
I was quite confused when I first started writing this article, because you can find a lot of information by searching online for "what happens from entering the URL to the page display". Moreover, this interview question is basically a required question. During the interview in February, although I knew what happened in the process, when the interviewer continued to ask questions step by step, many details were not clear.
#The purpose of this article is to summarize and expand knowledge through what happens after entering the url. So the article may be complicated.
The overall process is as follows:
When we start in the browser When you enter a URL, the browser is actually already intelligently matching possible URLs. It will find the URL that may correspond to the entered string from history records, bookmarks, etc., and then give intelligent prompts so that you can fill in the URL. Full url address. For Google's Chrome browser, it will even display the web page directly from the cache. That is to say, the page will come out before you press enter.
1. Once the request is initiated, the first thing the browser does is to resolve the domain name. Generally speaking, browsing The server will first check the hosts file on the local hard disk to see if there are any rules corresponding to this domain name. If so, it will directly use the IP address in the hosts file.
2. If the corresponding IP address cannot be found in the local hosts file, the browser will send a DNS request to the local DNS server. Local DNS servers are generally provided by your network access server provider, such as China Telecom and China Mobile.
3. After the DNS request for the URL you entered reaches the local DNS server, the local DNS server will first query its cache record. If there is this record in the cache, you can directly Returning results, this process is a recursive query. If not, the local DNS server will also query the DNS root server.
4. The root DNS server does not record the specific correspondence between domain names and IP addresses. Instead, it tells the local DNS server that you can go to the domain server to continue querying and give the domain server. the address of. This process is an iterative process.
5. The local DNS server continues to make requests to the domain server. In this example, the request object is the .com domain server. After the .com domain server receives the request, it will not directly return the correspondence between the domain name and the IP address. Instead, it will tell the local DNS server the address of the resolution server for your domain name.
6. Finally, the local DNS server sends a request to the domain name resolution server, and then receives a correspondence between the domain name and the IP address. The local DNS server not only returns the IP address to the user's computer, but also Save this correspondence in the cache so that the next time another user queries, the results can be returned directly to speed up network access.
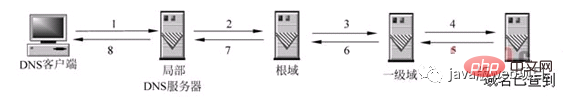
The picture below explains this process perfectly:

DNS (Domain Name System, domain name system), a distributed mapping of domain names and IP addresses on the Internet The database allows users to access the Internet more conveniently without having to remember IP strings that can be directly read by machines. The process of finally obtaining the IP address corresponding to the host name through the host name is called domain name resolution (or host name resolution).
Generally speaking, we are more accustomed to remembering the name of a website, such as www.baidu.com, rather than remembering its IP address, such as: 167.23.10.2. And computers are better at remembering the IP address of a website, rather than links like www.baidu.com. Because DNS is equivalent to a phone book. For example, if you are looking for the domain name www.baidu.com, then I look through my phone book and I will know, oh, its phone number (IP) is 167.23.10.2.
1. Recursive analysis
When the local DNS server itself cannot answer the client's DNS query, it needs to query other DNS servers. There are two methods at this time. The one shown in the figure is the recursive method. The local DNS server is responsible for querying other DNS servers. Generally, it first queries the root domain server of the domain name, and then the root domain name server queries downwards one level at a time. The final query result is returned to the local DNS server, and then the local DNS server returns it to the client.
2. Iterative analysis
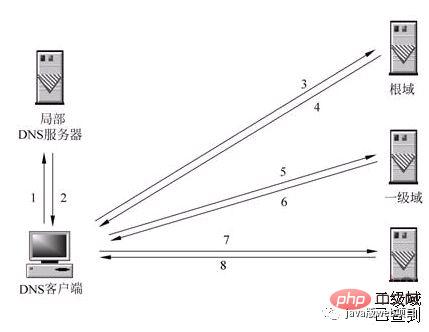
When the local DNS server itself cannot answer the client's DNS query, it can also be resolved through iterative query, as shown in the figure. The local DNS server does not query other DNS servers by itself, but returns the IP addresses of other DNS servers that can resolve the domain name to the client DNS program. The client DNS program then continues to query these DNS servers until the query results are obtained. until. In other words, iterative analysis only helps you find relevant servers, but will not help you check them. For example: the server IP address of baidu.com is here 192.168.4.5. You can check it yourself. I am very busy, so I can only help you here.
We are here As mentioned earlier, the root DNS server and the domain DNS server are how the DNS domain name space is organized. The five categories used to describe DNS domain names in the namespace are described in the table below, along with examples of each name type.
#4)DNS Load Balancing
After getting the IP address corresponding to the domain name, the browser will send a random port (1024
After this connection request reaches the server (through various routing devices, except in the LAN), it enters the network card, and then enters the TCP/IP protocol stack of the kernel (used to identify the Connection request, decapsulation packet, peeling off layer by layer), and may also have to be filtered by the Netfilter firewall (a module belonging to the kernel), and finally reaches the WEB program, and finally establishes a TCP/IP connection. <span style="font-size: 16px;"></span>TCP connection is shown in the figure:
After establishing the TCP connection, initiate an http request. A typical http request header generally needs to include the request method, such as GET or POST. Less commonly used ones include PUT and DELETE, HEAD, OPTION and TRACE methods. General browsers can only initiate GET or POST requests.
When the client initiates an http request to the server, there will be some request information. The request information contains three parts:
| Request method URI protocol/version
| Request Header
| Request text:
The following is a complete HTTP request example:
GET/sample.jspHTTP/1.1Accept:image/gif.image/jpeg,*/*Accept-Language:zh-cn Connection:Keep-Alive Host:localhost User-Agent:Mozila/4.0(compatible;MSIE5.01;Window NT5.0) Accept-Encoding:gzip,deflate username=jinqiao&password=1234
Note: There is a blank line after the last request header, and a carriage return and line feed are sent. character, informing the server that there are no more request headers below.
(1) The first line of the request is "Method URL proposal/version": GET/sample.jsp HTTP/1.1
(2) Request Header (Request Header)
Request The header contains a lot of useful information about the client environment and the request body. For example, the request header can declare the language used by the browser, the length of the request body, etc.
Accept:image/gif.image/jpeg.*/* Accept-Language:zh-cn Connection:Keep-Alive Host:localhost User-Agent:Mozila/4.0(compatible:MSIE5.01:Windows NT5.0) Accept-Encoding:gzip,deflate.
(3) Request body
There is a blank line between the request header and the request body. This line is very important. It indicates that the request header has ended, and the next step is the request text. The request body can contain the query string information submitted by the customer:
username=jinqiao&password=1234
The server responds to the browser with a 301 Permanently redirect the response so the browser goes to "http://www.google.com/" instead of "http://google.com/".
Why does the server have to redirect instead of directly sending the web page content that the user wants to see? One of the reasons has to do with search engine rankings. If a page has two addresses, such as http://www.yy.com/ and http://yy.com/, search engines will think that they are two websites. As a result, each search link will be reduced and the search result will be reduced. Ranking. And search engines know what 301 permanent redirection means, so they will rank addresses with and without www under the same website ranking. Also, using different addresses will make cache friendliness worse. When a page has several names, it may appear in the cache several times.
Both 301 and 302 status codes indicate redirection, which means that the browser will automatically jump to a new URL address after getting the status code returned by the server. This address can Obtained from the Location header of the response (the effect the user sees is that the address A he entered instantly changes to another address B) - this is what they have in common.
The difference is. 301 indicates that the resource at the old address A has been permanently removed (this resource is no longer accessible). The search engine will also exchange the old URL for the redirected URL while crawling the new content;
302 means that the resources at the old address A are still there (still accessible). This redirect only temporarily jumps from the old address A to the address B. Search engines will crawl Get the new content and save the old URL. SEO302 is better than 301
2) Reason for redirection:
(1) Website adjustment (such as changing the web page directory Structure);
(2) The web page is moved to a new address;
(3) The web page extension is changed (if the application needs to change .php to .Html or .shtml).
In this case, if there is no redirection, the old address in the user's favorites or search engine database will only cause the visiting customer to get a 404 page error message, and the access traffic will be lost in vain; in addition, some registrations Websites with multiple domain names also need to redirect users who visit these domain names to automatically jump to the main site.
When a website or web page is temporarily moved to a new location within 24-48 hours, a 302 jump will be performed. The scenario where a 301 jump is used is that the previous website was damaged due to some reason. The reason needs to be removed and then accessed from a new address, which is permanent.
To be clear and specific: The general scenarios for using 301 jump are as follows:
1. The domain name expires and you don’t want to renew it (or you have found a domain name that is more suitable for the website), and you want to change the domain name.
2. The domain name without www appears in the search results of the search engine, but the domain name with www is not included. At this time, you can use 301 redirection to tell the search engine which domain name our target is. .
3. The space server is unstable and when changing space.
Now the browser knows that "http://www.google.com/" is the correct address to visit, so it Another http request will be sent. There is nothing to say here
After the previous steps, we finally sent our http request to the server. In fact, the previous steps The orientation has reached the server, so how does the server handle our request?
后端从在固定的端口接收到TCP报文开始,它会对TCP连接进行处理,对HTTP协议进行解析,并按照报文格式进一步封装成HTTP Request对象,供上层使用。
一些大一点的网站会将你的请求到反向代理服务器中,因为当网站访问量非常大,网站越来越慢,一台服务器已经不够用了。于是将同一个应用部署在多台服务器上,将大量用户的请求分配给多台机器处理。此时,客户端不是直接通过HTTP协议访问某网站应用服务器,而是先请求到Nginx,Nginx再请求应用服务器,然后将结果返回给客户端,这里Nginx的作用是反向代理服务器。同时也带来了一个好处,其中一台服务器万一挂了,只要还有其他服务器正常运行,就不会影响用户使用。
如图所示:
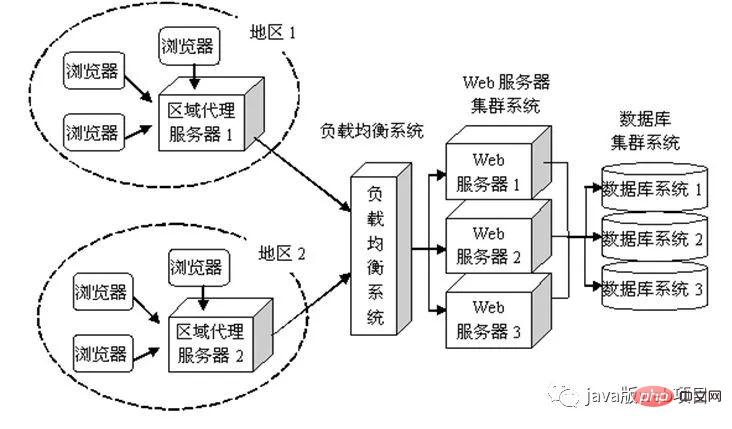
通过Nginx的反向代理,我们到达了web服务器,服务端脚本处理我们的请求,访问我们的数据库,获取需要获取的内容等等,当然,这个过程涉及很多后端脚本的复杂操作。由于对这一块不熟,所以这一块只能介绍这么多了。
经过前面的6个步骤,服务器收到了我们的请求,也处理我们的请求,到这一步,它会把它的处理结果返回,也就是返回一个HTPP响应。
HTTP响应与HTTP请求相似,HTTP响应也由3个部分构成,分别是:
l 状态行
l 响应头(Response Header)
l 响应正文
HTTP/1.1 200 OK Date: Sat, 31 Dec 2005 23:59:59 GMT Content-Type: text/html;charset=ISO-8859-1 Content-Length: 122<html> <head> <title>http</title> </head><body> <!-- body goes here --> </body> </html>
状态行:
状态行由协议版本、数字形式的状态代码、及相应的状态描述,各元素之间以空格分隔。
格式: HTTP-Version Status-Code Reason-Phrase CRLF
例如: HTTP/1.1 200 OK
-- Protocol version: Whether to use http1.0 or other versions
##-- Status description: Status description Gives a brief textual description of the status code. For example, when the status code is 200, the description is ok
##--Status code: The status code consists of three digits, and the first digit defines the category of the response. , and has five possible values. As follows
1xx: Informational status code, indicating that the server has received the client request and the client can continue to send requests.
100 Continue101 Switching Protocols
2xx:Success Status code indicating that the server has successfully received the request and processed it.
200 OK indicates that the client request is successful204 No Content is successful, but does not return the main part of any entity
206 Partial Content successfully executed a range (Range) request
3xx: Redirect status code, indicating that the server requires the client to redirect .
301 Moved Permanently permanent redirection, the Location header of the response message should have the new URL of the resource302 Found Temporary redirection Orientation, the URL given in the Location header of the response message is used to temporarily locate the resource
303 See Other The requested resource has another URI, and the client should use the GET method to direct the request. Resources
304 Not Modified The server content has not been updated and the browser cache can be read directly
307 Temporary Redirect Temporary redirect. The same meaning as 302 Found. 302 prohibits the conversion of POST into GET, but this is not necessarily the case in actual use. 307 more browsers may follow this standard, but it also depends on the specific implementation of the browser
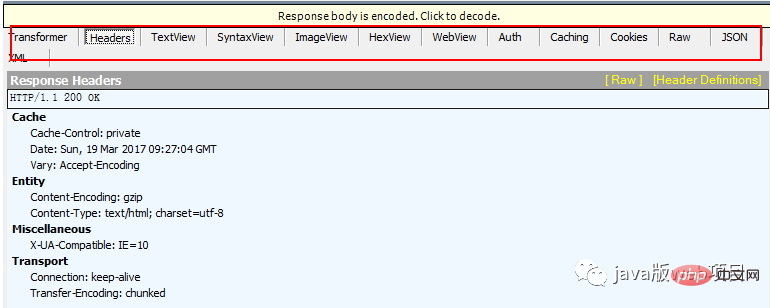
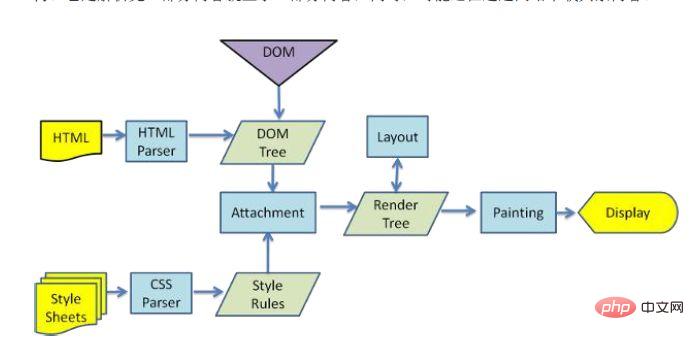
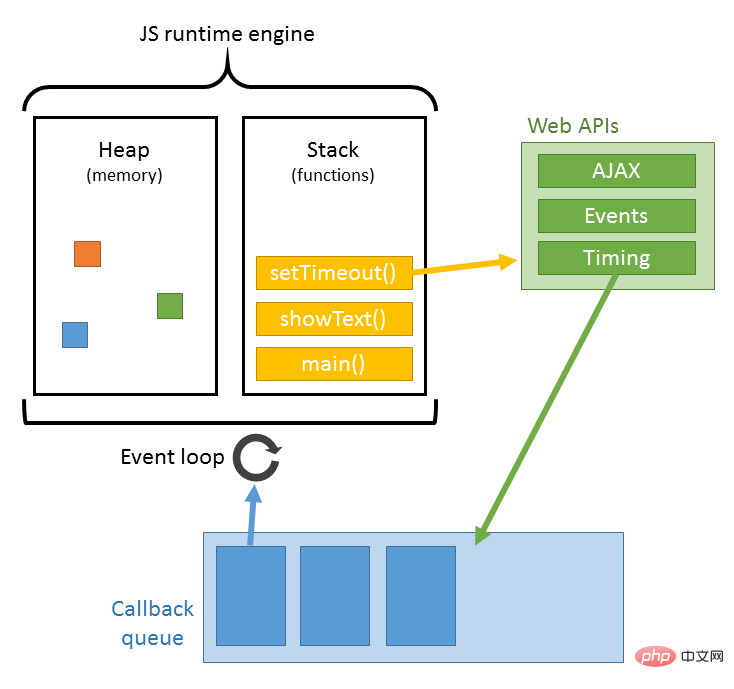
4xx: Client error status code, indicating that the client's request contains illegal content. 400 Bad Request indicates that the client request has a syntax error and cannot be understood by the server 401 Unauthonzed indicates that the request is unauthorized. This status code must be consistent with WWW-Authenticate Use header fields together 403 Forbidden means that the server received the request but refused to provide the service. The reason for not providing the service is usually given in the response body 404 Not Found The requested resource does not exist, for example, the wrong URL was entered 5xx: Server error status code, indicating that the server failed to function properly An unexpected error occurred while processing the client's request. 500 Internel Server Error means that an unexpected error occurred in the server, resulting in the inability to complete the client's request 503 Service Unavailable means that the server is currently unable to Processing the client's request, after a period of time, the server may return to normal Response header: Response header Part: It consists of keyword/value pairs, one pair per line. The keywords and values are separated by English colons ":". Typical response headers are: The response text contains some specific information we need, such as cookies, html, image, request data returned by the backend, etc. It should be noted here that there is a line of spaces between the response body and the response header, which means that the response header information reaches the space. The picture below is the request body captured by fiddler. In the red box: Response body: When the browser does not fully accept all HTML documents, it This page has started to be displayed. How does the browser present the page on the screen? Different browsers may have different parsing processes. Here we only introduce the rendering process of webkit. The figure below corresponds to the rendering process of WebKit. This process includes: Parse HTML to build dom tree-> Build render tree-> Layout render tree-> Draw render tree When the browser parses the html file, it will load it "from top to bottom" and perform parsing and rendering during the loading process. During the parsing process, if there is a request for external resources, such as pictures, external link CSS, iconfont, etc., the request process is asynchronous and will not affect the loading of the HTML document. During the parsing process, the browser will first parse the HTML file to build the DOM tree, and then parse the CSS file to build the rendering tree. After the rendering tree is built, the browser begins to lay out the rendering tree and which is drawn to the screen. This process is relatively complex and involves two concepts: reflow and repaint. Each element in the DOM node exists in the form of a box model, which requires the browser to calculate its position and size. This process is called relow; when the box model After the position, size and other attributes, such as color, font, etc. are determined, the browser begins to draw the content. This process is called repaint. The page will inevitably experience reflow and repain when it is first loaded. The reflow and repain process is very performance-consuming, especially on mobile devices. It will destroy the user experience and sometimes cause the page to freeze. So we should reduce reflow and repain as little as possible. When a js file is encountered during document loading, the HTML document will hang rendering (loading parsing rendering Synchronization) thread must not only wait for the js file in the document to be loaded, but also wait for the parsing execution to be completed before the rendering thread of the html document can be resumed. Because JS may modify the DOM, the most classic document.write, this means that the subsequent download of all resources may not be necessary before JS execution is completed. This is the fundamental reason why js blocks subsequent resource downloads. So I understand that in the usual code, js is placed at the end of the html document. The parsing of JS is completed by the JS parsing engine in the browser, such as Google's V8. JS runs in a single thread, which means that it can only do one thing at the same time. All tasks need to be queued. The previous task ends before the next one can start. However, there are some tasks that are time-consuming, such as IO reading and writing, etc., so a mechanism is needed to execute the later tasks first, which are: synchronous tasks (synchronous) and asynchronous tasks (asynchronous). The execution mechanism of JS can be regarded as a main thread plus a task queue. Synchronous tasks are tasks executed on the main thread, and asynchronous tasks are tasks placed in the task queue. All synchronous tasks are executed on the main thread, forming an execution stack; an asynchronous task will place an event in the task queue when it has the running result; when the script is running, it will first run the execution stack in sequence, and then extract the event from the task queue and run For tasks in the task queue, this process is repeated continuously, so it is also called an event loop. For the specific process, you can read my article: click here In fact, this step can be paralleled in step 8. When the browser displays the HTML, it notices tags that need to get the content of other addresses. At this point, the browser will send a fetch request to retrieve the files. For example, I want to get external pictures, CSS, JS files, etc., similar to the following link: Picture: http://static.ak.fbcdn.net/rsrc.php/z12E0 /hash/8q2anwu7.gif CSS style sheet: http://static.ak.fbcdn.net/rsrc.php/z448Z/hash/2plh8s4n.css JavaScript file: http://static.ak.fbcdn.net/rsrc.php/zEMOA/hash/c8yzb6ub.js These addresses must be experienced A process similar to HTML reading. So the browser will look up these domain names in DNS, send requests, redirect, etc... Unlike dynamic pages, static files will allow the browser to cache them. Some files may not need to communicate with the server, but can be read directly from the cache, or can be placed in a CDN At this point, the process from inputting the URL to page display is finally completed. . Of course, the writing style is limited and there are any errors. You are welcome to point out that this article refers to many articles, but I can’t remember the links to many articles, so I only list the following three reference links. The above is the detailed content of Must-ask questions in interviews: What exactly happens from entering the URL to page display?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!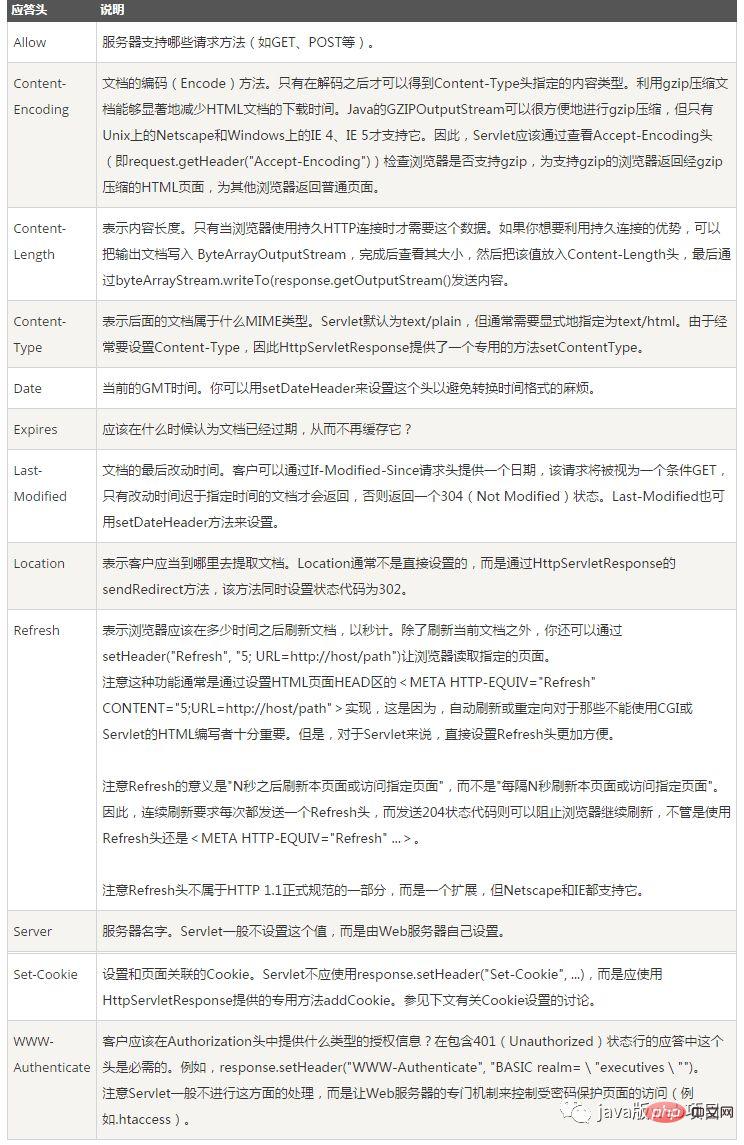
8. The browser displays HTML
9. The browser sends a request to obtain resources embedded in HTML (such as images, audio, video, CSS, JS, etc.)
 What does url mean?
What does url mean?
 what does url mean
what does url mean
 what is url
what is url
 Three commonly used encoding methods
Three commonly used encoding methods
 The difference between html and url
The difference between html and url
 Why is there no sound in Tencent meetings?
Why is there no sound in Tencent meetings?
 How to write mysql check constraints
How to write mysql check constraints
 How to make charts and data analysis charts in PPT
How to make charts and data analysis charts in PPT
 The most prominent features of computer networks
The most prominent features of computer networks