 Operation and Maintenance
Operation and Maintenance
 Linux Operation and Maintenance
Linux Operation and Maintenance
 Configuring Linux systems to support edge computing and smart device development
Configuring Linux systems to support edge computing and smart device development
Configuring Linux systems to support edge computing and smart device development
Configuring Linux systems to support edge computing and smart device development
With the rapid development of edge computing and smart devices, more and more developers are turning their attention to how to perform edge computing on Linux systems. Computing and smart device development. This article will describe how to configure a Linux system to support both aspects of development, and provide some code examples.
1. Install the Linux system
First, we need to choose a Linux distribution suitable for edge computing and smart device development, such as Ubuntu or Debian. You can download the image file from the official website and install it according to the official guide. During the installation process, you can choose to install additional development toolsets.
2. Update the Linux system
After the installation is completed, we need to ensure that the Linux system is up to date. Execute the following command to update system packages:
sudo apt update sudo apt upgrade
This will update all packages on the system to the latest version.
3. Install development tools
Next, we need to install some necessary development tools. The following are some commonly used development tools:
- GNU tool chain: An essential tool chain for embedded development on Linux systems, including gcc, g, make, etc. Execute the following command to install:
sudo apt install build-essential
- CMake: used to build cross-platform projects, allowing developers to use device configurations that are independent of operating systems and compilers. Execute the following command to install:
sudo apt install cmake
- Python Development Kit: Many edge computing and smart device developments use the Python programming language. Execute the following command to install:
sudo apt install python-dev python-pip
- Hardware-specific SDK: If you are using a specific smart device for development, there is usually a hardware-specific SDK for developers to use. You can download it from the official website of the device and follow the instructions to install it.
4. Configure environment variables
After completing the above steps, we need to configure environment variables so that we can access the development tools normally in the terminal.
- Open the terminal and execute the following command:
nano ~/.bashrc
- In the opened file, add the following content:
export PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/bin
- Press Ctrl X to save and exit.
- Execute the following command to make the changes take effect:
source ~/.bashrc
5. Code example
The following is a simple code example showing how to implement it through Python on a Linux system A basic edge computing task. In this example, we will use Python's socket module to create a simple server and listen on a port to receive requests from clients.
import socket
def main():
# 创建socket对象
server_socket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
# 绑定IP地址和端口
server_socket.bind(('0.0.0.0', 8080))
# 监听端口,最大连接数为5
server_socket.listen(5)
while True:
# 接受客户端连接
client_socket, client_address = server_socket.accept()
# 接收客户端请求
data = client_socket.recv(1024)
# 处理请求
response = 'Hello, World!'
# 发送响应
client_socket.sendall(response.encode())
# 关闭连接
client_socket.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()The above code creates a simple server that listens for connections with IP address 0.0.0.0 and port 8080, and returns a simple response after receiving a client request.
6. Summary
Through the configuration and code examples in this article, you can easily develop edge computing and smart devices on Linux systems. Of course, this article only gives some basic configurations and examples, and the actual development process may involve more tools and technologies. I hope this article can provide some help for you in edge computing and smart device development on Linux.
The above is the detailed content of Configuring Linux systems to support edge computing and smart device development. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
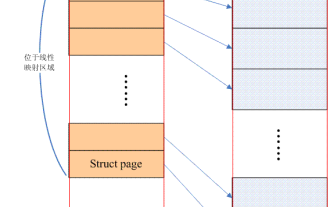 Linux Memory Model: A Deeper Understanding of Memory Management
Feb 13, 2024 pm 03:15 PM
Linux Memory Model: A Deeper Understanding of Memory Management
Feb 13, 2024 pm 03:15 PM
Have you ever encountered various memory problems in Linux systems? Such as memory leaks, memory fragmentation, etc. These problems can be solved through a deep understanding of the Linux memory model. 1. Introduction The Linux kernel supports three memory models, namely flatmemorymodel, Discontiguousmemorymodel and sparsememorymodel. The so-called memory model actually refers to the distribution of physical memory from the perspective of the CPU and the method used to manage these physical memories in the Linux kernel. In addition, it should be noted that this article mainly focuses on sharememo
 The application potential of Golang technology in blockchain edge computing
May 09, 2024 am 11:03 AM
The application potential of Golang technology in blockchain edge computing
May 09, 2024 am 11:03 AM
The Go language is ideal for developing blockchain edge computing applications because of its concurrency, high performance, and rich ecosystem. Use cases include smart contract execution, data collection and analysis, and identity verification. Go code examples demonstrate executing smart contracts and collecting and analyzing data on edge devices.
 Combination practice and architecture design of MongoDB and edge computing
Nov 02, 2023 pm 01:44 PM
Combination practice and architecture design of MongoDB and edge computing
Nov 02, 2023 pm 01:44 PM
With the rapid development of the Internet of Things and cloud computing, edge computing has gradually become a new hot area. Edge computing refers to the transfer of data processing and computing capabilities from traditional cloud computing centers to edge nodes of physical devices to improve data processing efficiency and reduce latency. As a powerful NoSQL database, MongoDB is attracting more and more attention for its application in the field of edge computing. 1. Practice of combining MongoDB with edge computing In edge computing, devices usually have limited computing and storage resources. And MongoDB
 The trend of combining java framework and edge computing
Jun 05, 2024 pm 10:06 PM
The trend of combining java framework and edge computing
Jun 05, 2024 pm 10:06 PM
Java frameworks are combined with edge computing to enable innovative applications. They create new opportunities for the Internet of Things, smart cities and other fields by reducing latency, improving data security, and optimizing costs. The main integration steps include selecting an edge computing platform, deploying Java applications, managing edge devices, and cloud integration. Benefits of this combination include reduced latency, data localization, cost optimization, scalability and resiliency.
 One article to understand edge computing technology in autonomous driving systems
Apr 08, 2023 pm 05:01 PM
One article to understand edge computing technology in autonomous driving systems
Apr 08, 2023 pm 05:01 PM
With the advent of the 5G era, edge computing has become a new business growth point in autonomous driving systems. In the future, more than 60% of data and applications will be generated and processed at the edge. Edge computing is a new computing model that performs calculations at the edge of the network. Its data processing mainly includes two parts, one is the downlink cloud service, and the other is the uplink Internet of Everything service. "Edge" is actually a relative concept, referring to any computing, storage and network-related resources on the path from data to the cloud computing center. From one end of the data to the other end of the cloud service center, the edge can be represented as one or more resource nodes on this path based on the specific needs of the application and actual application scenarios. The business essence of edge computing is the aggregation of cloud computing outside the data center
 Configuring Linux systems to support edge computing and smart device development
Jul 04, 2023 pm 09:00 PM
Configuring Linux systems to support edge computing and smart device development
Jul 04, 2023 pm 09:00 PM
Configuring Linux Systems to Support Edge Computing and Smart Device Development With the rapid development of edge computing and smart devices, more and more developers are turning their attention to how to perform edge computing and smart device development on Linux systems. This article will describe how to configure a Linux system to support both aspects of development, and provide some code examples. 1. Install the Linux system. First, we need to choose a Linux distribution suitable for edge computing and smart device development, such as Ubuntu or Debian. Can
 Enhancing instant insights: The synergy of computer vision and edge computing
Sep 13, 2023 pm 01:01 PM
Enhancing instant insights: The synergy of computer vision and edge computing
Sep 13, 2023 pm 01:01 PM
In today's fast-paced world, seamless integration of cutting-edge technologies has become the cornerstone of innovation. What’s rewritten: Across industries, computer vision and edge computing stand out as two key pillars. Computer vision is a technology driven by artificial intelligence that enables machines to interpret, analyze and understand visual information from the world. Edge computing supports real-time data processing and analysis at the edge of the network, closer to the data source, reducing latency and improving efficiency. Benefits of integrating computer vision with edge computing The integration of computer vision and edge computing opens up a new field of possibilities, especially In areas where real-time data analysis and low latency are critical. By bringing intelligence closer to the data source, businesses can now make faster, more informed decisions. This synergy enables
 Java Programming Guide: Huawei Cloud Edge Computing Interface Interconnection Example Sharing
Jul 05, 2023 am 08:17 AM
Java Programming Guide: Huawei Cloud Edge Computing Interface Interconnection Example Sharing
Jul 05, 2023 am 08:17 AM
Java Programming Guide: Huawei Cloud Edge Computing Interface Interconnection Example Sharing In recent years, with the continuous development of edge computing technology, more and more enterprises have begun to push computing resources to the edge to reduce data transmission delays and improve service quality. As a leading cloud computing service provider, Huawei Cloud also provides powerful edge computing capabilities and provides a wealth of development interfaces and tools to facilitate application development and docking for developers. This article will use a specific example to share how to use Java programming to connect to Huawei Cloud edge computing interface. first



