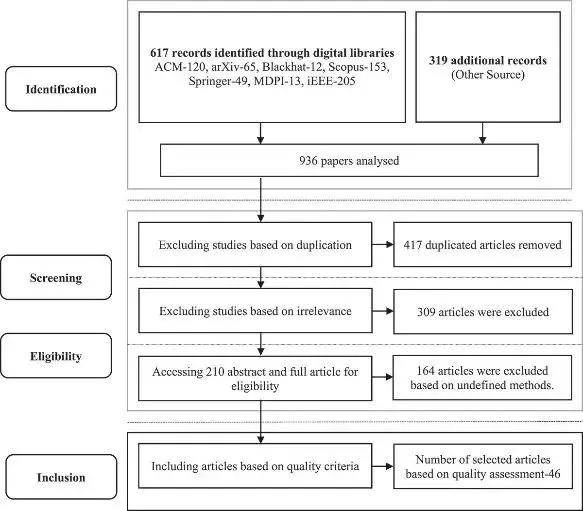
PRISMA flowchart illustrating the systematic review process and article selection at various stages
文章摘要:
Cyberattacks are becoming more sophisticated and ubiquitous. Cybercriminals are inevitably adopting Artificial Intelligence (AI) techniques to evade the cyberspace and cause greater damages without being noticed. Researchers in cybersecurity domain have not researched the concept behind AI-powered cyberattacks enough to understand the level of sophistication this type of attack possesses. This paper aims to investigate the emerging threat of AI-powered cyberattacks and provide insights into malicious used of AI in cyberattacks. The study was performed through a three-step process by selecting only articles based on quality, exclusion, and inclusion criteria that focus on AI-driven cyberattacks. Searches in ACM, arXiv Blackhat, Scopus, Springer, MDPI, IEEE Xplore and other sources were executed to retrieve relevant articles. Out of the 936 papers that met our search criteria, a total of 46 articles were finally selected for this study. The result shows that 56% of the AI-Driven cyberattack technique identified was demonstrated in the access and penetration phase, 12% was demonstrated in exploitation, and command and control phase, respectively; 11% was demonstrated in the reconnaissance phase; 9% was demonstrated in the delivery phase of the cybersecurity kill chain. The findings in this study shows that existing cyber defence infrastructures will become inadequate to address the increasing speed, and complex decision logic of AI-driven attacks. Hence, organizations need to invest in AI cybersecurity infrastructures to combat these emerging threats.
审稿周期
- 从提交稿件到获取初审意见,平均需要61天
- 获取首个同行评审决定,平均需要62天
- 稿件一旦接受后,在线出版平均需要15天
文章出版费(APC)
您可以通过我们的作者服务网站查询本期刊的标准文章出版费。
Taylor & Francis Group 现在开通APC便捷支付功能,可以一键通过微信、支付宝和银联使用人民币便捷付款。
为帮助更多科研人员选择更加合适的期刊,Taylor & Francis推出专栏——刊·见,该专栏致力于为读者和广大科研人员带来Taylor & Francis旗下期刊的详细解读,从期刊的基本情况、编委阵容、社会影响力到审稿速度、高被引文章等实用信息,专栏将为您带来最详细的介绍,让您更加全面地了解Taylor & Francis旗下优秀的国际期刊,帮助更多中国卓越科研成果顺利在国际期刊上发表。
以上内容可能更新,请以期刊官网主页为准。
The above is the detailed content of Journal·See | Capturing the latest developments in the field of artificial intelligence? Save Applied Artificial Intelligence to your favorites. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 I Tried Vibe Coding with Cursor AI and It's Amazing!
Mar 20, 2025 pm 03:34 PM
I Tried Vibe Coding with Cursor AI and It's Amazing!
Mar 20, 2025 pm 03:34 PM
Vibe coding is reshaping the world of software development by letting us create applications using natural language instead of endless lines of code. Inspired by visionaries like Andrej Karpathy, this innovative approach lets dev
 Top 5 GenAI Launches of February 2025: GPT-4.5, Grok-3 & More!
Mar 22, 2025 am 10:58 AM
Top 5 GenAI Launches of February 2025: GPT-4.5, Grok-3 & More!
Mar 22, 2025 am 10:58 AM
February 2025 has been yet another game-changing month for generative AI, bringing us some of the most anticipated model upgrades and groundbreaking new features. From xAI’s Grok 3 and Anthropic’s Claude 3.7 Sonnet, to OpenAI’s G
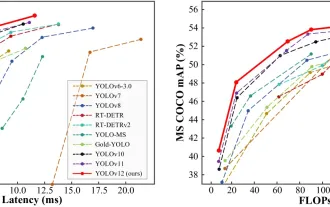 How to Use YOLO v12 for Object Detection?
Mar 22, 2025 am 11:07 AM
How to Use YOLO v12 for Object Detection?
Mar 22, 2025 am 11:07 AM
YOLO (You Only Look Once) has been a leading real-time object detection framework, with each iteration improving upon the previous versions. The latest version YOLO v12 introduces advancements that significantly enhance accuracy
 Best AI Art Generators (Free & Paid) for Creative Projects
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:10 PM
Best AI Art Generators (Free & Paid) for Creative Projects
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:10 PM
The article reviews top AI art generators, discussing their features, suitability for creative projects, and value. It highlights Midjourney as the best value for professionals and recommends DALL-E 2 for high-quality, customizable art.
 Is ChatGPT 4 O available?
Mar 28, 2025 pm 05:29 PM
Is ChatGPT 4 O available?
Mar 28, 2025 pm 05:29 PM
ChatGPT 4 is currently available and widely used, demonstrating significant improvements in understanding context and generating coherent responses compared to its predecessors like ChatGPT 3.5. Future developments may include more personalized interactions and real-time data processing capabilities, further enhancing its potential for various applications.
 Best AI Chatbots Compared (ChatGPT, Gemini, Claude & More)
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:09 PM
Best AI Chatbots Compared (ChatGPT, Gemini, Claude & More)
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:09 PM
The article compares top AI chatbots like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Claude, focusing on their unique features, customization options, and performance in natural language processing and reliability.
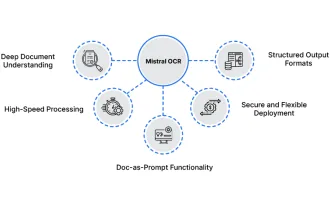 How to Use Mistral OCR for Your Next RAG Model
Mar 21, 2025 am 11:11 AM
How to Use Mistral OCR for Your Next RAG Model
Mar 21, 2025 am 11:11 AM
Mistral OCR: Revolutionizing Retrieval-Augmented Generation with Multimodal Document Understanding Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems have significantly advanced AI capabilities, enabling access to vast data stores for more informed respons
 Top AI Writing Assistants to Boost Your Content Creation
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:11 PM
Top AI Writing Assistants to Boost Your Content Creation
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:11 PM
The article discusses top AI writing assistants like Grammarly, Jasper, Copy.ai, Writesonic, and Rytr, focusing on their unique features for content creation. It argues that Jasper excels in SEO optimization, while AI tools help maintain tone consist



