 Database
Database
 Mysql Tutorial
Mysql Tutorial
 MySQL and Oracle: Comparison of support for data encryption and secure transmission
MySQL and Oracle: Comparison of support for data encryption and secure transmission
MySQL and Oracle: Comparison of support for data encryption and secure transmission
MySQL and Oracle: Comparison of support for data encryption and secure transmission
Introduction:
Data security has become increasingly important in today's information age. From personal privacy to business secrets, maintaining the confidentiality and integrity of data is critical for any organization. Among database management systems (DBMS), MySQL and Oracle are the two most popular options. In this article, we will compare the extent to which MySQL and Oracle support data encryption and secure transmission, and provide some code examples.
1. MySQL data encryption and secure transmission
MySQL supports a variety of encryption technologies, including encryption of data transmission and data storage. The following are commonly used data encryption functions and secure transmission methods in MySQL:
- SSL/TLS encrypted transmission:
MySQL supports encrypted transmission of data through the SSL/TLS protocol. By using digital certificates and asymmetric encryption algorithms, an encrypted channel is established between the client and the server to ensure the confidentiality of data during transmission.
The following is a code example for using SSL/TLS encrypted transmission in MySQL:
-- 启用SSL/TLS加密传输 GRANT USAGE ON *.* TO 'ssl_user'@'localhost' REQUIRE SSL; -- 创建或使用具有必要权限的用户并进行连接 mysql --ssl-ca=ca.pem --ssl-cert=client-cert.pem --ssl-key=client-key.pem -u ssl_user -h localhost
- Encryption of data storage:
MySQL 5.7 and above supports InnoDB tables of data encryption. Data confidentiality is achieved at the storage engine level by using the AES algorithm to encrypt and decrypt data.
The following is a code example for using data storage encryption in MySQL:
-- 创建一个加密的InnoDB表
CREATE TABLE encrypted_table (
id INT PRIMARY KEY,
sensitive_data VARBINARY(255)
) ENCRYPTION='Y';
-- 插入数据到加密表中
INSERT INTO encrypted_table VALUES (1, AES_ENCRYPT('sensitive data', 'encryption_key'));
-- 从加密表中检索数据
SELECT id, AES_DECRYPT(sensitive_data, 'encryption_key') FROM encrypted_table;2. Oracle’s data encryption and secure transmission
Oracle provides some powerful Data encryption and secure transmission capabilities. The following are commonly used data encryption functions and secure transmission methods in Oracle:
- Transparent Data Encryption (TDE) Transparent Data Encryption:
Oracle TDE is a function that implements data encryption at the database level . Data is protected from physical and logical access threats by using database encryption keys to encrypt and decrypt data stored on disk.
The following is a code example for using transparent data encryption in Oracle:
-- 启用TDE功能
ALTER SYSTEM SET ENCRYPTION KEY IDENTIFIED BY "encryption_key";
-- 创建加密表空间
CREATE TABLESPACE encrypted_data DATAFILE 'encrypted_data.dbf' SIZE 10M ENCRYPTION USING 'AES256';
-- 创建加密表
CREATE TABLE encrypted_table (
id NUMBER PRIMARY KEY,
sensitive_data VARCHAR2(255)
) TABLESPACE encrypted_data;
-- 插入数据到加密表中
INSERT INTO encrypted_table VALUES (1, 'sensitive data');
-- 从加密表中检索数据
SELECT id, sensitive_data FROM encrypted_table;- SSL/TLS encrypted transmission:
Oracle supports the use of SSL/TLS protocol for database The connection is encrypted. By configuring Oracle Net Services, secure communication between clients and servers can be achieved.
The following is a code example for using SSL/TLS encrypted transmission in Oracle:
-- 创建一个包含SSL配置的监听器
LISTENER =
(DESCRIPTION_LIST =
(DESCRIPTION =
(ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCP)(HOST = localhost)(PORT = 1521))
)
)
SSL_CLIENT_AUTHENTICATION = FALSE
SSL_CIPHER_SUITES = (SSL_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA, SSL_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA)
ADMIN_RESTRICTIONS=ON
SSL_SERVER_DN_MATCH=no
-- 启动监听器
LSNRCTL startConclusion:
Both MySQL and Oracle provide data encryption and secure transmission functions. There are different methods and strategies for protecting data confidentiality. MySQL is simpler and easier to use, and supports the more open SSL/TLS encrypted transmission. Oracle is more powerful in data encryption, supporting transparent data encryption and rich encryption functions. When choosing an appropriate data encryption and secure transmission method, you need to consider the specific needs and environment, comprehensively evaluate various factors, and choose a solution that suits you.
The above is the detailed content of MySQL and Oracle: Comparison of support for data encryption and secure transmission. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 How to enable nfc function on Xiaomi Mi 14 Pro?
Mar 19, 2024 pm 02:28 PM
How to enable nfc function on Xiaomi Mi 14 Pro?
Mar 19, 2024 pm 02:28 PM
Nowadays, the performance and functions of mobile phones are becoming more and more powerful. Almost all mobile phones are equipped with convenient NFC functions to facilitate users for mobile payment and identity authentication. However, some Xiaomi 14Pro users may not know how to enable the NFC function. Next, let me introduce it to you in detail. How to enable nfc function on Xiaomi 14Pro? Step 1: Open the settings menu of your phone. Step 2: Find and click the "Connect and Share" or "Wireless & Networks" option. Step 3: In the Connection & Sharing or Wireless & Networks menu, find and click "NFC & Payments". Step 4: Find and click "NFC Switch". Normally, the default is off. Step 5: On the NFC switch page, click the switch button to switch it to on.
 How to use TikTok on Huawei Pocket2 remotely?
Mar 18, 2024 pm 03:00 PM
How to use TikTok on Huawei Pocket2 remotely?
Mar 18, 2024 pm 03:00 PM
Sliding the screen through the air is a feature of Huawei that is highly praised in the Huawei mate60 series. This feature uses the laser sensor on the phone and the 3D depth camera of the front camera to complete a series of functions that do not require The function of touching the screen is, for example, to use TikTok from a distance. But how should Huawei Pocket 2 use TikTok from a distance? How to take screenshots from the air with Huawei Pocket2? 1. Open the settings of Huawei Pocket2 2. Then select [Accessibility]. 3. Click to open [Smart Perception]. 4. Just turn on the [Air Swipe Screen], [Air Screenshot], and [Air Press] switches. 5. When using it, you need to stand 20~40CM away from the screen, open your palm, and wait until the palm icon appears on the screen.
 iPhone 16 Pro CAD drawings exposed, adding a second new button
Mar 09, 2024 pm 09:07 PM
iPhone 16 Pro CAD drawings exposed, adding a second new button
Mar 09, 2024 pm 09:07 PM
The CAD files of the iPhone 16 Pro have been exposed, and the design is consistent with previous rumors. Last fall, the iPhone 15 Pro added an Action button, and this fall, Apple appears to be planning to make minor adjustments to the size of the hardware. Adding a Capture button According to rumors, the iPhone 16 Pro may add a second new button, which will be the second consecutive year to add a new button after last year. It is rumored that the new Capture button will be set on the lower right side of the iPhone 16 Pro. This design is expected to make camera control more convenient and also allow the Action button to be used for other functions. This button will no longer be just an ordinary shutter button. Regarding the camera, from the current iP
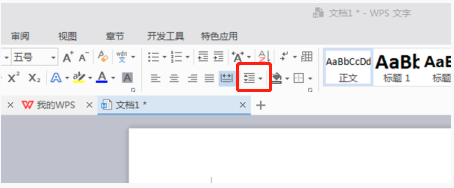 How to set line spacing in WPS Word to make the document neater
Mar 20, 2024 pm 04:30 PM
How to set line spacing in WPS Word to make the document neater
Mar 20, 2024 pm 04:30 PM
WPS is our commonly used office software. When editing long articles, the fonts are often too small to be seen clearly, so the fonts and the entire document are adjusted. For example: adjusting the line spacing of the document will make the entire document very clear. I suggest that all friends learn this operation step. I will share it with you today. The specific operation steps are as follows, come and take a look! Open the WPS text file you want to adjust, find the paragraph setting toolbar in the [Start] menu, and you will see the small line spacing setting icon (shown as a red circle in the picture). 2. Click the small inverted triangle in the lower right corner of the line spacing setting, and the corresponding line spacing value will appear. You can choose 1 to 3 times the line spacing (as shown by the arrow in the figure). 3. Or right-click the paragraph and it will appear.
 Three secrets for deploying large models in the cloud
Apr 24, 2024 pm 03:00 PM
Three secrets for deploying large models in the cloud
Apr 24, 2024 pm 03:00 PM
Compilation|Produced by Xingxuan|51CTO Technology Stack (WeChat ID: blog51cto) In the past two years, I have been more involved in generative AI projects using large language models (LLMs) rather than traditional systems. I'm starting to miss serverless cloud computing. Their applications range from enhancing conversational AI to providing complex analytics solutions for various industries, and many other capabilities. Many enterprises deploy these models on cloud platforms because public cloud providers already provide a ready-made ecosystem and it is the path of least resistance. However, it doesn't come cheap. The cloud also offers other benefits such as scalability, efficiency and advanced computing capabilities (GPUs available on demand). There are some little-known aspects of deploying LLM on public cloud platforms
 TrendX Research Institute: Merlin Chain project analysis and ecological inventory
Mar 24, 2024 am 09:01 AM
TrendX Research Institute: Merlin Chain project analysis and ecological inventory
Mar 24, 2024 am 09:01 AM
According to statistics on March 2, the total TVL of Bitcoin’s second-layer network MerlinChain has reached US$3 billion. Among them, Bitcoin ecological assets accounted for 90.83%, including BTC worth US$1.596 billion and BRC-20 assets worth US$404 million. Last month, MerlinChain’s total TVL reached US$1.97 billion within 14 days of launching staking activities, surpassing Blast, which was launched in November last year and is also the most recent and equally eye-catching. On February 26, the total value of NFTs in the MerlinChain ecosystem exceeded US$420 million, becoming the public chain project with the highest NFT market value besides Ethereum. Project Introduction MerlinChain is an OKX support
 The difference and comparative analysis between C language and PHP
Mar 20, 2024 am 08:54 AM
The difference and comparative analysis between C language and PHP
Mar 20, 2024 am 08:54 AM
Differences and comparative analysis between C language and PHP C language and PHP are both common programming languages, but they have obvious differences in many aspects. This article will conduct a comparative analysis of C language and PHP and illustrate the differences between them through specific code examples. 1. Syntax and usage: C language: C language is a process-oriented programming language, mainly used for system-level programming and embedded development. The syntax of C language is relatively simple and low-level, can directly operate memory, and is efficient and flexible. C language emphasizes the programmer's completeness of the program
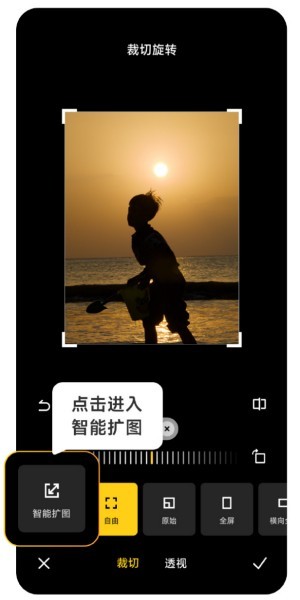 How to use Xiaomi Mi 14 Ultra AI smart image expansion?
Mar 16, 2024 pm 12:37 PM
How to use Xiaomi Mi 14 Ultra AI smart image expansion?
Mar 16, 2024 pm 12:37 PM
The progress of the times has made many people's incomes higher and higher, and the mobile phones they usually use will be changed frequently. The Xiaomi Mi 14 Ultra recently launched by Xiaomi must be familiar to users. It has very high performance configuration and can provide users with more In order to provide a comfortable and smooth experience, new mobile phones will inevitably encounter many functions that are not used. For example, how to use Xiaomi 14UltraAI smart image expansion? Come and take a look at the usage tutorial below! How to use Xiaomi 14UltraAI smart image expansion? First open Xiaomi 14Ultra, enter the photo album, select the picture you want to enlarge, and enter the photo album editing option. Click Crop Rotate, click Crop, and click Smart Expand in the selection that appears. Finally, choose the way to expand the image according to your own needs.



