 Backend Development
Backend Development
 Golang
Golang
 An article to help you understand the basic functions of Go language (Part 1)
An article to help you understand the basic functions of Go language (Part 1)
An article to help you understand the basic functions of Go language (Part 1)
Why we need functions
Functions are called functions in all programming languages, including Java, PHP, Python, JS, etc. They are all called functions.
The role of a function
is generally described as follows: a function can encapsulate repeated or specific functions into a convenient thing.
Note:In Go, functions support closures of.
When the function is not used
Code
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
//模拟一个打开文件,写入一行内容进入文件,在关闭文件的功能
var file_name = "a.txt" //文件名
var w_content = "爱我中华" //写入的内容
fmt.Println(fmt.Sprintf("打开 %s 文件",file_name))
fmt.Println(fmt.Sprintf("向 %s 文件写入了 %s ", file_name, w_content))
fmt.Println(fmt.Sprintf("关闭 %s 文件",file_name))
//如果再再向其他文件写入内容,还需要复制一次
var file_name2 = "b.txt" //文件名
var w_content2 = "中国威武" //写入的内容
fmt.Println(fmt.Sprintf("打开 %s 文件",file_name2))
fmt.Println(fmt.Sprintf("向 %s 文件写入了 %s ", file_name2, w_content2))
fmt.Println(fmt.Sprintf("关闭 %s 文件",file_name2))
}Use After the function,
encapsulates the same function into a function.
package main
import "fmt"
func w_file(filename string, w_content string) {
fmt.Println(fmt.Sprintf("打开 %s 文件", filename))
fmt.Println(fmt.Sprintf("向 %s 文件写入了 %s ", filename, w_content))
fmt.Println(fmt.Sprintf("关闭 %s 文件", filename))
}
func main() {
//将相同功能封装成函数
w_file("a.txt", "爱我中华")
w_file("b.txt", "中国威武")
}The results of executing the above code are as follows

##ps:But it can be clearly seen that by using functions to extract the same functions, the code will become simpler and neater.
Function usage
Function name naming rules
Try to name functions in camel case, for example: getName, connectData, etc. .
Syntax
In Go, the function language is defined using func Keywords.
func 函数名([参数1 参数类型1,参数2 参数类型2,...]) [(返回值 返回值类型,...)]{
逻辑代码
}
//中括号表示可选参数无参数,无返回值
package main
import "fmt"
func say1() {
fmt.Println("我终于会说话了...")
}有参数,无返回值
func say2(c string) {
fmt.Println("我终于会说" + c + "了")
}有或者无参数,有返回值
func say3(c string) (string) {
fmt.Println("我终于会说" + c + "了")
return "哦耶"
}main函数
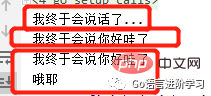
func main() {
say1()
say2("你好哇")
result := say3("你好哇")
fmt.Printf(result)
}结果
调用函数
函数名+括号调用函数,如果有参数传入相关参数即可。
package main
import "fmt"
func say() string{
fmt.Println("我终于会说话了...")
return ""
}
func main() {
//函数名+括号调用函数
say() //结果:我终于会说话了...
}注:如果函数有返回值,可以不接收。
函数参数特性
在Go中,如果函数参数都是统一类型,可以这样写。
//arg1, arg2, arg3, arg4参数类型都是string
func say(arg1, arg2, arg3, arg4 string) {
fmt.Println("我终于会说话了...")
}
//arg1,arg2参数是int类型,arg4,arg4是string类型,
func say(arg1, arg2, int, arg3, arg4 string) {
//表示arg1, arg2, arg3, arg4参数类型都是string
fmt.Println("我终于会说话了...")
}大概意思就是,如果参数不写类型,会以后面碰到的类型为准。
函数的...参数
...参数,也叫可变长参数,有点像Python中的*args。
功能是当不知道接收多少个参数时,接收多的参数会放在...中。
...参数需要放在最后面。
代码
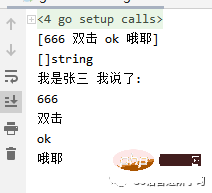
package main
import "fmt"
func say(name string, content ...string) {
fmt.Println(content) //结果:[666 双击 ok 哦耶]
fmt.Printf("%T\n", content) //结果:[]string,是切片类型
fmt.Println("我是"+name, "我说了:")
//循环切片
for _, v := range content {
fmt.Println(v)
}
}
func main() {
//函数名+括号调用函数
say("张三", "666", "双击", "ok", "哦耶") //结果:我终于会说话了...
}结果如图所示
注:参数是...类型的,他的值是一个切片类型。
函数的返回值
返回值是一个的
package main
import "fmt"
//返回值是一个
func say1() string {
return "ok"
}返回值是多个的,需要用括号括起来
//返回值是多个的,需要用括号括起来
func say2() (int, string) {
return 1, "ok"
}返回值是命名的
//返回值是命名的,不管是多个返回值还是一个返回值,都需要括号
//如果是命名返回值,需要在逻辑代码中,将变量赋值
func say3() (a int, b string) {
//逻辑代码
a = 18
b = "666"
/*
直接return即可,不需要retrun a,b
return的默认就是 a 和 b
不用跟上述返回一样,返回具体值
*/
return
}main函数
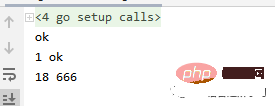
func main() {
s := say1()
fmt.Println(s)
a1, b1 := say2()
fmt.Println(a1, b1)
a2, b2 := say3()
fmt.Println(a2, b2)
}结果
The above is the detailed content of An article to help you understand the basic functions of Go language (Part 1). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 What is the problem with Queue thread in Go's crawler Colly?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 02:09 PM
What is the problem with Queue thread in Go's crawler Colly?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 02:09 PM
Queue threading problem in Go crawler Colly explores the problem of using the Colly crawler library in Go language, developers often encounter problems with threads and request queues. �...
 What libraries are used for floating point number operations in Go?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 02:06 PM
What libraries are used for floating point number operations in Go?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 02:06 PM
The library used for floating-point number operation in Go language introduces how to ensure the accuracy is...
 How to solve the user_id type conversion problem when using Redis Stream to implement message queues in Go language?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 04:54 PM
How to solve the user_id type conversion problem when using Redis Stream to implement message queues in Go language?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 04:54 PM
The problem of using RedisStream to implement message queues in Go language is using Go language and Redis...
 In Go, why does printing strings with Println and string() functions have different effects?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 02:03 PM
In Go, why does printing strings with Println and string() functions have different effects?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 02:03 PM
The difference between string printing in Go language: The difference in the effect of using Println and string() functions is in Go...
 What should I do if the custom structure labels in GoLand are not displayed?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 05:09 PM
What should I do if the custom structure labels in GoLand are not displayed?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 05:09 PM
What should I do if the custom structure labels in GoLand are not displayed? When using GoLand for Go language development, many developers will encounter custom structure tags...
 What is the difference between `var` and `type` keyword definition structure in Go language?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 12:57 PM
What is the difference between `var` and `type` keyword definition structure in Go language?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 12:57 PM
Two ways to define structures in Go language: the difference between var and type keywords. When defining structures, Go language often sees two different ways of writing: First...
 Which libraries in Go are developed by large companies or provided by well-known open source projects?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 04:12 PM
Which libraries in Go are developed by large companies or provided by well-known open source projects?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 04:12 PM
Which libraries in Go are developed by large companies or well-known open source projects? When programming in Go, developers often encounter some common needs, ...
 Why is it necessary to pass pointers when using Go and viper libraries?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 04:00 PM
Why is it necessary to pass pointers when using Go and viper libraries?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 04:00 PM
Go pointer syntax and addressing problems in the use of viper library When programming in Go language, it is crucial to understand the syntax and usage of pointers, especially in...



