 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals
 AI
AI
 Huawei's large model appears in the official issue of Nature! Reviewer: Let people reexamine the future of forecast models
Huawei's large model appears in the official issue of Nature! Reviewer: Let people reexamine the future of forecast models
Huawei's large model appears in the official issue of Nature! Reviewer: Let people reexamine the future of forecast models
It is 10,000 times faster than the traditional method and only takes 1.4 seconds to complete the 24-hour global weather forecast - it is from Huawei Cloud's Pangu Weather Model.
Today, it was published in Nature. It is said to be the first official Nature paper published in recent years with a Chinese technology company as the sole signature unit (that is, the sole author of Huawei Cloud).
 Picture
Picture
The reviewers gave it high praise. This model allows humans to re-examine the future of weather forecast models.
The implication is that with it, the original traditional methods are no longer fragrant.
 Picture
Picture
So, how was it developed? What key challenges were solved? What are the specific results and applications?
Follow this paper and take you through it all.
Solving the problem of insufficient accuracy of existing AI weather forecast models
Since the 1920s, especially in the past three decades, with the rapid development of computing power, traditional numerical weather forecasting has Great success has been achieved in weather forecasting, extreme disaster warning, climate change prediction and other fields.
However, as the growth of computing power slows down and the physical model gradually becomes more complex, the bottleneck of this method becomes increasingly prominent.
So researchers began to explore new weather forecasting paradigms such as using deep learning methods to predict future weather.
The Huawei Cloud R&D team started research in this area 2 years ago.
They found that in the fields where numerical methods are most widely used, such as medium and long-term forecasting, the accuracy of existing AI forecasting methods is still significantly lower than numerical forecasting methods, and suffers from lack of interpretability and inaccurate extreme weather predictions. constraints and other issues.
There are two main reasons why the AI weather forecast modelis insufficient in accuracy:
First, existing AI weather forecast models are based on 2D neural networks and cannot handle uneven 3D weather data well; Second, AI methods lack mathematical and physical mechanism constraints, so in Iteration errors will continue to accumulate during the iteration process. Here, Huawei Cloud researchers proposed3D Earth-Specific Transformer (3DEST) to handle complex and complex Uniform 3D weather data to create a large Pangu weather model.
The main idea is to use a 3D variant of the visual transformer to handle complex uneven meteorological elements, and use a hierarchical temporal aggregation strategy , trained 4 models with different forecast intervals (respectively 1 hour interval, 3 hour interval, 6 hour interval, 24 hour interval) , making the prediction The number of iterations for meteorological conditions at a specific time is minimized, thereby reducing iteration errors and avoiding the consumption of training resources caused by recursive training.
To train each model, the researchers used meteorological data from 1979-2021, sampled on an hourly basis, and trained for 100 epochs. Each model requires 16 days of training on 192 V100 graphics cards. In fact, even after 100 epochs, these models still have not fully converged. In other words, with more sufficient computing resources, the accuracy of AI forecasts can be further improved. In the final reasoning, the Pangu weather model only needs 1.4 seconds to run on a V100 graphics card to complete 24-hour global weather forecast, including geopotential, humidity, wind speed, temperature, sea level pressure, etc. The horizontal spatial resolution reaches 0.25∘×0.25∘, the temporal resolution is 1 hour, covering 13 vertical layers, and can accurately predict fine-grained meteorological characteristics. As the first AI method whose accuracy exceeds that of traditional numerical forecasting methods, its calculation speed is more than 10,000 times higher than that of traditional numerical forecasting. Can be directly applied to multiple downstream scenariosIn May this year, the direction of Typhoon "Mawa" received widespread attention. The Central Meteorological Administration stated that the Huawei Cloud Pangu large model performed well in predicting the path of "Mava" and predicted its diversion path in the eastern waters of Taiwan Island five days in advance.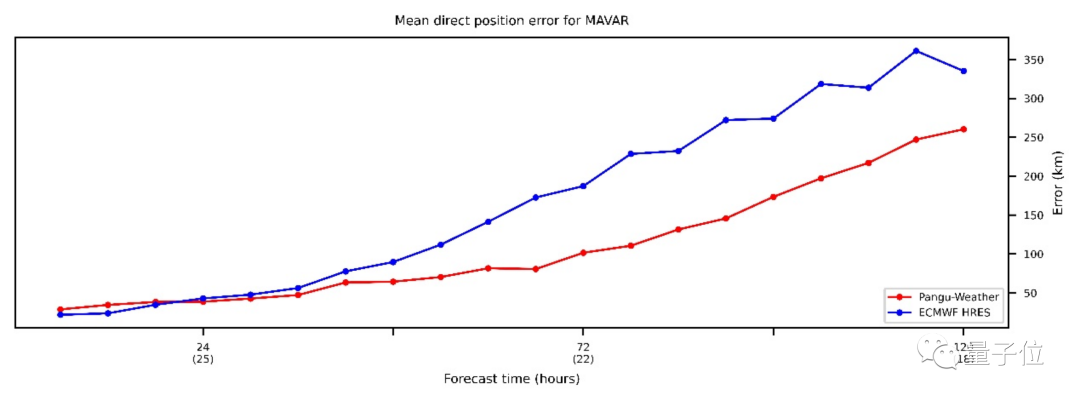 Picture
Picture
In order to explore the ability of AI to capture extreme weather, we studied a case in Finland in February this year, when a cold wave of -29°C was observed. We found that Pangu recognized the seriousness of this event earlier.
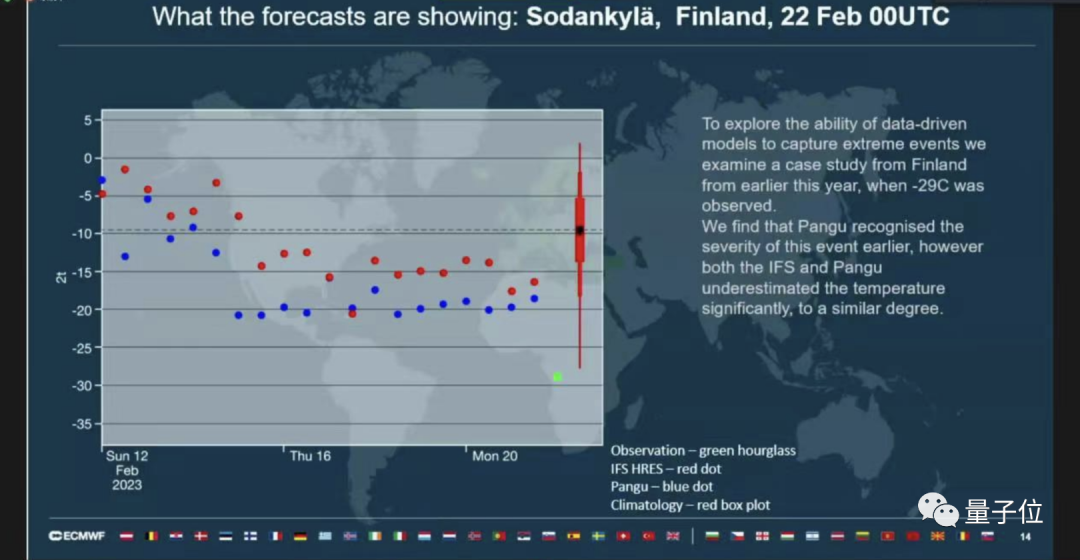 Picture
Picture
Florence Habiye also emphasized that AI prediction methods consume less resources and provide important opportunities for developing countries because It no longer requires large-scale supercomputing resources and provides a rare opportunity to improve global forecasting capabilities.
As for Huawei Cloud choosing the field of AI weather forecasting as a "breakthrough", on the one hand, weather forecasting, especially the accurate prediction of extreme weather such as heavy rains, typhoons, droughts, and cold waves, is related to the international people's livelihood. On the other hand, meteorology The prediction problem is very complex. AI can mine new atmospheric evolution patterns from massive data, which has huge potential for improvement in accuracy and speed.
It is understood that the WMO 2024-2027 strategic plan to be released by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) absorbs elements of artificial intelligence, making it an important force in promoting the development of meteorological science and technology.
WMO will also actively promote the demonstration application of AI in the fields of nowcasting and numerical weather forecasting, create an international comparison platform for artificial intelligence product applications, formulate AI meteorological application standards and guidelines, and promote the sharing of artificial intelligence data sets, etc. Related work, explore and leverage the application potential of AI in the field of meteorology, and effectively support the national early warning initiative.
Three Keys to the Future
Finally, how does the Huawei Cloud Pangu Weather Model team view the future of AI weather forecasting?
The answer is three keys:
First,Big data. Huge meteorological data is the cornerstone of AI models. Currently, the large-scale Pangu meteorological model only uses part of the ERA5 reanalysis data. Future AI models will be based on massive and more refined global observation data.
Secondly, Big computing power. The ultra-high resolution of meteorological data poses a huge challenge to the training of AI models. The current input resolution of the Pangu meteorological model is 1440×720×14×5, compared with the commonly used resolution of 224×224×3 for computational vision tasks. About 500 times. As the resolution further increases and the model grows, the computing resources required will also increase rapidly.
Finally, Big model. The complex meteorological laws, ultra-high resolution and huge amount of data all determine that AI weather forecasting requires the use of AI models with extremely high computational costs. At the same time, if you want to continuously iterate the leading AI weather forecast model, a stable cloud environment, work suite and corresponding operation and maintenance are also essential.
Paper address: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-023-06185-3
The above is the detailed content of Huawei's large model appears in the official issue of Nature! Reviewer: Let people reexamine the future of forecast models. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Yu Chengdong revealed that Huawei's tri-fold screen mobile phone will be unveiled in September: the price is not expected to be cheap
Aug 20, 2024 am 06:36 AM
Yu Chengdong revealed that Huawei's tri-fold screen mobile phone will be unveiled in September: the price is not expected to be cheap
Aug 20, 2024 am 06:36 AM
On August 19, Hongmeng held a delivery ceremony for the first batch of Xiangjie S9 owners in Shanghai. Huawei executive Yu Chengdong personally attended and delivered the vehicles to the owners. At the scene, a car owner who already owned Wenjie M5, M7, and M9 asked Yu Chengdong when he could buy Huawei's three-fold screen mobile phone. Yu Chengdong responded that it would be available next month. Fenyefenye Previously, real shots of what appeared to be Huawei's three-fold screen phone had leaked on the Internet, causing widespread concern. In the picture, the new phone held by Yu Chengdong shows extraordinary visual impact. Its screen size is far larger than that of conventional folding screen mobile phones. It has a unique design and is not a tablet but is better than a tablet. There is a central hole-punch camera inlaid on the top of the left side, as well as a vaguely visible double-fold design. The side of the phone is suspected to be equipped with a stylus. These clues all point to this
 The best time to buy Huawei Mate 60 series, new AI elimination + image upgrade, and enjoy autumn promotions
Aug 29, 2024 pm 03:33 PM
The best time to buy Huawei Mate 60 series, new AI elimination + image upgrade, and enjoy autumn promotions
Aug 29, 2024 pm 03:33 PM
Since the Huawei Mate60 series went on sale last year, I personally have been using the Mate60Pro as my main phone. In nearly a year, Huawei Mate60Pro has undergone multiple OTA upgrades, and the overall experience has been significantly improved, giving people a feeling of being constantly new. For example, recently, the Huawei Mate60 series has once again received a major upgrade in imaging capabilities. The first is the new AI elimination function, which can intelligently eliminate passers-by and debris and automatically fill in the blank areas; secondly, the color accuracy and telephoto clarity of the main camera have been significantly upgraded. Considering that it is the back-to-school season, Huawei Mate60 series has also launched an autumn promotion: you can enjoy a discount of up to 800 yuan when purchasing the phone, and the starting price is as low as 4,999 yuan. Commonly used and often new products with great value
 Huawei will launch the Xuanji sensing system in the field of smart wearables, which can assess the user's emotional state based on heart rate
Aug 29, 2024 pm 03:30 PM
Huawei will launch the Xuanji sensing system in the field of smart wearables, which can assess the user's emotional state based on heart rate
Aug 29, 2024 pm 03:30 PM
Recently, Huawei announced that it will launch a new smart wearable product equipped with Xuanji sensing system in September, which is expected to be Huawei's latest smart watch. This new product will integrate advanced emotional health monitoring functions. The Xuanji Perception System provides users with a comprehensive health assessment with its six characteristics - accuracy, comprehensiveness, speed, flexibility, openness and scalability. The system uses a super-sensing module and optimizes the multi-channel optical path architecture technology, which greatly improves the monitoring accuracy of basic indicators such as heart rate, blood oxygen and respiration rate. In addition, the Xuanji Sensing System has also expanded the research on emotional states based on heart rate data. It is not limited to physiological indicators, but can also evaluate the user's emotional state and stress level. It supports the monitoring of more than 60 sports health indicators, covering cardiovascular, respiratory, neurological, endocrine,
 Apple and Huawei both wanted to make a buttonless phone, but Xiaomi made it first?
Aug 29, 2024 pm 03:33 PM
Apple and Huawei both wanted to make a buttonless phone, but Xiaomi made it first?
Aug 29, 2024 pm 03:33 PM
According to a report from Smartprix, Xiaomi is developing a buttonless mobile phone codenamed "Suzaku". According to this news, this mobile phone codenamed Zhuque will be designed with an integrated concept, use an under-screen camera, and be equipped with Qualcomm Snapdragon 8gen4 processor. If the plan does not change, we are likely to see its arrival in 2025. When I saw this news, I thought I was back in 2019 - at that time, Xiaomi released the Mi MIX Alpha concept phone, and the surround-screen button-less design was quite amazing. This is the first time I have seen the charm of a buttonless mobile phone. If you want a piece of "magic glass", you must first kill the buttons. In "The Biography of Steve Jobs", Jobs once expressed that he hoped that the mobile phone could be like a piece of "magic glass".
 The price of Mate 60 is reduced by 800 yuan, and the price of Pura 70 is reduced by 1,000 yuan: Just wait until Huawei releases Mate 70!
Aug 16, 2024 pm 03:45 PM
The price of Mate 60 is reduced by 800 yuan, and the price of Pura 70 is reduced by 1,000 yuan: Just wait until Huawei releases Mate 70!
Aug 16, 2024 pm 03:45 PM
According to news on August 16, for current Huawei mobile phones, they are already working hard to clear the way for the launch of new models, so everyone has seen the prices of the Mate60 series and Pura70 series being reduced one after another. With Huawei officially announcing price cuts for the Mate60 series on August 15, the latest models of Huawei’s two flagship series have completed price adjustments. In July this year, Huawei officially announced that the Huawei Pura70 series would be on sale, with prices reduced by up to 1,000 yuan. Among them, Huawei Pura70 has a direct discount of 500 yuan, with a starting price of 4999 yuan; Huawei Pura70 Beidou Satellite News Edition has a direct discount of 500 yuan, with a starting price of 5099 yuan; Huawei Pura70Pro has a direct discount of 800 yuan, with a starting price of 5699 yuan; Huawei Pura70Pr
 2024Q2 Global Mobile Programmatic Advertising Report: Apple iPhone leads the way with 51% voice share, followed by Samsung, Huawei and Xiaomi
Aug 22, 2024 pm 02:05 PM
2024Q2 Global Mobile Programmatic Advertising Report: Apple iPhone leads the way with 51% voice share, followed by Samsung, Huawei and Xiaomi
Aug 22, 2024 pm 02:05 PM
According to news from this website on August 22, market research agency Pixalate released a report yesterday (August 21), stating that in the global mobile programmatic advertising market, Apple ranked first with a share of voice (SOV) of 51%. Explanation of related terms: This site briefly introduces the proper terms: Programmatic Advertising: Programmatic advertising refers to the use of advertising technology to purchase and sell digital advertising. Programmatic advertising can show your audience relevant ads through automated steps in less than a second. Share of Voice (SOV): Percentage of open programmatic ad sales related to specific device types in each region, as measured by Pixalate
 Huawei offers discounts on Mate X5 and other models, with prices reduced by up to thousands of yuan
Aug 29, 2024 pm 03:32 PM
Huawei offers discounts on Mate X5 and other models, with prices reduced by up to thousands of yuan
Aug 29, 2024 pm 03:32 PM
On August 29, Huawei Terminal officially announced that the Huawei Pioneer Thanksgiving Feedback Season has begun! Buy Huawei MateX5, Huawei Pocket2, Huawei novaFlip, Huawei Pura70 series, and Huawei Mate60 series immediately to enjoy purchasing privileges. However, Huawei officials did not elaborate on the specific rights and interests of the "purchase privileges". 1. Huawei Mate , limited to 10 o'clock/16 o'clock/20 o'clock, order placed every hour
 The world's first three-fold screen! Huawei Mate XT screen supplier exposed
Sep 03, 2024 pm 06:34 PM
The world's first three-fold screen! Huawei Mate XT screen supplier exposed
Sep 03, 2024 pm 06:34 PM
According to news on September 3, today, Huawei Terminal announced a new member of the Extraordinary Master series-MateXT. Huawei's Yu Chengdong forwarded this Weibo, and the mobile phone he used was the MateXT Extraordinary Master. It is reported that Mate Blogger Digital Chat Station hinted that the screen supplier for Huawei’s new MateXT Extraordinary Master product is BOE, which is also the first screen factory in the industry to mass-produce three-folding screens. Previously in August this year, Yu Chengdong was photographed using a three-fold screen mobile phone on an airplane. Judging from the exposed pictures, Huawei's three-fold screen mobile phone is very thin. Huawei three-fold screen mobile phone 1.





