ASCII code comparison table

1. Introduction to ASCII code
ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange, American Standard Code for Information Interchange) is a set of character encodings based on Latin letters. A total of 128 characters are included, which can be stored in one byte. It is equivalent to the international standard ISO/IEC 646. The ASCII specification was first published in 1967 and last updated in 1986.
The ASCII encoding range is 0x00-0x7F, which is 0-127 in decimal, defining 128 single-byte characters. It contains 33 control characters (characters that have some special functions but cannot be displayed) and 95 displayable characters (numbers, letters, symbols). The national standard code GB18030 and the international code Unicode are both compatible with ASCII encoding.
2.ASCII code comparison table
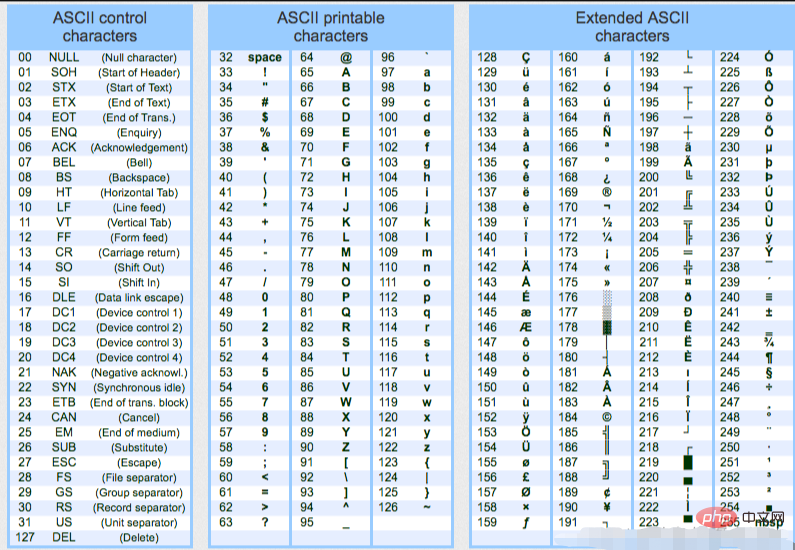
3.The reason for the generation of ASCII code
In the computer, all data is stored and processed Binary numbers must be used when expressing (because computers use high and low levels to represent 1 and 0 respectively). For example, 52 letters (including uppercase) like a, b, c, d and numbers such as 0 and 1 are also represented. Some commonly used symbols (such as *, #, @, etc.) are also represented by binary numbers when stored in the computer. Of course, everyone can agree on which binary numbers are used to represent which symbol. (This is (called encoding), and if everyone wants to communicate with each other without causing confusion, then everyone must use the same encoding rules. Therefore, the relevant standardization organizations in the United States introduced ASCII encoding, which uniformly stipulates which binary numbers are used to represent the above common symbols. .
The American Standard Code for Information Interchange was developed by the American National Standard Institute (ANSI) and is a standard single-byte character encoding scheme for text-based data. It was originally an American national standard and was used as a common Western character encoding standard for different computers to communicate with each other. Later, it was established as an international standard by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), called the ISO 646 standard. Applies to all Latin script letters.
The above is the detailed content of ASCII code comparison table. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 ASCII code comparison table
Jun 21, 2023 pm 05:36 PM
ASCII code comparison table
Jun 21, 2023 pm 05:36 PM
ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange, American Standard Code for Information Interchange) is a set of character encodings based on Latin letters. It contains a total of 128 characters and can be stored in one byte. It is equivalent to the international standard ISO/IEC 646 . The ASCII specification was first published in 1967 and last updated in 1986.
 What is the ascii code value of d
Feb 02, 2023 am 11:26 AM
What is the ascii code value of d
Feb 02, 2023 am 11:26 AM
The ASCII code value of d is 100; because the ASCII code value of a is the hexadecimal number 61H, that is, the decimal value is 97, and d is the last three digits of a, then the ASCII code value of d is "97+3=100" ;ASCII code uses a specified 7-bit or 8-bit binary number combination to represent 128 or 256 possible characters.
 How many bytes does an ascii code occupy?
Sep 07, 2023 pm 04:03 PM
How many bytes does an ascii code occupy?
Sep 07, 2023 pm 04:03 PM
An ASCII code occupies one byte. ASCII code is a coding standard used to represent characters. It uses 7-bit binary numbers to represent 128 different characters, including letters, numbers, punctuation marks, special characters, etc. A byte is the basic unit of computer storage unit. It consists of 8 binary bits. Each binary bit can be 0 or 1. One byte can represent 256 different values, so it can represent all characters in the ASCII code.
 what does ascii code mean
Jul 18, 2022 am 11:15 AM
what does ascii code mean
Jul 18, 2022 am 11:15 AM
ascii code is a computer coding system based on Latin letters; ascii code is the abbreviation of "American Standard Code for Information Interchange". It is mainly used to display modern English and other Western European languages. It is the most common information exchange standard, using the designated 7 bit or 8-bit binary number combination to represent 128 or 256 possible characters.
 Does the standard ascii code of one character occupy one byte of storage?
Aug 02, 2022 pm 04:39 PM
Does the standard ascii code of one character occupy one byte of storage?
Aug 02, 2022 pm 04:39 PM
Yes, the ASCII code of one character occupies 1 byte of storage space. In the ASCII code table, the order from small to large code values is: control characters, numeric characters, uppercase English letters, and lowercase English letters. ASCII code is a Western encoding, mainly used to display modern English and other Western European languages. One code occupies one byte.
 ASCII code comparison table
Jan 15, 2024 pm 04:30 PM
ASCII code comparison table
Jan 15, 2024 pm 04:30 PM
ASCII code is "American Standard Code for Information Interchange", American Standard Code for Information Interchange: 1, 0, NUL; 2, 1, SOH; 3, 2, STX; 4, 3, ETX, etc. ASCII code includes many other characters and symbols. Each character corresponds to a unique integer value, and these integer values are called ASCII codes.
 What are the differences between unicode and ascii
Sep 06, 2023 am 11:56 AM
What are the differences between unicode and ascii
Sep 06, 2023 am 11:56 AM
The differences between unicode and ascii include different encoding ranges, different storage spaces, and different compatibility. Detailed introduction: 1. The encoding range is different. The encoding range of ASCII is 0-127, which is mainly used to represent English letters. The encoding range of Unicode is much wider and can represent almost all language characters; 2. The storage space is different. ASCII usually Use 1 byte to store a character, while unicode may use 2 or more bytes to store a character; 3. Different compatibility, etc.
 What is the largest ascii code?
Mar 06, 2023 pm 01:48 PM
What is the largest ascii code?
Mar 06, 2023 pm 01:48 PM
The largest ascii code is 127. ASCII code is the American Standard Code for Information Interchange, a computer coding system based on the Latin alphabet, mainly used to display modern English and other Western European languages. The standard ASCII code uses 7 binary bits to represent one character, and there are 128 codes in total; 0 to 31 and 127 are control characters or special communication characters (the rest are displayable characters), 32 to 126 are characters, and 65 to 90 are There are 26 uppercase English letters, numbers 97 to 122 are lowercase English letters, and the rest are some punctuation marks, arithmetic symbols, etc.



