A line of log caused an online accident of P1
Online accident review
Some time ago, my colleague added a very simple function. Before going online in the eveningreview When he was coding, he thought of the company's values of hard work and enterprising and temporarily added a line of logs. He thought that there was basically no problem with a simple line of logs. As a result, there were a lot of alarms after just finishing the line. He quickly rolled back the code, found the problem and deleted it. Add the log code and go online again.
Scenario restoration
##❝defined ACountryDTO
❞public class CountryDTO { private String country; public void setCountry(String country) { this.country = country; } public String getCountry() { return this.country; } public Boolean isChinaName() { return this.country.equals("中国"); } }Copy after login
❝Define Test ClassNull PointerFastJonTest
❞##Run Timespublic class FastJonTest { @Test public void testSerialize() { CountryDTO countryDTO = new CountryDTO(); String str = JSON.toJSONString(countryDTO); System.out.println(str); } }Copy after login
Error:
It can be seen from the error message that the isChinaName() method was executed during the serialization process. At this time, the this.country variable is empty, so the problem arises:
Why does serialization execute isChinaName()?By extension, what methods will be executed during the serialization process?
Source code Analysis
Observe the stack information of the calling link through debug
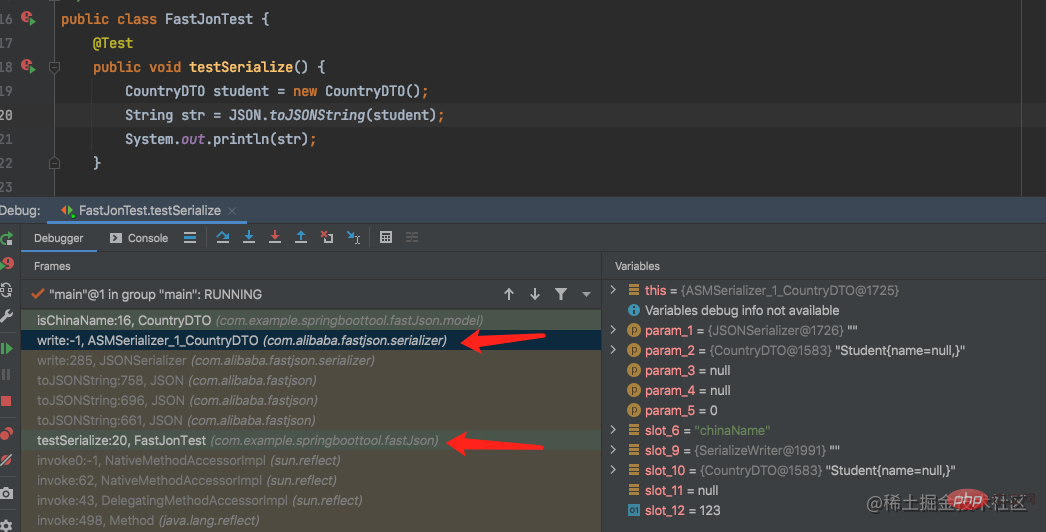
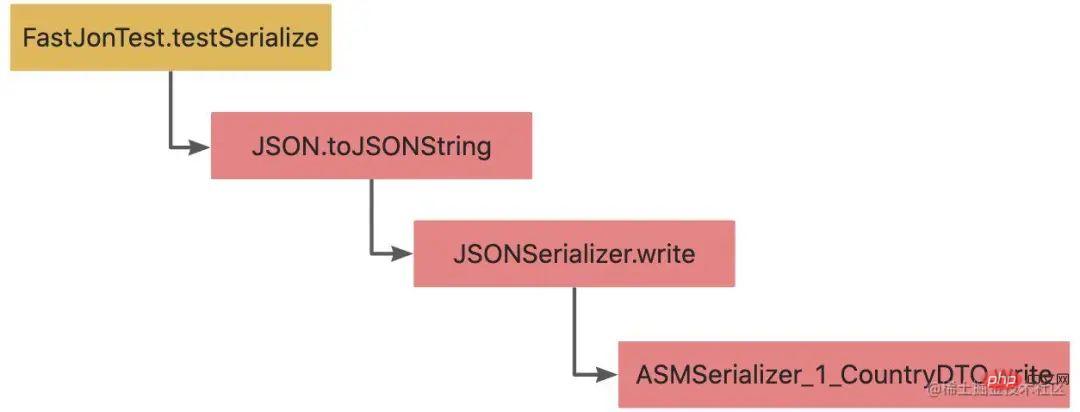
The ASMSerializer_1_CountryDTO.write in the call chain is FastJson using asmTechnology dynamically generated a classASMSerializer_1_CountryDTO.
❝
asm技术其中一项使用场景就是通过到动态生成类用来代替
java反射,从而避免重复执行时的反射开销❞
JavaBeanSerizlier序列化原理
通过下图看出序列化的过程中,主要是调用JavaBeanSerializer类的write()方法。
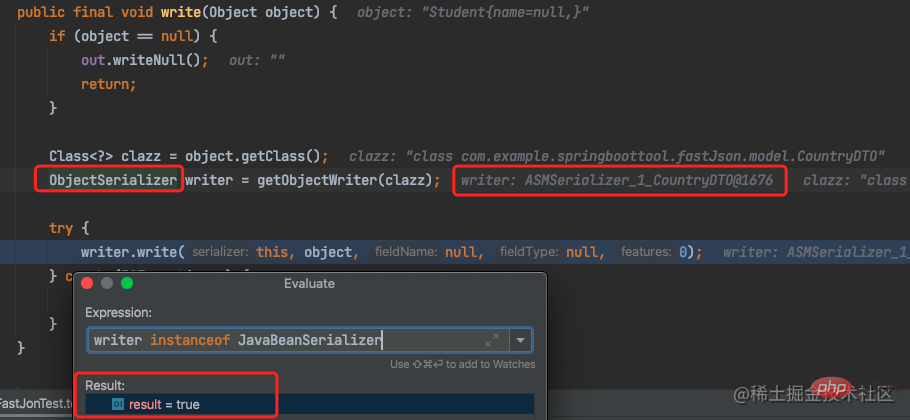 ObjectSerializer实现类JavaBeanSerializer
ObjectSerializer实现类JavaBeanSerializer
而JavaBeanSerializer主要是通过getObjectWriter()方法获取,通过对getObjectWriter()执行过程的调试,找到比较关键的com.alibaba.fastjson.serializer.SerializeConfig#createJavaBeanSerializer方法,进而找到 com.alibaba.fastjson.util.TypeUtils#computeGetters
public static List<FieldInfo> computeGetters(Class<?> clazz, //
JSONType jsonType, //
Map<String,String> aliasMap, //
Map<String,Field> fieldCacheMap, //
boolean sorted, //
PropertyNamingStrategy propertyNamingStrategy //
){
//省略部分代码....
Method[] methods = clazz.getMethods();
for(Method method : methods){
//省略部分代码...
if(method.getReturnType().equals(Void.TYPE)){
continue;
}
if(method.getParameterTypes().length != 0){
continue;
}
//省略部分代码...
JSONField annotation = TypeUtils.getAnnotation(method, JSONField.class);
//省略部分代码...
if(annotation != null){
if(!annotation.serialize()){
continue;
}
if(annotation.name().length() != 0){
//省略部分代码...
}
}
if(methodName.startsWith("get")){
//省略部分代码...
}
if(methodName.startsWith("is")){
//省略部分代码...
}
}
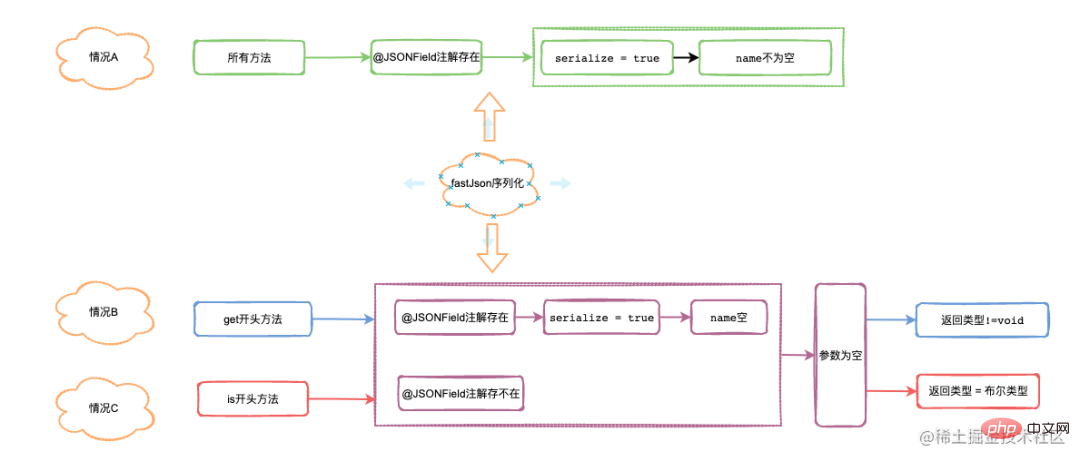
}从代码中大致分为三种情况:
@JSONField(.serialize = false, name = "xxx")注解getXxx(): get开头的方法isXxx():is开头的方法
序列化流程图
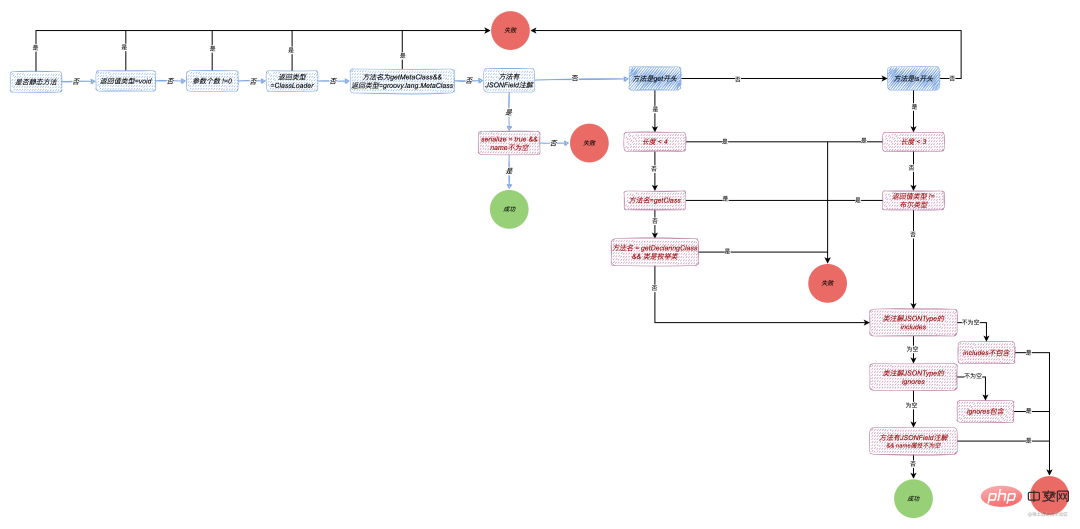 序列化流程图
序列化流程图
示例代码
/**
* case1: @JSONField(serialize = false)
* case2: getXxx()返回值为void
* case3: isXxx()返回值不等于布尔类型
* case4: @JSONType(ignores = "xxx")
*/
@JSONType(ignores = "otherName")
public class CountryDTO {
private String country;
public void setCountry(String country) {
this.country = country;
}
public String getCountry() {
return this.country;
}
public static void queryCountryList() {
System.out.println("queryCountryList()执行!!");
}
public Boolean isChinaName() {
System.out.println("isChinaName()执行!!");
return true;
}
public String getEnglishName() {
System.out.println("getEnglishName()执行!!");
return "lucy";
}
public String getOtherName() {
System.out.println("getOtherName()执行!!");
return "lucy";
}
/**
* case1: @JSONField(serialize = false)
*/
@JSONField(serialize = false)
public String getEnglishName2() {
System.out.println("getEnglishName2()执行!!");
return "lucy";
}
/**
* case2: getXxx()返回值为void
*/
public void getEnglishName3() {
System.out.println("getEnglishName3()执行!!");
}
/**
* case3: isXxx()返回值不等于布尔类型
*/
public String isChinaName2() {
System.out.println("isChinaName2()执行!!");
return "isChinaName2";
}
}运行结果为:
isChinaName()执行!!
getEnglishName()执行!!
{"chinaName":true,"englishName":"lucy"}代码规范
可以看出来序列化的规则还是很多的,比如有时需要关注返回值,有时需要关注参数个数,有时需要关注@JSONType注解,有时需要关注@JSONField注解;当一个事物的判别方式有多种的时候,由于团队人员掌握知识点的程度不一样,这个方差很容易导致代码问题,所以尽量有一种推荐方案。
这里推荐使用@JSONField(serialize = false)来显式的标注方法不参与序列化,下面是使用@JSONField注解后的代码,是不是一眼就能看出来哪些方法不需要参与序列化了。
public class CountryDTO {
private String country;
public void setCountry(String country) {
this.country = country;
}
public String getCountry() {
return this.country;
}
@JSONField(serialize = false)
public static void queryCountryList() {
System.out.println("queryCountryList()执行!!");
}
public Boolean isChinaName() {
System.out.println("isChinaName()执行!!");
return true;
}
public String getEnglishName() {
System.out.println("getEnglishName()执行!!");
return "lucy";
}
@JSONField(serialize = false)
public String getOtherName() {
System.out.println("getOtherName()执行!!");
return "lucy";
}
@JSONField(serialize = false)
public String getEnglishName2() {
System.out.println("getEnglishName2()执行!!");
return "lucy";
}
@JSONField(serialize = false)
public void getEnglishName3() {
System.out.println("getEnglishName3()执行!!");
}
@JSONField(serialize = false)
public String isChinaName2() {
System.out.println("isChinaName2()执行!!");
return "isChinaName2";
}
}三个频率高的序列化的情况
 三个频率高的序列化的情况
三个频率高的序列化的情况
以上流程基本遵循,发现问题 --> 原理分析 --> 解决问题 --> 升华(编程规范)。
围绕业务上:解决问题 -> 如何选择一种好的额解决方案 -> 好的解决方式如何扩展 n 个系统应用; 围绕技术上:解决单个问题,顺着单个问题掌握这条线上的原理。
但其实这段代码我并不满意,原因是和 FastJson 依赖太高了。我想要的效果是,不依赖任何特定的 JSON 序列化框架。当我需要替换掉它的时候,随时可以替换掉。
并且在写代码时,不要过于依赖日志。打日志只需要打紧要且关键的信息即可,不要什么日志都打,我曾见过一个系统,一个小时,把 128G 磁盘跑满的管理系统。几乎没啥并发,但几乎每个请求都输出几 M 的日志,这件事我后面会单独拿出来讲讲。
关于@JSONField和@JSONType等特性注解,后面我会在团队内规范并给出新的解耦方案,把它们移除掉。
The above is the detailed content of A line of log caused an online accident of P1. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1377
1377
 52
52
 How does Java's classloading mechanism work, including different classloaders and their delegation models?
Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:35 PM
How does Java's classloading mechanism work, including different classloaders and their delegation models?
Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:35 PM
Java's classloading involves loading, linking, and initializing classes using a hierarchical system with Bootstrap, Extension, and Application classloaders. The parent delegation model ensures core classes are loaded first, affecting custom class loa
 How do I implement multi-level caching in Java applications using libraries like Caffeine or Guava Cache?
Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:44 PM
How do I implement multi-level caching in Java applications using libraries like Caffeine or Guava Cache?
Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:44 PM
The article discusses implementing multi-level caching in Java using Caffeine and Guava Cache to enhance application performance. It covers setup, integration, and performance benefits, along with configuration and eviction policy management best pra
 How can I use JPA (Java Persistence API) for object-relational mapping with advanced features like caching and lazy loading?
Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:43 PM
How can I use JPA (Java Persistence API) for object-relational mapping with advanced features like caching and lazy loading?
Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:43 PM
The article discusses using JPA for object-relational mapping with advanced features like caching and lazy loading. It covers setup, entity mapping, and best practices for optimizing performance while highlighting potential pitfalls.[159 characters]
 How do I use Maven or Gradle for advanced Java project management, build automation, and dependency resolution?
Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:46 PM
How do I use Maven or Gradle for advanced Java project management, build automation, and dependency resolution?
Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:46 PM
The article discusses using Maven and Gradle for Java project management, build automation, and dependency resolution, comparing their approaches and optimization strategies.
 How do I create and use custom Java libraries (JAR files) with proper versioning and dependency management?
Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:45 PM
How do I create and use custom Java libraries (JAR files) with proper versioning and dependency management?
Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:45 PM
The article discusses creating and using custom Java libraries (JAR files) with proper versioning and dependency management, using tools like Maven and Gradle.




