 Backend Development
Backend Development
 Golang
Golang
 An article to help you understand the basic variables of Go language
An article to help you understand the basic variables of Go language
An article to help you understand the basic variables of Go language
Why variables are needed
To put it simply, the program we write defaultsData are all stored in the memory stick. It is impossible for us to find this variable directly through the address because the address is too long and difficult to remember.
Usually we find the address corresponding to through the variable name ##The above value is , and then perform a series of operations.
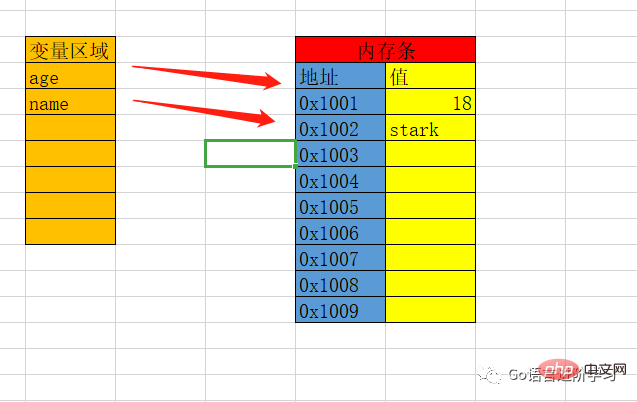
Variable types
Now, no matter what language it is, commonly used variables are divided into the following types.
Integer, 1, 6, 2, 8, 4...
Floating point number, 1.1, 5.7767, 23.99...
Boolean,
True, FalseString Type,
"Zhang San", "李思"...List
Map
It will probably be divided into the above types, but you don’t need to remember this, just understand it.
Variable definition
Declaration of variables
The format is as follows.
var 变量名 变量类型 例如: var age int var gender bool
Batch declaration
The variables declared above are declared one by one. If you need to declare them all at once Some variables can be written like this.
var (
age int
gender bool
name string
id int
height int
...
)声明时赋值
上述方式,只是声明了变量,但是并没有赋值,在后期需要时可以在赋值。
如果在声明时,就确定值是什么,可以直接赋值。
格式如下。
var 变量名 类型 = 值 例如: var age int = 18 var name string = "张三"
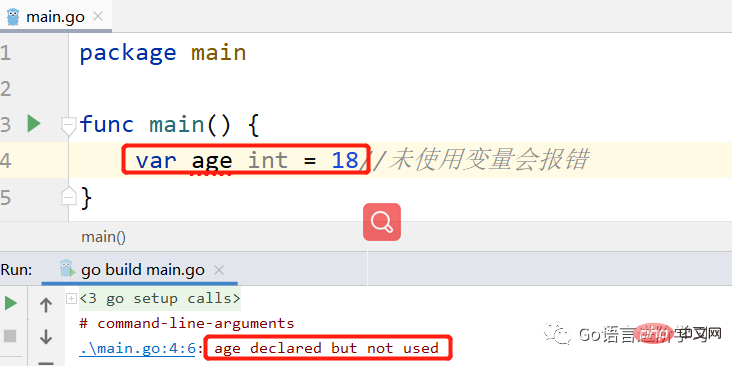
在Go中的一个强制要求
在Go中,变量必须使用,至少需要fmt.Println(变量)。
类型推导方式声明变量赋值
在上述声明变量并且赋值时,还需要指定变量类型。
在Go,Go具有类型推导方式声明时赋值变量。
var age = 18 var name = "张三"
其实就是变量名后面不用写变量类型了。
:=方式变量赋值
在Go,还有一种更简单的方式声明变量赋值。
格式如下。
age := 18 name := "张三"
学过Python的可能有点开心了,除了多个一个:号,其他基本和Pyton定义变量方式一样。
注意:
age := 18 //本质是执行的两句话 //同上 var age int age = 18
全局变量
简单说就是,在最外面的定义的变量就是全局变量。
在Go中,全局变量是有要求的。
package main
//全局变量:
// 方式一,声明全局变量,必须跟类型
//var age int
//方式二,声明变量且赋值,类型可以不用写
//var age = 18
//var age int = 18
//方式三,错误示例,全局变量要么只声明变量,要么声明就赋值
//var age int
//age =18
//方式四,错误示例,:=方式声明赋值
// 方式四其实就等于方式三的写法,所以不能用在全局变量中
//age := 18
func main() {
}PS:全局变量要么只声明,要么声明时就赋值,不能写两行赋值,所以:=方式不能应用在全局变量中
匿名变量
匿名变量多用于函数返回值场景中,比如函数返回了俩值,俩值要第一个值,就可以使用匿名变量。
因为Go中,变量必须使用,如果某个变量需要忽略,使用_即可。
值得注意的是,匿名变量不会占用内存。
package main
func get_info() (string, int) {
return "张三", 18
}
func main() {
//标准写法
//name, age := get_info()
//fmt.Println(name, age)
//匿名变量方式
//name, _ := get_info()
//fmt.Println(name)
//_,age := get_info()
//fmt.Println(age)
}常量
其实常量和变量基本一样,但是常量是不能修改的。
通常常量以大写定义。
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
//单个声明
const PI1 int = 3
const PI2 = 3.14
//同时声明多个
const (
PI3 = 3.14
PI4 = 3.14
)
//同上声明多个变量时,如果省略了值表示和上一行相同
const (
girl1 = 18
girl2 // 18,和上一行相同
girl3 // 18,和上一行相同
girl4 = 17
girl5 // 17,和上一行相同
)
fmt.Println(girl3, girl5)
}注:常量声明时就必须赋值
错误示例。
package main
func main() {
const age int
age = 18
//error
}The above is the detailed content of An article to help you understand the basic variables of Go language. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1387
1387
 52
52
 What libraries are used for floating point number operations in Go?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 02:06 PM
What libraries are used for floating point number operations in Go?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 02:06 PM
The library used for floating-point number operation in Go language introduces how to ensure the accuracy is...
 What is the problem with Queue thread in Go's crawler Colly?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 02:09 PM
What is the problem with Queue thread in Go's crawler Colly?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 02:09 PM
Queue threading problem in Go crawler Colly explores the problem of using the Colly crawler library in Go language, developers often encounter problems with threads and request queues. �...
 How to solve the user_id type conversion problem when using Redis Stream to implement message queues in Go language?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 04:54 PM
How to solve the user_id type conversion problem when using Redis Stream to implement message queues in Go language?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 04:54 PM
The problem of using RedisStream to implement message queues in Go language is using Go language and Redis...
 In Go, why does printing strings with Println and string() functions have different effects?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 02:03 PM
In Go, why does printing strings with Println and string() functions have different effects?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 02:03 PM
The difference between string printing in Go language: The difference in the effect of using Println and string() functions is in Go...
 What should I do if the custom structure labels in GoLand are not displayed?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 05:09 PM
What should I do if the custom structure labels in GoLand are not displayed?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 05:09 PM
What should I do if the custom structure labels in GoLand are not displayed? When using GoLand for Go language development, many developers will encounter custom structure tags...
 What is the difference between `var` and `type` keyword definition structure in Go language?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 12:57 PM
What is the difference between `var` and `type` keyword definition structure in Go language?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 12:57 PM
Two ways to define structures in Go language: the difference between var and type keywords. When defining structures, Go language often sees two different ways of writing: First...
 Which libraries in Go are developed by large companies or provided by well-known open source projects?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 04:12 PM
Which libraries in Go are developed by large companies or provided by well-known open source projects?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 04:12 PM
Which libraries in Go are developed by large companies or well-known open source projects? When programming in Go, developers often encounter some common needs, ...
 Why is it necessary to pass pointers when using Go and viper libraries?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 04:00 PM
Why is it necessary to pass pointers when using Go and viper libraries?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 04:00 PM
Go pointer syntax and addressing problems in the use of viper library When programming in Go language, it is crucial to understand the syntax and usage of pointers, especially in...



