What is the most commonly used character encoding in computers?
The most commonly used character encoding in computers is Unicode. Unicode encoding uses 16-bit or 32-bit encoding and can represent more than 130,000 characters. In the past, different countries and regions used different character encodings to cause interoperability problems. Now Unicode It solves the conversion problem between different character encodings and realizes the unified representation of global characters.

#The operating environment of this article: Windows 10 system, dell g3 computer.
In computers, the most commonly used character encoding is Unicode. Unicode is a character set used to assign unique numeric identifiers to nearly all characters and symbols in the world.
Unicode encoding uses 16-bit (2 bytes) or 32-bit (4 bytes) encoding and can represent more than 130,000 characters. Among them, the Basic Multilingual Plane (BMP) uses 16-bit encoding and covers commonly used language symbols, such as English letters, Arabic numerals, Latin letters, Greek letters, Cyrillic letters, Chinese characters, etc. The remaining characters use 32-bit encoding.
The emergence of Unicode has solved the interoperability problems caused by different countries and regions using different character encodings in the past. In the past, each country and region had its own character encoding, such as ASCII, GB2312, BIG5, etc. These encodings can only represent characters in a specific language or region, but cannot uniformly represent global characters. Therefore, in an international environment, conversion between different character encodings is a tedious and error-prone task.
In order to allow Unicode encoding to be used in computers, the Unicode Transformation Format (UTF) came into being. UTF-8 is one of the most commonly used UTF encodings. It uses a variable-length encoding scheme and can represent any character in the Unicode character set. UTF-8 uses 1-byte encoding for ASCII characters, while Chinese characters usually use 3-byte encoding. UTF-16 and UTF-32 are two other commonly used Unicode encoding formats.
Due to the popularity of Unicode, operating systems, applications and Internet standards on computers have fully supported Unicode. This means that now users will not be restricted by character encoding whether they are entering characters in a text editor, accessing web pages in a browser, or using file names in the operating system.
Summary
Unicode is the most commonly used character encoding in computers. It solves the problem of conversion between different character encodings and achieves a unified representation of global characters. With the development of the global Internet and the advancement of computer technology, the importance of Unicode will become increasingly prominent.
The above is the detailed content of What is the most commonly used character encoding in computers?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1387
1387
 52
52
 11 common classification feature encoding techniques
Apr 12, 2023 pm 12:16 PM
11 common classification feature encoding techniques
Apr 12, 2023 pm 12:16 PM
Machine learning algorithms only accept numerical input, so if we encounter categorical features, we will encode the categorical features. This article summarizes 11 common categorical variable encoding methods. 1. ONE HOT ENCODING The most popular and commonly used encoding method is One Hot Enoding. A single variable with n observations and d distinct values is converted into d binary variables with n observations, each binary variable is identified by a bit (0, 1). For example: the simplest implementation after coding is to use pandas' get_dummiesnew_df=pd.get_dummies(columns=[‘Sex’], data=df)2,
 How to solve the problem of garbled characters in tomcat logs?
Dec 28, 2023 pm 01:50 PM
How to solve the problem of garbled characters in tomcat logs?
Dec 28, 2023 pm 01:50 PM
What are the methods to solve the problem of garbled tomcat logs? Tomcat is a popular open source JavaServlet container that is widely used to support the deployment and running of JavaWeb applications. However, sometimes garbled characters appear when using Tomcat to record logs, which causes a lot of trouble to developers. This article will introduce several methods to solve the problem of garbled Tomcat logs. Adjust Tomcat's character encoding settings. Tomcat uses ISO-8859-1 character encoding by default.
 How many bytes do utf8 encoded Chinese characters occupy?
Feb 21, 2023 am 11:40 AM
How many bytes do utf8 encoded Chinese characters occupy?
Feb 21, 2023 am 11:40 AM
UTF8 encoded Chinese characters occupy 3 bytes. In UTF-8 encoding, one Chinese character is equal to three bytes, and one Chinese punctuation mark occupies three bytes; while in Unicode encoding, one Chinese character (including traditional Chinese) is equal to two bytes. UTF-8 uses 1~4 bytes to encode each character. One US-ASCIl character only needs 1 byte to encode. Latin, Greek, Cyrillic, Armenian, and Hebrew with diacritical marks. , Arabic, Syriac and other letters require 2-byte encoding.
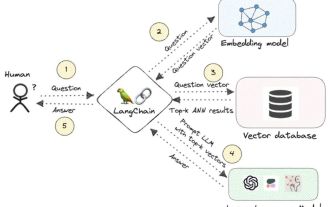 Knowledge graph: the ideal partner for large models
Jan 29, 2024 am 09:21 AM
Knowledge graph: the ideal partner for large models
Jan 29, 2024 am 09:21 AM
Large language models (LLMs) have the ability to generate smooth and coherent text, bringing new prospects to areas such as artificial intelligence conversation and creative writing. However, LLM also has some key limitations. First, their knowledge is limited to patterns recognized from training data, lacking a true understanding of the world. Second, reasoning skills are limited and cannot make logical inferences or fuse facts from multiple data sources. When faced with more complex and open-ended questions, LLM's answers may become absurd or contradictory, known as "illusions." Therefore, although LLM is very useful in some aspects, it still has certain limitations when dealing with complex problems and real-world situations. In order to bridge these gaps, retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) systems have emerged in recent years. The core idea is
 Several common encoding methods
Oct 24, 2023 am 10:09 AM
Several common encoding methods
Oct 24, 2023 am 10:09 AM
Common encoding methods include ASCII encoding, Unicode encoding, UTF-8 encoding, UTF-16 encoding, GBK encoding, etc. Detailed introduction: 1. ASCII encoding is the earliest character encoding standard, using 7-bit binary numbers to represent 128 characters, including English letters, numbers, punctuation marks, control characters, etc.; 2. Unicode encoding is a method used to represent all characters in the world The standard encoding method of characters, which assigns a unique digital code point to each character; 3. UTF-8 encoding, etc.
 PHP coding tips: How to generate a QR code with anti-counterfeiting verification function?
Aug 17, 2023 pm 02:42 PM
PHP coding tips: How to generate a QR code with anti-counterfeiting verification function?
Aug 17, 2023 pm 02:42 PM
PHP coding tips: How to generate a QR code with anti-counterfeiting verification function? With the development of e-commerce and the Internet, QR codes are increasingly used in various industries. In the process of using QR codes, in order to ensure product safety and prevent counterfeiting, it is very important to add anti-counterfeiting verification functions to the QR codes. This article will introduce how to use PHP to generate a QR code with anti-counterfeiting verification function, and attach corresponding code examples. Before starting, we need to prepare the following necessary tools and libraries: PHPQRCode: PHP
 Effective method to solve the problem of garbled characters in the eclipse editor
Jan 04, 2024 pm 06:56 PM
Effective method to solve the problem of garbled characters in the eclipse editor
Jan 04, 2024 pm 06:56 PM
An effective method to solve the garbled problem of eclipse requires specific code examples. In recent years, with the rapid development of software development, eclipse, as one of the most popular integrated development environments, has provided convenience and efficiency to many developers. However, you may encounter garbled code problems when using eclipse, which brings trouble to project development and code reading. This article will introduce some effective methods to solve the problem of garbled characters in Eclipse and provide specific code examples. Modify eclipse file encoding settings: in eclip
 How to handle character encoding conversion exceptions in Java development
Jul 01, 2023 pm 05:10 PM
How to handle character encoding conversion exceptions in Java development
Jul 01, 2023 pm 05:10 PM
How to deal with character encoding conversion exceptions in Java development In Java development, character encoding conversion is a common problem. When we process files, network transmissions, databases, etc., different systems or platforms may use different character encoding methods, causing abnormalities in character parsing and conversion. This article will introduce some common causes and solutions of character encoding conversion exceptions. 1. The basic concept of character encoding. Character encoding is the rules and methods used to convert characters into binary data. Common character encoding methods include AS



