After joining the company, I understood what Cache is
##Preface
The thing is actually like this. At that time, the leader handed over I have a perf hardware performance monitoring task. During the process of using perf, I entered the command perf list and I saw the following information: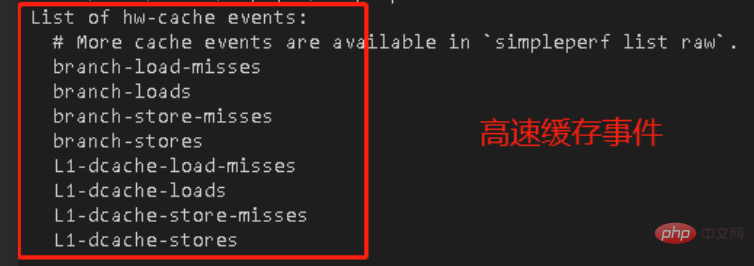
misses and loads mean.
1. What is Cache?
First of all, we need to know that the CPU does not access the memory directly, but needs to go through the Cache first. Why? Cause: The data in the CPU is stored in registers. The speed of accessing registers is very fast, but the register capacity is small. The memory capacity is large, but the speed is slow.In order to solve the problem of speed and capacity between CPU and memory, cache Cache is introduced.
Cache is located between the CPU and the main memory. When the CPU accesses the main memory, it first accesses the Cache to see if there is such data in the Cache. If so, it returns the data from the Cache. To the CPU; if there is no data in the Cache, access the main memory again.
2. Multi-level Cache storage structure
Generally speaking, there is more than one Cache, but multiple , that is, multi-level Cache, why?
Reason: The CPU access cache is also very fast. But we cannot achieve complete compatibility between speed and capacity. If the speed of the CPU accessing the cache is similar to the speed of the CPU accessing the register, it means that the cache is very fast, but the capacity is very small. Such a small cache capacity is not enough to satisfy us. needs, so multi-level Cache was introduced.
Multi-level Cache divides Cache into multiple levels L1, L2, L3, etc.
According to speed, the order is L1>L2>L3.
According to the storage capacity, the order is L3>L2>L1.
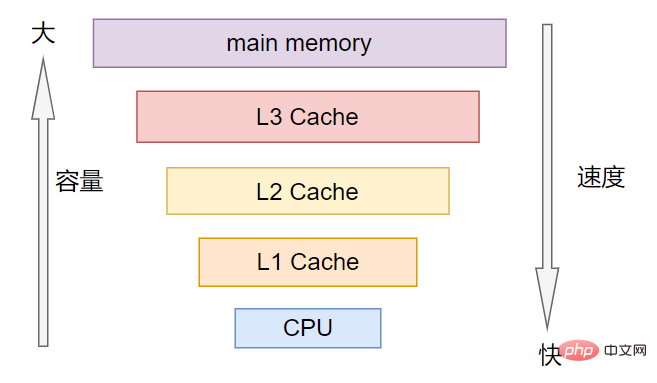
L1 is closest to the CPU and L3 is closest to the main memory.
Usually L1 is divided into instruction cache (ICache) and data cache (DCache), and the L1 cache is private to the CPU, and each CPU There is an L1 cache.
#3. What do "hit" and "missing" mean?
Hit: The data to be accessed by the CPU is cached in the cache, which is called a "hit", that is, cache hit
Missing: The data to be accessed by the CPU is not cached in the cache, which is called "missing", that is, cache miss
4. What is cache line?
cache line: Cache line, the cache is evenly divided into many equal blocks, and the size of each block is called cache line.
The cache line is also the smallest unit of data transfer between cache and main memory.
When the CPU tries to load a byte of data, if the cache is missing , then the cache controller will load cache line-sized data from the main memory into the cache at one time. For example, the cache line size is 8 bytes. Even if the CPU reads one byte, after the cache is missing, the cache will load 8 bytes from the main memory to fill the entire cache line.
The address encoding when the CPU accesses the cache usually consists of three parts: tag, index and offset:
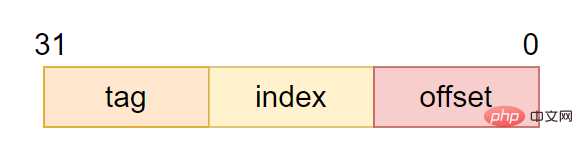
tag(tag field) : Used to determine whether the address of the data cached in the cache line is consistent with the processor addressing address.
- index(Index field): Used to index and find which line in the cache the address is
offset(offset) : Offset within the cache line. The contents of the cache line can be addressed by words or bytes
The relationship between cache line and tag, index, offset, etc. is as shown in the figure:
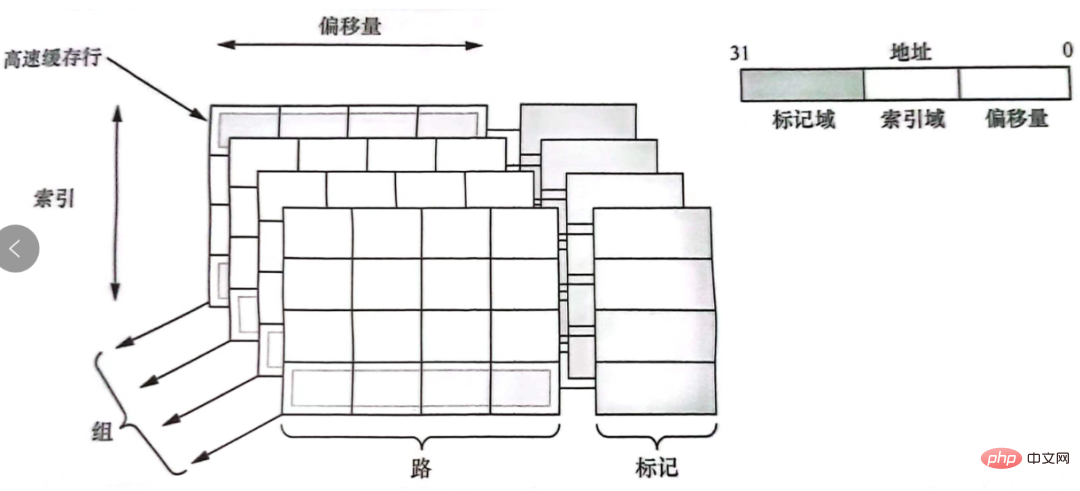
5. Does the cache access a virtual address or a physical address?
We know that the CPU accesses the memory not directly, but the CPU issues a virtual address, which is then converted into a physical address by the MMU, and then the data is fetched from the memory according to the physical address. . So is the cache accessing a virtual address or a physical address?
Answer: Not necessarily. It can be either a virtual address, a physical address, or a combination of virtual and physical addresses.
Because cache has many ways of organizing in hardware design:
VIVTVirtual Cache: The index of the virtual address and the tag of the virtual address.PIPTPhysical cache: The index of the physical address, the tag of the physical address.VIPTPhysically tagged virtual cache: the index of the virtual address, the tag of the physical address.
# 6. What are ambiguity and aliasing issues?
Ambiguity (homonyms): The same virtual address corresponds to different physical addresses
Alias (alias): Multiple virtual addresses are mapped to the same physical address (multiple virtual addresses are called aliases).
For example, the VIVT method mentioned above will have an alias problem. Which method is better, VIVT, PIPT or VIPT?
PIPT is actually ideal, because both index and tag use physical addresses, The software level does not require any maintenance to avoid ambiguity and alias problems.
VIPT's tag uses a physical address, so there is no ambiguity problem, but the index is a virtual address, so may also have an alias problem.
With the VIVT method, ambiguity and aliasing problems exist.
In fact, what is currently used in hardware is basically PIPT or VIPT. VIVT has too many problems. It has become history and no one will use it. In addition, the PIVT method does not exist, because it has only shortcomings and no advantages. Not only is it slow, but ambiguity and aliasing problems also exist.
The organization of cache, as well as ambiguity and alias issues, are relatively large pieces of content. Here you only need to know that the address accessed by the cache can be either a virtual address, a physical address, or a combination of a virtual address and a physical address. And different organizational methods will have ambiguity and alias problems.
#7. Cache allocation strategy?
refers to how the cache is allocated when a cache miss occurs.
Read allocation: When CPU reads data, cache is missing. In this case, a cache line cache will be allocated. Data read from main memory. By default, cache supports read allocation.
Write allocation: When the CPU write data cache is missing, the write allocation strategy will be considered. When we do not support write allocation, the write instruction will only update the main memory data and then end. When write allocation is supported, we first load data from main memory into cache line (equivalent to doing a read allocation first), and then update the data in cache line .
8. Cache update strategy?
refers to how the write operation should update the data when the cache hits.
Write passthrough: When the CPU executes the store instruction and the cache hits, we update the data in the cache and update the data in the main memory. The data in cache and main memory are always consistent.
Writeback: We only update cache## when CPU executes the store instruction and hits in cache The data in #. And there will be a bit bit in each cache line to record whether the data has been modified, which is called dirty bit. We will set the dirty bit. Data in main memory will only be updated when the cache line is replaced or the explicit clean operation is performed. Therefore, the data in the main memory may be unmodified data, while the modified data lies in the cache. The data in cache and main memory may be inconsistent.
Finally
About cache, TLB, MESI, memory consistency model, etc. Etc. is something that requires precipitation and summary to truly master. But many people may not use it. Only when it comes to performance issues and when you need to improve the cache hit rate, will you know the importance of this knowledge. Regarding the knowledge discussed in this article, I summarized a mind map of the basic knowledge of cache: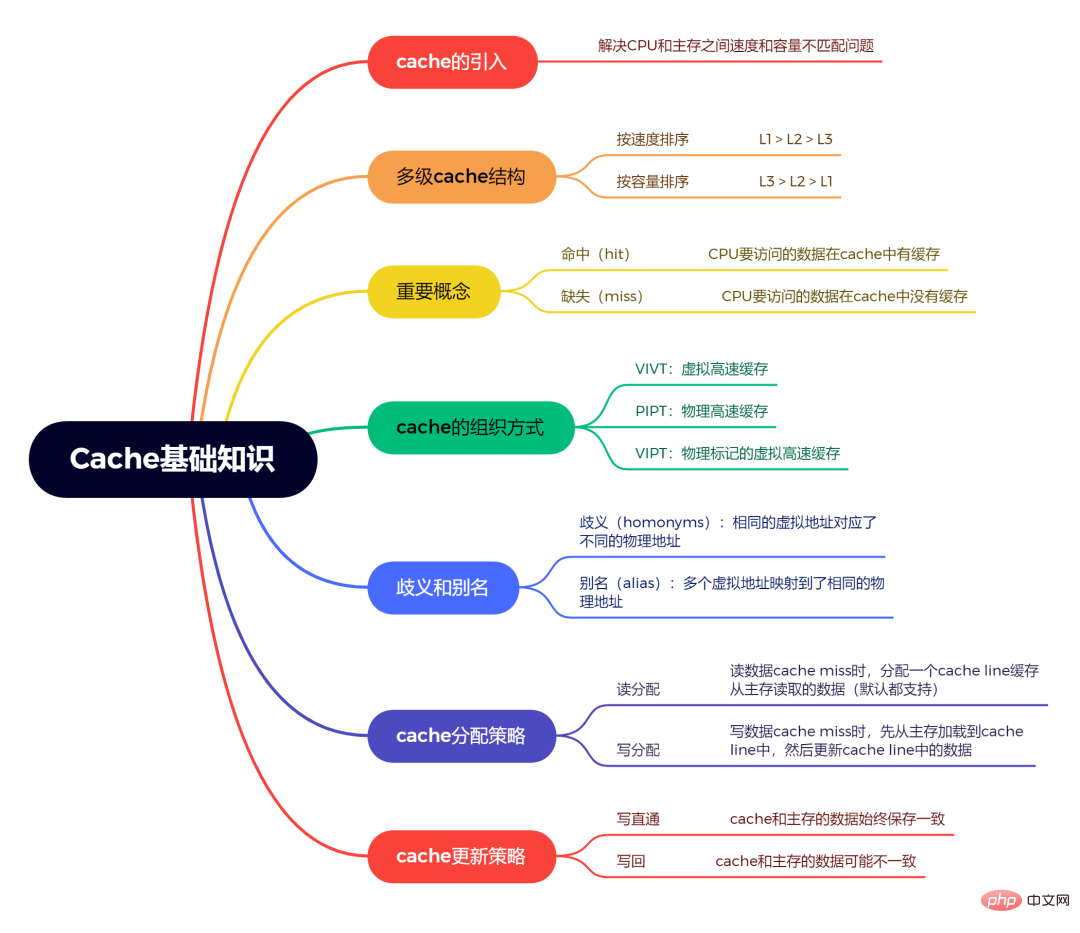
The above is the detailed content of After joining the company, I understood what Cache is. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1375
1375
 52
52
 After joining the company, I understood what Cache is
Jul 31, 2023 pm 04:03 PM
After joining the company, I understood what Cache is
Jul 31, 2023 pm 04:03 PM
The thing is actually like this. At that time, my leader gave me a perf hardware performance monitoring task. During the process of using perf, I entered the command perf list and I saw the following information: My task is to enable these cache events to be counted normally. But the point is, I have no idea what these misses and loads mean.
 Why does using cache increase computer speed?
Dec 09, 2020 am 11:28 AM
Why does using cache increase computer speed?
Dec 09, 2020 am 11:28 AM
Using the cache can increase the speed of the computer because the cache shortens the waiting time of the CPU. Cache is a small but high-speed memory located between the CPU and the main memory DRAM. The function of Cache is to increase the rate of CPU data input and output; Cache has a small capacity but fast speed, while the memory speed is low but has a large capacity. By optimizing the scheduling algorithm, the performance of the system will be greatly improved.
 What is cache?
Nov 25, 2022 am 11:48 AM
What is cache?
Nov 25, 2022 am 11:48 AM
Cache is called cache memory. It is a high-speed small-capacity memory between the central processing unit and the main memory. It is generally composed of high-speed SRAM. This kind of local memory is oriented to the CPU. It is introduced to reduce or eliminate the gap between the CPU and the memory. The impact of the speed difference between them on system performance. Cache capacity is small but fast, memory speed is low but capacity is large. By optimizing the scheduling algorithm, the performance of the system will be greatly improved.
 nginx reverse proxy caching tutorial.
Feb 18, 2024 pm 04:48 PM
nginx reverse proxy caching tutorial.
Feb 18, 2024 pm 04:48 PM
Here is the tutorial for nginx reverse proxy caching: Install nginx: sudoaptupdatesudoaptinstallnginx Configure reverse proxy: Open nginx configuration file: sudonano/etc/nginx/nginx.conf Add the following configuration in the http block to enable caching: http{...proxy_cache_path /var/cache/nginxlevels=1:2keys_zone=my_cache:10mmax_size=10ginactive=60muse_temp_path=off;proxy_cache
 Nginx Cache configuration plan and how to solve related memory usage problems
May 23, 2023 pm 02:01 PM
Nginx Cache configuration plan and how to solve related memory usage problems
May 23, 2023 pm 02:01 PM
5 options for nginx caching cache 1. One of the traditional caches (404) This method is to direct the 404 error of nginx to the backend, and then use proxy_store to save the page returned by the backend. Configuration: location/{root/home/html/;#Home directory expires1d;#Expiration time of the web page error_page404=200/fetch$request_uri;#404 directed to the /fetch directory} Location/fetch/{#404 directed here internal ;#Indicates that this directory cannot be directly accessed externally
 How to use cache in SpringBoot project
May 16, 2023 pm 02:34 PM
How to use cache in SpringBoot project
May 16, 2023 pm 02:34 PM
Preface Caching can effectively improve system performance and stability by storing frequently accessed data in memory, reducing the pressure on underlying data sources such as databases. I think everyone has used it more or less in their projects, and our project is no exception. However, when I was reviewing the company's code recently, the writing was very stupid and low. The rough writing is as follows: publicUsergetById(Stringid){Useruser=cache. getUser();if(user!=null){returnuser;}//Get user from the database=loadFromDB(id);cahce.put(id,user);returnu
 What are the characteristics of cache, rom and ram?
Aug 26, 2022 pm 04:05 PM
What are the characteristics of cache, rom and ram?
Aug 26, 2022 pm 04:05 PM
Characteristics of cache: A one- or two-level high-speed, small-capacity memory set between the CPU and the main memory. The information is naturally lost when the computer is powered off. Characteristics of ROM: it can only read data from the memory, but cannot write information into it. The data will still exist after the computer is powered off. Characteristics of ram: it can read data from the memory and write information to the memory; it is used to store commands, programs and data required to run the program; information is naturally lost when the computer is powered off.
 How to implement Caffeine+Redis second-level cache based on Spring Cache
Jun 01, 2023 am 10:13 AM
How to implement Caffeine+Redis second-level cache based on Spring Cache
Jun 01, 2023 am 10:13 AM
The details are as follows: 1. Let’s talk about what is hard-coded cache? Before learning SpringCache, I often used caching in a hard-coded way. Let's take a practical example. In order to improve the query efficiency of user information, we use caching for user information. The sample code is as follows: @AutowireprivateUserMapperuserMapper; @AutowireprivateRedisCacheredisCache;//Query users publicUsergetUserById(LonguserId){//Define cache keyStringcacheKey= "userId_



