Build an adaptive Spring Cloud microservice architecture
With the continuous development and expansion of enterprise applications, microservice architecture has become a trend in enterprise development. Microservice architecture can help enterprises quickly build, deploy and manage various applications. Spring Cloud is an excellent open source framework that provides various tools and services for building microservices-based applications. This article will introduce how to build an adaptive Spring Cloud microservice architecture.
- Design an adaptive service registration center
The service registration center is one of the core components of the microservice architecture. It provides a mechanism for various microservices to discover and coordinate with each other. When building an adaptive Spring Cloud microservice architecture, we need to design an adaptive service registration center. This service registry can automatically adjust based on the resources and services available in the current environment.
- Build a scalable service gateway
The service gateway is another important component, it is the entry point for all microservices. It controls traffic, parses requests, and routes them to the correct service as needed. When building an adaptive Spring Cloud microservice architecture, we need to build an extensible service gateway. This services gateway automatically scales based on current traffic load and available resources.
- Realizing elastic microservices
In the microservice architecture, each microservice is independent of each other. This means that the failure of one service does not affect other services. When building an adaptive Spring Cloud microservice architecture, we need to implement elastic microservices. These microservices should be able to automatically handle failures, make decisions, and recover themselves, as well as work in coordination with other services.
- Deploying containerized microservices
Containerization has become another trend in enterprise application development. Containers help us deploy, scale, and manage applications faster. When building an adaptive Spring Cloud microservice architecture, we need to deploy containerized microservices. This will allow us to better manage different microservices and automatically scale container instances up and down as needed.
- Implementing observability and measurement
In the microservice architecture, each service is relatively independent, but there is an interdependence relationship. When a problem occurs, it is necessary to quickly locate the problem and take appropriate measures. Therefore, when building an adaptive Spring Cloud microservices architecture, we need to implement observability and measurement. This includes logging, measuring service performance and real-time monitoring.
Summary
By designing an adaptive service registry, building a scalable service gateway, implementing elastic microservices, deploying containerized microservices, and achieving observability and measurement, we An adaptive Spring Cloud microservices architecture can be built. This will enable us to better manage and scale enterprise applications and respond to changing business needs in a more flexible manner.
The above is the detailed content of Build an adaptive Spring Cloud microservice architecture. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1377
1377
 52
52
 How steep is the learning curve of golang framework architecture?
Jun 05, 2024 pm 06:59 PM
How steep is the learning curve of golang framework architecture?
Jun 05, 2024 pm 06:59 PM
The learning curve of the Go framework architecture depends on familiarity with the Go language and back-end development and the complexity of the chosen framework: a good understanding of the basics of the Go language. It helps to have backend development experience. Frameworks that differ in complexity lead to differences in learning curves.
 PHP Frameworks and Microservices: Cloud Native Deployment and Containerization
Jun 04, 2024 pm 12:48 PM
PHP Frameworks and Microservices: Cloud Native Deployment and Containerization
Jun 04, 2024 pm 12:48 PM
Benefits of combining PHP framework with microservices: Scalability: Easily extend the application, add new features or handle more load. Flexibility: Microservices are deployed and maintained independently, making it easier to make changes and updates. High availability: The failure of one microservice does not affect other parts, ensuring higher availability. Practical case: Deploying microservices using Laravel and Kubernetes Steps: Create a Laravel project. Define microservice controllers. Create Dockerfile. Create a Kubernetes manifest. Deploy microservices. Test microservices.
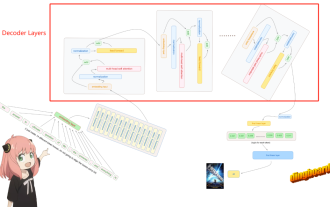 Hand-tearing Llama3 layer 1: Implementing llama3 from scratch
Jun 01, 2024 pm 05:45 PM
Hand-tearing Llama3 layer 1: Implementing llama3 from scratch
Jun 01, 2024 pm 05:45 PM
1. Architecture of Llama3 In this series of articles, we implement llama3 from scratch. The overall architecture of Llama3: Picture the model parameters of Llama3: Let's take a look at the actual values of these parameters in the Llama3 model. Picture [1] Context window (context-window) When instantiating the LlaMa class, the variable max_seq_len defines context-window. There are other parameters in the class, but this parameter is most directly related to the transformer model. The max_seq_len here is 8K. Picture [2] Vocabulary-size and AttentionL
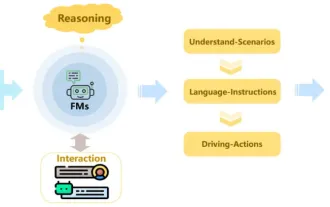 Review! Comprehensively summarize the important role of basic models in promoting autonomous driving
Jun 11, 2024 pm 05:29 PM
Review! Comprehensively summarize the important role of basic models in promoting autonomous driving
Jun 11, 2024 pm 05:29 PM
Written above & the author’s personal understanding: Recently, with the development and breakthroughs of deep learning technology, large-scale foundation models (Foundation Models) have achieved significant results in the fields of natural language processing and computer vision. The application of basic models in autonomous driving also has great development prospects, which can improve the understanding and reasoning of scenarios. Through pre-training on rich language and visual data, the basic model can understand and interpret various elements in autonomous driving scenarios and perform reasoning, providing language and action commands for driving decision-making and planning. The base model can be data augmented with an understanding of the driving scenario to provide those rare feasible features in long-tail distributions that are unlikely to be encountered during routine driving and data collection.
 How does the Java framework support horizontal scaling of microservices?
Jun 04, 2024 pm 04:34 PM
How does the Java framework support horizontal scaling of microservices?
Jun 04, 2024 pm 04:34 PM
The Java framework supports horizontal expansion of microservices. Specific methods include: Spring Cloud provides Ribbon and Feign for server-side and client-side load balancing. NetflixOSS provides Eureka and Zuul to implement service discovery, load balancing and failover. Kubernetes simplifies horizontal scaling with autoscaling, health checks, and automatic restarts.
 Create distributed systems using the Golang microservices framework
Jun 05, 2024 pm 06:36 PM
Create distributed systems using the Golang microservices framework
Jun 05, 2024 pm 06:36 PM
Create a distributed system using the Golang microservices framework: Install Golang, choose a microservices framework (such as Gin), create a Gin microservice, add endpoints to deploy the microservice, build and run the application, create an order and inventory microservice, use the endpoint to process orders and inventory Use messaging systems such as Kafka to connect microservices Use the sarama library to produce and consume order information
 What are the challenges in building a microservices architecture using Java frameworks?
Jun 02, 2024 pm 03:22 PM
What are the challenges in building a microservices architecture using Java frameworks?
Jun 02, 2024 pm 03:22 PM
Building a microservice architecture using a Java framework involves the following challenges: Inter-service communication: Choose an appropriate communication mechanism such as REST API, HTTP, gRPC or message queue. Distributed data management: Maintain data consistency and avoid distributed transactions. Service discovery and registration: Integrate mechanisms such as SpringCloudEureka or HashiCorpConsul. Configuration management: Use SpringCloudConfigServer or HashiCorpVault to centrally manage configurations. Monitoring and observability: Integrate Prometheus and Grafana for indicator monitoring, and use SpringBootActuator to provide operational indicators.
 Microservice architecture monitoring and alarming in Java framework
Jun 02, 2024 pm 12:39 PM
Microservice architecture monitoring and alarming in Java framework
Jun 02, 2024 pm 12:39 PM
Microservice architecture monitoring and alarming in the Java framework In the microservice architecture, monitoring and alarming are crucial to ensuring system health and reliable operation. This article will introduce how to use Java framework to implement monitoring and alarming of microservice architecture. Practical case: Use SpringBoot+Prometheus+Alertmanager1. Integrate Prometheus@ConfigurationpublicclassPrometheusConfig{@BeanpublicSpringBootMetricsCollectorspringBootMetric




