 Backend Development
Backend Development
 Python Tutorial
Python Tutorial
 An article to help you understand Python's iteration knowledge
An article to help you understand Python's iteration knowledge
An article to help you understand Python's iteration knowledge
1. Foreword
Hello everyone, I am a Go advanced person. If a list or tuple is given, the list or tuple can be traversed through a for loop. This traversal is called iteration.
2. Case
#In Python, iteration is through for ... in is done, and in many languages such as C or Java, iterating over the list is done through subscripts.
For example, Java code:
for (i=0; i<list.length; i++) {
n = list[i];
} Note:
It can be seen that the abstraction level of Python's for loop is higher than that of Java's for loop, because Python's for loop can not only be used on lists or tuples, but also on other iterable objects.
Although the data type list has subscripts, many other data types do not have subscripts. However, as long as it is an iterable object, it can be iterated regardless of whether there is a subscript.
For example, dict can be iterated.
d = {'a': 1, 'b': 2, 'c': 3}
for key in d:
print(key)
注:
因为dict的存储不是按照list的方式顺序排列,所以,迭代出的结果顺序很可能不一样。
默认情况下,dict迭代的是key。如果要迭代value,可以用for value in d.values(),如果要同时迭代key和value,可以用for k, v in d.items()。
1. 字符串也是可迭代对象。
因此,也可以作用于for循环:
for ch in 'ABC': print(ch)

所以,当使用for循环时,只要作用于一个可迭代对象,for循环就可以正常运行,而不太关心该对象究竟是list还是其他数据类型。
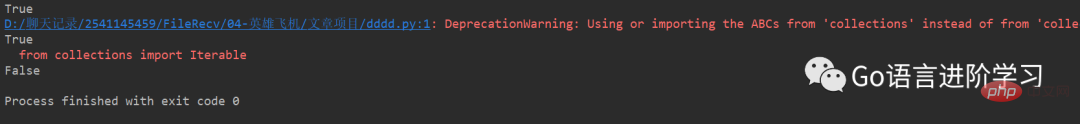
那么,如何判断一个对象是可迭代对象呢?方法是通过collections模块的Iterable类型判断:
from collections import Iterable print(isinstance('abc', Iterable)) # str是否可迭代True print(isinstance([1, 2, 3], Iterable)) # list是否可迭代True print(isinstance(123, Iterable) ) # 整数是否可迭代False
如果要对list实现类似Java那样的下标循环怎么办?
Python内置的enumerate函数可以把一个list变成索引-元素对,这样就可以在for循环中同时迭代索引和元素本身:
for i, value in enumerate(['A', 'B', 'C']): print(i, value)

上面的for循环里,同时引用了两个变量,在Python里是很常见的,
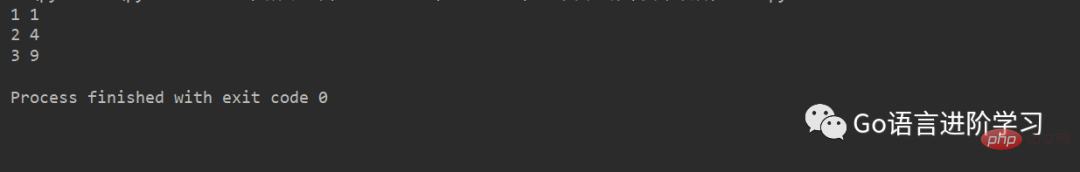
比如下面的代码:
for x, y in [(1, 1), (2, 4), (3, 9)]: print(x, y)
2. 迭代dict的key和value
了解了如何迭代 dict 的key和value,那么,在一个 for 循环中,能否同时迭代 key和value?答案是肯定的。
首先,看看 dict 对象的 items() 方法返回的值:
d = {'Adam': 95, 'Lisa': 85, 'Bart': 59}
print(d.items())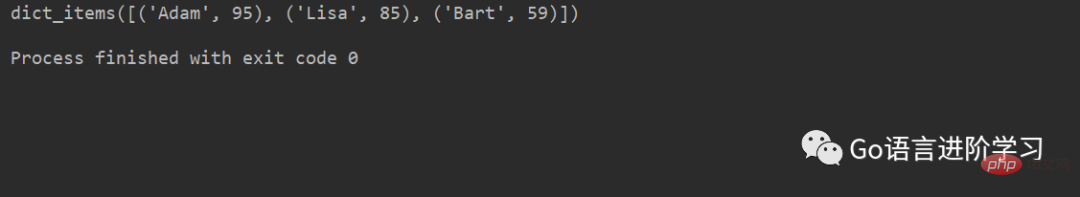
可以看到,items() 方法把dict对象转换成了包含tuple的list,对这个list进行迭代,可以同时获得key和value:
for key, value in d.items():
print( key, ':', value)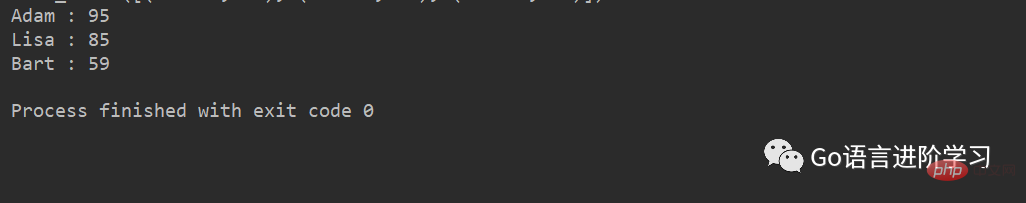
注:
和values() 有一个 itervalues() 类似, items() 也有一个对应的 iteritems(),iteritems() 不把dict转换成list,而是在迭代过程中不断给出 tuple。
所以, iteritems() 不占用额外的内存。
3. Summary
This article is based on the basics of Python and introduces the use of Python iteration. Any iterable object can be used in a for loop, including custom data types. As long as the iteration conditions are met, a for loop can be used. Through case analysis, two common iteration methods are introduced. Provide effective solutions to the difficulties encountered in actual operations.
The above is the detailed content of An article to help you understand Python's iteration knowledge. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 PHP and Python: Code Examples and Comparison
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:07 AM
PHP and Python: Code Examples and Comparison
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:07 AM
PHP and Python have their own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice depends on project needs and personal preferences. 1.PHP is suitable for rapid development and maintenance of large-scale web applications. 2. Python dominates the field of data science and machine learning.
 How to train PyTorch model on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 03:03 PM
How to train PyTorch model on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 03:03 PM
Efficient training of PyTorch models on CentOS systems requires steps, and this article will provide detailed guides. 1. Environment preparation: Python and dependency installation: CentOS system usually preinstalls Python, but the version may be older. It is recommended to use yum or dnf to install Python 3 and upgrade pip: sudoyumupdatepython3 (or sudodnfupdatepython3), pip3install--upgradepip. CUDA and cuDNN (GPU acceleration): If you use NVIDIAGPU, you need to install CUDATool
 Detailed explanation of docker principle
Apr 14, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
Detailed explanation of docker principle
Apr 14, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
Docker uses Linux kernel features to provide an efficient and isolated application running environment. Its working principle is as follows: 1. The mirror is used as a read-only template, which contains everything you need to run the application; 2. The Union File System (UnionFS) stacks multiple file systems, only storing the differences, saving space and speeding up; 3. The daemon manages the mirrors and containers, and the client uses them for interaction; 4. Namespaces and cgroups implement container isolation and resource limitations; 5. Multiple network modes support container interconnection. Only by understanding these core concepts can you better utilize Docker.
 How is the GPU support for PyTorch on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 06:48 PM
How is the GPU support for PyTorch on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 06:48 PM
Enable PyTorch GPU acceleration on CentOS system requires the installation of CUDA, cuDNN and GPU versions of PyTorch. The following steps will guide you through the process: CUDA and cuDNN installation determine CUDA version compatibility: Use the nvidia-smi command to view the CUDA version supported by your NVIDIA graphics card. For example, your MX450 graphics card may support CUDA11.1 or higher. Download and install CUDAToolkit: Visit the official website of NVIDIACUDAToolkit and download and install the corresponding version according to the highest CUDA version supported by your graphics card. Install cuDNN library:
 Python vs. JavaScript: Community, Libraries, and Resources
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:16 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Community, Libraries, and Resources
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:16 AM
Python and JavaScript have their own advantages and disadvantages in terms of community, libraries and resources. 1) The Python community is friendly and suitable for beginners, but the front-end development resources are not as rich as JavaScript. 2) Python is powerful in data science and machine learning libraries, while JavaScript is better in front-end development libraries and frameworks. 3) Both have rich learning resources, but Python is suitable for starting with official documents, while JavaScript is better with MDNWebDocs. The choice should be based on project needs and personal interests.
 How to choose the PyTorch version under CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 02:51 PM
How to choose the PyTorch version under CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 02:51 PM
When selecting a PyTorch version under CentOS, the following key factors need to be considered: 1. CUDA version compatibility GPU support: If you have NVIDIA GPU and want to utilize GPU acceleration, you need to choose PyTorch that supports the corresponding CUDA version. You can view the CUDA version supported by running the nvidia-smi command. CPU version: If you don't have a GPU or don't want to use a GPU, you can choose a CPU version of PyTorch. 2. Python version PyTorch
 How to install nginx in centos
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:06 PM
How to install nginx in centos
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:06 PM
CentOS Installing Nginx requires following the following steps: Installing dependencies such as development tools, pcre-devel, and openssl-devel. Download the Nginx source code package, unzip it and compile and install it, and specify the installation path as /usr/local/nginx. Create Nginx users and user groups and set permissions. Modify the configuration file nginx.conf, and configure the listening port and domain name/IP address. Start the Nginx service. Common errors need to be paid attention to, such as dependency issues, port conflicts, and configuration file errors. Performance optimization needs to be adjusted according to the specific situation, such as turning on cache and adjusting the number of worker processes.
 How to do data preprocessing with PyTorch on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 02:15 PM
How to do data preprocessing with PyTorch on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 02:15 PM
Efficiently process PyTorch data on CentOS system, the following steps are required: Dependency installation: First update the system and install Python3 and pip: sudoyumupdate-ysudoyuminstallpython3-ysudoyuminstallpython3-pip-y Then, download and install CUDAToolkit and cuDNN from the NVIDIA official website according to your CentOS version and GPU model. Virtual environment configuration (recommended): Use conda to create and activate a new virtual environment, for example: condacreate-n



