 Operation and Maintenance
Operation and Maintenance
 Linux Operation and Maintenance
Linux Operation and Maintenance
 Configure Linux systems to support file system and storage device driver development
Configure Linux systems to support file system and storage device driver development
Configure Linux systems to support file system and storage device driver development
Configuring the Linux system to support file system and storage device driver development
In the Linux operating system, the file system and storage device driver are very important components. They provide for the normal operation of the operating system and data storage. Provided necessary support. In order to develop file systems and storage device drivers, we need to configure the Linux system accordingly. This article will introduce how to configure a Linux system to support file system and storage device driver development, and provide corresponding code examples.
1. Install the Linux system
First, we need to install the Linux system on the computer. Choose a suitable Linux distribution, such as Ubuntu, CentOS, etc., and install it according to the official documentation or wizard. After the installation is completed, the system will automatically configure the basic file system and storage device driver.
2. Choose a suitable development environment
Before developing the file system and storage device driver, we need to choose a suitable development environment. The following are several commonly used development environment options:
- Local development environment: Build a development environment on your own computer to facilitate the writing and debugging of file systems and drivers.
- Virtual machine development environment: Create a virtual machine on the computer through virtual machine software, such as VirtualBox, VMware, etc., and install the Linux system in it for development.
- Remote development environment: Develop on a remote Linux server through remote login methods such as SSH, suitable for multi-person collaboration or scenarios that require powerful computing capabilities.
Choose a development environment that suits you based on actual needs.
3. Configuring the file system
- File system driver compilation
Before developing the file system, we need to compile the corresponding file system driver in advance . Taking the ext4 file system as an example, you first need to obtain and compile the source code of the ext4 file system. Execute the following command in the terminal:
$ git clone https://github.com/tytso/ext4.git $ cd ext4 $ make
After the compilation is completed, a driver file named ext4.ko will be generated.
- Loading the file system driver
After compilation is completed, we need to load the file system driver into the kernel. Execute the following command in the terminal:
$ sudo insmod ext4.ko
Through the above command, we successfully loaded the ext4 file system driver into the Linux kernel.
4. Configure storage device driver
- Storage device driver compilation
For storage device driver development, we also need to compile the corresponding driver in advance . Taking the SATA hard drive as an example, you first need to obtain and compile the source code of the SATA hard drive. Execute the following command in the terminal:
$ git clone https://github.com/torvalds/linux.git $ cd linux $ make menuconfig
After the make menuconfig command is executed, a graphical interface will open where you can select and configure different drivers and functions. We need to find the configuration items related to the SATA hard drive, select them and save them.
Next, execute the following command to compile:
$ make
After the compilation is completed, a driver file named sata.ko will be generated.
- Loading the storage device driver
After compilation is completed, we need to load the storage device driver into the kernel. Execute the following command in the terminal:
$ sudo insmod sata.ko
Through the above command, we successfully loaded the SATA hard drive into the Linux kernel.
5. Writing sample code
After configuring the file system and storage device driver, we can start the corresponding development work. The following is a simple sample code that demonstrates how to read a file in Linux:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
FILE *fp;
char ch;
fp = fopen("test.txt", "r");
if(fp == NULL)
{
printf("File open failed.
");
exit(1);
}
while((ch = fgetc(fp)) != EOF)
printf("%c", ch);
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}The above code opens a file named test.txt through the fopen function and loops through each character in the file and Output to the terminal until the end of the file. Finally, the file is closed through the fclose function.
6. Summary
By configuring the Linux system accordingly, we can support the development of file systems and storage device drivers. This article uses the file system and SATA hard drive as examples to introduce the specific configuration process and provide corresponding code examples. I hope it will be helpful to beginners in the field of file system and storage device driver development.
The above is the detailed content of Configure Linux systems to support file system and storage device driver development. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
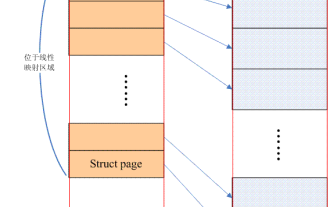 Linux Memory Model: A Deeper Understanding of Memory Management
Feb 13, 2024 pm 03:15 PM
Linux Memory Model: A Deeper Understanding of Memory Management
Feb 13, 2024 pm 03:15 PM
Have you ever encountered various memory problems in Linux systems? Such as memory leaks, memory fragmentation, etc. These problems can be solved through a deep understanding of the Linux memory model. 1. Introduction The Linux kernel supports three memory models, namely flatmemorymodel, Discontiguousmemorymodel and sparsememorymodel. The so-called memory model actually refers to the distribution of physical memory from the perspective of the CPU and the method used to manage these physical memories in the Linux kernel. In addition, it should be noted that this article mainly focuses on sharememo
 Configuring Linux systems to support edge computing and smart device development
Jul 04, 2023 pm 09:00 PM
Configuring Linux systems to support edge computing and smart device development
Jul 04, 2023 pm 09:00 PM
Configuring Linux Systems to Support Edge Computing and Smart Device Development With the rapid development of edge computing and smart devices, more and more developers are turning their attention to how to perform edge computing and smart device development on Linux systems. This article will describe how to configure a Linux system to support both aspects of development, and provide some code examples. 1. Install the Linux system. First, we need to choose a Linux distribution suitable for edge computing and smart device development, such as Ubuntu or Debian. Can
 Configure Linux systems to support embedded image processing and computer vision development
Jul 04, 2023 pm 04:21 PM
Configure Linux systems to support embedded image processing and computer vision development
Jul 04, 2023 pm 04:21 PM
Configuring Linux systems to support embedded image processing and computer vision development In the field of embedded image processing and computer vision development, Linux systems have a wide range of applications. By configuring a Linux system, we can provide developers with a powerful development environment to develop and debug various image processing and computer vision algorithms. This article will describe how to configure a Linux system to support embedded image processing and computer vision development, and provide some code examples. To install the Linux system first, we need to select
 Configuring Linux systems to support edge gateway and IoT gateway development
Jul 04, 2023 pm 06:12 PM
Configuring Linux systems to support edge gateway and IoT gateway development
Jul 04, 2023 pm 06:12 PM
Configuring Linux systems to support edge gateway and IoT gateway development In the development of the Internet of Things, edge computing and IoT gateways play a vital role. As a middleware for data transmission and processing, edge gateways connect devices and cloud systems to provide efficient and secure communication services for the Internet of Things. This article will describe how to configure a Linux system to support the development of edge gateways and IoT gateways. 1. Install the Linux system First, we need to install a suitable Linux distribution on the target device. Common Linux issues
 Even novices can do it easily! Linux system software installation guide
Mar 09, 2024 am 09:25 AM
Even novices can do it easily! Linux system software installation guide
Mar 09, 2024 am 09:25 AM
Faced with the increasingly popular technology, computers have been integrated into every corner of human life. Linux is popular for its open source nature, but installing applications on the system can still be challenging for novices. This article will comprehensively analyze the software installation steps in Linux systems to help you master this skill easily. 1. Use the package manager. In the Linux environment, the most common and convenient way to install software is to use the package manager. Each distribution version uses different package management tools due to its own characteristics. For example, the Debian camp uses the apt-get command to download Red Flag Linux, and the RedHat series chooses to use the yum command. Just enter the corresponding command on the console to quickly install the software.
 Configuring Linux systems to support multi-threaded programming
Jul 04, 2023 pm 07:05 PM
Configuring Linux systems to support multi-threaded programming
Jul 04, 2023 pm 07:05 PM
Configuring a Linux system to support multi-threaded programming Multi-threaded programming has become very common in the current development of computer applications. Multithreaded programming allows programs to perform multiple tasks simultaneously, thereby improving system performance and responsiveness. This article will introduce how to configure a Linux system to support multi-threaded programming and give some code examples. Install necessary software packages First, we need to install some necessary software packages for multi-threaded programming on Linux systems. These packages can be installed using the following command: sud
 Configuring Linux systems to support IoT application development
Jul 04, 2023 pm 10:49 PM
Configuring Linux systems to support IoT application development
Jul 04, 2023 pm 10:49 PM
Configuring Linux Systems to Support IoT Application Development The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the embedding of physical devices, vehicles, and other objects with electronics, sensors, software, and network connections that enable these objects to collect and exchange data. During the development process of IoT applications, it is essential to configure the Linux system to provide the necessary development environment and tools. This article will introduce how to configure a Linux system to support IoT application development and provide some code samples for reference. 1. Installation
 Configuring Linux systems to support smart power and energy management development
Jul 04, 2023 pm 10:45 PM
Configuring Linux systems to support smart power and energy management development
Jul 04, 2023 pm 10:45 PM
Configuring Linux systems to support smart power and energy management development Introduction: With the continuous development of smart power and energy management technology, more and more developers have begun to get involved in the development of related fields. As an open source operating system, Linux has strong flexibility and customizability, and has become the platform of choice for many developers. This article will show you how to configure a Linux system to support smart power and energy management development and provide some code examples. 1. Install the Linux operating system and choose a Linux that suits you



