 Operation and Maintenance
Operation and Maintenance
 Linux Operation and Maintenance
Linux Operation and Maintenance
 How to solve the problem of excessive memory and leakage in Linux system
How to solve the problem of excessive memory and leakage in Linux system
How to solve the problem of excessive memory and leakage in Linux system
How to deal with the frequent problems of high memory usage and memory leaks in Linux systems
In the process of using Linux systems, we sometimes encounter problems of high memory usage and memory leaks. These issues can cause system slowdowns, application crashes, and even system crashes. This article explores how to resolve these issues.
First, let’s understand the concepts of high memory usage and memory leaks.
- High memory usage
High memory usage means that there is very little memory available in the system, and most of the memory is in use. When memory usage exceeds a certain threshold, the system may become sluggish or even fail to function properly.
- Memory leak
A memory leak occurs when an application fails to properly release memory after it has finished using it, resulting in the memory being unusable again. Over time, the leaked memory will accumulate, eventually causing the system to run out of memory.
Next, let’s see how to solve these problems.
- Solutions to high memory usage
First of all, we can determine whether the memory usage is too high by checking the memory usage of the system. You can use the following command to check:
$ free -m
This command will display the total memory, used memory, available memory and other information in the system.
If you find that the memory usage is too high, you can solve it by the following methods:
- Check the memory usage of the application: Use the top command to check the memory usage of each process in the system , and find the process that takes up more memory. As needed, consider shutting down or reconfiguring these processes to reduce memory usage.
- Adjust the size of the swap space: Swap space is a kind of auxiliary memory storage. When the physical memory is insufficient, the system writes part of the memory data to the swap space. By adjusting the size of the swap space, you can increase the system's available memory. You can use the following command to adjust the size of the swap space:
$ sudo swapon /path/to/swapfile
where /path/to/swapfile is the path and file of the swap space name. You can freely set the size of the swap space according to your needs.
- Solutions to memory leaks
Memory leaks are caused by the application not properly releasing memory, so the key to solving the memory leak problem is to find and fix the leaked memory. code.
The following are some common methods to solve memory leak problems:
- Use memory leak detection tools: Use tools such as Valgrind to detect memory leaks in your program. Valgrind analyzes your application's memory usage and reports any memory leaks. By viewing the report, you can find and fix code that leaks memory.
- Check the code carefully: Check the code carefully to find places that may cause memory leaks. Pay special attention to situations where memory is not released correctly after dynamically allocated memory, such as malloc, calloc and other functions.
- Use smart pointers and garbage collection mechanism: Use smart pointers to automatically manage memory. Smart pointers can automatically release memory when an object is no longer used. The garbage collection mechanism can automatically identify and reclaim memory that is no longer used.
- Restart the application regularly: If you cannot find and fix the memory leak problem, you can consider restarting the application regularly. Restarting can clear the leaked memory and restore normal operation of the system.
Summary:
When dealing with frequent high memory usage and leak problems in Linux systems, we can check the system's memory usage and the application's memory usage situation to determine the specific cause of the problem and take appropriate solutions. Through reasonable configuration and optimization, the performance and stability of the system can be improved and frequent memory problems can be avoided.
The above is the detailed content of How to solve the problem of excessive memory and leakage in Linux system. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
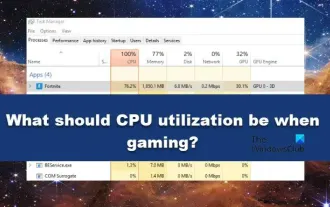 What should the CPU utilization be when gaming?
Feb 19, 2024 am 11:21 AM
What should the CPU utilization be when gaming?
Feb 19, 2024 am 11:21 AM
It's common for games to slow down your computer because they consume a lot of resources. It's crucial to understand your CPU usage when gaming so you can avoid overloading it. Therefore, keeping track of appropriate CPU usage is key to keeping your gaming experience smooth. In this article, we'll look at the appropriate CPU usage you should achieve while your game is running. CPU utilization during gaming CPU utilization is an important indicator of processor workload and depends on the performance specifications of the CPU. More powerful CPUs generally have higher usage. A CPU with more cores and threads can improve the overall performance of your system. Multi-threading support helps unleash the full potential of your CPU. In games, CPU usage depends on processor utilization, which can affect the game
 How to solve win11 memory leak. Analysis of the causes of win11 memory leak and various solutions.
Feb 29, 2024 am 09:58 AM
How to solve win11 memory leak. Analysis of the causes of win11 memory leak and various solutions.
Feb 29, 2024 am 09:58 AM
Recently, many friends who use win11 system have found that the memory occupied by their computer desktop window is very large, and there are also serious memory leaks, which will cause other programs to run unsmoothly. To address this problem, we should How can users solve it? We open the control panel of the computer, click to select the function of the power button, and uncheck the enable fast startup option. Restarting the computer will solve the problem. There may also be a problem with the graphics card driver. Just re-download the driver. . Causes of memory leaks: Memory leaks are caused by misaligned resources in a computer program due to incorrect memory allocation. This happens when unused RAM locations are still not freed. Do not confuse memory leaks with space leaks or memory leaks
 Golang function memory leak detection and resolution
Apr 23, 2024 pm 05:09 PM
Golang function memory leak detection and resolution
Apr 23, 2024 pm 05:09 PM
There is a function memory leak in the Go language, which will cause the application to continuously consume memory and crash. We can use the runtime/pprof package for detection and check if a function accidentally holds a reference to an unneeded resource. To solve a memory leak, we need to find the reference that caused the leak, usually by inspecting the function code and looking for global variables or closure references.
 Detailed analysis of common memory management issues in C++
Oct 10, 2023 am 10:51 AM
Detailed analysis of common memory management issues in C++
Oct 10, 2023 am 10:51 AM
C++ is a powerful programming language, but it is also a language that requires careful handling of memory management. When writing programs in C++, memory management problems are often encountered. This article will analyze common memory management issues in C++ in detail and provide specific code examples to help readers understand and solve these problems. 1. Memory leak (MemoryLeak) Memory leak means that the dynamically allocated memory in the program is not released correctly, resulting in a waste of memory resources. This is a common problem, especially on large or long runs
 How to deal with the 100% CPU utilization problem in win7
Jan 02, 2024 pm 08:17 PM
How to deal with the 100% CPU utilization problem in win7
Jan 02, 2024 pm 08:17 PM
Win7 CPU usage of 100 is a very depressing thing. Under normal circumstances, the computer is running less than 100%. Only in rare cases or malicious plug-ins and viruses can cause these problems. It may also be due to the hardware configuration. Let’s follow Let’s take a look at the solution. Solution to win7 CPU usage 100: If there is no problem with the hardware, it is recommended to reinstall the system. Reason 1: Viruses, Trojans, and a large number of worms replicate rapidly within the system, causing the CPU resource usage to remain high. Solution: Use reliable anti-virus software to completely clean the system memory and local hard disk, and open the system settings software to check whether there are any programs that start abnormally. Regularly update and upgrade anti-virus software and firewalls, strengthen anti-virus awareness, and master correct anti-virus knowledge
 How to solve the problem of excessive memory and leakage in Linux system
Jun 30, 2023 pm 02:21 PM
How to solve the problem of excessive memory and leakage in Linux system
Jun 30, 2023 pm 02:21 PM
How to deal with the frequent problems of high memory usage and memory leaks in Linux systems. In the process of using Linux systems, we sometimes encounter problems of high memory usage and memory leaks. These issues can cause system slowdowns, application crashes, and even system crashes. This article explores how to resolve these issues. First, let’s understand the concepts of high memory usage and memory leaks. High Memory Usage High memory usage means that there is very little memory available in the system and most of the memory is in use. When memory is used
 Memory leaks in PHP applications: causes, detection and resolution
May 09, 2024 pm 03:57 PM
Memory leaks in PHP applications: causes, detection and resolution
May 09, 2024 pm 03:57 PM
A PHP memory leak occurs when an application allocates memory and fails to release it, resulting in a reduction in the server's available memory and performance degradation. Causes include circular references, global variables, static variables, and expansion. Detection methods include Xdebug, Valgrind and PHPUnitMockObjects. The resolution steps are: identify the source of the leak, fix the leak, test and monitor. Practical examples illustrate memory leaks caused by circular references, and specific methods to solve the problem by breaking circular references through destructors.
 Golang development notes: How to avoid memory leak problems
Nov 23, 2023 am 09:38 AM
Golang development notes: How to avoid memory leak problems
Nov 23, 2023 am 09:38 AM
Golang is a fast and efficient development language that is widely popular for its powerful concurrency capabilities and built-in garbage collection mechanism. However, even when developing with Golang, it is still possible to encounter memory leaks. This article will introduce some common Golang development considerations to help developers avoid memory leak problems. Avoid circular references Circular references are one of the common memory leak problems in Golang. When two objects refer to each other, if the references to these objects are not released in a timely manner,



